| [1] |
陈建芳, 郑连福, WIESNER M G, 等, 1998. 基于沉积物捕获器的南海表层初级生产力及输出生产力估算[J]. 科学通报, 43(6):639-642.
|
|
CHEN JIANFANG, ZHENG LIANFU, WIESNER M G, et al, 1998. Estimations of primary production and export production in the South China Sea based on sediment trap experiments[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 43(6):583-586.
|
| [2] |
丛丕福, 牛铮, 蒙继华, 等, 2006. 1998~2003年卫星反演的中国陆架海叶绿素a浓度变化分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 25(1):30-33.
|
|
CONG PIFU, NIU ZHENG, MENG JIHUA, et al, 2006. Variability of chlorophyll a retrieved from satellite in Chinese shelf sea from 1998 to 2003[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 25(1):30-33 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
董泰锋, 蒙继华, 吴炳方, 等, 2011. 光合有效辐射(PAR)估算的研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 30(9):1125-1134.
|
|
DONG TAIFENG, MENG JIHUA, WU BINGFANG, et al, 2011. Overview on the estimation of Photosynthetically active radiation[J]. Progress in Geography, 30(9):1125-1134 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
金海燕, 林以安, 陈建芳, 等, 2005. 黄海、东海颗粒有机碳的分布特征及其影响因子分析[J]. 海洋学报, 27(5):46-53.
|
|
JIN HAIYAN, LIN YIAN, CHEN JIANFANG, et al, 2005. Analysis of driving factors and distribution of particulate organic carbon in the Huanghai Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 27(5):46-53 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
刘荣高, 刘纪远, 庄大方, 2004. 基于MODIS数据估算晴空陆地光合有效辐射[J]. 地理学报, 59(1):64-73.
|
|
LIU RONGGAO, LIU JIYUAN, ZHUANG DAFANG, 2004. Estimation of land Photosynthetically active radiation in clear sky using MODIS[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 59(1):64-73 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
马翱慧, 刘湘南, 李婷, 等, 2013. 南海北部海域叶绿素a浓度时空特征遥感分析[J]. 海洋学报, 35(4):98-105.
|
|
MA AOHUI, LIU XIANGNAN, LI TING, et al, 2013. The satellite remotely-sensed analysis of the temporal and spatial variability of chlorophyll a concentration in the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(4):98-105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
ACHTERBERG E P, STEIGENBERGER S, MARSAY C M, et al, 2018. Iron biogeochemistry in the high latitude North Atlantic Ocean[J]. Scientific Reports, 8(1):1283.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19472-1
pmid: 29352137
|
| [8] |
BAKER A R, FRENCH M, LINGE K L, 2006a. Trends in aerosol nutrient solubility along a west-east transect of the Saharan dust plume[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(7):L07805.
|
| [9] |
BAKER A R, JICKELLS T D, BISWAS K F, et al, 2006b. Nutrients in atmospheric aerosol particles along the Atlantic Meridional Transect[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 53(14-16):1706-1719.
|
| [10] |
BHARTI P K. 2012-03-25. OMTO3d. Version 003. OMI/Aura TOMS-Like Ozone, Aerosol Index, Cloud Radiance Fraction L3 1 day 1 degree x 1 degree V3. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Archived by National Aeronautics and Space Administration, U.S. Government, Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC). https://doi.org/10.5067/Aura/OMI/DATA3001. https://disc.gsfc.nasa. gov/datacollection/OMTO3d_003.html. Digital Science Data.
|
| [11] |
BISHOP J K B, DAVIS R E, SHERMAN J T, 2002. Robotic observations of dust storm enhancement of carbon biomass in the North Pacific[J]. Science, 298(5594):817-821.
pmid: 12399588
|
| [12] |
BOPP L, KOHFELD K E, LE QUÉRÉ C, et al, 2003. Dust impact on marine biota and atmospheric CO2 during glacial periods[J]. Paleoceanography, 18(2):1046.
|
| [13] |
BOPP L, LÉVY M, RESPLANDY L, et al, 2015. Pathways of anthropogenic carbon subduction in the global ocean[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 42(15):6416-6423.
|
| [14] |
CHELTON D B, SCHLAX M G, SAMELSON R M, 2011. Global observations of nonlinear mesoscale eddies[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 91(2):167-216.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2011.01.002
|
| [15] |
DARMENOVA K, SOKOLIK I N, DARMENOV A, 2005. Characterization of east Asian dust outbreaks in the spring of 2001 using ground-based and satellite data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 110(D2):D02204.
|
| [16] |
FUNG I Y, MEYN S K, TEGEN I, et al, 2000. Iron supply and demand in the upper ocean[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 14(1):281-295.
|
| [17] |
GROUSSET F E, GINOUX P, BORY A, et al, 2003. Case study of a Chinese dust plume reaching the French Alps[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(6):1277.
|
| [18] |
HAMME R C, WEBLEY P W, CRAWFORD W R, et al, 2010. Volcanic ash fuels anomalous plankton bloom in subarctic northeast Pacific[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 37(19):L19604.
|
| [19] |
HAN YONGXIANG, ZHAO TIANLIANG, SONG LIANCHUN, et al, 2011. A linkage between Asian dust, dissolved iron and marine export production in the deep ocean[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 45(25):4291-4298.
|
| [20] |
HERMAN J R, BHARTIA P K, TORRES O, et al, 1997. Global distribution of UV-absorbing aerosols from Nimbus 7/TOMS data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 102(D14):16911-16922.
|
| [21] |
IMAI K, NOJIRI Y, TSURUSHIMA N, et al, 2002. Time series of seasonal variation of primary productivity at station KNOT (44°N, 155°E) in the sub-arctic western North Pacific[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 49(24-25):5395-5408.
|
| [22] |
JICKELLS T D, AN Z S, ANDERSEN K K, et al, 2005. Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate[J]. Science, 308(5718):67-71.
doi: 10.1126/science.1105959
pmid: 15802595
|
| [23] |
JICKELLS T D, BAKER A R, CHANCE R, 2016. Atmospheric transport of trace elements and nutrients to the oceans[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 374(2081):20150286.
|
| [24] |
JO C O, LEE J Y, PARK K A, et al, 2007. Asian dust initiated early spring bloom in the northern East/Japan Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(5):L05602.
|
| [25] |
JOHNSON W K, MILLER L A, SUTHERLAND N E, et al, 2005. Iron transport by mesoscale Haida eddies in the Gulf of Alaska[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 52(7-8):933-953.
|
| [26] |
MAHOWALD N M, BAKER A R, BERGAMETTI G, et al, 2005. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 19(4): GB4025.
|
| [27] |
MAHOWALD N M, ENGELSTAEDTER S, LUO CHAO, et al, 2009. Atmospheric iron deposition: global distribution, variability, and human perturbations[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 1:245-278.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.marine.010908.163727
pmid: 21141037
|
| [28] |
MAHOWALD N M, HAMILTON D S, MACKEY K R M, et al, 2018. Aerosol trace metal leaching and impacts on marine microorganisms[J]. Nature Communications, 9(1):2614.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04970-7
pmid: 29977041
|
| [29] |
MARTIN J H, 1990. Glacial-interglacial CO2 change: the iron hypojournal[J]. Paleoceanography, 5(1):1-13.
|
| [30] |
MATSUMOTO K, HONDA M C, SASAOKA K, et al, 2014. Seasonal variability of primary production and phytoplankton biomass in the western Pacific subarctic gyre: control by light availability within the mixed layer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(9):6523-6534.
doi: 10.1002/2014JC009982
|
| [31] |
MOORE J K, BRAUCHER O, 2008. Sedimentary and mineral dust sources of dissolved iron to the world ocean[J]. Biogeosciences, 5(3):631-656.
doi: 10.5194/bg-5-631-2008
|
| [32] |
POULTON S W, RAISWELL R, 2002. The low-temperature geochemical cycle of iron: from continental fluxes to marine sediment deposition[J]. American Journal of Science, 302(9):774-805.
doi: 10.2475/ajs.302.9.774
|
| [33] |
PROSPERO J M, 1999. Long-range transport of mineral dust in the global atmosphere: impact of African dust on the environment of the southeastern United States[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96(7):3396-3403.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3396
pmid: 10097049
|
| [34] |
SCANZA R A, HAMILTON D S, PEREZ GARCIA-PANDO C, et al, 2018. Atmospheric processing of iron in mineral and combustion aerosols: development of an intermediate- complexity mechanism suitable for Earth system models[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18(19):14175-14196.
doi: 10.5194/acp-18-14175-2018
|
| [35] |
SHI JINHUI, GAO HUIWANG, ZHANG JING, et al, 2012. Examination of causative link between a spring bloom and dry/wet deposition of Asian dust in the Yellow Sea, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 117(D17):D17304.
|
| [36] |
TAKEMURA T, NAKAJIMA T, DUBOVIK O, et al, 2002. Single-scattering albedo and radiative forcing of various aerosol species with a global three-dimensional model[J]. Journal of Climate, 15(4):333-352.
|
| [37] |
TAKEMURA T, NOZAWA T, EMORI S, et al, 2005. Simulation of climate response to aerosol direct and indirect effects with aerosol transport-radiation model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 110(D2):D02202.
|
| [38] |
TAKEMURA T, OKAMOTO H, MARUYAMA Y, et al, 2000. Global three-dimensional simulation of aerosol optical thickness distribution of various origins[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 105(D14):17853-17873.
|
| [39] |
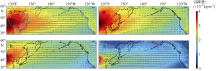
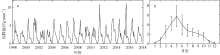
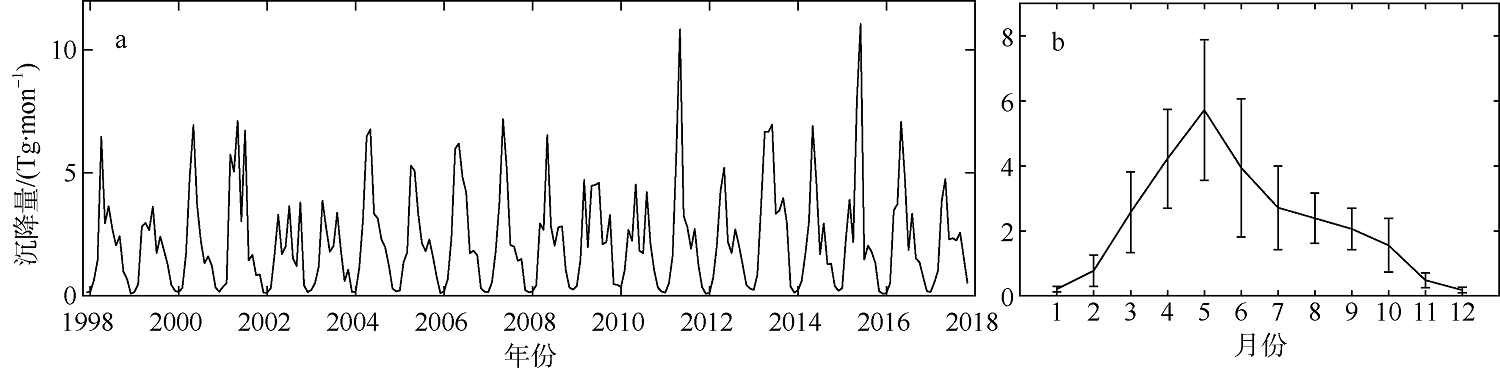
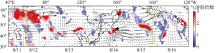
TAN SAICHUN, SHI GUANGYU, SHI JINHUI, et al, 2011. Correlation of Asian dust with chlorophyll and primary productivity in the coastal seas of China during the period from 1998 to 2008[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 116(G2):G02029.
|
| [40] |
TOMS Science Team ( Unrealeased), TOMS Earth-Probe Total Ozone (O3) Aerosol Index UV-Reflectivity UV-B Erythemal Irradiance Daily L3 Global 1 deg x 1.25 deg V008, Greenbelt, MD, Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC), Accessed:[2019], https://disc.gsfc.nasa. gov/datacollection/TOMSEPL3_008.html
|
| [41] |
YOON J E, KIM K, MACDONALD A M, et al, 2017. Spatial and temporal Variabilities of spring Asian dust events and their impacts on chlorophyll-a concentrations in the western North Pacific Ocean[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(3):1474-1482.
|
| [42] |
YOON J E, LIM J H, SHIM J M, et al, 2019. Spring 2018 Asian dust events: sources, transportation, and potential biogeochemical implications[J]. Atmosphere, 10(5):276.
|
| [43] |
YOUNG R W, CARDER K L, BETZER P R, et al, 1991. Atmospheric iron inputs and primary productivity: phytoplankton responses in the North Pacific[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 5(2):119-134.
doi: 10.1029/91GB00927
|
| [44] |
YUAN WEI, ZHANG JING, 2006. High correlations between Asian dust events and biological productivity in the western North Pacific[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(7):L07603.
|
| [45] |
ZHAO T L, GONG S L, ZHANG X Y, et al, 2003. Modeled size-segregated wet and dry deposition budgets of soil dust aerosol during ACE-Asia 2001: implications for trans-Pacific transport[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 108(D23):8665.
doi: 10.1029/2002JD003363
|
 ), WANG Yuntao2(
), WANG Yuntao2( ), QI Yiquan1, CHAI Fei2
), QI Yiquan1, CHAI Fei2