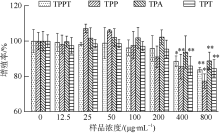
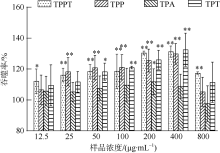
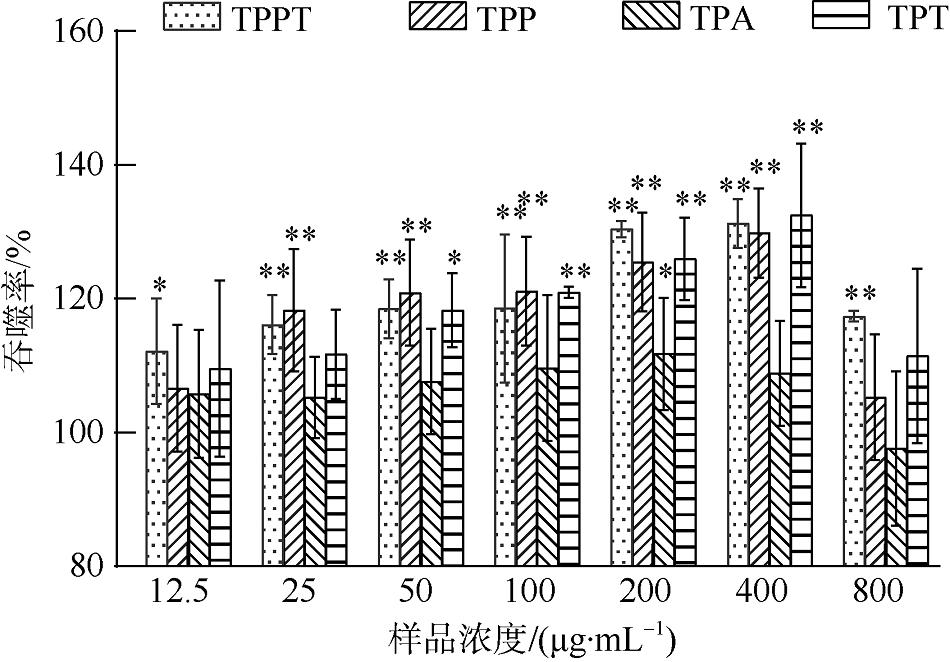
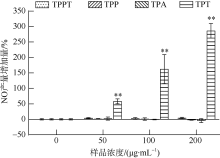
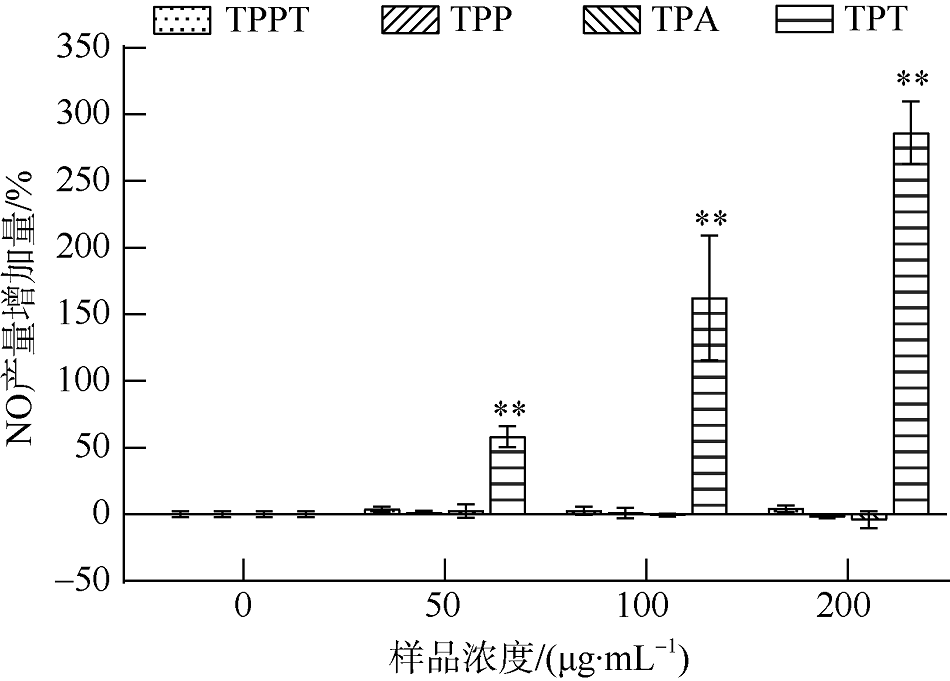
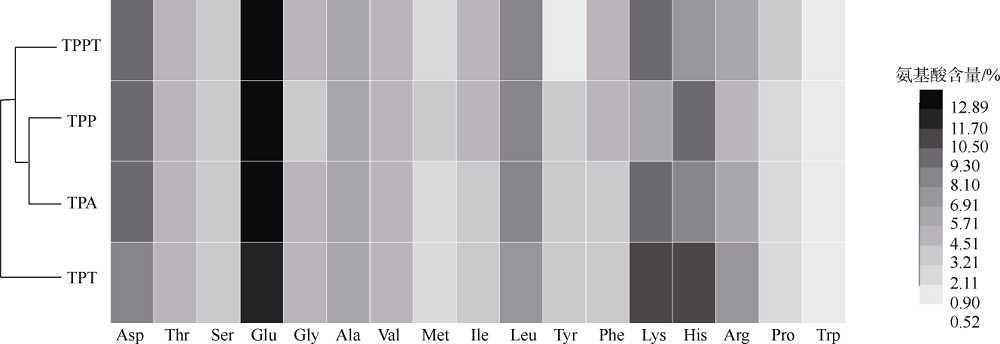
| [1] |
白生宾, 陈红香, 钟近洁, 等, 2011. MTT法检测RAW264.7细胞活力及可能因素分析[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 21(23):2831-2833.
|
|
BAI SHENGBIN, CHEN HONGXIANG, ZHONG JINJIE, et al, 2011. RAW264.7 cell viability via MTT assay and possible factor analysis[J]. China Journal of Modern Medicine, 21(23):2831-2833 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
杜帅, 宋茹, 罗红宇, 2014. 水解金枪鱼碎肉制备高F值寡肽[J]. 中国食品学报, 14(10):124-133.
|
|
DU SHUAI, SONG RU, LUO HONGYU, 2014. High fischer ratio oligo-peptide from hydrolysates of tuna meat[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 14(10):124-133 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
纪丽娜, 2012. 金枪鱼头酶解物免疫活性肽的分离及对小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞功能的影响[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学: 9-10.
|
|
JI LINA, 2012. Studies on separation of immune activity from tuna head hydrolysates and its effect on mouse peritoneal macrophages[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University: 9-10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站, 中国水产学会, 2019. 中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 38-40(in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
王晓芳, 陈同辛, 2013. 氨基酸与免疫功能的关系[J]. 国际儿科学杂志, 40(1):28-31.
|
|
WANG XIAOFANG, CHEN TONGXIN, 2013. Amino acids and immune functions[J]. International Journal of Pediatrics, 40(1):28-31 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
杨萍, 蔡本利, 洪鹏志, 等, 2009. 黄鳍金枪鱼头蛋白酶解液及其分级组分对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 28(1):131-135.
|
|
YANG PING, CAI BENLI, HONG PENGZHI, et al, 2009. Effect of tuna head enzymatic hydrolysate and its portions on inmmune function in mice[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 28(1):131-135 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
杨萍, 蔡本利, 洪鹏志, 2010. 黄鳍金枪鱼头蛋白酶解液及分级组分对小鼠脾淋巴细胞增殖的影响[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 22(3):498-501.
|
|
YANG PING, CAI BENLI, HONG PENGZHI, 2010. Effect of tuna head enzymatic hydrolysate and its portions on mouse spleen lymphocyte proliferation[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 22(3):498-501 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
叶盛旺, 杨最素, 李维, 等, 2019. 青蛤酶解多肽对RAW264.7巨噬细胞的免疫调节作用[J]. 食品科学, 40(7):185-191.
|
|
YE SHENGWANG, YANG ZUISU, LI WEI, et al, 2019. Immunomodulatory effects of peptides from enzymatic hydrolysate of Cyclina sinensis on RAW264.7 macrophages[J]. Food Science, 40(7):185-191 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
张爱琳, 段筱筠, 任斐, 等, 2016. 牛乳中主要过敏原的分离及其氨基酸成分分析[J]. 中国乳品工业, 44(12):4-6, 10.
|
|
ZHANG AILIN, DUAN XIAOJUN, REN FEI, et al, 2016. Study the separation on the main allergens in milk and its amino acid composition analysis[J]. China Dairy Industry, 44(12):4-6, 10 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
张彩梅, 张红梅, 于业军, 等, 2005. 扇贝多肽对小鼠免疫功能调节的研究[J]. 中国海洋药物, 24(3):18-21.
|
|
ZHANG CAIMEI, ZHANG HONGMEI, YU YEJUN, et al, 2005. Immunomodulation of polypeptides from Chlamys farreri (PCF) in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 2005, 24(3):18-21 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
张朋, 贺卯苏, 迟长凤, 等, 2014. 金枪鱼(Katsuwonus pelamis)碎肉蛋白降压肽的酶解制备及活性研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 45(5):1092-1098.
|
|
ZHANG PENG, HE MAOSU, CHI CHANGFENG, et al, 2014. Preparation and characterisation of an antihypertensive peptide from protein hydrolysate of askipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) ground meat[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 45(5):1092-1098 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
GHOSH S, PELLETT P L, AW-HASSAN A, et al, 2008. Impact of lysine-fortified wheat flour on morbidity and immunologic variables among members of rural families in northwest Syria[J]. Food and Nutrition Bulletin, 29(3):163-171.
doi: 10.1177/156482650802900302
|
| [13] |
GUERARD F, GUIMAS L, BINET A, 2002. Production of tuna waste hydrolysates by a commercial neutral protease preparation[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 19- 20:489-498.
|
| [14] |
HAN YUNA, BYUN S H, PARK J H, et al, 2015. Bioactive properties of enzymatic hydrolysates from abdominal skin gelatin of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares)[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 50(9):1996-2003.
doi: 10.1111/ijfs.2015.50.issue-9
|
| [15] |
HE WEIWEI, SU GUOWAN, SUN-WATERHOUSE D, et al, 2019. In vivo anti-hyperuricemic and xanthine oxidase inhibitory properties of tuna protein hydrolysates and its isolated fractions[J]. Food Chemistry, 272:453-461.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.057
|
| [16] |
HOU HU, FAN YAN, LI BAFANG, et al, 2012. Preparation of immunomodulatory hydrolysates from Alaska pollock frame[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 92(15):3029-3038.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.5719
|
| [17] |
HOU HU, FAN YAN, WANG SHIKAI, et al, 2016. Immunomodulatory activity of Alaska pollock hydrolysates obtained by glutamic acid biosensor- Artificial neural network and the identification of its active central fragment[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 24:37-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.03.033
|
| [18] |
LIN HUIWEN, LIU CHENGWEI, YANG D J, et al, 2017. Dunaliella salina alga extract inhibits the production of interleukin-6, nitric oxide, and reactive oxygen species by regulating nuclear factor-κB/Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription in virus-infected RAW264.7 cells[J]. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 25(4):908-918.
doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2016.11.018
|
| [19] |
LIND M, HAYES A, CAPMDA M, et al, 2017. Inducible nitric oxide synthase: Good or bad?[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 93:370-375.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.036
|
| [20] |
MIZOCK B A, 2010. Immunonutrition and critical illness: an update[J]. Nutrition, 26(7-8):701-707.
doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2009.11.010
|
| [21] |
PEZESHK S, OJAGH S M, REZAEI M, et al, 2019. Fractionation of protein hydrolysates of fish waste using membrane ultrafiltration: Investigation of antibacterial and antioxidant activities[J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 11(3):1015-1022.
doi: 10.1007/s12602-018-9483-y
|
| [22] |
SUTANBAWA Y, AKNES A, 2006. Tuna process waste an unexploited resource[J]. Infofish International, 3:37-40.
|
| [23] |
YANG FAN, COMTOIS A S, FANG LIWEI, et al, 2002. Nitric oxide-derived nitrate anion contributes to endotoxic shock and multiple organ injury/dysfunction[J]. Critical Care Medicine, 30(3):650-657.
doi: 10.1097/00003246-200203000-00026
|
 ), PAN Jianyu2, CAI Bingna2, TAO Shuhong1(
), PAN Jianyu2, CAI Bingna2, TAO Shuhong1( )
)