热带海洋学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 62-74.doi: 10.11978/2021015CSTR: 32234.14.2021015
基于精细温度观测的南海东北部陆坡-深海盆底层湍流混合*
李杨1,5( ), 黄鹏起1,5, 鲁远征1,2, 屈玲1,2, 郭双喜1,2,4,5, 岑显荣1,2, 周生启1,2,4,5(
), 黄鹏起1,5, 鲁远征1,2, 屈玲1,2, 郭双喜1,2,4,5, 岑显荣1,2, 周生启1,2,4,5( ), 张佳政2,3, 丘学林2,3,5
), 张佳政2,3, 丘学林2,3,5
- 1. 热带海洋环境国家重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
2. 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
3. 中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
4. 中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 广东 广州 510301
5. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2021-02-05修回日期:2021-04-13出版日期:2022-01-10发布日期:2021-04-16 -
通讯作者:周生启 -
作者简介:李杨(1996—), 女, 江苏省东台市人, 硕士, 从事深海动力学研究。email:liyang18@mails.ucas.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(91952106);国家自然科学基金项目(41776033);国家自然科学基金项目(42006196);广州市科技计划项目(201904010312);广州市科技计划项目(201804020056)
Bottom turbulent mixing of continental slope - deep sea basin in northeastern South China Sea based on high-resolution temperature observation
LI Yang1,5( ), HUANG Pengqi1,5, LU Yuanzheng1,2, QU Ling1,2, GUO Shuangxi1,2,4,5, CEN Xianrong1,2, ZHOU Shengqi1,2,4,5(
), HUANG Pengqi1,5, LU Yuanzheng1,2, QU Ling1,2, GUO Shuangxi1,2,4,5, CEN Xianrong1,2, ZHOU Shengqi1,2,4,5( ), ZHANG Jiazheng2,3, QIU Xuelin2,3,5
), ZHANG Jiazheng2,3, QIU Xuelin2,3,5
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
3. Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology of Chinese Academy of Sciences (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
4. Institute of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering (Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
5. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2021-02-05Revised:2021-04-13Online:2022-01-10Published:2021-04-16 -
Contact:ZHOU Shengqi -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(91952106);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41776033);National Natural Science Foundation of China(42006196);Science and Technology Foundation of Guangzhou(201904010312);Science and Technology Foundation of Guangzhou(201804020056)
摘要:
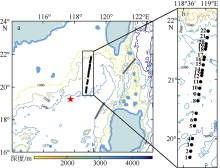
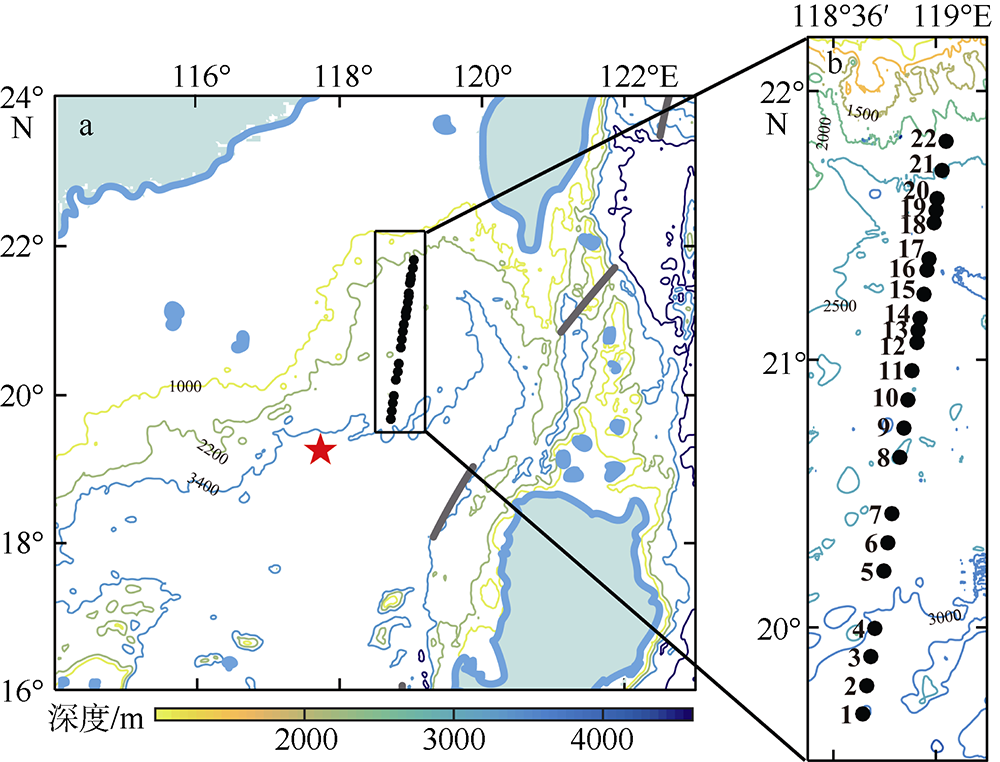
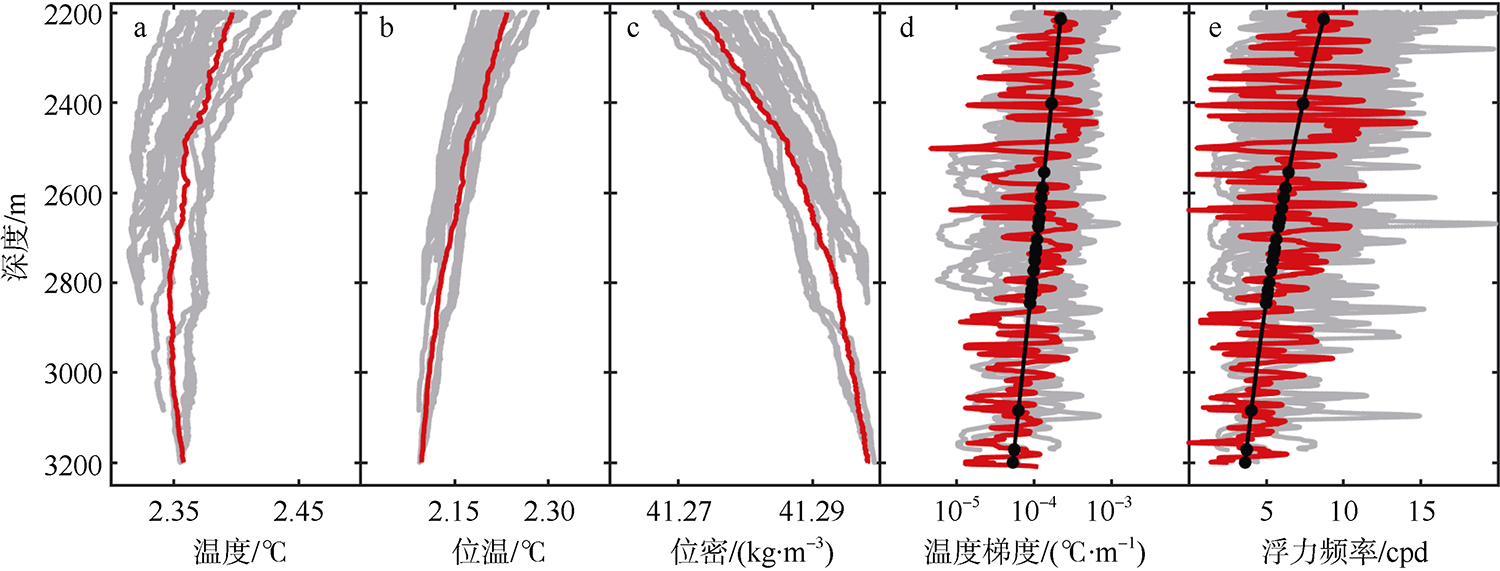
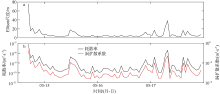
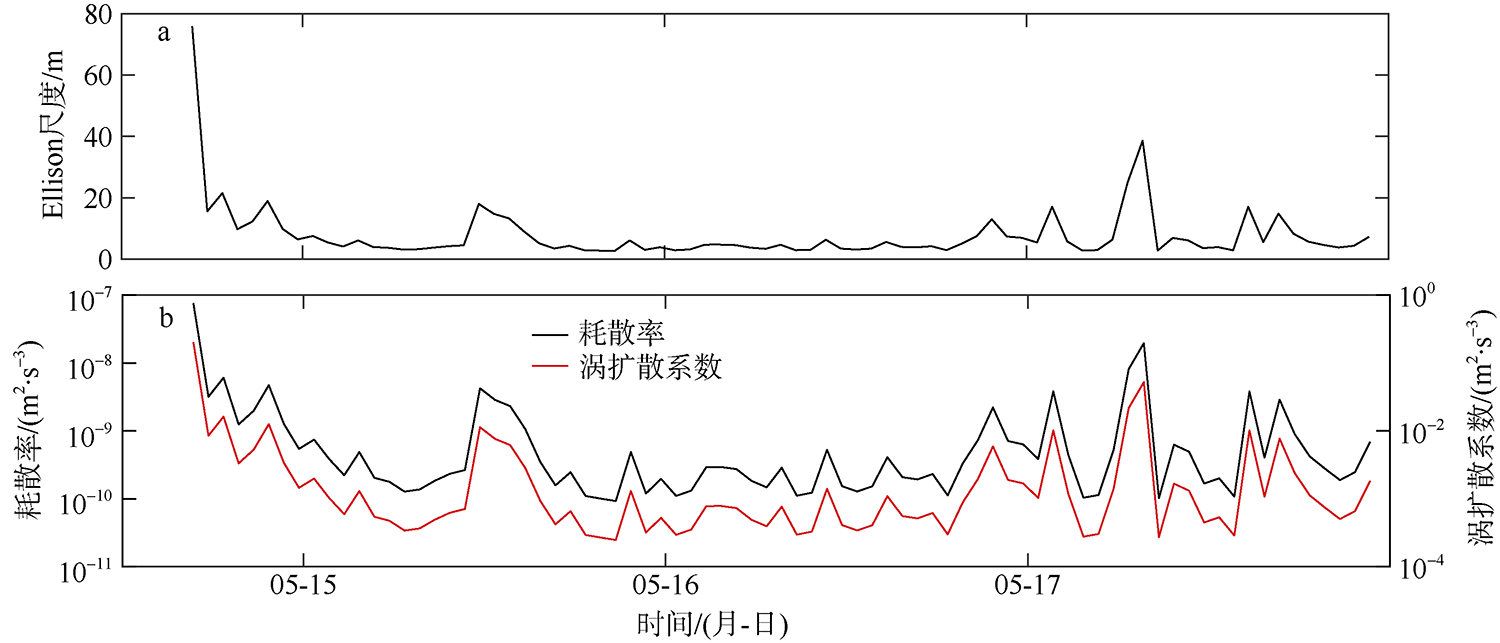
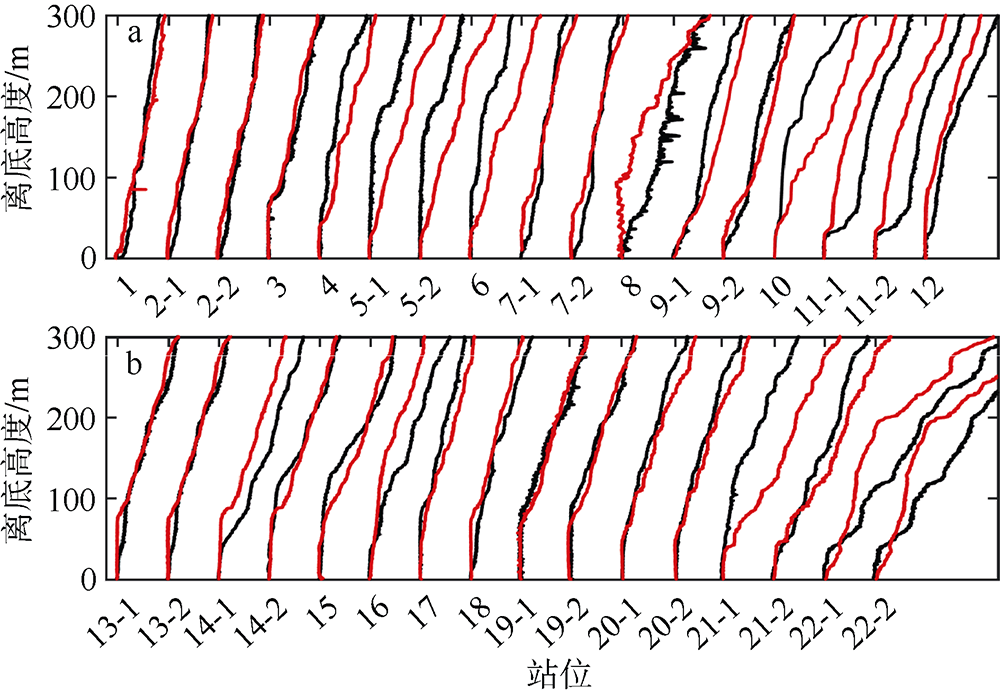
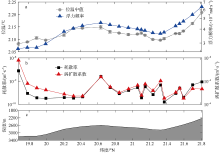
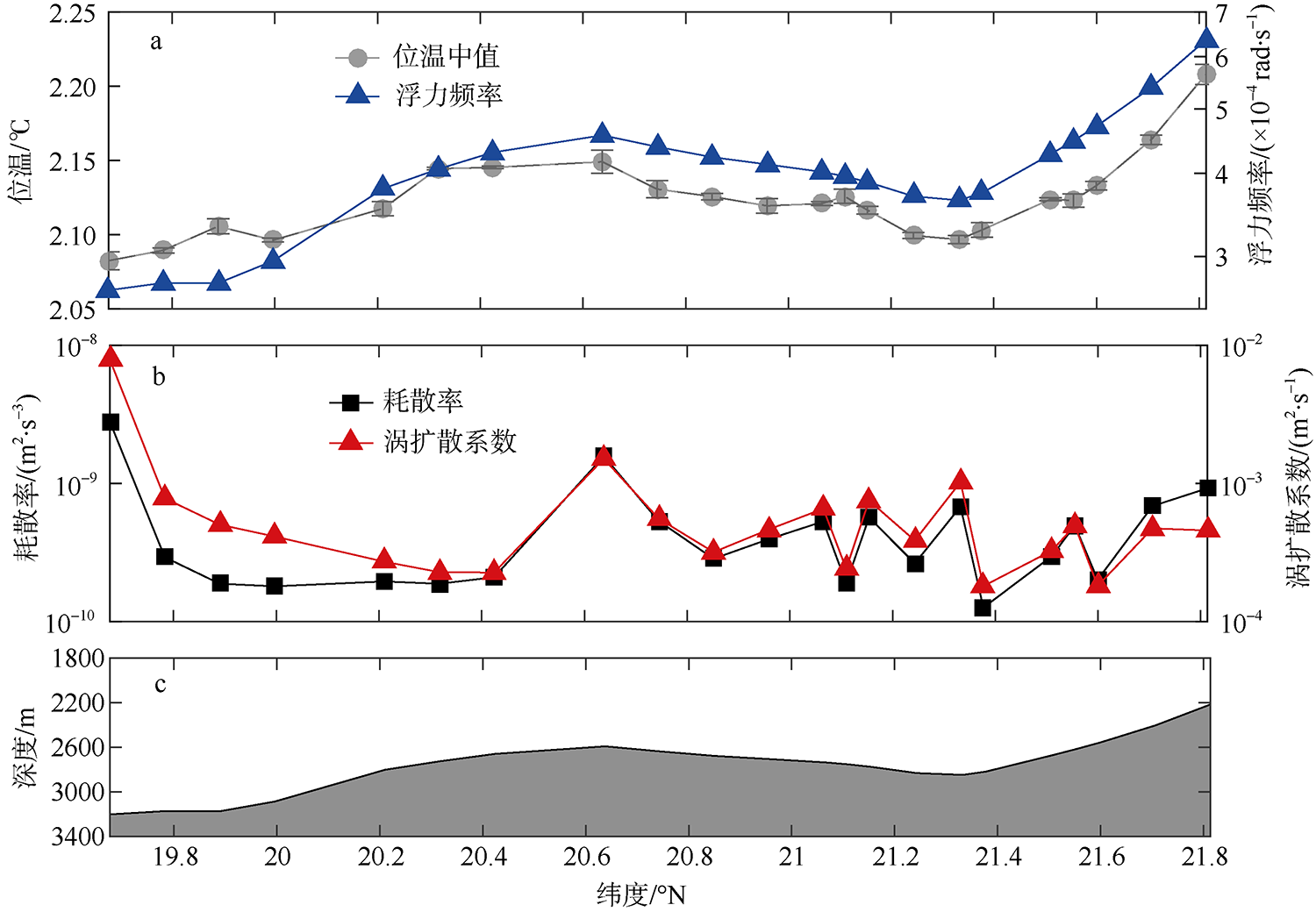
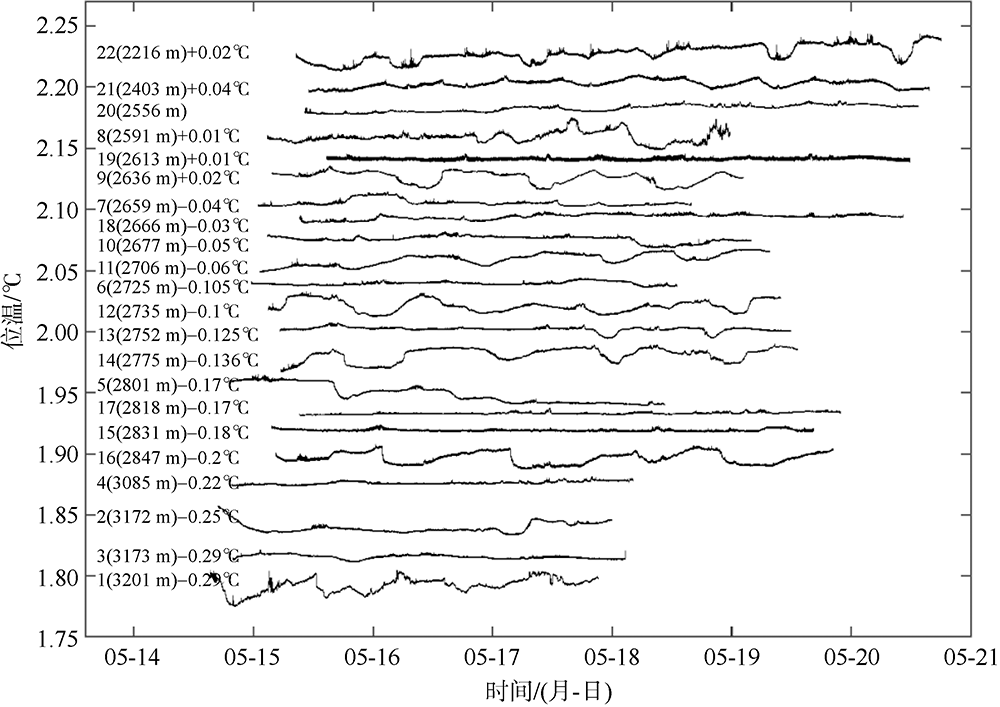
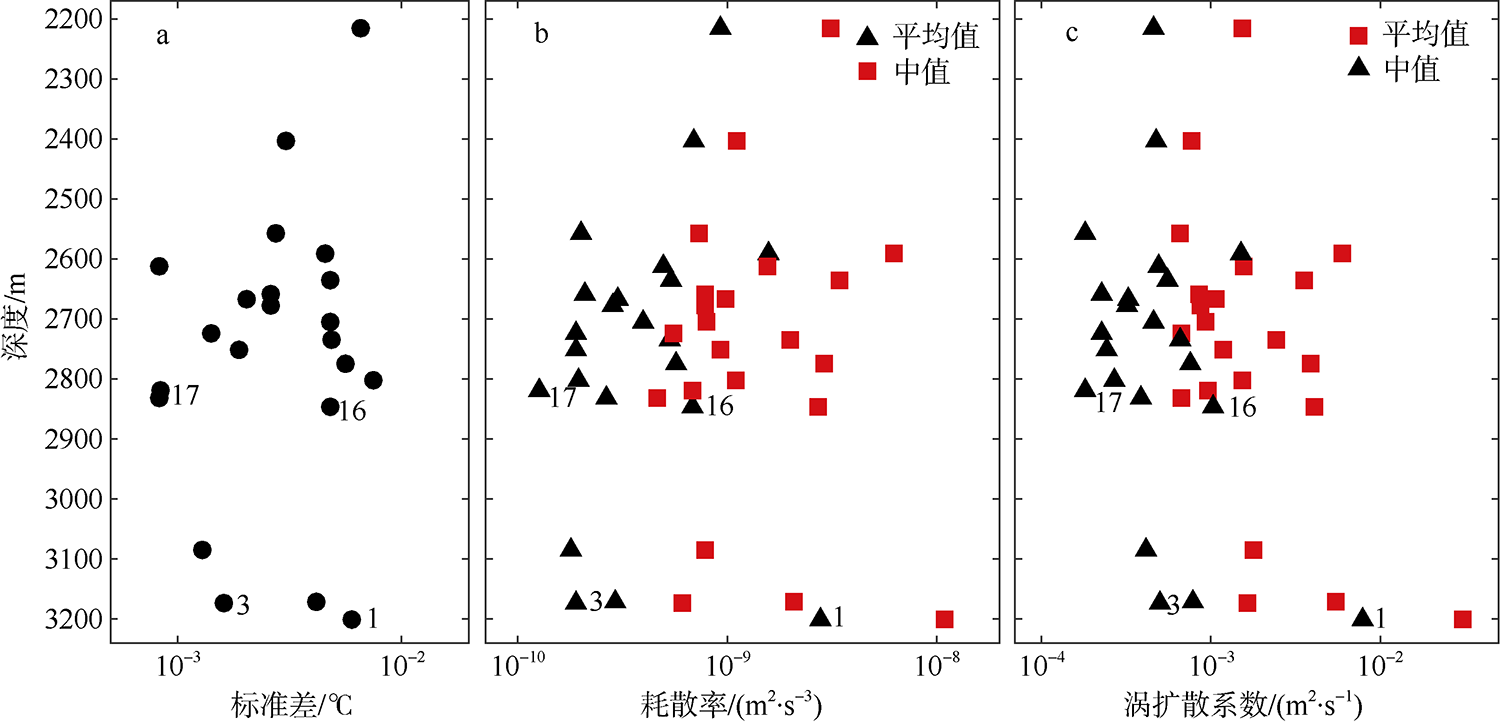
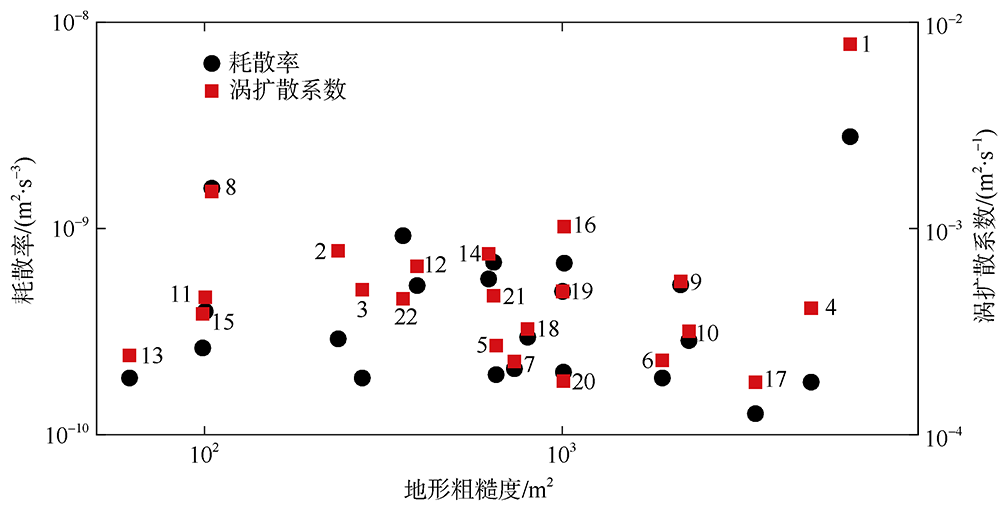
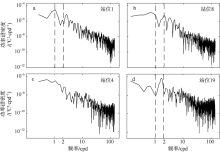
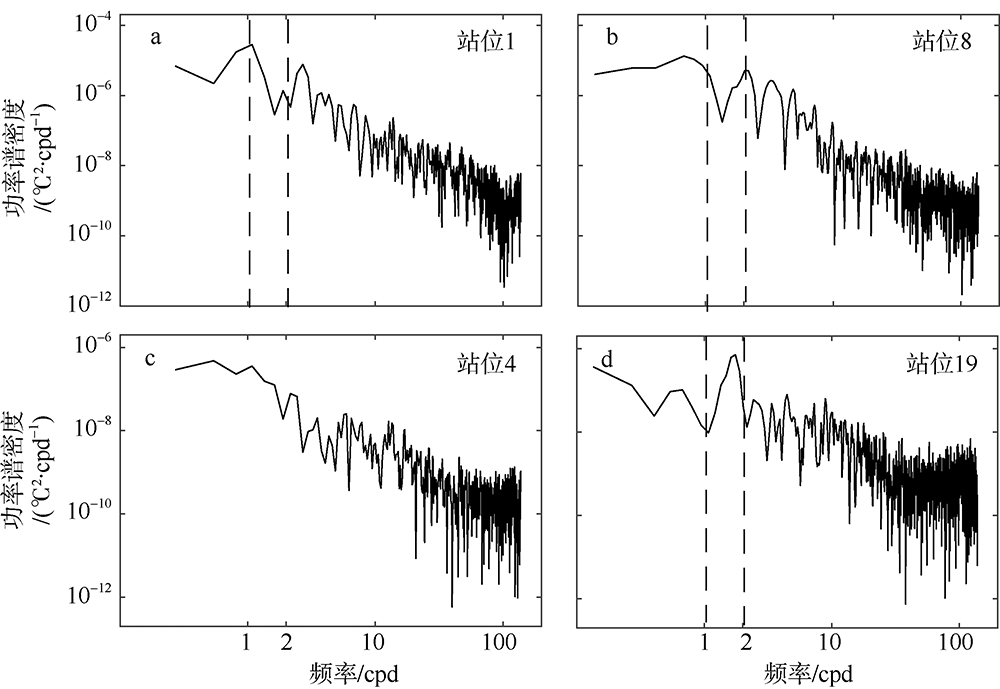
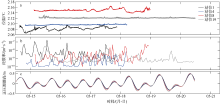
南海是存在强湍流混合的边缘海之一, 但前人对南海湍流混合的研究更多关注的是中上层, 对底层则鲜有关注。本文基于高分辨率温度传感器于2019年5月在南海东北部22个站位海底上方0.5m处持续观测4.4d的温度数据, 分析了2216~3200m深度范围内底层海水温度的时间变化特征, 并探讨了地形粗糙度和内潮对底层湍流混合的影响。分析结果表明, 南海东北部各站位底层海水的温度变化量级约为10-4~10-3℃; 温度变化趋势与正压潮变化趋势不同, 温度能谱显示多数站位在全日和半日频带区间出现谱峰, 温度变化更多地受斜压潮影响, 全日、半日内潮起主要调制作用。陆坡-深海盆过渡区及深海盆底层的湍动能耗散率量级为10-10~10-9m2∙s-3, 涡扩散系数量级为10-4~10-3m2∙s-1。观测数据未能显示底层湍流混合与地形粗糙度存在明显的相关性。底层湍流混合的空间分布与过去观测到的南海北部深海盆内潮的南北不对称性分布一致。
中图分类号:
- P731.26
引用本文
李杨, 黄鹏起, 鲁远征, 屈玲, 郭双喜, 岑显荣, 周生启, 张佳政, 丘学林. 基于精细温度观测的南海东北部陆坡-深海盆底层湍流混合*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 62-74.
LI Yang, HUANG Pengqi, LU Yuanzheng, QU Ling, GUO Shuangxi, CEN Xianrong, ZHOU Shengqi, ZHANG Jiazheng, QIU Xuelin. Bottom turbulent mixing of continental slope - deep sea basin in northeastern South China Sea based on high-resolution temperature observation[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 62-74.
表1
各测站详细信息"
| 站位 | 东经 | 北纬 | 深度 /m | 测试 时长/d | 地形粗 糙度/m2 | 温度梯度 /(℃∙m-1) | 浮力频率 /(rad∙s-1) | 底混合层厚度1/m | 底混合层厚度2/m | 湍动能耗散率中值/(m2∙s-3) | 涡扩散系数中值/(m2∙s-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 118°43′12″ | 19°40′48″ | 3201 | 3.24 | 6390 | 5.36×10-5 | 2.67×10-4 | 4 | 8 | 2.80×10-9 | 7.90×10-3 | ||||
| 2-1 | 118°43′48″ | 19°46′48″ | 3172 | 3.32 | 236 | 5.59×10-5 | 2.74×10-4 | 8 | 45 | 2.93×10-10 | 7.82×10-4 | ||||
| 2-2 | 118°43′48″ | 19°46′48″ | 3172 | 3.32 | 236 | 5.59×10-5 | 2.74×10-4 | 8 | 40 | 6.99×10-10 | 1.90×10-3 | ||||
| 3 | 118°45′0″ | 19°53′24″ | 3173 | 3.39 | 277 | 5.58×10-5 | 2.73×10-4 | 68 | 68 | 1.89×10-10 | 5.04×10-4 | ||||
| 4 | 118°45′36″ | 20°0′0″ | 3085 | 3.47 | 4970 | 6.33×10-5 | 2.95×10-4 | 63 | 40 | 1.80×10-10 | 4.14×10-4 | ||||
| 5-1 | 118°48′0″ | 20°12′36″ | 2801 | 3.62 | 653 | 9.55×10-5 | 3.79×10-4 | 151 | 21 | 1.96×10-10 | 2.72×10-4 | ||||
| 5-2 | 118°48′0″ | 20°12′36″ | 2801 | 3.62 | 653 | 9.55×10-5 | 3.79×10-4 | 151 | 21 | 4.55×10-10 | 6.32×10-4 | ||||
| 6 | 118°48′36″ | 20°19′12″ | 2725 | 3.69 | 1910 | 1.07×10-4 | 4.06×10-4 | 85 | 35 | 1.88×10-10 | 2.29×10-4 | ||||
| 7-1 | 118°49′48″ | 20°25′12″ | 2659 | 3.78 | 736 | 1.17×10-4 | 4.30×10-4 | 6 | 53 | 2.10×10-10 | 2.27×10-4 | ||||
| 7-2 | 118°49′48″ | 20°25′12″ | 2659 | 3.78 | 736 | 1.17×10-4 | 4.30×10-4 | 6 | 60 | 2.76×10-10 | 2.99×10-4 | ||||
| 8 | 118°51′36″ | 20°38′24″ | 2591 | 4.04 | 105 | 1.29×10-4 | 4.57×10-4 | 4 | 91 | 1.58×10-9 | 1.50×10-3 | ||||
| 9-1 | 118°52′48″ | 20°44′24″ | 2636 | 4.11 | 2150 | 1.21×10-4 | 4.39×10-4 | 8 | 30 | 5.36×10-10 | 5.57×10-4 | ||||
| 9-2 | 118°52′48″ | 20°44′24″ | 2636 | 4.11 | 2150 | 1.21×10-4 | 4.39×10-4 | 8 | 25 | 5.69×10-10 | 5.91×10-4 | ||||
| 10 | 118°53′24″ | 20°51′0″ | 2677 | 4.18 | 2260 | 1.14×10-4 | 4.23×10-4 | 27 | 40 | 2.86×10-10 | 3.19×10-4 | ||||
| 11-1 | 118°54′36″ | 20°57′36″ | 2706 | 4.26 | 100 | 1.10×10-4 | 4.13×10-4 | 29 | 30 | 3.95×10-10 | 4.64×10-4 | ||||
| 11-2 | 118°54′36″ | 20°57′36″ | 2706 | 4.26 | 100 | 1.10×10-4 | 4.13×10-4 | 30 | 35 | 3.88×10-10 | 4.56×10-4 | ||||
| 12 | 118°55′12″ | 21°4′12″ | 2735 | 4.33 | 392 | 1.05×10-4 | 4.02×10-4 | 30 | 80 | 5.32×10-10 | 6.58×10-4 | ||||
| 13-1 | 118°55′48″ | 21°6′36″ | 2752 | 4.38 | 62 | 1.02×10-4 | 3.96×10-4 | 32 | 69 | 1.90×10-10 | 2.42×10-4 | ||||
| 13-2 | 118°55′48″ | 21°6′36″ | 2752 | 4.38 | 62 | 1.02×10-4 | 3.96×10-4 | 32 | 70 | 3.18×10-10 | 4.06×10-4 | ||||
| 14-1 | 118°56′24″ | 21°9′0″ | 2775 | 5.53 | 624 | 9.92×10-5 | 3.88×10-4 | 25 | 75 | 5.68×10-10 | 7.54×10-4 | ||||
| 14-2 | 118°56′24″ | 21°9′0″ | 2775 | 5.53 | 624 | 9.92×10-5 | 3.88×10-4 | 40 | 75 | 7.47×10-10 | 9.91×10-4 | ||||
| 15 | 118°57′0″ | 21°14′24″ | 2831 | 4.52 | 99 | 9.15×10-5 | 3.70×10-4 | 80 | 41 | 2.64×10-10 | 3.87×10-4 | ||||
| 16 | 118°58′12″ | 21°19′48″ | 2847 | 4.65 | 1010 | 8.94×10-5 | 3.64×10-4 | 37 | 0 | 6.81×10-10 | 1.00×10-3 | ||||
| 17 | 118°58′12″ | 21°22′48″ | 2818 | 4.69 | 3480 | 9.32×10-5 | 3.74×10-4 | 78 | 53 | 1.27×10-10 | 1.84×10-4 | ||||
| 18 | 118°59′24″ | 21°30′36″ | 2666 | 5.17 | 800 | 1.16×10-4 | 4.27×10-4 | 10 | 70 | 2.99×10-10 | 3.27×10-4 | ||||
| 19-1 | 119°0′0″ | 21°33′0″ | 2613 | 5.21 | 1000 | 1.25×10-4 | 4.48×10-4 | 80 | 58 | 4.98×10-10 | 4.97×10-4 | ||||
| 19-2 | 119°0′0″ | 21°33′0″ | 2613 | 5.21 | 1000 | 1.25×10-4 | 4.48×10-4 | 93 | 58 | 1.82×10-10 | 1.81×10-4 | ||||
| 20-1 | 119°0′36″ | 21°36′0″ | 2556 | 5.53 | 1010 | 1.36×10-4 | 4.71×10-4 | 41 | 48 | 2.01×10-10 | 1.82×10-4 | ||||
| 20-2 | 119°0′36″ | 21°36′0″ | 2556 | 5.53 | 1010 | 1.36×10-4 | 4.71×10-4 | 41 | 48 | 2.40×10-10 | 2.16×10-4 | ||||
| 21-1 | 119°1′12″ | 21°42′36″ | 2403 | 5.32 | 643 | 1.70×10-4 | 5.39×10-4 | 4 | 35 | 6.87×10-10 | 4.74×10-4 | ||||
| 21-2 | 119°1′12″ | 21°42′36″ | 2403 | 5.32 | 643 | 1.70×10-4 | 5.39×10-4 | 6 | 42 | 6.63×10-10 | 4.57×10-4 | ||||
| 22-1 | 119°2′24″ | 21°48′36″ | 2216 | 5.39 | 359 | 2.22×10-4 | 6.35×10-4 | 15 | 12 | 9.23×10-10 | 4.57×10-4 | ||||
| 22-2 | 119°2′24″ | 21°48′36″ | 2216 | 5.39 | 359 | 2.22×10-4 | 6.35×10-4 | 15 | 12 | 8.89×10-10 | 4.40×10-4 | ||||
| [1] | 李敏, 2013. 基于Thorpe尺度对南海深层混合的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学. |
| LI MIN, 2013. Study of abyssal mixing in the South China Sea based on Thorpe Scale[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 梁辉, 郑洁, 田纪伟, 2016. 南海西北陆坡区内潮与近惯性内波观测研究[J]. 海洋学报, 38(11): 32-42. |
| LIANG HUI, ZHENG JIE, TIAN JIWEI,2016. Observation of internal tides and near-inertial internal waves on the continental slope in the northwestern South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 38(11): 32-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 刘倩, 2016. 南海内潮的结构与变化[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. |
| LIU QIAN, 2016. Structure and variability of internal tides in the South China Sea[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 尚晓东, 卢著敏, 谢晓辉, 等, 2010. 海洋湍流与海洋混合研究及其进展[C]// 第八届全国实验流体力学学术会议论文集. 广州: 中国力学学会: 1. (in Chinese) |
| [5] | SHANMUGAM G, 2017. 等深流沉积: 物理海洋学、过程沉积学和石油地质学[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 44(2): 177-195. |
| SHANMUGAM G, 2017. Contourites: Physical oceanography, process sedimentology, and petroleum geology[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 44(2): 177-195. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 谢皆烁, 2015. 水体层化及中尺度涡旋对南海北部内孤立波生成演化的影响[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. |
| XIE JIESHUO, 2015. Effects of the stratification and mesoscale eddy on the generation and evolution of internal solitary waves in the northern South China Sea[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 张效谦, 2005. 南海北部陆架陆坡区内波与混合研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学. |
| ZHANG XIAOQIAN, 2005. Study of waves and mixing in the continental slope of northern South China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 赵斌, 刘胜旋, 李丽青, 等, 2018. 南海冷泉分布特征及油气地质意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 34(10): 32-43. |
| ZHAO BIN, LIU SHENGXUAN, LI LIQING, et al, 2018. Distribution pattern of cold seeps in South China Sea and its geological significance[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 34(10): 32-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 赵玖强, 张艳伟, 刘志飞, 等, 2019. 南海北部深海潮汐的季节性变化特征[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 49(4): 717-730. |
| ZHAO JIUQIANG, ZHANG YANWEI, LIU ZHIFEI, et al, 2019. Seasonal variability of tides in the deep northern South China Sea[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 62(4): 671-683. | |
| [10] | BEAULIEU S, BALDWIN R, 1998. Temporal variability in currents and the benthic boundary layer at an abyssal station off central California[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 45(4-5): 587-615. |
| [11] |
CALLIES J, FERRARI R, 2018. Baroclinic instability in the presence of convection[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 48(1): 45-60.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-17-0028.1 |
| [12] |
CAO ANZHOU, GUO ZHENG, LV XIANQING, et al, 2017. Coherent and incoherent features, seasonal behaviors and spatial variations of internal tides in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 172: 75-83.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2017.03.005 |
| [13] |
CIMATORIBUS A A, VAN HAREN H, GOSTIAUX L, 2014. Comparison of Ellison and Thorpe scales from Eulerian ocean temperature observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(10): 7047-7065.
doi: 10.1002/2014JC010132 |
| [14] |
CRAWFORD W R, 1986. A comparison of length scales and decay times of turbulence in stably stratified flows[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 16(11): 1847-1854.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1986)016<1847:ACOLSA>2.0.CO;2 |
| [15] | DILLON T M, 1982. Vertical overturns: A comparison of Thorpe and Ozmidov length scales[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 87(C12): 9601-9613. |
| [16] |
EGBERT G D, RAY R D, 2000. Significant dissipation of tidal energy in the deep ocean inferred from satellite altimeter data[J]. Nature, 405(6788): 775-778.
doi: 10.1038/35015531 |
| [17] |
ELLISON T H, 1957. Turbulent transport of heat and momentum from an infinite rough plane[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2(5): 456-466.
doi: 10.1017/S0022112057000269 |
| [18] |
FERRON B, MERCIER H, SPEER K, et al, 1998. Mixing in the Romanche fracture zone[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 28(10): 1929-1945.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1998)028<1929:MITRFZ>2.0.CO;2 |
| [19] |
GARGETT A E, 1989. Ocean turbulence[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 21(1): 419-451.
doi: 10.1146/fluid.1989.21.issue-1 |
| [20] | GREGG M C, 1987. Diapycnal mixing in the thermocline: A review[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 92(C5): 5249-5286. |
| [21] |
HOLMES R M, DE LAVERGNE C, MCDOUGALL T J, 2019. Tracer transport within abyssal mixing layers[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 49(10): 2669-2695.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-19-0006.1 |
| [22] | HOLTERMANN P L, UMLAUF L, 2012. The Baltic sea tracer release experiment: 2. Mixing processes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117(C1): C01022. |
| [23] | HUANG PENGQI, CEN XIANRONG, GUO SHUANGXI, et al, 2021. Variance of bottom water temperature at the continental margin of the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 126(2): e2020JC015843. |
| [24] |
ITSWEIRE E C, 1984. Measurements of vertical overturns in a stably stratified turbulent flow[J]. The Physics of Fluids, 27(4): 764.
doi: 10.1063/1.864704 |
| [25] |
ITSWEIRE E C, KOSEFF J R, BRIGGS D A, et al, 1993. Turbulence in stratified shear flows: implications for interpreting shear-induced mixing in the ocean[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 23(7): 1508-1522.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1993)023<1508:TISSFI>2.0.CO;2 |
| [26] | JING ZHAO, WU LIXIN, LI LEI, et al, 2011. Turbulent diapycnal mixing in the subtropical northwestern Pacific: Spatial-seasonal variations and role of eddies[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C10): C10028. |
| [27] |
KUNZE E, MACKAY C, MCPHEE-SHAW E E, et al, 2012. Turbulent mixing and exchange with Interior waters on sloping boundaries[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 42(6): 910-927.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-11-075.1 |
| [28] |
LEDWELL J R, MONTGOMERY E T, POLZIN K L, et al, 2000. Evidence for enhanced mixing over rough topography in the abyssal ocean[J]. Nature, 403(6766): 179-182.
doi: 10.1038/35003164 |
| [29] |
LI YING, XU YONGSHENG, 2014. Penetration depth of diapycnal mixing generated by wind stress and flow over topography in the northwestern Pacific[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(8): 5501-5514.
doi: 10.1002/2013JC009681 |
| [30] |
LOZOVATSKY I D, SHAPOVALOV S M, 2012. Thickness of the mixed bottom layer in the Northern Atlantic[J]. Oceanology, 52(4): 447-452.
doi: 10.1134/S0001437012010134 |
| [31] |
MA B B, LIEN R C, KO D S, 2013. The variability of internal tides in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 69(5): 619-630.
doi: 10.1007/s10872-013-0198-0 |
| [32] |
MUNK W, WUNSCH C, 1998. Abyssal recipes Ⅱ: energetics of tidal and wind mixing[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 45(12): 1977-2010.
doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(98)00070-3 |
| [33] | NASH J D, ALFORD M H, KUNZE E, et al, 2007. Hotspots of deep ocean mixing on the Oregon continental slope[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(1): L01605. |
| [34] |
OSBORN T R, 1980. Estimates of the local rate of vertical diffusion from dissipation measurements[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 10(1): 83-89.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1980)010<0083:EOTLRO>2.0.CO;2 |
| [35] | OZMIDOV R V, 1965. On the turbulent exchange in a stably stratified ocean[J]. Izvestiya, Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics, 1: 853-860. |
| [36] | PETERS H, GREGG M C, SANFORD T B, 1995. Detail and scaling of turbulent overturns in the Pacific Equatorial Undercurrent[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 100(C9): 18349-18368. |
| [37] | POLZIN K L, TOOLE J M, LEDWELL J R, et al, 1997. Spatial variability of turbulent mixing in the Abyssal Ocean[J]. Science, 276(5309): 93-96. |
| [38] |
RAHMSTORF S, 2003. Thermohaline circulation: The current climate[J]. Nature, 421(6924): 699.
doi: 10.1038/421699a |
| [39] |
SHANG XIAODONG, LIANG CHANGRONG, CHEN GUIYING, 2017. Spatial distribution of turbulent mixing in the upper ocean of the South China Sea[J]. Ocean Science, 13(3): 503-519.
doi: 10.5194/os-13-503-2017 |
| [40] |
SIMMONS H, CHANG M H, CHANG Y T, et al, 2011. Modeling and prediction of internal waves in the South China Sea[J]. Oceanography, 24(4): 88-99.
doi: 10.5670/oceanog |
| [41] |
STANSFIELD K, GARRETT C, DEWEY R, 2001. The Probability distribution of the Thorpe displacement within overturns in Juan de Fuca Strait[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 31(12): 3421-3434.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(2001)031<3421:TPDOTT>2.0.CO;2 |
| [42] |
THORPE S A, 1977. Turbulence and mixing in a Scottish Loch[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 286(1334): 125-181.
doi: 10.1098/rsta.1977.0112 |
| [43] |
TIAN JIWEI, YANG QINGXUAN, ZHAO WEI, 2009. Enhanced diapycnal mixing in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 39(12): 3191-3203.
doi: 10.1175/2009JPO3899.1 |
| [44] |
TOOLE J. M., SCHMITT R. W., Polzin K. L., 1997, Near-boundary mixing above the flanks of a mid-latitude seamount, Journal of Geophysical Research, 102: 947-959.
doi: 10.1029/96JC03160 |
| [45] |
TSENG Y H, FERZIGER J H, 2001. Mixing and available potential energy in stratified flows[J]. Physics of Fluids, 13(5): 1281-1293.
doi: 10.1063/1.1358307 |
| [46] |
TURNEWITSCH R, GRAF G, 2003. Variability of particulate seawater properties related to bottom mixed layer-associated internal waves in shallow water on a time scale of hours[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 48(3): 1254-1264.
doi: 10.4319/lo.2003.48.3.1254 |
| [47] | VAN HAREN H, GOSTIAUX L, 2011. Large internal waves advection in very weakly stratified deep Mediterranean waters[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 28(22): L22603. |
| [48] |
WANG XIAOWEI, PENG SHIQIU, LIU ZHIYU, et al, 2016. Tidal mixing in the South China Sea: An estimate based on the internal tide energetics[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 46(1): 107-124.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-15-0082.1 |
| [49] |
WATERHOUSE A F, MACKINNON J A, NASH J D, et al, 2014. Global patterns of diapycnal mixing from measurements of the turbulent dissipation rate[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 44(7): 1854-1872.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-13-0104.1 |
| [50] |
XU ZHENHUA, YIN BAOSHU, HOU YIJUN, et al, 2013. Variability of internal tides and near-inertial waves on the continental slope of the northwestern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 118(1): 197-211.
doi: 10.1029/2012JC008212 |
| [51] |
XU ZHENHUA, YIN BAOSHU, HOU YIJUN, et al, 2014. Seasonal variability and north-south asymmetry of internal tides in the deep basin west of the Luzon Strait[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 134: 101-112.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2014.03.002 |
| [52] |
YANG QINGXUAN, TIAN JIWEI, ZHAO WEI, et al, 2014. Observations of turbulence on the shelf and slope of northern South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 87: 43-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2014.02.006 |
| [53] |
YANG QINGXUAN, ZHAO WEI, LIANG XINFENG, et al, 2016. Three-dimensional distribution of Turbulent Mixing in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 46(3): 769-788.
doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-14-0220.1 |
| [54] |
ZHANG ZHIWEI, TIAN JIWEI, QIU BO, et al, 2016. Observed 3D structure, generation, and dissipation of oceanic mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 6(1): 24349.
doi: 10.1038/srep24349 |
| [55] |
ZHAO XIAOLONG, ZHOU CHUN, ZHAO WEI, et al, 2016. Deepwater overflow observed by three bottom-anchored moorings in the Bashi Channel[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 110: 65-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2016.01.007 |
| [56] | ZHAO ZHONGXIANG, KLEMAS V, ZHENG QUANAN, et al, 2004. Remote sensing evidence for baroclinic tide origin of internal solitary waves in the Northeastern South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(6): L06302. |
| [1] | 谢波涛, 黄必桂, 杨威, 李锐祥, 张燕, 刘同木, 李向一. 南海北部东沙岛以西陆坡区2021年秋季内波特征统计与分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 29-41. |
| [2] | 王雪松, 陈忠, 许安涛, 田雨杭, 曹立, 张斌. 南海东北部深海盆末次冰盛期以来陆源碎屑粒度特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 158-170. |
| [3] | 李博安, 胡善政, 阎贫, 于俊辉, 王潇, 唐群署. 南海东北部大陆坡地震反射异常体的属性分析与岩性识别*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 204-214. |
| [4] | 李开枝, 任玉正, 柯志新, 李刚, 谭烨辉. 南海东北部陆坡区中上层浮游动物的垂直分布*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(2): 61-73. |
| [5] | 徐文龙, 王桂芬, 周雯, 许占堂, 曹文熙. 南海东北部夏季叶绿素a浓度垂向变化特征及其对水动力过程的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(5): 62-73. |
| [6] | 刘谊, 王晓玮, 彭世球. 印度尼西亚海内潮生成及传播过程研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(2): 1-9. |
| [7] | 刘甲星, 周林滨, 李刚, 谭烨辉, 刘华健, 赵春宇, 柯志新, 李佳俊, 姜歆. 秋季南海东北部表层水体固氮及其对初级生产力贡献*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(5): 38-47. |
| [8] | 周鹏,李冬梅,刘广山,门武,纪利红. 南海东北部和南部海域表层沉积物生物硅研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(4): 40-47. |
| [9] | 赵俊峰,施小斌,丘学林,刘海龄. 南海东北部居里面特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(1): 126-131. |
|
||