热带海洋学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 61-73.doi: 10.11978/2020061CSTR: 32234.14.2020061
南海东北部陆坡区中上层浮游动物的垂直分布*
李开枝1,2,3( ), 任玉正1,4, 柯志新1,2,3, 李刚1,2,3, 谭烨辉1,2,3,4(
), 任玉正1,4, 柯志新1,2,3, 李刚1,2,3, 谭烨辉1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1.中国科学院热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
3.广东省应用海洋生物学重点实验室, 广东 广州 510301
4.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2020-06-13修回日期:2020-08-02出版日期:2021-03-10发布日期:2020-08-09 -
通讯作者:谭烨辉 -
作者简介:李开枝(1977—), 女, 河南省信阳市人, 研究员, 主要从事海洋浮游动物多样性和生态学研究。email:likaizhi@scsio.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(31971432);国家自然科学基金项目(41976112);南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(GML2019ZD0401);国家科技基础资源调查专项(2017FY201404);中国科学院战略先导专项(XDA11020200)
Vertical distributions of epipelagic and mesopelagic zooplankton in the continental slope of the northeastern South China Sea*
LI Kaizhi1,2,3( ), REN Yuzheng1,4, KE Zhixin1,2,3, LI Gang1,2,3, TAN Yehui1,2,3,4(
), REN Yuzheng1,4, KE Zhixin1,2,3, LI Gang1,2,3, TAN Yehui1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
3. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, Guangzhou 510301, China
4. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2020-06-13Revised:2020-08-02Online:2021-03-10Published:2020-08-09 -
Contact:TAN Yehui -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(31971432);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976112);Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0401);Science and Technology Basic Resources Investigation Program of China(2017FY201404);Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA11020200)
摘要:
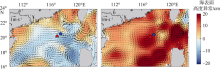
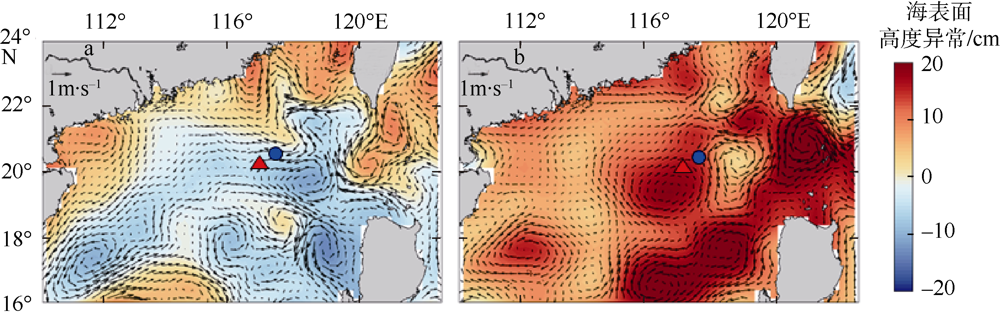
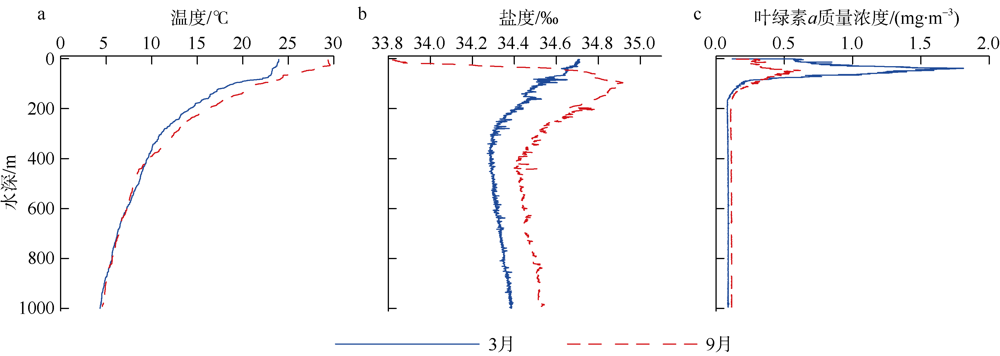
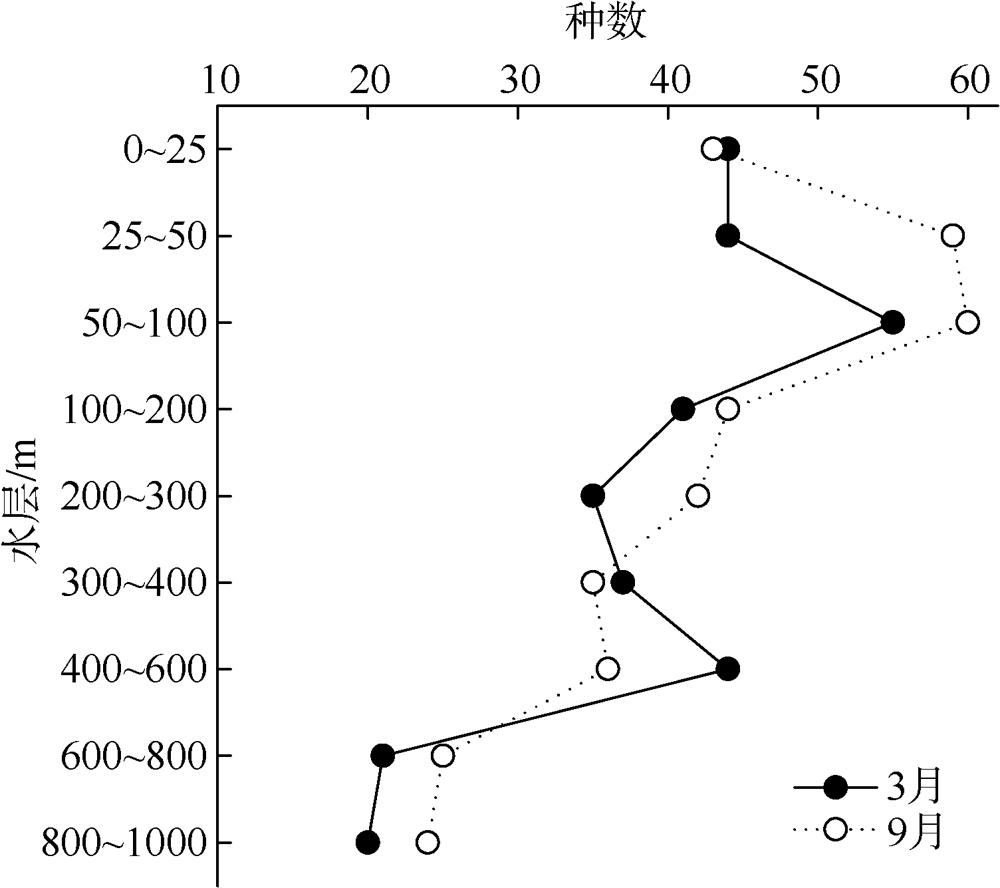
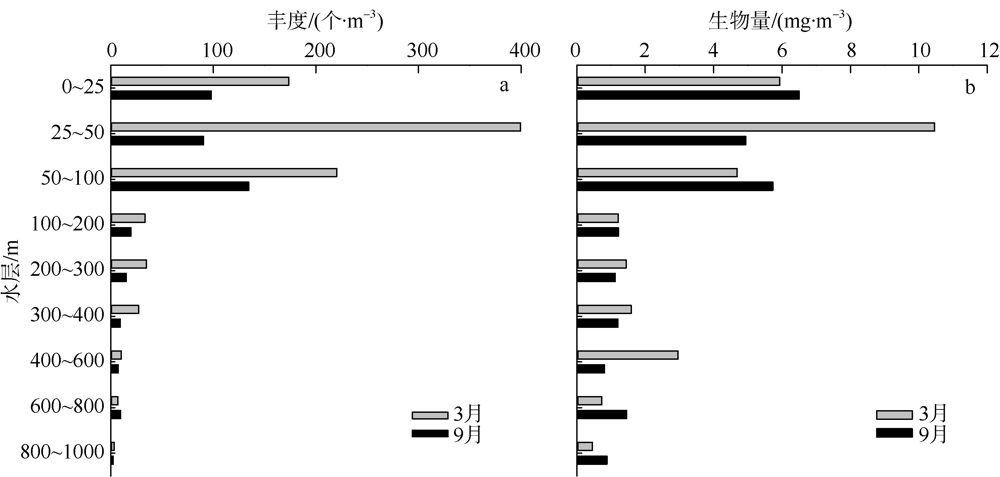
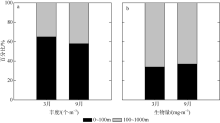
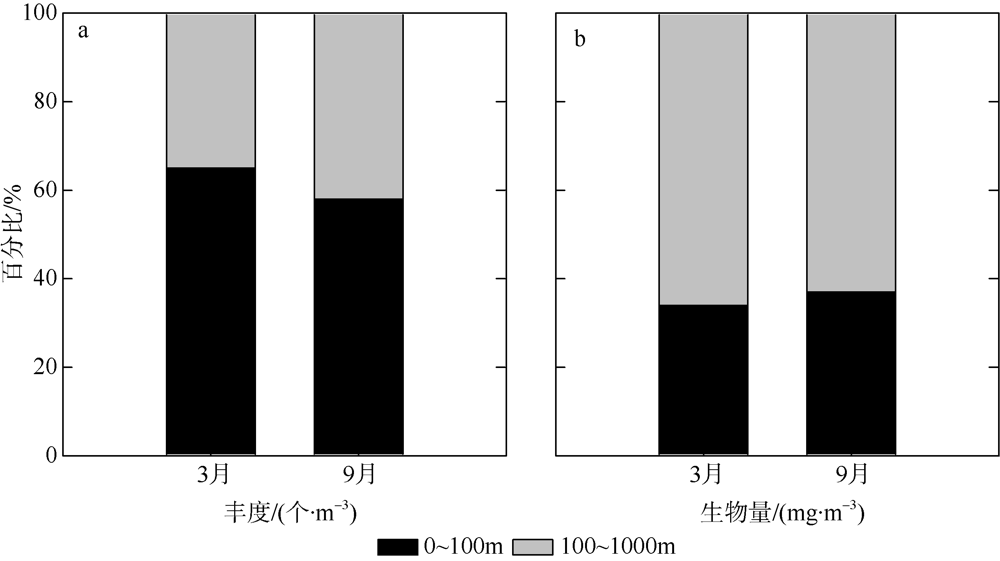
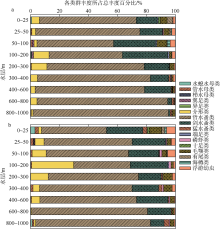
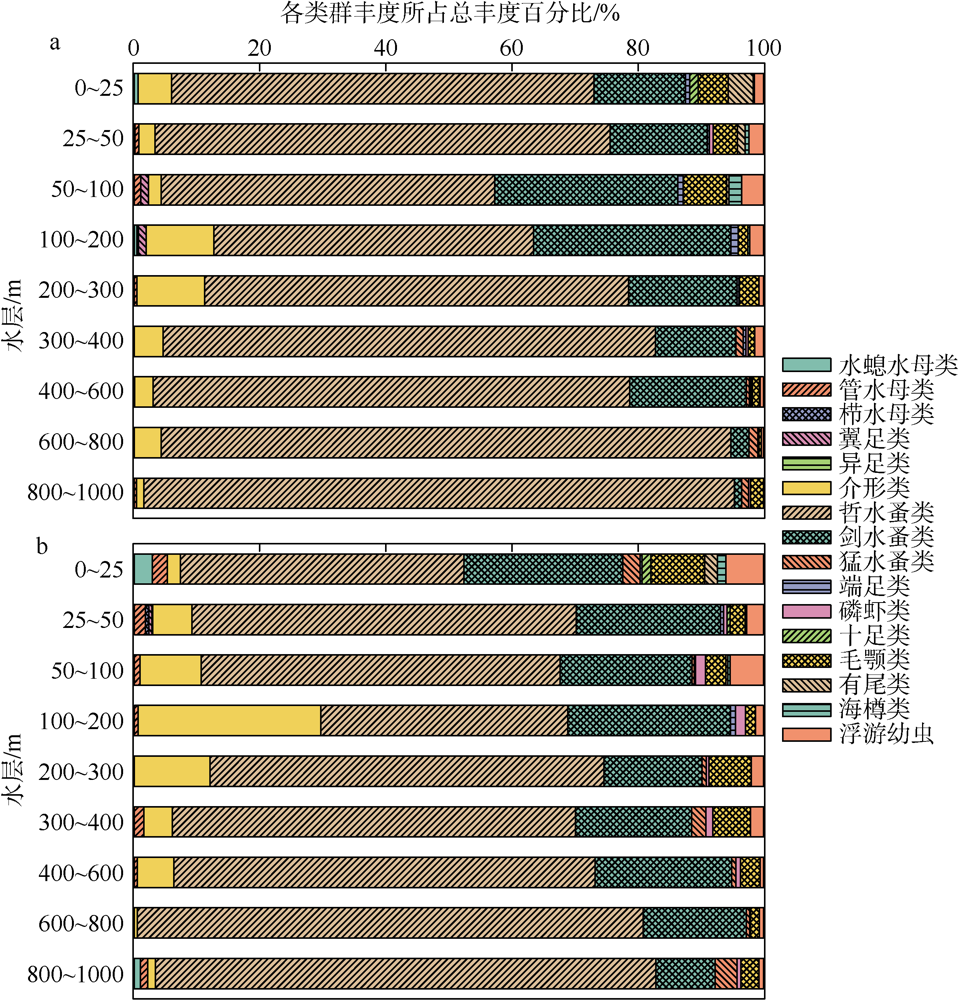
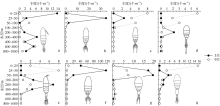
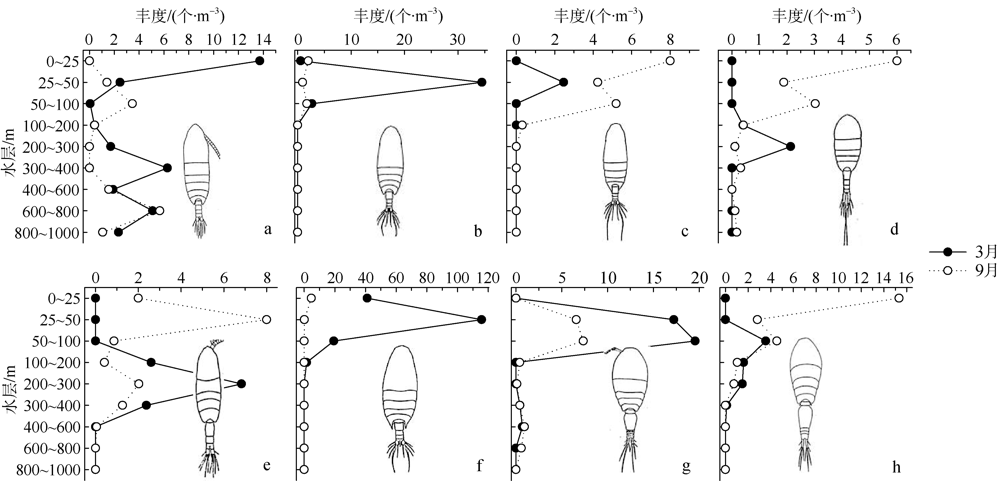
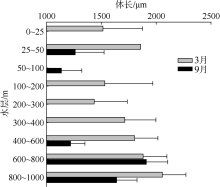
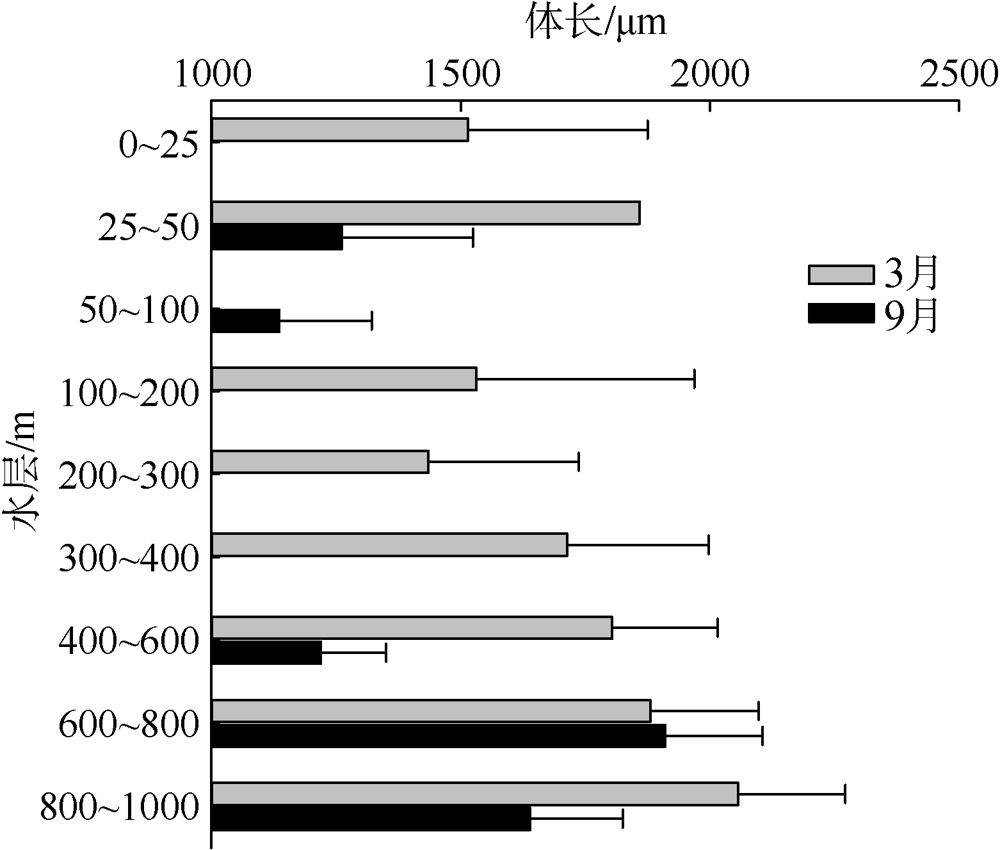
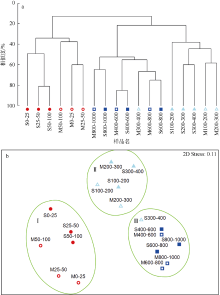
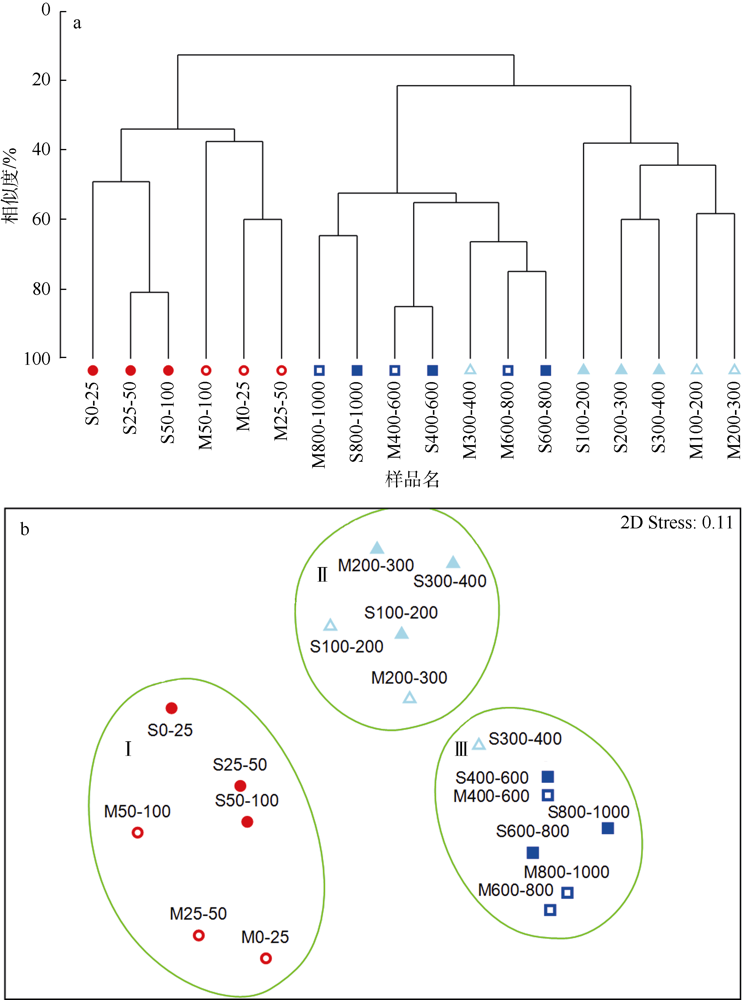
根据2016年3月和9月南海东北部陆坡区浮游动物垂直分层采样, 比较浮游动物种类组成、丰度和生物量的垂直分布和季节变化, 探讨影响其差异的原因。文中共鉴定浮游动物225种, 其中3月和9月分别出现150种和169种; 桡足类种数达132种, 其次是毛颚类和管水母类, 各18种; 浮游动物种数在50~100m水层最高, 一般随水深增加而减少。浮游动物丰度和生物量主要集中在0~100m, 二者在100m以深水层随深度增加而降低, 而水柱生物量在100~1000m占总水柱生物量的60%以上。浮游动物优势种季节和垂直变化明显, 3月近海种如普通波水蚤(Undinula vulgaris)和微刺哲水蚤(Canthocalanus pauper)等在100m以上水层丰度较高; 9月外海种如达氏筛哲水蚤(Cosmocalanus darwinii)和黄角光水蚤(Lucicutia flavicornis)等在100m以浅水层相对于3月丰度增加; 隆线似哲水蚤(Calanoides carinatus)在3月丰度和平均体长高于9月, 并且体长较大者主要分布在深层。浮游动物可分0~100m、100~400m和400~1000m三个群落, 因不同水层种类组成和丰度差异引起。浮游动物丰度和生物量的垂直变化与温度、叶绿素a质量浓度等因子呈显著正相关。南海东北部陆坡浮游动物季节和垂直变化受季风、沿岸流和中尺度涡的影响。
中图分类号:
- P735.13
引用本文
李开枝, 任玉正, 柯志新, 李刚, 谭烨辉. 南海东北部陆坡区中上层浮游动物的垂直分布*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(2): 61-73.
LI Kaizhi, REN Yuzheng, KE Zhixin, LI Gang, TAN Yehui. Vertical distributions of epipelagic and mesopelagic zooplankton in the continental slope of the northeastern South China Sea*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(2): 61-73.
表1
南海东北部陆坡区浮游动物各类群在3月和9月出现的种数及所占百分比"
| 类群 | 3月种数 | 9月种数 | 合计 | 百分比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水螅水母类Hydromedusae | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1.78 |
| 管水母类Siphonophores | 7 | 15 | 18 | 8.00 |
| 栉水母类Ctenophores | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.44 |
| 浮游翼足类Pteropods | 3 | 2 | 5 | 2.22 |
| 浮游异足类Heteropods | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.44 |
| 介形类Ostracods | 10 | 12 | 17 | 7.56 |
| 哲水蚤类Calanoids | 75 | 69 | 97 | 43.11 |
| 剑水蚤类Cyclopoids | 24 | 22 | 31 | 13.78 |
| 猛水蚤类Harpacticoids | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1.78 |
| 端足类Amphipods | 2 | 5 | 7 | 3.11 |
| 磷虾类Euphausiacea | 3 | 7 | 7 | 3.11 |
| 十足类Decapods | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.89 |
| 毛颚类Chaetognaths | 12 | 15 | 18 | 8.00 |
| 有尾类Appendicularians | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.89 |
| 全肌目类Doliolids | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.89 |
| 半肌目类Salps | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.89 |
| 火体虫类Pyrosomatids | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.44 |
| 浮游幼虫Meroplankton | 4 | 5 | 6 | 2.67 |
| 合计 | 150 | 169 | 225 | 100 |
表2
南海东北部陆坡区3月和9月浮游动物优势种及优势度"
| 优势种 | 3月优势度 | 9月优势度 |
|---|---|---|
| 隆线似哲水蚤Calanoides carinatus | 0.037 | 0.023 |
| 微刺哲水蚤Canthocalanus pauper | 0.018 | 0.004 |
| 达氏筛哲水蚤Cosmocalanus darwinii | 0.000 | 0.026 |
| 黄角光水蚤Lucicutia flavicornis | 0.001 | 0.028 |
| 痩乳点水蚤Pleuromamma gracilis | 0.004 | 0.029 |
| 普通波水蚤Undinula vulgaris | 0.087 | 0.003 |
| 中隆水蚤Oncaea media | 0.019 | 0.033 |
| 丽隆水蚤Oncaea venusta | 0.003 | 0.035 |
| [1] | 陈清潮, 章淑珍, 1965. 黄海和东海浮游桡足类Ⅰ: 哲水蚤目[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 7: 20-131. |
| CHEN QINGCHAO, ZHANG SHUZHEN, 1965. The planktonic copepods of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea Ⅰ. Calanoida[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 7: 20-131 (in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 陈清潮, 章淑珍, 朱长寿, 1974. 黄海和东海的浮游桡足类Ⅱ: 剑水蚤目和猛水蚤目[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 9: 27-100. |
| CHEN QINGCHAO, ZHANG SHUZHEN, ZHU CHANGSHOU, 1974. On planktonic copepods of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea Ⅱ. Cycopoida and Harpacticoida[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 9: 27-100 (in Chinese). | |
| [3] | 陈瑞祥, 蔡秉及, 林茂, 等, 1988. 南海中部海域浮游动物的垂直分布[J]. 海洋学报, 10(3):337-341. |
| CHEN RUIXIANG, CAI BINGJI, LIN MAO, et al, 1988. Vertical distribution of zooplankton in the central South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 10(3):337-341 (in Chinese). | |
| [4] | 程旭华, 齐义泉, 王卫强, 2005. 南海中尺度涡的季节和年际变化特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 24(4):51-59. |
| CHENG XUHUA, QI YIQUAN, WANG WEIQIANG, 2005. Seasonal and interannual variabilities of mesoscale eddies in South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 24(4):51-59 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 杜飞雁, 王雪辉, 谷阳光, 等, 2014. 南沙群岛西南大陆斜坡海域浮游动物的垂直分布[J]. 海洋学报, 36(6):94-103. |
| DU FEIYAN, WANG XUEHUI, GU YANGGUANG, et al, 2014. Vertical distribution of zooplankton in the continental slope southwest of Nansha Islands, South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36(6):94-103 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 冯士筰, 李凤岐, 李少菁, 1999. 海洋科学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 1-503. |
| FENG SHIZUO, LI FEGNQI, LI SHAOJING, 1999. An Introduction to Marine Science[M]. Beijing: High Education Press: 1-503(in Chinese). | |
| [7] | 龚玉艳, 杨玉滔, 范江涛, 等, 2017. 南海北部陆架斜坡海域夏季浮游动物群落的空间分布[J]. 南方水产科学, 13(5):8-15. |
| GONG YUYAN, YANG YUTAO, FAN JIANGTAO, et al, 2017. Spatial distribution of zooplankton in continental slope of northern South China Sea in summer[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 13(5):8-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 龚玉艳, 杨玉滔, 孔啸兰, 等, 2018. 南海北部陆坡海域瓦氏眶灯鱼的渔业生物学特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 25(5):1091-1101. |
| GONG YUYAN, YANG YUTAO, KONG XIAOLAN, et al, 2018. A preliminary study on the fishery-relevant biology of Diaphus watasei in the continental slope of the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 25(5):1091-1101 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 连光山, 钱宏林, 1984. 西太平洋热带水域的浮游桡足类[C]// 西太平洋热带水域浮游生物论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社: 118-205. |
| LIAN GUANGSHAN, QIAN HONGLIN, 1984. On the pelagic copepods: from tropical waters of the western Pacific Ocean[C]// Proceedings of the plankton from the tropical waters of the western Pacific Ocean. Beijing: Ocean Press: 118-205(in Chinese). | |
| [10] | 刘长建, 庄伟, 夏华永, 等, 2012. 2009—2010年冬季南海东北部中尺度过程观测[J]. 海洋学报, 34(1):8-16. |
| LIU CHANGJIAN, ZHUANG WEI, XIA HUAYONG, et al, 2012. Mesoscale observation in the northeast South China Sea during winter 2009—2010[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(1):8-16 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 舒业强, 王强, 俎婷婷, 2018. 南海北部陆架陆坡流系研究进展[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 48(3):276-287. |
| SHU YEQIANG, WANG QIANG, ZU TINGTING, 2018. Progress on shelf and slope circulation in the northern South China Sea[J]. Science China Series D: Earth Sciences, 61(5):560-571 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 苏纪兰, 2005. 南海环流动力机制研究综述[J]. 海洋学报, 27(6):1-8. |
| SU JILAN, 2005. Overview of the South China Sea circulation and its dynamics[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 27(6):1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] |
孙栋, 王春生, 2017. 深远海浮游动物生态学研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 37(10):3219-3231.
doi: 10.5846/stxb201603060393 |
|
SUN DONG, WANG CHUNSHENG, 2017. A review of open ocean zooplankton ecology[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(10):3219-3231 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.5846/stxb201603060393 |
|
| [14] | 王翠, 郭晓峰, 方婧, 等, 2018. 闽浙沿岸流扩展范围的季节特征及其对典型海湾的影响[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 37(1):1-8. |
| WANG CUI, GUO XIAOFENG, FANG JING, et al, 2018. Characteristics of seasonal spatial expansion of Fujian and Zhejiang Coastal Current and their bay effects[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 37(1):1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿, 1989. 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 8(4):13-15, 19. |
| XU ZHAOLI, CHEN YAQU, 1989. Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 8(4):13-15, 19 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 尹健强, 黄良民, 李开枝, 等, 2013. 南海西北部陆架区沿岸流和上升流对中华哲水蚤分布的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 35(2):143-153. |
| YIN JIANQIANG, HUANG LIANGMIN, LI KAIZHI, et al, 2013. Effects of coastal current and upwelling on the distributions of Calanus sinicus on the northwest continental shelf of the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(2):143-153 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [17] | 于君, 邱永松, 2016. 黑潮入侵对南海东北部初级生产力的影响[J]. 南方水产科学, 12(4):17-27. |
| YU JUN, QIU YONGSONG, 2016. Influence of Kuroshio intrusion on primary productivity in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 12(4):17-27 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] | 张博, 曾丽丽, 陈举, 等, 2018. 基于南海北部开放航次观测的2004—2005年次表层盐度异常特征与形成机制[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 49(1):9-16. |
| ZHANG BO, ZENG LILI, CHEN JU, et al, 2018. Abnormal high salinity in subsurface of the northern South China Sea observed in the open cruises 2004-2005: characteristics and formation mechanism[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 49(1):9-16 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [19] | 张谷贤, 陈清潮, 1983. 南海北部和中部的毛颚类[C]// 南海海洋生物研究论文集(一). 北京: 海洋出版社: 17-63. |
| ZHANG GUXIAN, CHEN QINGCHAO, 1983. Studies on chaetognaths in the central and northern parts of the South China Sea[C]//. Contributions on marine biological research of the South China Sea (Ⅰ). Beijing: Ocean Press: 17-63(in Chinese). | |
| [20] | 张金标, 2005. 中国海洋浮游管水母类[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-151. |
| ZHANG JINBIAO, 2005. Pelagic siphonophora in China Sea [M]. Beijing: Ocean Press: 1-151(in Chinese). | |
| [21] | 张武昌, 赵楠, 陶振铖, 等, 2010. 中国海洋浮游桡足类图谱[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-468. |
| ZHANG WUCHANG, ZHAO NAN, TAO ZHENCHENG, et al, 2010. An illustrated guide to marine planktonic copepods in China Seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-468(in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [22] | 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 1985. 南海海区综合调查研究报告(二)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 357-378(in Chinese). |
| [23] | BOLTOVSKOY D, 1999. South Atlantic zooplankton[M]. Leiden: Backhuys Publishers: 869-1098. |
| [24] | CHEN LEI, LI CHAOLUN, TAO ZHENCHENG, et al, 2018. Comparative study of trophic and elemental characteristics of zooplankton in deep (500~3500m) and shallow (0~200m) layers[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ: Oceanographic Research Papers, 142(1):107-115. |
| [25] | DAI LUPING, LI CHAOLUN, TAO ZHENGCHENG, et al, 2017. Zooplankton abundance, biovolume and size spectra down to 3000 m depth in the western tropical North Pacific during autumn 2014[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ: Oceanographic Research Papers, 121(5):1-13. |
| [26] |
FERNANDES V, RAMAIAH N, 2013. Mesozooplankton community structure in the upper 1000 m along the western Bay of Bengal during the 2002 fall intermonsoon[J]. Zoological Studies, 52(1):31.
doi: 10.1186/1810-522X-52-31 |
| [27] | HUANG BANGQIN, HU JUN, XU HONGZHOU, et al, 2010. Phytoplankton community at warm eddies in the northern South China Sea in winter 2003/2004[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 57(19-20):1792-1798. |
| [28] |
JIANG XIN, LI JIAJUN, KE ZHIXIN, et al, 2017. Characteristics of picoplankton abundances during a Thalassiosira diporocyclus bloom in the Taiwan Bank in late winter[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 117(1-2):66-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.01.042 pmid: 28139232 |
| [29] | KOSOBOKOVA K N, HOPCROFT R R, 2010. Diversity and vertical distribution of mesozooplankton in the Arctic’s Canada Basin[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 57(1-2):96-110. |
| [30] |
LEBRATO M, PAHLOW M, FORST J R, et al, 2019. Sinking of gelatinous zooplankton biomass increases deep carbon transfer efficiency globally[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 33(12):1764-1783.
doi: 10.1029/2019GB006265 |
| [31] |
LI JIAJUN, JIANG XIN, LI GANG, et al, 2017. Distribution of picoplankton in the northeastern South China Sea with special reference to the effects of the Kuroshio intrusion and the associated mesoscale eddies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 589(C11):1-10.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.208 |
| [32] |
LI KAIZHI, YIN JIANQIANG, HUANG LIANGMIN, et al, 2012. Comparison of siphonophore distributions during the southwest and northeast monsoons on the northwest continental shelf of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 34(7):636-641.
doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbs035 |
| [33] |
LIU HUAJIAN, ZHU MINGLIANG, GUO SHUJIN, et al, 2020. Effects of an anticyclonic eddy on the distribution and community structure of zooplankton in the South China Sea northern slope[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 205: 103311.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2020.103311 |
| [34] | ROBINSON C, STEINBERG D K, ANDERSON T R, et al, 2010. Mesopelagic zone ecology and biogeochemistry - a synjournal[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 57(16):1504-1518. |
| [35] | ROFF J C, HOPCROFT R R, 1986. High precision microcomputer based measuring system for ecological research[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 43(10):2044-2048. |
| [36] | SMITH K JR L, KAUFMANN R S, BALDWIN R J, et al, 2001. Pelagic-benthic coupling in the abyssal eastern North Pacific: An 8-year time-series study of food supply and demand[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 46(3):543-556. |
| [37] | STENIBERG D K, COPE J S, WILSON S E, et al, 2008. A comparison of mesopelagic mesozooplankton community structure in the subtropical and subarctic North Pacific Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 55(14-15):1615-1635. |
| [38] |
SUTTON T T, 2013. Vertical ecology of the pelagic ocean: classical patterns and new perspectives[J]. Journal of Fish Biology, 83(6):1508-1527.
doi: 10.1111/jfb.12263 pmid: 24298949 |
| [39] | TIMONIN A G, ARASHKEVICH E G, DRITS A V, et al, 1992. Zooplankton dynamics in the northern Benguela ecosystem, with special reference to the copepod Calanoides carinatus[J]. South African Journal of Marine Science, 12(1):545-560. |
| [40] | VIÑAS M D, BLANCO-BERCIAL L, BUCKLIN A, et al, 2015. Phylogeography of the copepod Calanoides carinatus s.l. (Krøyer) reveals cryptic species and delimits C. carinatus s.s. distribution in SW Atlantic Ocean[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 468: 97-104. |
| [41] | VIÑAS M D, NEGRI R M, RAMÍREZ F C, et al, 2002. Zooplankton assemblages and hydrography in the spawning area of anchovy (Engraulis anchoita) off Río de la Plata estuary (Argentina-Uruguay)[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 53(6):1031-1043. |
| [42] | WAITE A M, RAES E, BECKLEY L E, et al, 2019. Production and ecosystem structure in cold-core vs warm-core eddies: Implications for the zooplankton isoscape and rock lobster larvae[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 64(6):2405-2423. |
| [43] | WANG DONGXIAO, XU HONGZHOU, LIN JING, et al, 2008. Anticyclonic eddies in the northeastern South China Sea during winter 2003/2004[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 64(6):925-935. |
| [44] | WANG GUIHUA, SU JILAN, CHU P C, 2003. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea observed with altimeter data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(21):2121. |
| [45] | XIU PENG, CHAI FEI, SHI LEI, et al, 2010. A census of eddy activities in the South China Sea during 1993—2007[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115: C03012. |
| [1] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | 胡思敏, 周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 李涛, 黄晖. 悬浮物对三亚珊瑚礁区浮游动物群落结构及其摄食的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [3] | 谢波涛, 黄必桂, 杨威, 李锐祥, 张燕, 刘同木, 李向一. 南海北部东沙岛以西陆坡区2021年秋季内波特征统计与分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 29-41. |
| [4] | 张兰兰, 程夏雯, 向荣, 邱卓雅, 常虎. 2019年春季孟加拉湾中部放射虫群落结构垂向变化*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [5] | 郭键林, 孙显, 杨宇峰, 王庆. 广西涠洲岛大型海藻场及其邻近海域桡足类群落结构演替特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 155-165. |
| [6] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [7] | 李若飞, 柯志新, 李开枝, 刘甲星, 谭烨辉. 基于ZooScan图像分析“海马”冷泉区浮游动物垂直分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 87-96. |
| [8] | 尹天齐, 王庆, 杨宇峰, 岑竞仪. 基于形态学和DNA分子鉴定的珠江口浮游动物群落结构比较研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 172-185. |
| [9] | 尹健强, 李开枝, 谭烨辉. 南海南部海域浮游介形类新种——南沙深海浮萤*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 193-197. |
| [10] | 李开枝, 柯志新, 王军星, 谭烨辉. 西沙群岛珊瑚礁海域浮游动物群落结构初步分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 121-131. |
| [11] | 马梦真, 李芊, 吴正超, 陈寅超, 俞建成. 南海北部最小含氧带水下滑翔机观测结果初步分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 131-142. |
| [12] | 李博安, 胡善政, 阎贫, 于俊辉, 王潇, 唐群署. 南海东北部大陆坡地震反射异常体的属性分析与岩性识别*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 204-214. |
| [13] | 李杨, 黄鹏起, 鲁远征, 屈玲, 郭双喜, 岑显荣, 周生启, 张佳政, 丘学林. 基于精细温度观测的南海东北部陆坡-深海盆底层湍流混合*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 62-74. |
| [14] | 王雪松, 陈忠, 许安涛, 田雨杭, 曹立, 张斌. 南海东北部深海盆末次冰盛期以来陆源碎屑粒度特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 158-170. |
| [15] | 任玉正, 柯志新, 谭烨辉, 李开枝. 广东省南澳岛东部海域浮游动物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 65-76. |
|
||