热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 98-113.doi: 10.11978/2022037CSTR: 32234.14.2022037
8000a BP以来东沙西南海域深水珊瑚的发育演化特征及其控制因素*
张斌1,2,3( ), 陈忠1,2(
), 陈忠1,2( ), 许安涛2, 王雪松4, 田雨杭1,2, 张应威1,2,3
), 许安涛2, 王雪松4, 田雨杭1,2, 张应威1,2,3
- 1.三亚海洋生态环境工程研究院, 海南 三亚 572000
2.中国科学院边缘海与大洋地质重点实验室, 南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
3.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
4.中国地质大学, 湖北 武汉 430074
-
收稿日期:2022-02-24修回日期:2022-04-11出版日期:2023-01-10发布日期:2022-04-14 -
通讯作者:陈忠。email:chzhsouth@scsio.ac.cn -
作者简介:张斌(1997—), 安徽省阜阳市人, 硕士研究生, 主要从事海洋沉积与环境变化研究。email: zhangbin@scsio.ac.cn*感谢各位审稿专家对本文提出的宝贵建议, 感谢曹立博士在成文过程中提供的有益讨论, 感谢中国科学院南海海洋研究所“实验1”号科学考察船提供研究样品。 -
基金资助:三亚崖州湾科技管理局2022年度科技计划项目(SKJC-2020-01-012); 国家自然科学基金项目(41976065); 国家自然科学基金项目(41776061); 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(GML2019ZD0104)
Evolution characteristics and controlling factors of deep-water corals in the southwest Dongsha Sea area since 8000 a BP*
ZHANG Bin1,2,3( ), CHEN Zhong1,2(
), CHEN Zhong1,2( ), XU Antao2, WANG Xuesong4, TIAN Yuhang1,2, ZHANG Yingwei1,2,3
), XU Antao2, WANG Xuesong4, TIAN Yuhang1,2, ZHANG Yingwei1,2,3
- 1. Sanya Institute of Ocean Eco-Environmental Engineering, Sanya 572000, China
2. Key Laboratory of Ocean and Marginal Sea Geology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4. China University of Geosciences, Wuhan 430074, China
-
Received:2022-02-24Revised:2022-04-11Online:2023-01-10Published:2022-04-14 -
Contact:CHEN Zhong. email:chzhsouth@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:The 2020 Research Program of Sanya Yazhou Bay Science and Technology City(SKJC-2020-01-012); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976065); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41776061); Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0104)
摘要:
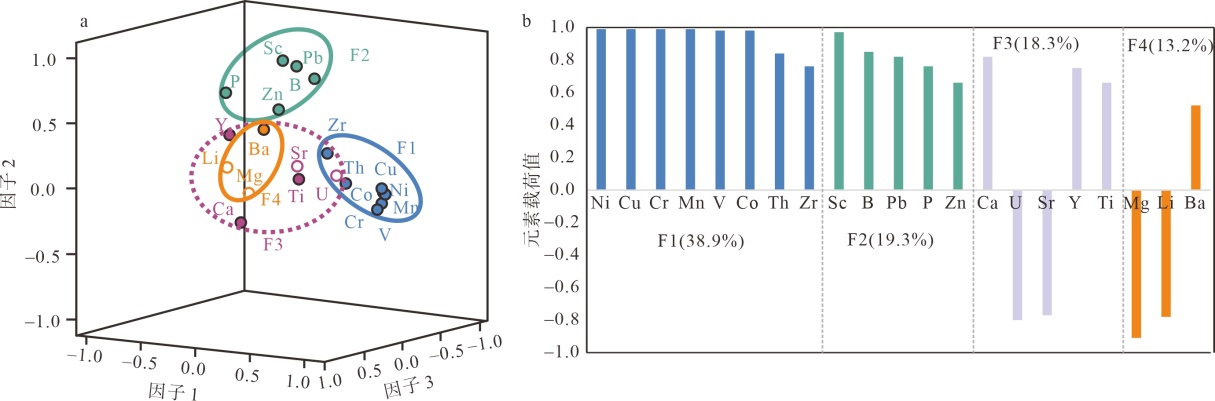
深水珊瑚骨骼记录了珊瑚生长环境的精细变化, 但目前对南海深水珊瑚生长的影响因素、演化阶段及其对海洋环境变化的响应仍缺乏了解。本文通过对东沙西南海域深水珊瑚骨骼的化学元素、U-Th年龄进行测定和研究, 揭示8000a BP以来东沙西南海域深水珊瑚的发育演化特征及其控制因素。深水珊瑚常微量元素组合及因子分析表明, 底流活动、初级生产力、陆源物质影响了东沙西南海域深水珊瑚的生长和演化。根据U-Th年龄将深水珊瑚演化划分为4个阶段, 分别为Ⅰ (8000~4500a BP)、Ⅱ (4500~2500a BP)、Ⅲ (2500~1200a BP)、Ⅳ (1200a BP至今)。海底流速、有机颗粒物、海水温度与热含量、生源元素供给的剧烈动荡变化导致了4500~2500a BP珊瑚发育间断, 较强底流活动、较强冬季风和有机颗粒物供给的消长变化影响了东沙西南海域深水珊瑚的演化阶段及其特征。本文研究为深入探究大洋边缘深水珊瑚影响因素、发育演化特征及其对海洋过程的响应提供了新视角。
引用本文
张斌, 陈忠, 许安涛, 王雪松, 田雨杭, 张应威. 8000a BP以来东沙西南海域深水珊瑚的发育演化特征及其控制因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 98-113.
ZHANG Bin, CHEN Zhong, XU Antao, WANG Xuesong, TIAN Yuhang, ZHANG Yingwei. Evolution characteristics and controlling factors of deep-water corals in the southwest Dongsha Sea area since 8000 a BP*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 98-113.
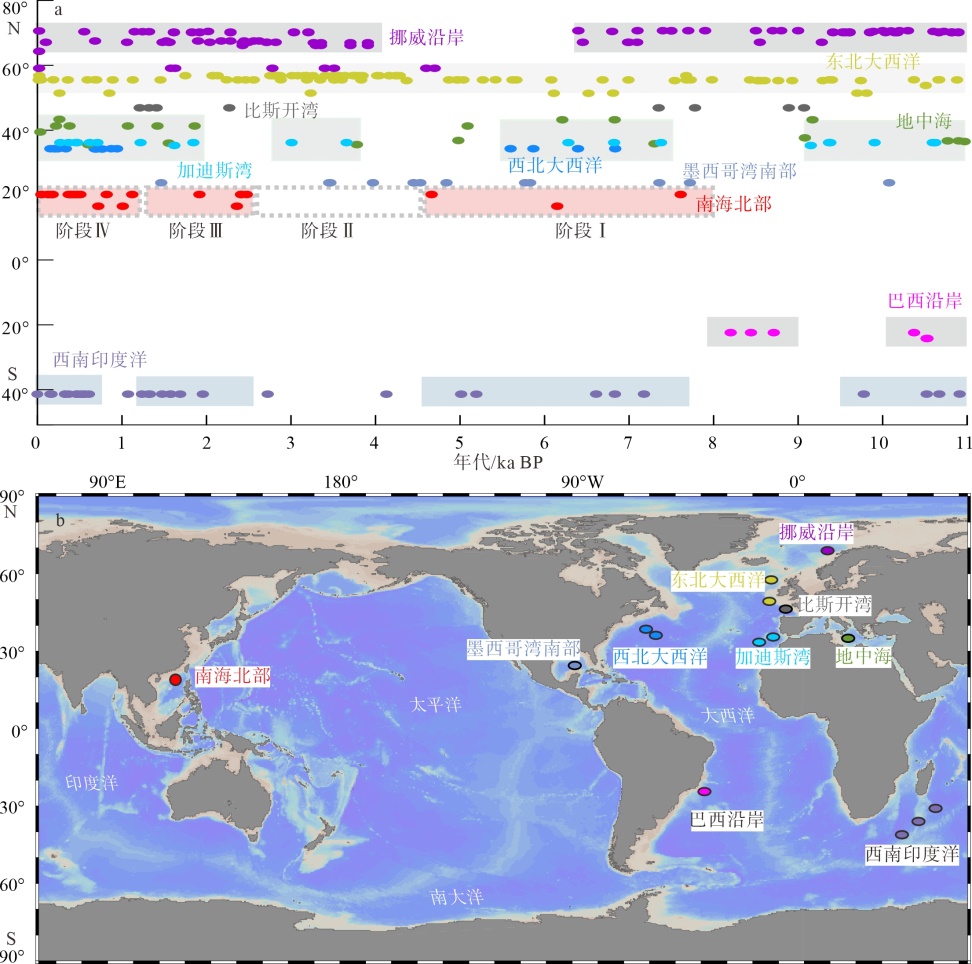
图1
南海北部深水珊瑚分布(a)、研究区地质概况(b)及连接深水珊瑚站位的剖面地形变化(c) 该图基于国家测绘地理信息局标准地图服务网站下载的审图号为GS(2021)5447号的标准地图制作。图中五角星为本文珊瑚站位, 黄色圆点为西沙珊瑚站位(Li et al, 2019), 粉色圆点为台西南珊瑚站位(Deng et al, 2019), 灰色圆点为对比研究站位(王雪松 等, 2022; Du et al, 2021; Yang et al, 2020; Wan et al, 2015); 图a中箭头1和2分别为冬季风和夏季风, 灰色箭头及数字代表陆源输入(Liu et al, 2016), 黑色实线为图c剖面路径, NPDW为北太平洋深层水(Wang et al, 2020), slope current为斜坡流(Wang et al, 2020); 图b中图例1代表珊瑚站位, 2代表冷泉碳酸盐岩站位, 3代表泥火山站位, 4代表泥底辟站位, 5代表等深线"
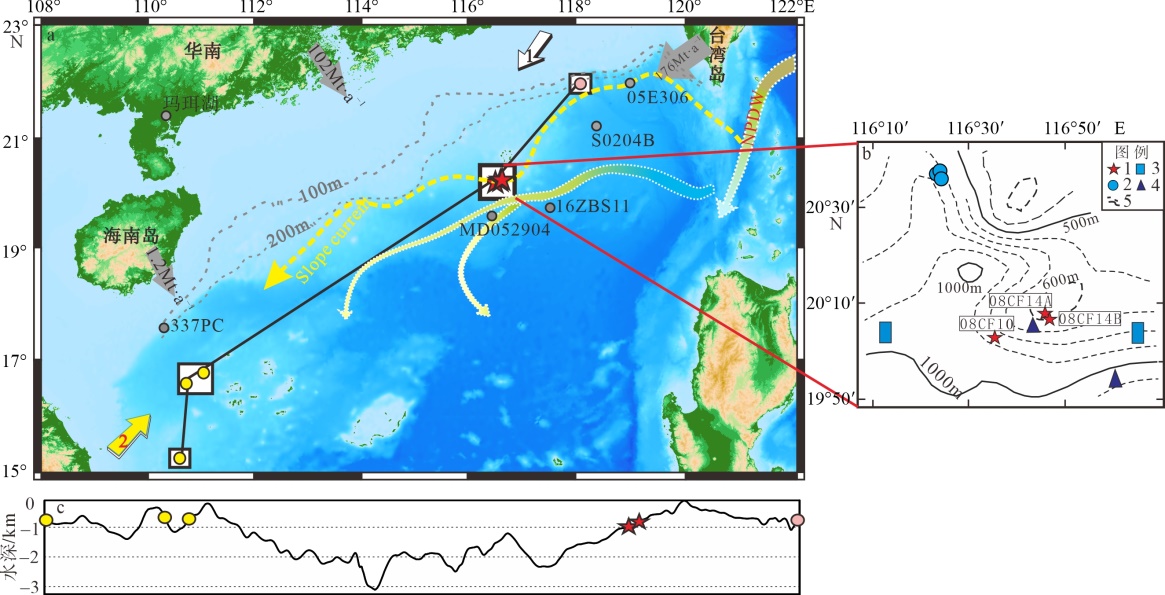
表1
南海北部全新世以来深水珊瑚年龄数据"
| 样品编号 | 珊瑚类型 | 238U /(×10-9, ±2σ) | 230Th 年龄/(a BP, ±2σ) | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2 | 石珊瑚 | 4578.4±6.2 | 1990±18 | 本文 |
| C4-1 | 石珊瑚 | 4409.4 ±8.6 | 51±8 | 本文 |
| C4-2 | 石珊瑚 | 4340.0±9.1 | 125±10 | 本文 |
| C5 | 石珊瑚 | 4230. ±8.9 | 47±9 | 本文 |
| C7 | 石珊瑚 | 4330.4±6.7 | 440±9 | 本文 |
| C8-1 | 石珊瑚 | 4164.2±7.9 | 476±9 | 本文 |
| C8-2 | 石珊瑚 | 4377.9±8.3 | 471±9 | 本文 |
| C9 | 石珊瑚 | 4621.4 ±8.8 | 412±9 | 本文 |
| C10 | 石珊瑚 | 4114.7±7.4 | 391±10 | 本文 |
| C11 | 石珊瑚 | 4777.7 ±9.2 | 1122±9 | 本文 |
| C12 | 石珊瑚 | 3735.5±7.1 | 2410±19 | 本文 |
| C13 | 石珊瑚 | 3974.7 ±7.9 | 2435±23 | 本文 |
| C14 | 石珊瑚 | 4555.4±9.2 | 370±9 | 本文 |
| C16 | 石珊瑚 | 4207.6±6.4 | 180±11 | 本文 |
| C17 | 石珊瑚 | 4270.6 ±7.1 | 4664±20 | 本文 |
| C18 | 石珊瑚 | 4553.9±8.2 | 7610±26 | 本文 |
| C19 | 石珊瑚 | 3873.0±6.3 | 2476±22 | 本文 |
| C35 | 石珊瑚 | 4885.6±13.5 | 96±25 | 本文 |
| C36 | 石珊瑚 | 4675.2±8.2 | 55±23 | 本文 |
| C37 | 石珊瑚 | 4461.2±10.4 | 749±43 | 本文 |
| C38 | 石珊瑚 | 4552.4±8.5 | 437±26 | 本文 |
| SY067-9-3 | 柳珊瑚 | 25.6±0.1 | 1 010±237 | 黄恩清 等, |
| SY068-7-2 | 柳珊瑚 | 47.8±0.1 | 9387±3148 | 黄恩清 等, |
| SY075-16-2 | 石珊瑚 | 3799.7±8.5 | 718.0±44 | 黄恩清 等, |
| SY076-9 | 石珊瑚 | 3830.7±5.5 | 6154±94 | 黄恩清 等, |
表2
深水珊瑚的常量和微量元素含量"
| 序号 | Ca | Mg | Mn | P | Ti | Li | B | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Sr | Y | Zr | Ba | Pb | Th | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2 | 0.39 | 0.60 | 0.45 | 82.39 | 0.41 | 0.69 | 37.55 | 0.60 | 0.10 | 0.82 | 0.96 | 11.42 | 0.27 | 3.04 | 8.46 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 16.75 | 0.41 | 0.001 | 4.37 |
| C4-1 | 0.39 | 0.56 | 1.13 | 76.48 | 0.39 | 0.69 | 36.04 | 0.59 | 0.11 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 11.12 | 0.27 | 2.96 | 8.64 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 16.77 | 0.35 | 0.001 | 4.38 |
| C4-2 | 0.39 | 0.59 | 1.19 | 77.98 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 37.98 | 0.60 | 0.10 | 0.80 | 0.99 | 11.24 | 0.28 | 5.08 | 8.64 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 17.02 | 0.49 | 0.001 | 4.47 |
| C5 | 0.39 | 0.60 | 2.44 | 89.67 | 0.58 | 0.65 | 29.79 | 0.57 | 0.14 | 0.80 | 1.07 | 11.76 | 0.27 | 3.38 | 8.45 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 18.62 | 0.53 | 0.002 | 4.36 |
| C7 | 0.39 | 0.62 | 0.96 | 133.1 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 35.21 | 0.66 | 0.11 | 1.05 | 1.09 | 11.83 | 0.42 | 4.35 | 8.44 | 0.31 | 0.02 | 19.51 | 0.53 | 0.002 | 4.24 |
| C8-1 | 0.38 | 0.62 | 0.97 | 98.35 | 0.49 | 0.71 | 31.81 | 0.61 | 0.12 | 0.77 | 1.01 | 11.38 | 0.35 | 2.98 | 8.56 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 16.82 | 0.47 | 0.001 | 4.04 |
| C8-2 | 0.38 | 0.59 | 0.58 | 70.49 | 0.38 | 0.68 | 25.33 | 0.49 | 0.09 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 11.71 | 0.24 | 2.45 | 8.82 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 17.28 | 0.35 | 0.001 | 4.48 |
| C9 | 0.39 | 0.67 | 0.72 | 94.21 | 0.44 | 0.75 | 31.94 | 0.61 | 0.12 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 11.68 | 0.36 | 3.08 | 8.26 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 16.29 | 0.64 | 0.001 | 3.49 |
| C10 | 0.39 | 0.58 | 0.73 | 73.19 | 0.38 | 0.68 | 28.07 | 0.52 | 0.13 | 0.67 | 1.01 | 12.47 | 0.32 | 3.16 | 8.62 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 16.99 | 0.43 | 0.001 | 4.27 |
| C11 | 0.39 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 82.68 | 0.42 | 0.68 | 35.24 | 0.63 | 0.10 | 0.85 | 1.01 | 11.60 | 0.30 | 3.48 | 8.39 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 17.24 | 0.45 | 0.001 | 4.12 |
| C12 | 0.38 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 91.14 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 32.58 | 0.64 | 0.10 | 0.83 | 1.01 | 11.69 | 0.36 | 3.22 | 8.73 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 17.21 | 0.56 | 0.001 | 4.65 |
| C13 | 0.39 | 0.67 | 0.79 | 129.9 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 39.26 | 0.70 | 0.14 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 11.27 | 0.94 | 3.32 | 8.20 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 17.19 | 0.45 | 0.002 | 3.17 |
| C14 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 0.95 | 114.2 | 0.77 | 0.63 | 31.61 | 0.73 | 0.11 | 0.94 | 1.10 | 12.19 | 0.58 | 5.54 | 8.37 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 17.84 | 0.6 | 0.003 | 3.6 |
| C16 | 0.39 | 0.53 | 2.12 | 132.0 | 0.95 | 0.61 | 31.94 | 0.74 | 0.12 | 0.97 | 1.17 | 12.17 | 0.67 | 7.64 | 8.41 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 20.02 | 0.72 | 0.005 | 3.92 |
| C17 | 0.40 | 0.58 | 23.54 | 69.35 | 1.19 | 0.57 | 16.74 | 0.49 | 0.86 | 381.2 | 2.40 | 145.4 | 14.27 | 4.28 | 8.07 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 14.58 | 0.44 | 0.006 | 3.73 |
| C18 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 35.96 | 98.02 | 0.91 | 0.61 | 34.34 | 0.68 | 1.01 | 464.8 | 3.27 | 229 | 23.08 | 4.81 | 8.39 | 0.32 | 0.06 | 19.88 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 4.32 |
| C19 | 0.38 | 0.57 | 13.95 | 113.4 | 0.76 | 0.63 | 51.15 | 0.90 | 0.37 | 168.6 | 1.87 | 92.59 | 9.08 | 6.68 | 8.51 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 17.19 | 1.18 | 0.003 | 4.43 |
| 最大值 | 0.40 | 0.67 | 35.96 | 133.1 | 1.19 | 0.86 | 51.15 | 0.90 | 1.01 | 464.8 | 3.27 | 229.0 | 23.08 | 7.64 | 8.82 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 20.02 | 1.18 | 0.01 | 4.65 |
| 最小值 | 0.38 | 0.53 | 0.45 | 69.35 | 0.38 | 0.57 | 16.74 | 0.49 | 0.09 | 0.62 | 0.96 | 11.12 | 0.24 | 2.45 | 8.07 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 14.58 | 0.35 | 0.001 | 3.17 |
| 平均值 | 0.39 | 0.59 | 5.15 | 95.68 | 0.61 | 0.68 | 33.33 | 0.63 | 0.23 | 60.38 | 1.29 | 37.09 | 3.06 | 4.09 | 8.47 | 0.30 | 0.02 | 17.48 | 0.54 | 0.002 | 4.12 |
表3
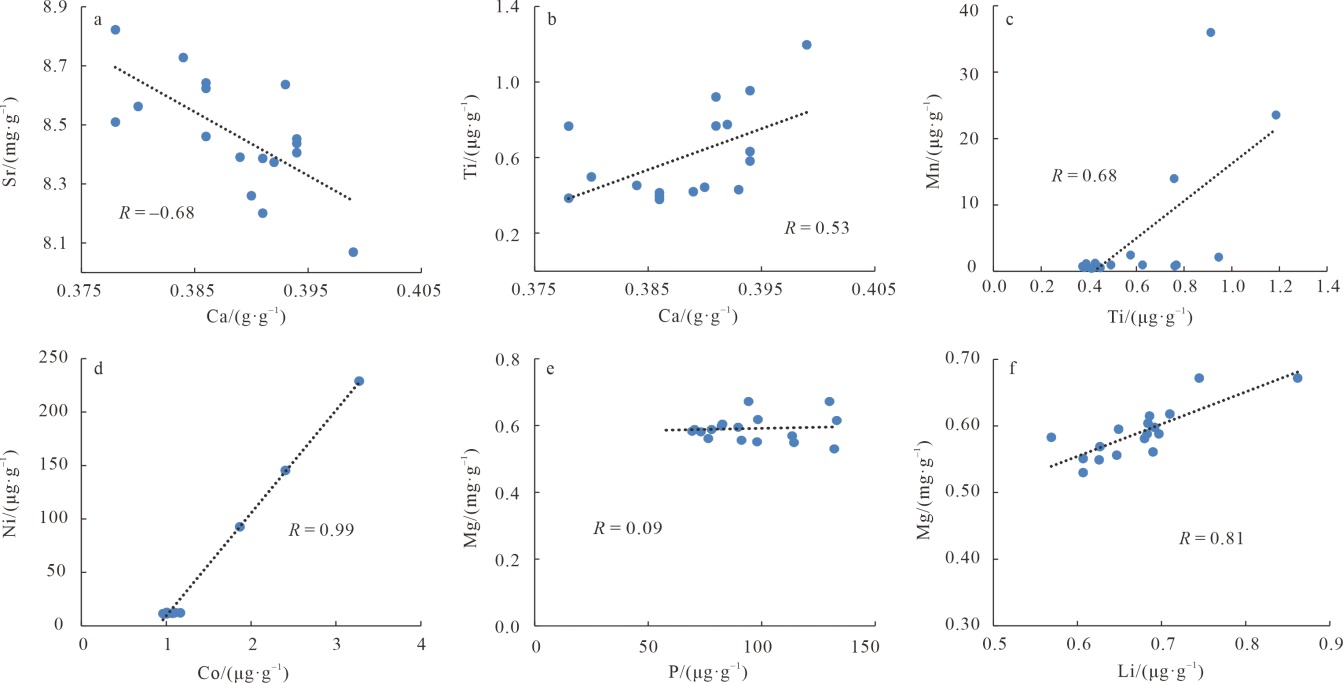
深水珊瑚常量与微量元素间的皮尔逊相关性"
| 序号 | Ca | Mg | Mn | P | Ti | Li | B | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Sr | Y | Zr | Ba | Pb | Th | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mg | 0.02 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mn | 0.21 | -0.30 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| P | 0.18 | 0.09 | -0.07 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| Ti | 0.53* | -0.26 | 0.68** | 0.40 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| Li | -0.17 | 0.81** | -0.52* | 0.18 | -0.46 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| B | -0.37 | 0.06 | -0.10 | 0.44 | -0.20 | 0.30 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| Sc | -0.13 | -0.18 | 0.13 | 0.75** | 0.32 | -0.05 | 0.78** | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| V | 0.29 | -0.24 | 0.98** | -0.12 | 0.71** | -0.50* | -0.22 | 0.02 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| Cr | 0.24 | -0.27 | 0.99** | -0.12 | 0.70** | -0.52* | -0.18 | 0.06 | 0.99** | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| Co | 0.22 | -0.32 | 0.99** | -0.02 | 0.70** | -0.54* | -0.09 | 0.16 | 0.98** | 0.99** | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Ni | 0.18 | -0.29 | 0.99** | -0.07 | 0.66** | -0.50* | -0.08 | 0.13 | 0.98** | 0.99** | 0.99** | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Cu | 0.19 | -0.28 | 0.99** | -0.05 | 0.67** | -0.49* | -0.07 | 0.15 | 0.98** | 0.99** | 0.99** | 1.00** | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Zn | 0.27 | -0.52* | 0.30 | 0.55* | 0.62** | -0.50* | 0.32 | 0.71** | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Sr | -0.68** | -0.35 | -0.37 | -0.32 | -0.69** | -0.02 | 0.15 | -0.15 | -0.45 | -0.42 | -0.38 | -0.36 | -0.37 | -0.23 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Y | 0.33 | -0.21 | 0.13 | 0.76** | 0.71** | -0.08 | 0.06 | 0.57* | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.64** | -0.45 | 1.00 | |||||
| Zr | 0.36 | -0.27 | 0.81** | 0.47 | 0.88** | -0.36 | 0.04 | 0.46 | 0.79** | 0.78** | 0.84** | 0.81** | 0.82** | 0.59* | -0.54* | 0.65** | 1.00 | ||||
| Ba | 0.15 | -0.34 | 0.09 | 0.61** | 0.15 | -0.16 | 0.25 | 0.41 | -0.01 | -0.01 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.45 | 0.13 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 1.00 | |||
| Pb | -0.18 | -0.22 | 0.28 | 0.49* | 0.36 | -0.30 | 0.59* | 0.84** | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.72** | -0.12 | 0.34 | 0.42 | 0.24 | 1.00 | ||
| Th | 0.41 | -0.42 | 0.90** | 0.20 | 0.82** | -0.55 | -0.15 | 0.23 | 0.88** | 0.88** | 0.92** | 0.89** | 0.90** | 0.51* | -0.45 | 0.45 | 0.94** | 0.38 | 0.28 | 1.00 | |
| U | -0.43 | -0.52* | 0.03 | -0.42 | -0.43 | -0.40 | 0.16 | -0.12 | -0.05 | -0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | -0.07 | 0.78** | -0.58* | -0.30 | 0.18 | 0.03 | -0.12 | 1.00 |
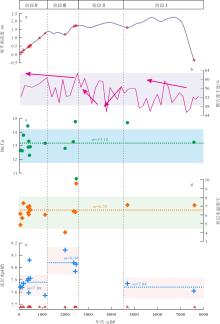
图4
8000a BP以来深水珊瑚的地球化学特征及其重建的环境变化 a. 南海北部海平面高度, 据余克服(2012); b. 南海东北部MD052904站位的颗石藻含量变化, 据Su等(2013); c. 本文深水珊瑚骨骼的Ba/Ca(μmol/mol)比值变化, Ba/Ca营养盐指标据Raddatz等(2014); d. 深水珊瑚重建的底层水温度变化, 温度重建公式为Li/Mg (mmol/mol)=5.41exp(-0.049T), 据Montagna等(2014); e. 深水珊瑚重建的底层水pH值变化, pH值重建公式为pH=(U/Ca-16.18)/ (-1.82), 据Raddatz等(2014)。图中红色三角形代表东沙西南海域的深水珊瑚发育年龄; 水平虚线及m表示各阶段参数的平均值"
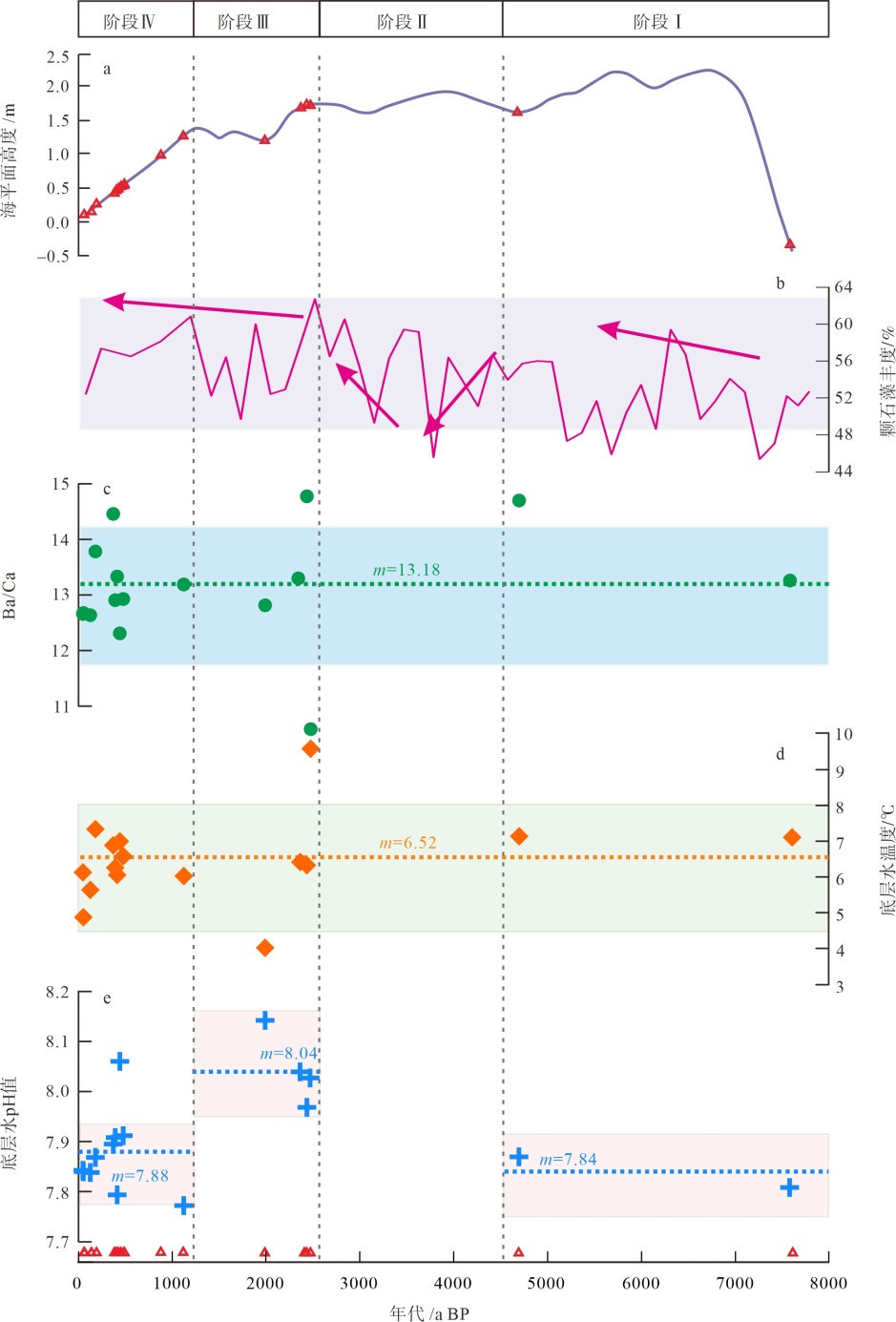
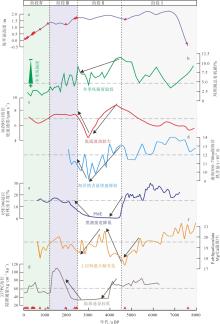
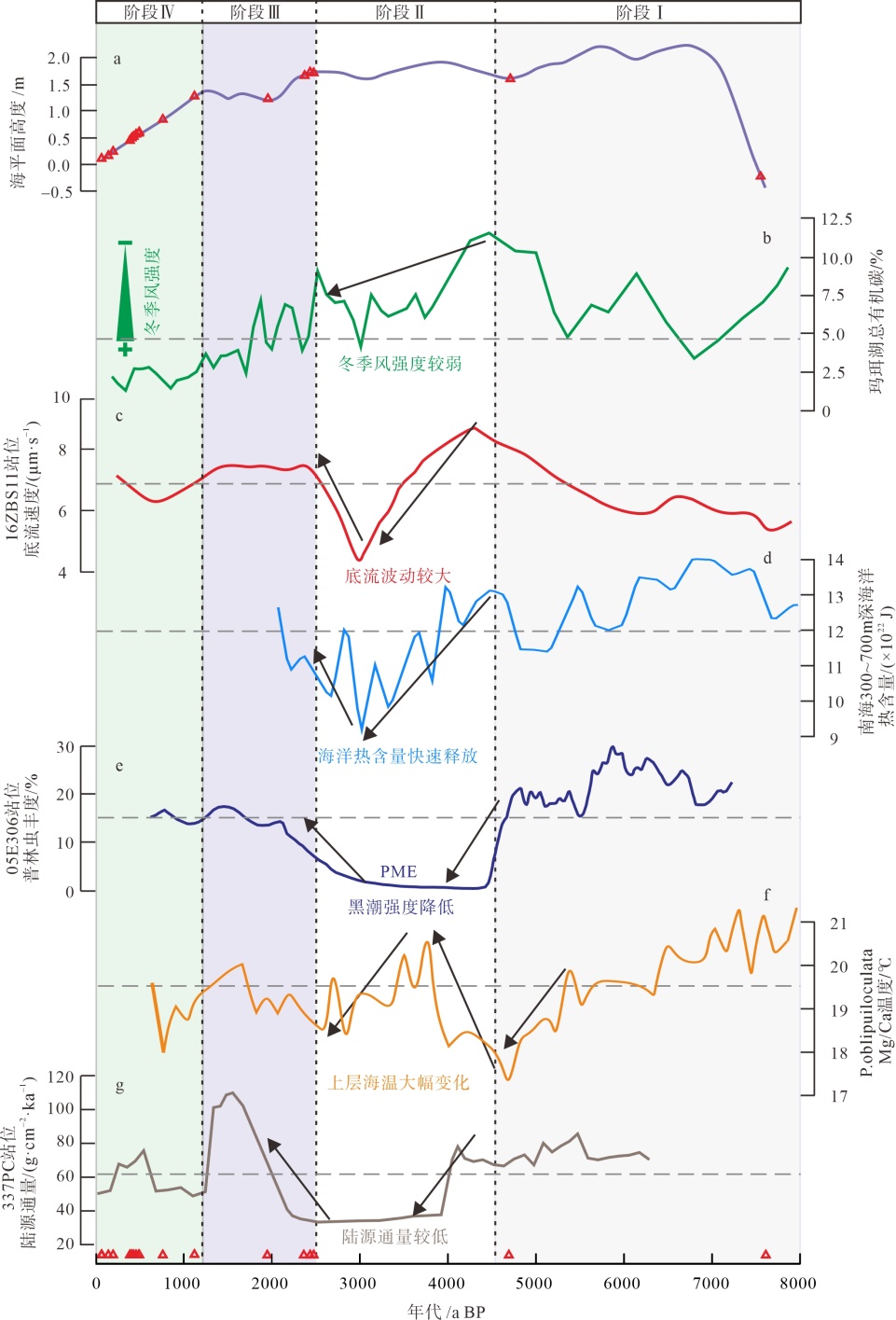
图6
东沙西南海域深水珊瑚演化阶段及影响因素变化图 a. 南海北部海平面变化曲线(余克服, 2012); b. 玛珥湖总有机碳变化曲线(Yancheva et al, 2007); c. 南海东北部16ZBS1站位底流速度变化(王雪松 等, 2022); d. 南海水深300~700m处海洋热含量变化曲线(Yang et al, 2020); e. 南海北部05E306站位普林虫丰度变化(Du et al, 2021); f. 南海北部有孔虫Mg/Ca重建的水体温度(Yang et al, 2020); g. 南海北部陆源输入通量变化(Wan et al, 2015); 图中红色三角形代表深水珊瑚发育年龄"
| [1] |
安阳, 翦知湣, 2009. 末次冰消期南海南部的普林虫低值事件[J]. 科学通报, 54(17): 2527-2532.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
蔡观强, 邱燕, 彭学超, 等, 2010. 南海西南海域表层沉积物中微量元素Ba的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 24(3): 560-569.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈建芳, 郑连福,
|
|
doi: 10.1007/BF02883645 |
|
| [4] |
陈越, 王跃, 党皓文, 等, 2021. 南海东北部末次冰盛期以来的水文气候变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 41(4): 1031-1043.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
陈忠, 杨华平, 黄奇瑜, 等, 2008. 南海东沙西南海域冷泉碳酸盐岩特征及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 22(3): 382-389.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
陈忠, 莫爱彬, 赵美霞, 等, 2018. 南海北部冷泉区深水珊瑚的发现及其特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(1): 64-71.
doi: 10.11978/2017022 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2017022 |
|
| [7] |
党皓文, 马小林, 杨策, 等, 2019. 重建高分辨率深海环境变化: 冷水竹节珊瑚无机地球化学方法[J]. 地球科学进展, 34(12): 1262-1272.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.12.1262 |
|
|
|
| [8] |
黄恩清, 孔乐, 田军, 2019. 冷水珊瑚测年与大洋中-深层水碳储库[J]. 地球科学进展, 34(12): 1243-1251.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.12.1243 |
|
|
|
| [9] |
姜大膀, 田芝平, 王娜, 等, 2022. 末次冰盛期和中全新世气候模拟分析进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 37(1): 1-13, doi: 10.11867/j. issn.1001-8166.2021.098.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2021.098 |
|
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2021.098 |
|
| [10] |
邵磊, 李学杰, 耿建华, 等, 2007. 南海北部深水底流沉积作用[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 37(6): 771-777.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
王东晓, 肖劲根, 舒业强, 等, 2016. 南海深层环流与经向翻转环流的研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 46(10): 1317-1323.
|
|
doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-5324-6 |
|
| [12] |
王东晓, 王强, 蔡树群, 等, 2019. 南海中深层动力格局与演变机制研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 49(12): 1919-1932.
|
|
doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9546-3 |
|
| [13] |
王雪松, 陈忠, 许安涛, 等, 2022. 南海东北部深海盆末次冰盛期以来陆源碎屑粒度特征及影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(1): 158-170.
doi: 10.11978/2021027 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2021027 |
|
| [14] |
许安涛, 2019. 南海东沙海域冷水珊瑚发育演化的成因模式及其对洋流模态转变的响应[D]. 广州: 中国科学院南海海洋研究所: 1-90.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
阎贫, 王彦林, 于俊辉, 等, 2021. 东沙海区泥火山调查进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(3): 34-43.
doi: 10.11978/YG2020008 |
|
doi: 10.11978/YG2020008 |
|
| [16] |
余克服, 2012. 南海珊瑚礁及其对全新世环境变化的记录与响应[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 42(8): 1160-1172.
|
|
doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4449-5 |
|
| [17] |
邹建军, 石学法, 2017. 末次冰期以来北太平洋中层水演化: 研究进展与展望[J]. 地学前缘, 24(4): 141-151.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
邹仁林, 蒙致民, 关锡廉, 1983. 南海北部大陆架深水石珊瑚的生态分析[J]. 热带海洋, 2(3): 238-243.
|
|
ZOU RENLIN, MENG, ZHIMIN,
|
|
| [19] |
邹仁林, 1988. 南海深水石珊瑚的研究——Ⅱ. 种属记述及时空分布特点[J]. 热带海洋, (1): 76-85.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2011.02.019 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.5194/bg-17-5883-2020 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.06.008 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aag1015 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aac6159 pmid: 26404835 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1038/s41561-020-0638-6 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00422-6 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106783 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.03.038 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1038/nature02150 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.3390/min9120742 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.05.023 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.110093 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.12.007 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2021.09.018 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00354 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2009.08.007 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1007/BF02667712 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.05.045 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00132 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1007/BF02369011 |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
doi: 10.1029/2018GL078568 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51797-3 pmid: 31664067 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb3807 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.11.003 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.005 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.02.041 |
| [50] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2015.09.003 |
| [51] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2017.08.012 |
| [52] |
doi: 10.1038/nature02494 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106581 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.02.005 |
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.05.008 |
| [58] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2019.05.009 |
| [59] |
doi: 10.1111/ggr.2000.24.issue-1 |
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
pmid: 16645087 |
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2008.05.013 |
| [64] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106223 |
| [65] |
doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.08.016 |
| [66] |
doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00214-7 |
| [67] |
doi: 10.1111/sed.12206 |
| [68] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.01.011 |
| [69] |
doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-121211-172322 pmid: 22809181 |
| [70] |
doi: 10.1130/G36570.1 |
| [71] |
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.02.007 |
| [72] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2020.103317 |
| [73] |
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.08.017 |
| [74] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2009.05.016 |
| [75] |
doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.02.012 |
| [76] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2019.05.003 |
| [77] |
doi: 10.1038/nature05431 |
| [78] |
doi: 10.1130/G47271.1 |
| [79] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2021.11.006 pmid: 36546161 |
| [80] |
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.02.017 |
| [81] |
doi: 10.1002/grl.v43.16 |
| [1] | 阎贫, 王彦林, 于俊辉, 罗伟, 刘兴健, 靳永斌, 李鹏春, 刘杰, 钟广见, 易海. 东沙海区泥火山调查进展*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 34-43. |
| [2] | 张玲芝, 向荣, 唐灵刚, 杨艺萍, 钟福昌. 安达曼海浮游有孔虫群落对全新世海洋环境变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(6): 51-61. |
| [3] | 莫文渊,韦惺,吴超羽. 全新世以来珠江三角洲海鸥沙形成过程的地貌动力学分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(3): 68-78. |
| [4] | 王文洁, 徐建. 印-太暖池区全新世Mg/Ca温度转换中的盐度因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2014, 33(2): 94-100. |
|
||