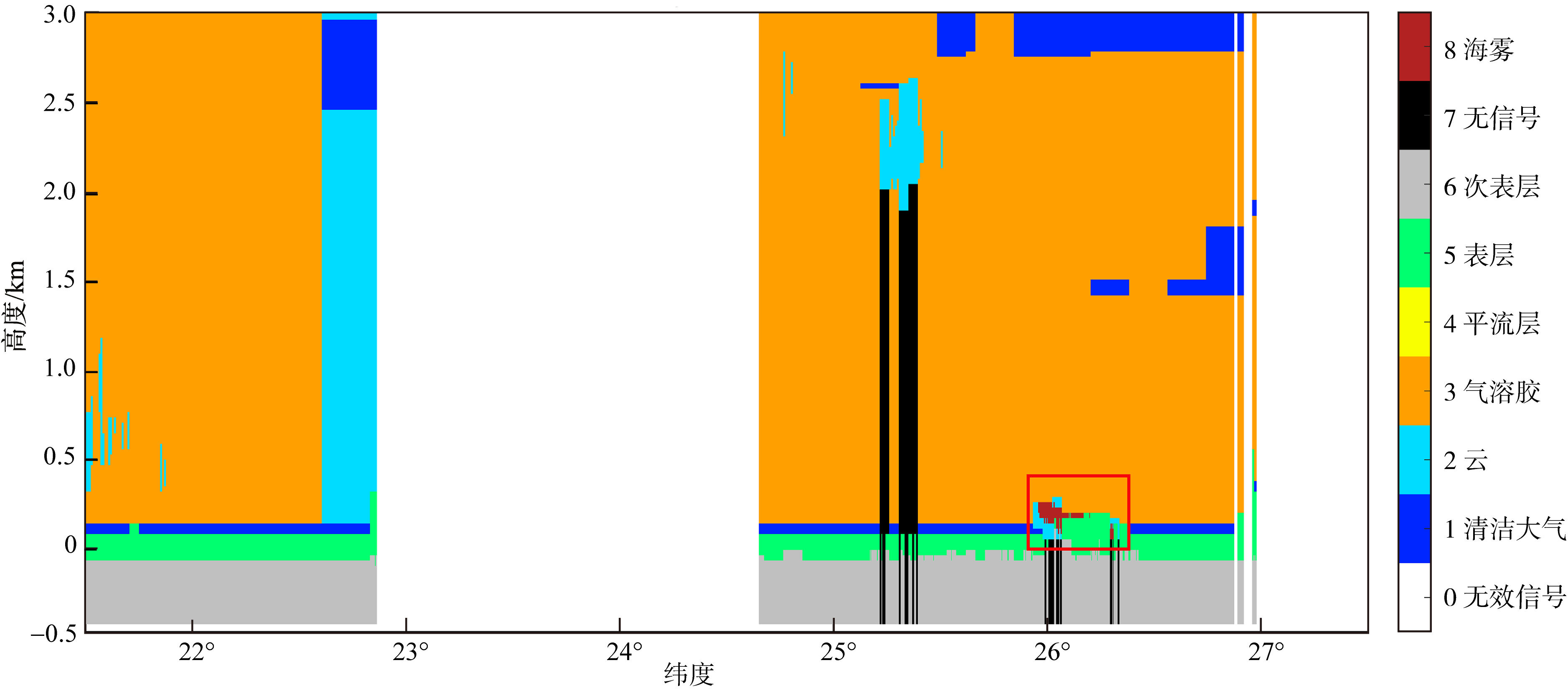
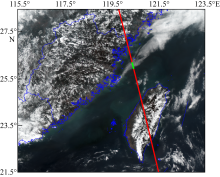
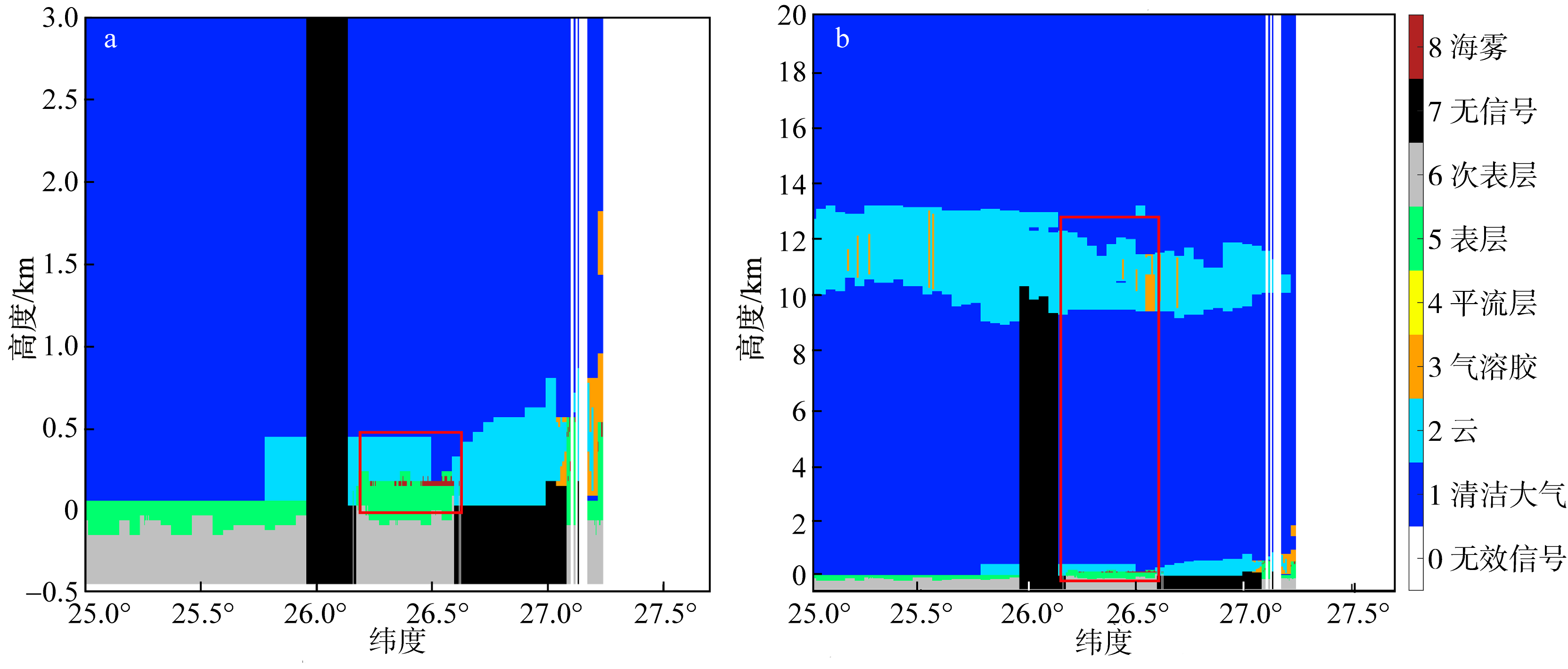
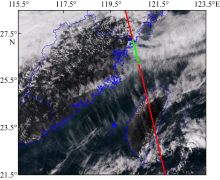
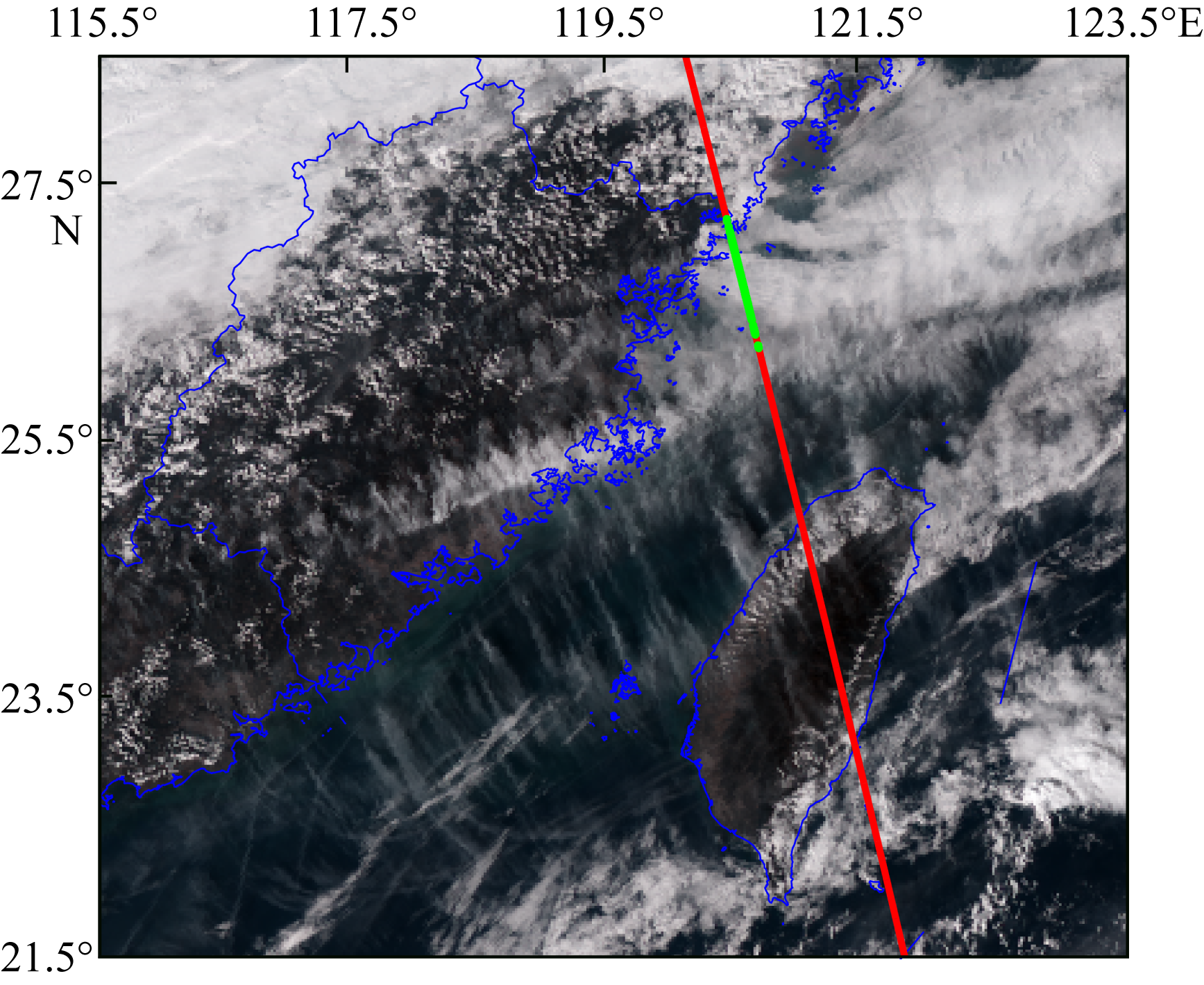
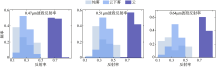
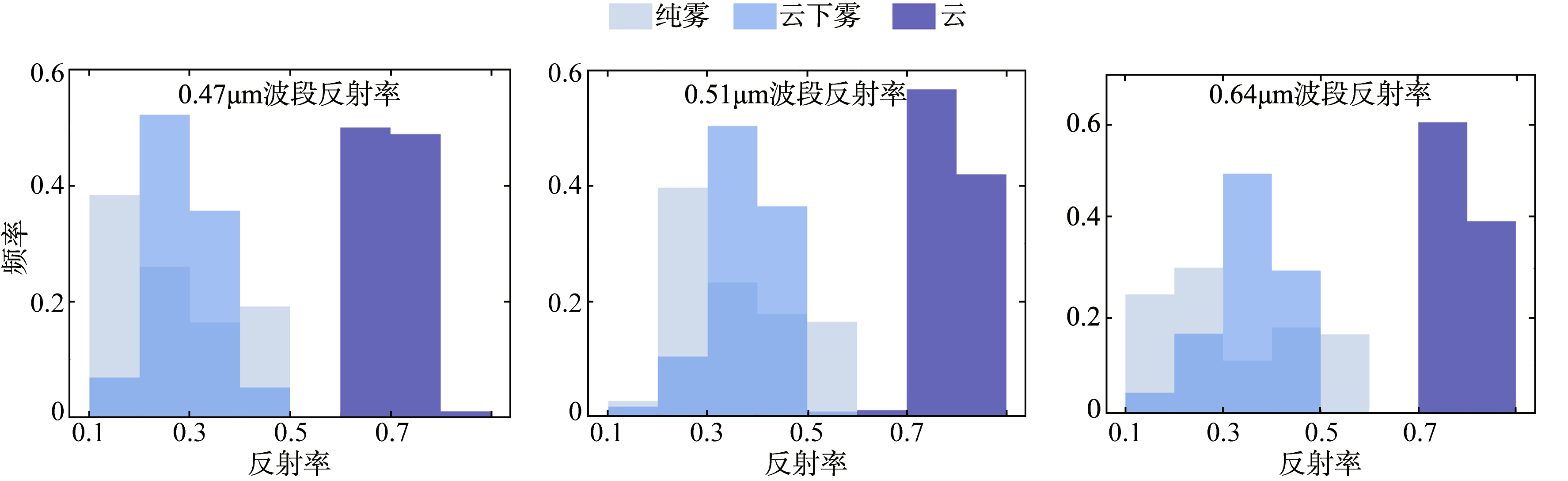
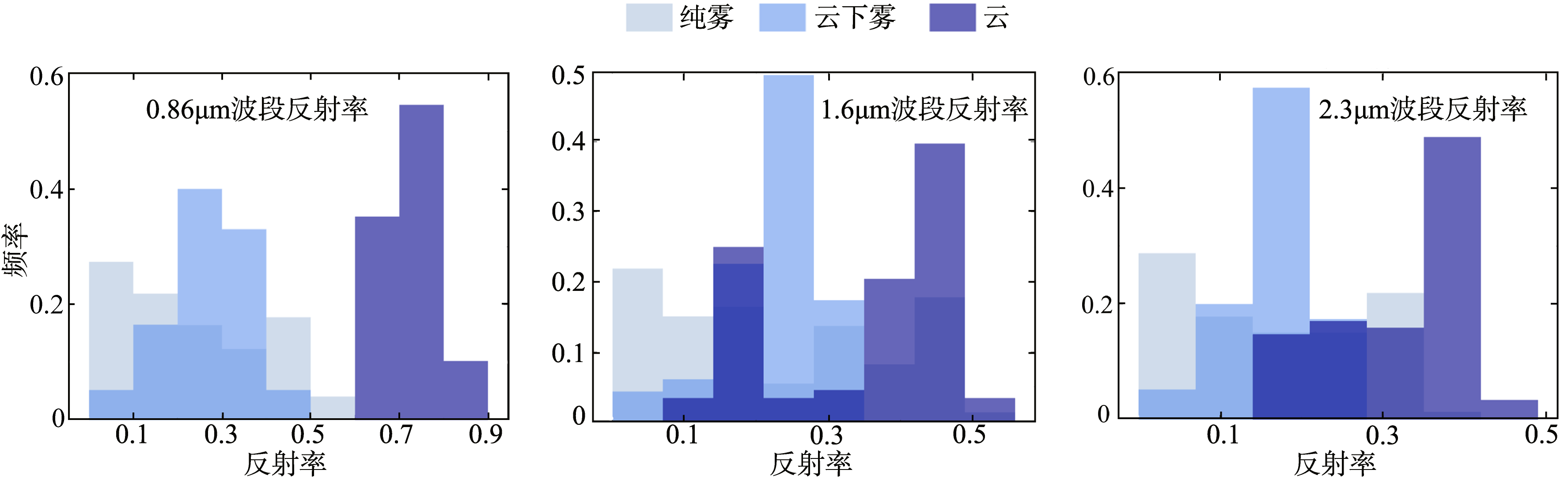
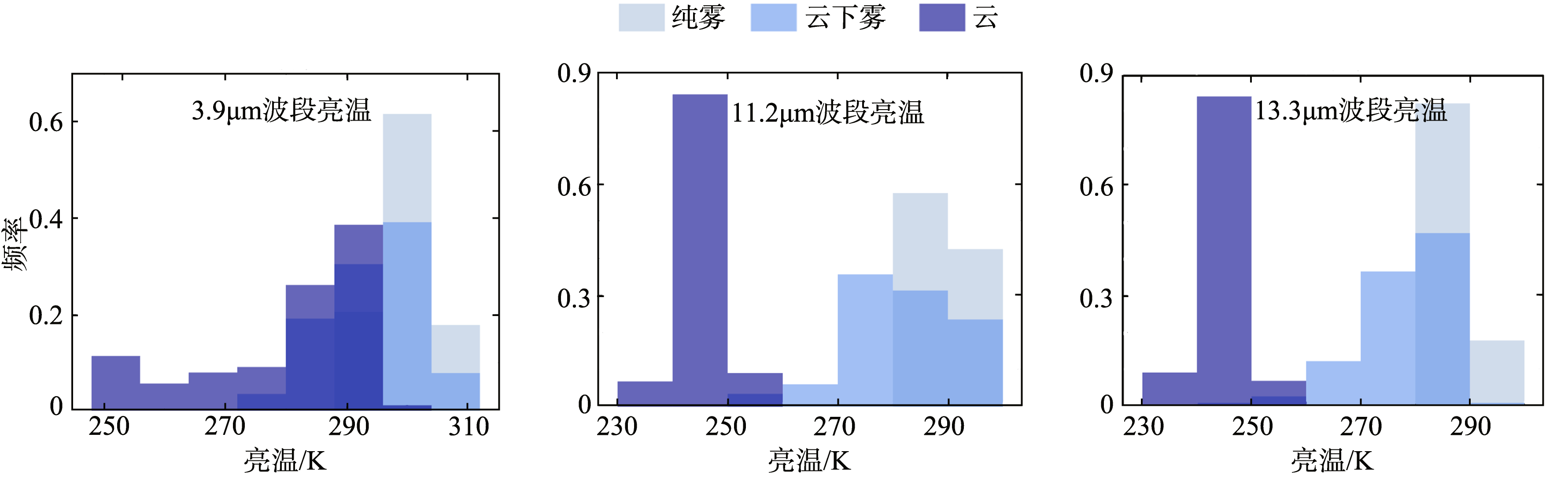
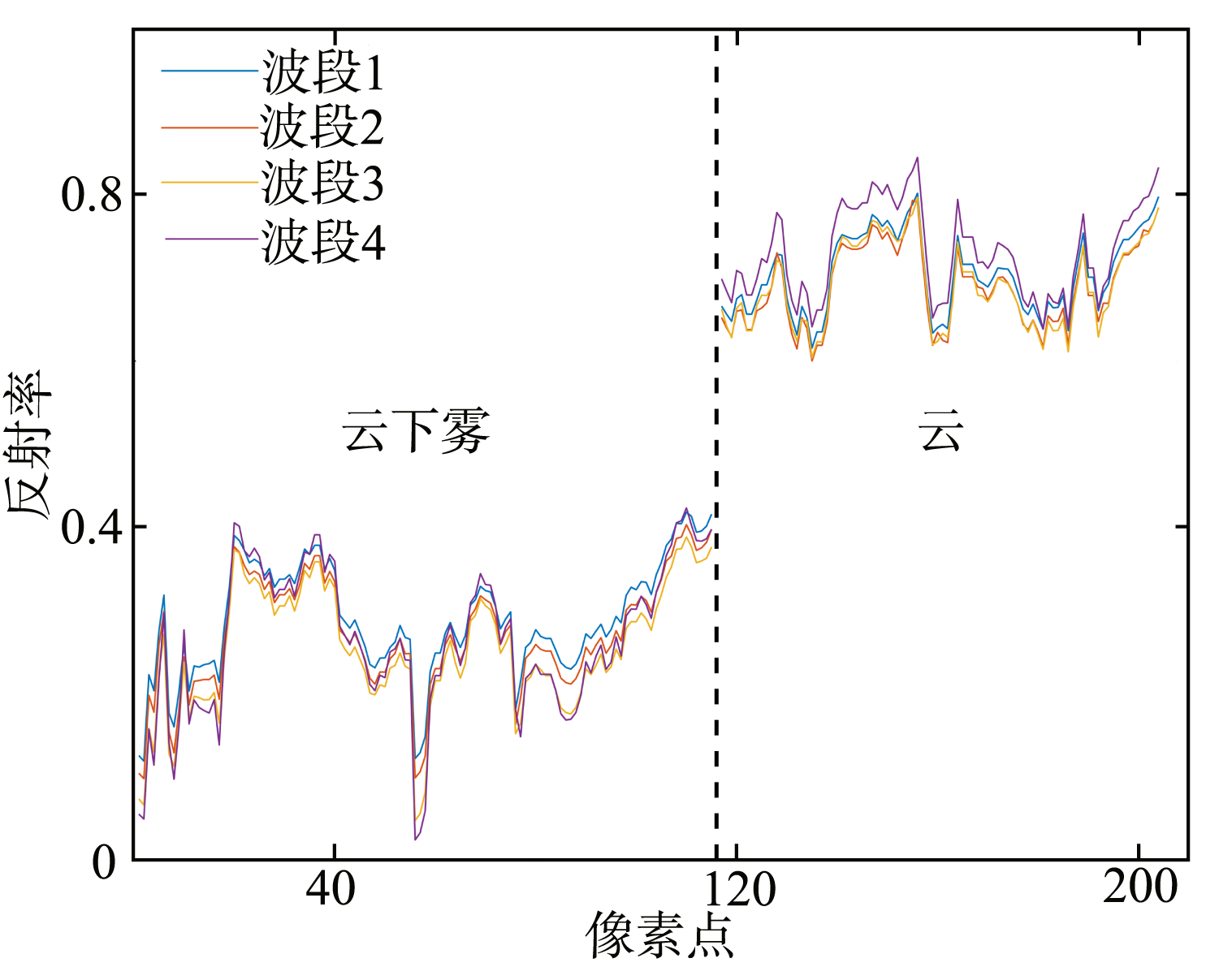
| [1] |
郝姝馨, 郝增周, 黄海清, 等, 2021. 基于Himawari-8数据的夜间海雾识别[J]. 海洋学报, 43(11): 166-180.
|
|
HAO SHUXIN, HAO ZENGZHOU, HUANG HAIQING, et al, 2021. Nighttime sea fog recognition based on Himawari-8 data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 43(11): 166-180 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
李琦, 蔡淼, 周毓荃, 等, 2021. 基于探空云识别方法的云垂直结构分布特征[J]. 大气科学, 45(6): 1161-1172.
|
|
LI QI, CAI MIAO, ZHOU YUQUAN, et al, 2021. Characteristics of cloud vertical distribution based on cloud identification by radiosonde[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 45(6): 1161-1172 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
李昀英, 王汉杰, 2000. 台湾海峡地区雾形成的天气类型分析[J]. 热带海洋, (4): 65-70.
|
|
LI YUNYING, WANG HANJIE, 2000. A synoptic analysis on fog formation in Taiwan strait[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, (4): 65-70 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
刘柏鑫, 李栋梁, 2018. 我国云量时空变化特征及其与副热带夏季风北边缘带关系研究[J]. 气象, 44(3): 382-395.
|
|
LIU BOXIN, LI DONGLIANG, 2018. Spatio-temporal variation features of cloud cover in China and its correlation to north boundary belt of subtropical summer monsoon[J]. Meteorlogical Monthly, 44(3): 382-395 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
刘少军, 吴胜安, 李伟光, 等, 2017. 基于 FY-3B 卫星资料的中国南海海区 1-3 月海雾时空分布特征研究[J]. 海洋气象学报, 37(4): 85-90.
|
|
LIU SHAOJUN, WU SHENGAN, LI WEIGUANG, et al, 2017. Study on spatial-temporal distribution of sea fog in the south China sea from January to March based on FY-3B sea fog retrieval data[J]. Journal of Marine Meteorology, 37(4): 85-90 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
马静, 于芸, 魏立新, 2012. 东海近海海雾日变化特征及生成的水文气象条件分析[J]. 海洋预报, 29(6): 58-65.
|
|
MA JING, YU YUN, WEI LIXIN, 2012. Analysis of the daily variation of sea fog in the East China Sea and the weather condition to the sea fog formation[J]. Marine Forecasts, 29(6): 58-65 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
孙艺, 杨悦, 甄晴, 2020. CALIPSO卫星资料的春夏季黄海海雾高度特征分析[J]. 海洋预报, 37(3): 54-61.
|
|
SUN YI, YANG YUE, ZHEN QING, 2020. The characteristics of the top height of sea fog over the Yellow Sea in spring and summer based on CALIPSO satellite data[J]. Marine Forecasts, 37(3): 54-61 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
田永杰, 2016. 基于风云 2 号静止卫星数据的白天海雾监测算法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学.
|
|
TIAN YONGJIE, 2016. Study of algorithm of detection of daytime sea fog using FY-2 geostationary satellite data[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
张春桂, 蔡义勇, 张加春, 2009. MODIS 遥感数据在我国台湾海峡海雾监测中的应用[J]. 应用气象学报, 20(1): 8-16.
|
|
ZHANG CHUNGUI, CAI YIYONG, ZHANG JIACHUN, 2009. The application of monitoring sea fog in Taiwan Strait using MODIS remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology Science, 20(1): 8-16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
张春桂, 何金德, 马治国, 2013. 福建沿海海雾的卫星遥感监测[J]. 中国农业气象, 34(3): 366-373.
|
|
ZHANG CHUNGUI, HE JINDE, MA ZHIGUO, 2013. Remote sensing monitor of sea fog in Fujian coastal region[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 34(3): 366-373 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
张春桂, 林炳青, 2018. 基于 FY-2E 卫星数据的福建沿海海雾遥感监测[J]. 国土资源遥感, 30(1): 7-13.
|
|
ZHANG CHUNGUI, LIN BINGQING, 2018. Application of FY-2E data to remote sensing monitoring of sea fog in Fujian coastal region[J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 30(1): 7-13 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
张苏平, 鲍献文, 2018. 近十年中国海雾研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 359-366.
|
|
ZHANG SUPING, BAO XIANWEN, 2018. The main advances in sea fog research in China[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science Edition), 38(3): 359-366 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
赵耀天, 吴东, 2020. CALIOP、CPR 数据在探测海雾中的应用[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 50(10): 125-133.
|
|
ZHAO YAOTIAN, WU DONG, 2020. Application of CALIOP and CPR data in detecting sea fog[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science Edition), 50(10): 125-133 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
BESSHO K, DATE K, HAYASHI M, et al, 2016. An introduction to Himawari-8/9—Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satellites[J]. Journal of The Meteorological Society of Japan. Ser. II, 94(2): 151-183.
doi: 10.2151/jmsj.2016-009
|
| [15] |
CERMAK J, BENDIX J, 2007. Dynamical nighttime fog/low stratus detection based on Meteosat SEVIRI data: A feasibility study[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 164(7): 1179-1192.
doi: 10.1007/s00024-007-0213-8
|
| [16] |
EYRE J R, BROWNSCOMBE J L, Allam R J, 1984. Detection of fog at night using Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) imagery[J]. Meteor Magzine, 113(1346): 266-271.
|
| [17] |
GURKA J J, 1974. Using satellite data for forecasting fog and stratus dissipation[C]. Conference on Weather Forecasting and Analysis, 5th. Saint Louis, Mo. 54-57.
|
| [18] |
HEO K Y, MIN S Y, HA K J, et al, 2008. Discrimination between sea fog and low stratus using texture structure of MODIS satellite images[J]. Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, 24(6): 571-581.
|
| [19] |
JEON H K, KIM S, EDWIN J, et al, 2020. Sea fog identification from GOCI images using CNN transfer learning models[J]. Electronics, 9(2): 311.
doi: 10.3390/electronics9020311
|
| [20] |
TURNER J, ALLAM R J, MAINE D R, 1986. A case study of the detection of fog at night using channels 3 and 4 on the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR)[J]. Meteorological Magazine, 115: 285-290.
|
| [21] |
RYU H S, HONG S, 2020. Sea fog detection based on normalized difference snow index using advanced Himawari imager observations[J]. Remote Sensing, 12(9): 1521.
doi: 10.3390/rs12091521
|
| [22] |
WAN JIANHUA, LI JIAJIA, XU MINGMING, et al, 2022. Node-splitting optimized canonical correlation forest algorithm for sea fog detection using MODIS data[J]. Optics Express, 30(8): 13810-13824.
doi: 10.1364/OE.454570
pmid: 35472986
|
| [23] |
WINKER D M, VAUGHAN M A, OMAR A, et al, 2009. Overview of the CALIPSO mission and CALIOP data processing algorithms[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 26(11): 2310-2323.
doi: 10.1175/2009JTECHA1281.1
|
| [24] |
WU DONG, LU BO, ZHANG TIANCHE, et al, 2015. A method of detecting sea fogs using CALIOP data and its application to improve MODIS-based sea fog detection[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 153: 88-94.
doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2014.09.021
|
| [25] |
YANG J H, YOO J M, CHOI Y S, 2021. Advanced dual-satellite method for detection of low stratus and fog near Japan at dawn from FY-4A and Himawari-8[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(5): 1042.
doi: 10.3390/rs13051042
|
 ), 丘仲锋1, 廖廓2(
), 丘仲锋1, 廖廓2( ), 赵冬至1, 吴到懋3
), 赵冬至1, 吴到懋3
 ), QIU Zhongfeng1, LIAO Kuo2(
), QIU Zhongfeng1, LIAO Kuo2( ), ZHAO Dongzhi1, WU Daomao3
), ZHAO Dongzhi1, WU Daomao3