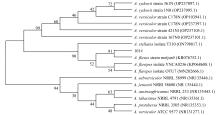
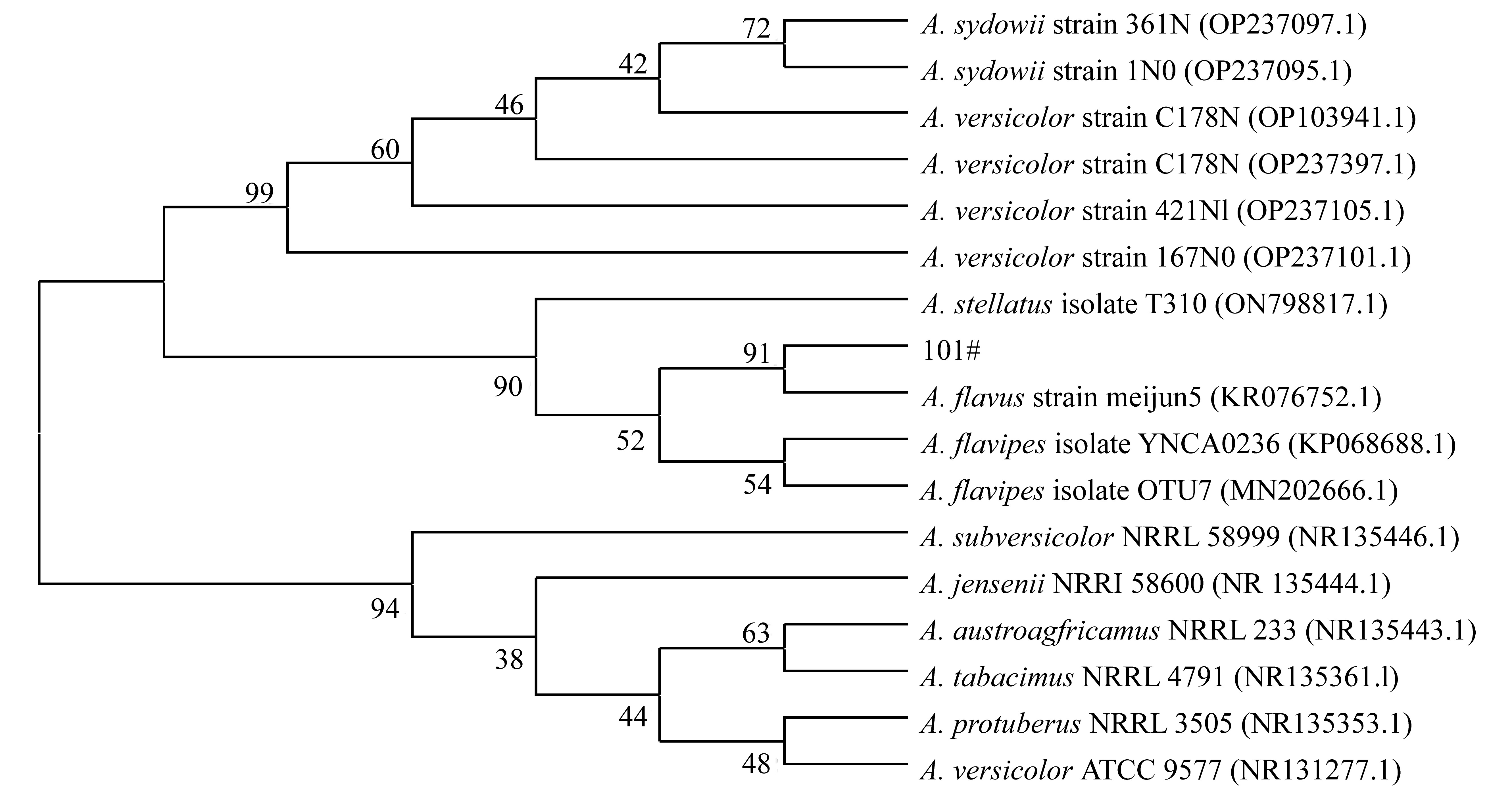
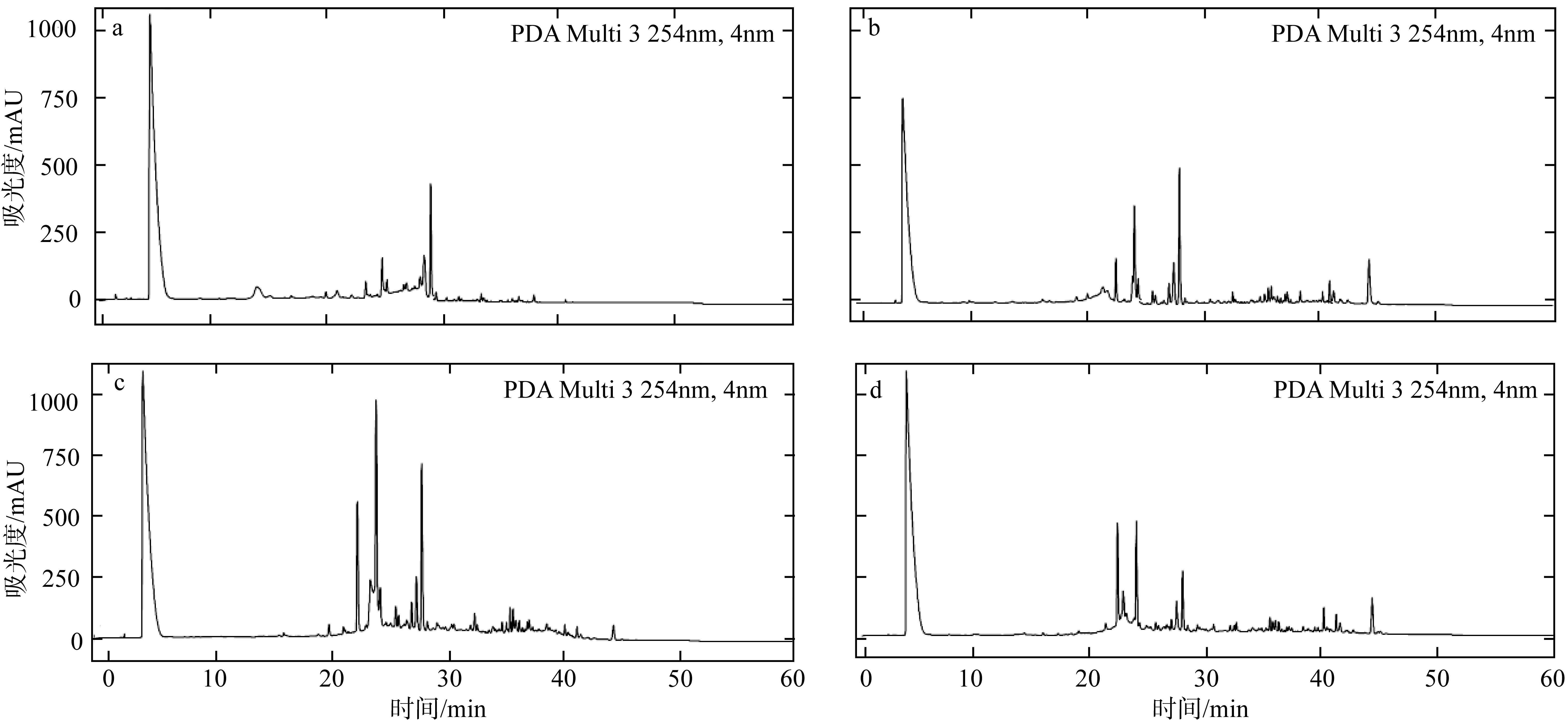
| [1] |
安昶亮, 2019. 海洋真菌Aspergillus sp. SCS-KFD66的次级代谢产物及其活性研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学:1-121.
|
|
AN CHANGLIANG, 2019. Secondary metabolites and activities of marine fungus Aspergillus sp. SCS-KFD66[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University: 1-121 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
董怡飞, 徐秀丽, 张新婉, 等, 2022. 深海真菌Aspergillus sp.20220129的次级代谢产物及抑菌活性研究[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 47(5): 494-500.
|
|
DONG YIFEI, XU XIULI, ZHANG XINWAN, et al, 2022. Study on secondary metabolites from the deep-sea fungus aspergillus sp. 20220129 and their antibacterial activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 47(5): 494-500 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
黄智, 王发左, 田新朋, 等, 2012. 一株南海北部深海沉积环境真菌00457的鉴定及其活性研究[J]. 生物技术通报, (10): 199-204.
|
|
HUANG ZHI, WANG FAZUO, TIAN XINPEN, et al, 2012. Identification and activity study of a deep-sea sedimentary environment fungus 00457 in northern South China Sea[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, (10): 199-204 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
江北, 吕梦霞, 蒋冬花, 2019. 曲霉属真菌活性代谢产物及在农业生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 微生物学杂志, 39(2): 103-110.
|
|
JIANG BEI, LV MENGXIA, JIANG DONGHUA, 2019. Advances in aspergillus active metabolites and application in agricultural production[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 39(2): 103-110 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
罗寒, 李晓栋, 李晓明, 等, 2017. 红树林来源内生真菌杂色曲霉Aspergillus versicolor MA-229次级代谢产物研究[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 42(4): 334-340.
|
|
LUO HAN, LI XIAODONG, LI XIAOMING, et al, 2017. Secondary metabolites of endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor MA-229 from mangrove[J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 42(4): 334-340 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
潘力, 崔翠, 王斌, 2010. 一种用于PCR扩增的丝状真菌DNA快速提取方法[J]. 微生物学通报, 37(3): 450-453.
|
|
PAN LI, CUI CUI, WANG BIN, 2010. Rapid extraction of filamentous fungal DNA for PCR amplification[J]. Microbiology China, 37(3): 450-453 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
钱生辉, 2022. 南海红树林底泥海洋放线菌抗菌/抗群体感应活性菌株的筛选及次级代谢产物的初步研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学: 1-90.
|
|
QIAN SHENGHUI, 2022. Screening of antimicrobial/quorum sensing-resistant strains of marine actinomycetes from mangrove sediments in the South China Sea and preliminary study on secondary metabolites[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University: 1-90 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
单体壮, 2020. 海洋真菌Aspergillus ruber的次级代谢产物及其生物活性研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学: 1-137.
|
|
SHAN TIZHUANG, 2020. Secondary metabolites of marine fungus Aspergillus ruber and their bioactivities[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University: 1-137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
谭雁鸿, 李基兴, 林秀萍, 等, 2019. 中国南海软珊瑚真菌Eupenicillium sp. DX-SER3 (KC871024) 的次级代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(2): 43-47.
doi: 10.11978/2018072
|
|
TAN YANHONG, LI JIXING, LIN XIUPING, et al, 2019. Study on the secondary metabolites from the South China Sea soft coral-derived fungus Eupenicillium sp. DX-SER3(KC871024)[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(2): 43-47 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [10] |
王发左, 2008. 海洋真菌抗肿瘤活性次级代谢产物及其生物转化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学: 21-22.
|
|
WANG FAZUO, 2008. Studies on the antitumor constituents and biotransformation of secondary metabolites produced by marine-derived Fungi[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China: 21-22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
叶禹秀, 罗小卫, 杨斌, 等, 2022. 南海礁栖海藻共附生真菌Pestalotiopsis neglecta SCSIO41 403次级代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(3): 186-190.
doi: 10.11978/2021089
|
|
YE YUXIU, LUO XIAOWEI, YANG BIN, et al, 2022. Study on the secondary metabolites of reef habitat algae-derived fungus Pestalotiopsis neglecta SCSIO41403 from the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 41(3): 186-190 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
于清武, 胡丽琴, 李菲, 等, 2015. 南海深海沉积物可培养细菌多样性及其生物毒性分析[J]. 南方农业学报, 46(12): 2203-2208.
|
|
YU QINGWU, HU LIQIN, LI FE, et al, 2015. Diversity and toxicity of culturable bacteria in deep-sea sediments of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 46(12): 2203-2208 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
曾奇, 仲伟茂, 向瑶, 等, 2018. 南海深海沉积物中52株真菌的初步分离鉴定及其代谢产物活性[J]. 微生物学通报, 45(9): 1904-1915.
|
|
ZENG QI, ZHONG WEIMAO, XIANG YAO, et al, 2018. Isolation, identification and evaluation of 52 fungi from the deep-sea sediments of South China Sea[J]. Microbiology China, 45(9): 1904-1915 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
张长生, 李文利, 2018. 海洋微生物学: 新机遇, 新挑战[J]. 微生物学通报, 49(5): 1841-1842.
|
|
ZHANG CHANGSHENG, LI WENLI, 2018. Marine microbiology: new opportunities and new challenges[J]. Microbiology China, 49(5): 1841-1842 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
ANCHEEVA E, L KÜPPERS, AKONE S H, et al, 2017. Expanding the metabolic profile of the fungus Chaetomium sp. through Co-culture with autoclaved pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. European Journal of Organic Chemistry, (22): 3256-3264.
|
| [16] |
BLUNT J W, CARROLL A R, COPP B R, et al, 2018. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 35(1): 8-53.
doi: 10.1039/c7np00052a
pmid: 29335692
|
| [17] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2021. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 38(2): 362-413.
doi: 10.1039/d0np00089b
pmid: 33570537
|
| [18] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2022. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 39(6): 1122-1171.
doi: 10.1039/D1NP00076D
|
| [19] |
CHENG XIA, LIANG XIAO, YAO FEIHUA, et al, 2021. Fusidane-type antibiotics from the marine-derived fungus Simplicillium sp. SCSIO 41513[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 84(11): 2945-2952.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00776
|
| [20] |
DAVIS R A, 2005. Isolation and structure elucidation of the new fungal metabolite (-)-xylariamide A[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 68(5): 769-772.
pmid: 15921427
|
| [21] |
DING LIJIAN, XU PENG, LI TE, et al, 2019. Asperfurandiones A and B, two antifungal furandione analogs from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor[J]. Natural Product Research, 33(23): 3404-3408.
doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1480622
|
| [22] |
HU JIANSEN, LI ZHENG, GAO JIEYU, et al, 2019. New diketopiperazines from a marine-derived fungus strain Aspergillus versicolor MF180151[J]. Marine Drugs, 17(5): 262.
doi: 10.3390/md17050262
|
| [23] |
ITSUO U, YOSHIKUNI I, TAKAYUKI N, et al, 1986. Structure and synthesis of WF 3681, a novel aldose reductase inhibitor[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 27(18): 2015-2018.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)84436-6
|
| [24] |
KADIN S B, 1972. Antiinflammatory 2, 3-Dhiydro-2-oxobenzofuran-3-carboxanilides[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 15(5): 551-552.
doi: 10.1021/jm00275a029
|
| [25] |
NEWMAN D J, CRAGG G M, 2020. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 83(3): 770-803.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285
pmid: 32162523
|
| [26] |
SCICUTELLA F, MANNELLI F, DAGHIO M, et al, 2021. Polyphenols and organic acids as alternatives to antimicrobials in poultry rearing: a review[J]. Antibiotics, 10(8): 1010.
doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10081010
|
| [27] |
WANG YANAN, MENG LINGHONG, WANG BINGUI, 2020. Progress in research on bioactive secondary metabolites from deep-sea derived microorganisms[J]. Marine Drugs, 18(12): 164.
doi: 10.3390/md18030164
|
| [28] |
XIE YUHUI, SONG YUE, CONG ZIWEN, et al, 2022. New diterpene and indole alkaloid analogues from the Streptomyces malaysiensis SCSIO 41397[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 19(10): e202200731.
|
| [29] |
YAO FEIHUA, LIANG XIAO, CHENG XIA, et al, 2021. Antifungal peptides from the marine gorgonian-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO41501[J]. Phytochemistry, 192: 112967.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112967
|
| [30] |
ZHANG LU, QIU PANPAN, DING LIJIAN, et al, 2020. A new antibacterial chlorinated amino acid derivative from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. LS53[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 56(1): 109-111.
doi: 10.1007/s10600-020-02955-x
|
| [31] |
ZHU JINGXUAN, DING LIJIAN, HE SHAN, 2019. Discovery of a new biphenyl derivative by epigenetic manipulation of marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor[J]. Natural Product Research, 33(8): 1191-1195.
doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1465423
|
 ), 梁志凤1, 罗琴琴3, 曾玲3, 杨长庚1, 王锂韫1, 孙玉林1,2(
), 梁志凤1, 罗琴琴3, 曾玲3, 杨长庚1, 王锂韫1, 孙玉林1,2( )
)
 ), LIANG Zhifeng1, LUO Qinqin3, ZENG Ling3, YANG Changgeng1, WANG Liyun1, SUN Yulin1,2(
), LIANG Zhifeng1, LUO Qinqin3, ZENG Ling3, YANG Changgeng1, WANG Liyun1, SUN Yulin1,2( )
)