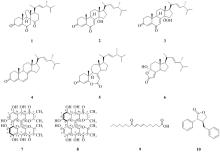
| [1] |
白猛, 郑彩娟, 陈光英, 2020. 1株红树内生真菌Penicillium sp. JY246次级代谢产物及其活性研究[J]. 中国海洋药物, 39(2): 11-18.
|
|
BAI MENG, ZHENG CAIJUAN, CHEN GUANGYING, 2020. Study on bioactive secondary metabolites from a mangrove-derived fungus Penicillium sp. JY246[J]. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 39(2): 11-18 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
高亚欣, 王昊, 戴好富, 等, 2023. 西沙短指软珊瑚Sinularia flexibilis中具有肿瘤细胞毒活性的甾体化合物[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(5): 56-63.
|
|
GAO YAXIN, WANG HAO, DAI HAOFU, et al, 2023. Cytotoxic steroids from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis collected off the Xisha[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 42(5): 56-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
胡晓峰, 柴海全, 贾林川, 等, 2021. 一株太子参内生真菌Aspergillus terreus TZS-201607中抗肿瘤活性代谢产物研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 33(7): 1156-1164.
|
|
HU XIAOFENG, CHAI HAIQUAN, JIA LINCHUAN, et al, 2021. Antitumor secondary metabolites of an endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus TZS-201607 from Pseudostellaria heterophylla[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 33(7): 1156-1164 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
李海生, 欧阳美霞, 曾婷, 等, 2019. 广州南沙大角山海滨公园红树林植物资源研究[J]. 广东第二师范学院学报, 39(5): 43-47.
|
|
LI HAISHENG, OUYANG MEIXIA, ZENG TING, et al, 2019. The research on the mangrove resources in Dajiaoshan seaside park, Nansha, Guangzhou[J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Education, 39(5): 43-47 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
李元跃, 刘韶松, 高苏蕊, 等, 2021. 红树植物老鼠簕的化学成分和药理活性研究进展[J]. 集美大学学报(自然科学版), 26(6): 489-500.
|
|
LI YUANYUE, LIU SHAOSONG, GAO SURUI, et al, 2021. Progress in the research on the chemical constituents and Pharmacologic activities of mangrove plants of Acanthus ilicifolius[J]. Journal of Jimei University (Natural Science), 26(6): 489-500 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
梁寒峭, 陈文凤, 范益铠, 等, 2023. 红树林来源曲霉属和木霉属内生真菌次生代谢产物及活性研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(4): 12-24.
|
|
LIANG HANQIAO, CHEN WENFENG, FAN YIKAI, et al, 2023. Research progress on the secondary metabolites and activities of endophytic fungi of genus Aspergillus and Trichoderma from mangroves[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 42(4): 12-24 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
刘镜法, 2005. 北仑河口国家级自然保护区的老鼠簕群落[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 22(1): 41-43.
|
|
LIU JINGFA, 2005. Mouse community of the national nature reserve in the mouth of Beilong River[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 22(1): 41-43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
马新玥, 方圣涛, 赵业, 等, 2018. 海洋沉积物来源草酸青霉T4-6化学成分及其生物活性研究[J]. 化学与生物工程, 35(1): 17-22.
|
|
MA XINYUE, FANG SHENGTAO, ZHAO YE, et al, 2018. Chemical constituents of marine sediment-derived fungus Penicillium oxalicum T4-6 and their biological activities[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 35(1): 17-22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
谭玉莹, 曹广萍, 黄炯丽, 等, 2022. 红树老鼠簕来源内生青霉Penicillium sp. GXIMD 03101的次级代谢产物研究[J]. 广西科学, 29(5): 839-845.
|
|
TAN YUYING, CAO GUANGPING, HUANG JIONGLI, et al, 2022. Studies on secondary metabolites of endophytic fungus Penicillium sp. GXIMD 03101 from mangrove Acanthus ilicifolius L.[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 29(5): 839-845 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
解双双, 吴野, 张娜, 等, 2019. 青灰叶下珠内生菌Phomopsis sp. TJ507A的化学成分及生物活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 31(1): 61-68.
|
|
XIE SHUANGSHAUNG, WU YE, ZHANG NA, et al, 2019. The bioactive secondary metabolites from Phyllanthus glaucus-associated fungus Phomopsis sp. TJ507A[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 31(1): 61-68 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
AMAGATA T, TANAKA M, YAMADA T, et al, 2007. Variation in cytostatic constituents of a sponge-derived Gymnascella dankaliensis by manipulating the carbon source[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 70(11): 1731-1740.
|
| [12] |
BAI MENG, ZHENG CAIJUAN, TANG DEQING, et al, 2019. Two new secondary metabolites from a mangrove-derived fungus Cladosporium sp. JS1-2[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 72(10): 779-782.
|
| [13] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2020. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 37(2): 175-223.
doi: 10.1039/c9np00069k
pmid: 32025684
|
| [14] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2021. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 38(2): 362-413.
doi: 10.1039/d0np00089b
pmid: 33570537
|
| [15] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2022. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 39(6): 1122-1171.
|
| [16] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2023. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 40(2): 275-325.
doi: 10.1039/d2np00083k
pmid: 36786022
|
| [17] |
CHEN LEI, CHAI WEIYUN, WANG WENLING, et al, 2017. Cytotoxic bagremycins from mangrove-derived Streptomyces sp. Q22[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 80(5): 1450-1456.
|
| [18] |
CHEN SENHUA, CAI RUNLIN, LIU ZHAOMING, et al, 2022. Secondary metabolites from mangrove-associated fungi: source, chemistry and bioactivities[J]. Natural Product Reports, 39(3): 560-595.
|
| [19] |
DUPERRON S, BENIDDIR M A, DURAND S, et al, 2019. New benthic cyanobacteria from Guadeloupe mangroves as producers of antimicrobials[J]. Marine Drugs, 18(1): 16.
|
| [20] |
FUJIMOTO H, NAKAMURA E, OKUYAMA E, et al, 2004. Six immunosuppressive features from an ascomycete, Zopfiella longicaudata, found in a screening study monitored by immunomodulatory activity[J]. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 52(8): 1005-1008.
|
| [21] |
LIAO HAIXIA, SHAO TAIMING, MEI RONGQING, et al, 2019. Bioactive secondary metabolites from the culture of the mangrove-derived fungus Daldinia eschscholtzii HJ004[J]. Marine Drugs, 17(12): 710.
|
| [22] |
PIERCE C G, UPPULURI P, TRISTAN A R, et al, 2008. A simple and reproducible 96-well plate-based method for the formation of fungal biofilms and its application to antifungal susceptibility testing[J]. Nature Protocols, 3(9): 1494-1500.
doi: 10.1038/nport.2008.141
pmid: 18772877
|
| [23] |
UGAKI N, YAMAZAKI H, UCHIDA R, et al, 2012. New isochaetochromin, an inhibitor of triacylglycerol synthesis in mammalian cells, produced by Penicillium sp. FKI-4942: Ⅱ. Structure elucidation[J]. The Journal of Antibiotics, 65(1): 21-24.
|
| [24] |
WANG GUOKAI, LI YUAN, LIU HAITAO, et al, 2021. Aspergilfuranones A-D, four norlignanolides from the peucedanum praeruptorum endophytic fungus Aspergillus udagawae[J]. Tetrahedron, 82: 131951.
|
| [25] |
XU GUOBO, YANG TAO, BAO JINKU, et al, 2014. Isochaetomium A2, a new bis(naphthodihydropyran-4-one) with antimicrobial and immunological activities from fungus Chaetomium microcephalum[J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 37(5): 575-579.
|
| [26] |
ZHAO ZHENZHU, HAN KAIYUE, LI ZHENGHUI, et al, 2019. Cytotoxic ergosteroids from the fungus Stereum hirsutum[J]. Phytochemistry Letters, 30: 143-149.
|
| [27] |
ZHANG YING, LIU JINZHAO, GUO ZIXIAN, et al, 2021. Chemical constituents from Urtica fissa stem and their inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase activity[J]. Natural Product Research, 35(18): 3011-3017.
|
 ), 姜悦1,2, 王宇1,2, 曹广萍1,2, 高程海1,2, 刘永宏1,2, 易湘茜1,2(
), 姜悦1,2, 王宇1,2, 曹广萍1,2, 高程海1,2, 刘永宏1,2, 易湘茜1,2( ), 白猛1,2(
), 白猛1,2( )
)
 ), JIANG Yue1,2, WANG Yu1,2, CAO Guangping1,2, GAO Chenghai1,2, LIU Yonghong1,2, YI Xiangxi1,2(
), JIANG Yue1,2, WANG Yu1,2, CAO Guangping1,2, GAO Chenghai1,2, LIU Yonghong1,2, YI Xiangxi1,2( ), BAI Meng1,2(
), BAI Meng1,2( )
)