热带海洋学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 32-42.doi: 10.11978/2018101CSTR: 32234.14.2018101
基于遥感反演的珠江河口表层悬沙浓度分位数趋势分析 *
- 1. 热带海洋环境国家重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
2. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2018-10-09修回日期:2018-11-06出版日期:2019-05-20发布日期:2019-06-17 -
通讯作者:詹海刚 -
作者简介:詹伟康(1991—), 男, 广东省潮州市人, 博士研究生, 主要从事河口悬沙遥感研究。E-mail:zhanweikang13@mails.ucas.ac.cn -
基金资助:广州市科技项目(201607020042);热带海洋环境国家重点实验室自主研究项目(LTOZZ1503)
Quantile trend analysis for suspended sediment concentration in the Pearl River Estuary based on remote sensing
Weikang ZHAN1,2,Jie WU1,2,Xing WEI1,Shilin TANG1,Haigang ZHAN1( )
)
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2018-10-09Revised:2018-11-06Online:2019-05-20Published:2019-06-17 -
Contact:Haigang ZHAN -
Supported by:Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China(201607020042);Self-research Program of the State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography(LTOZZ1503)
摘要:
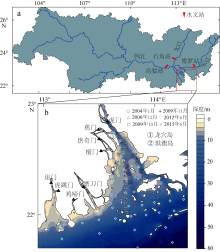
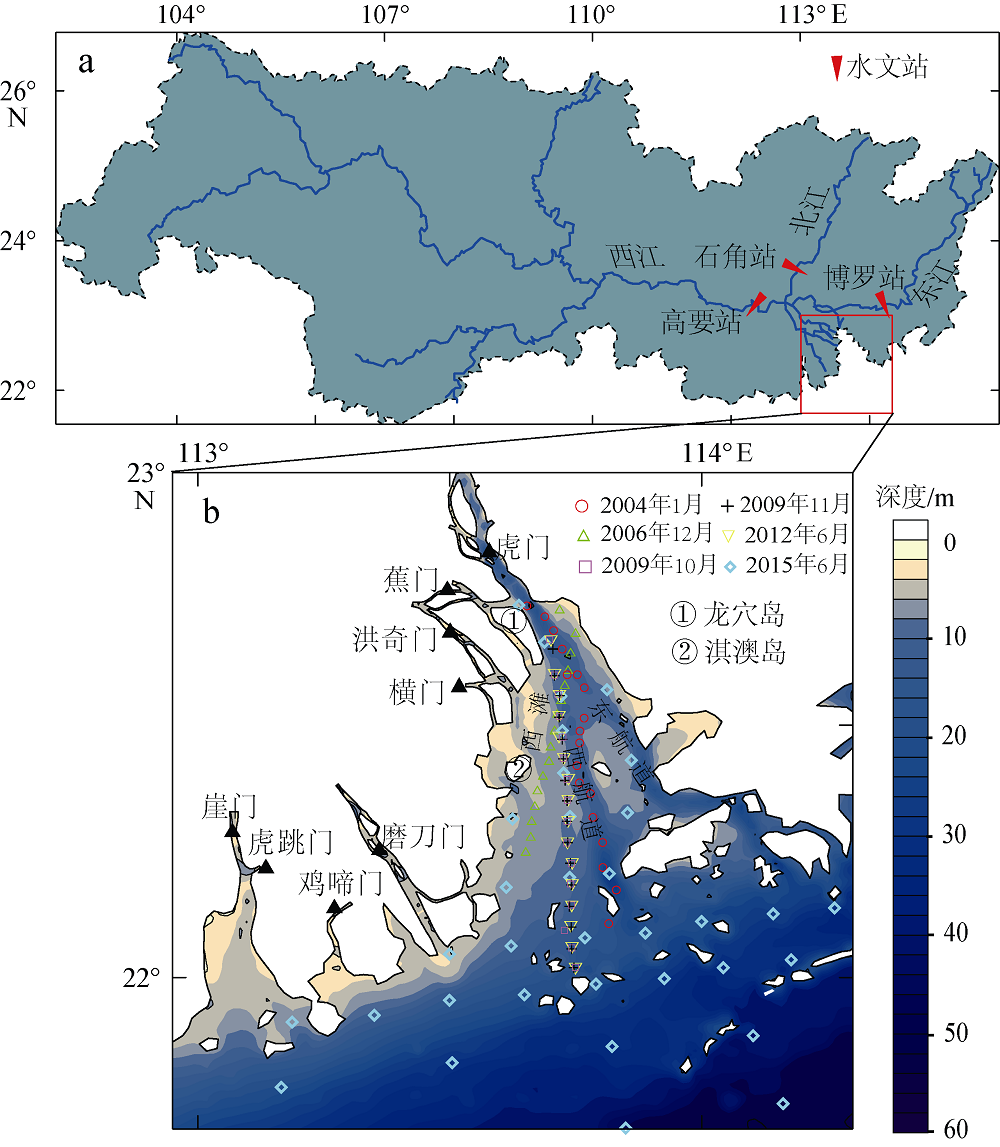
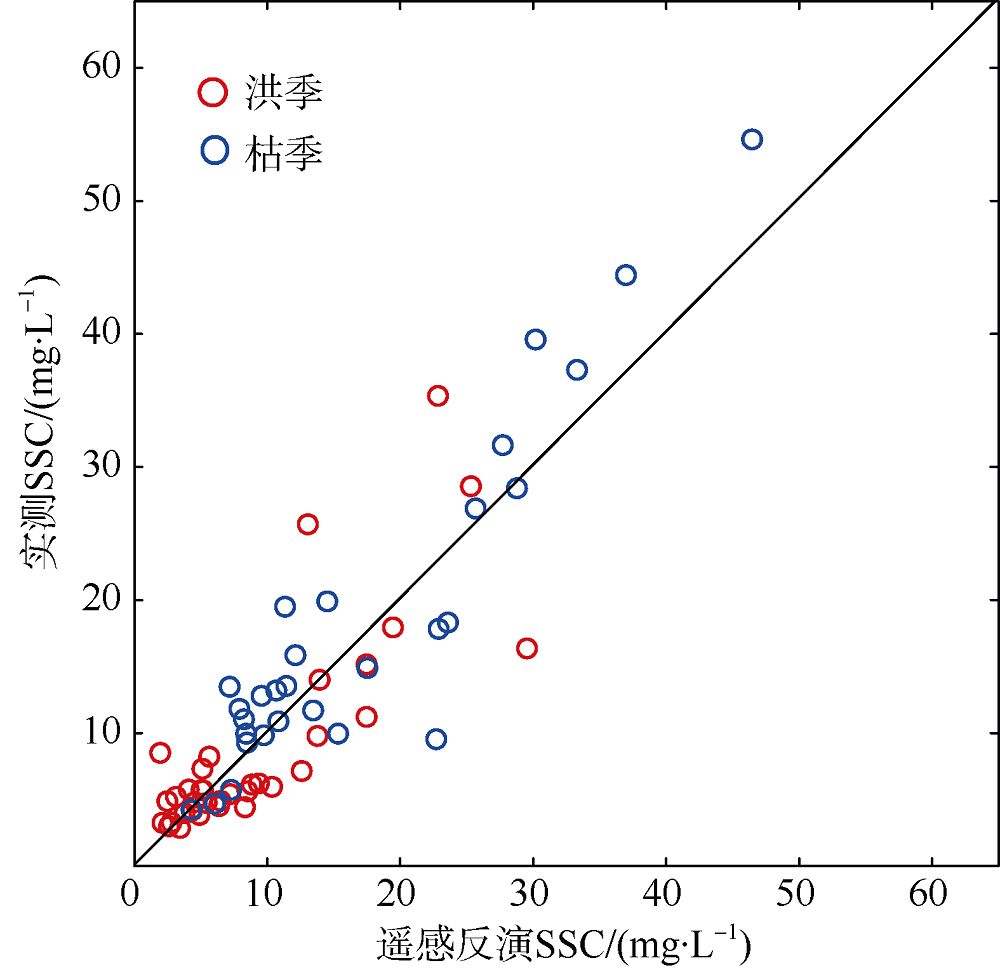
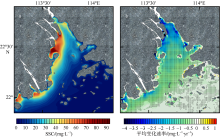
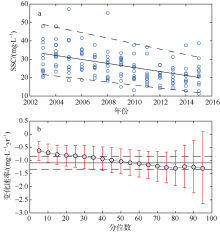
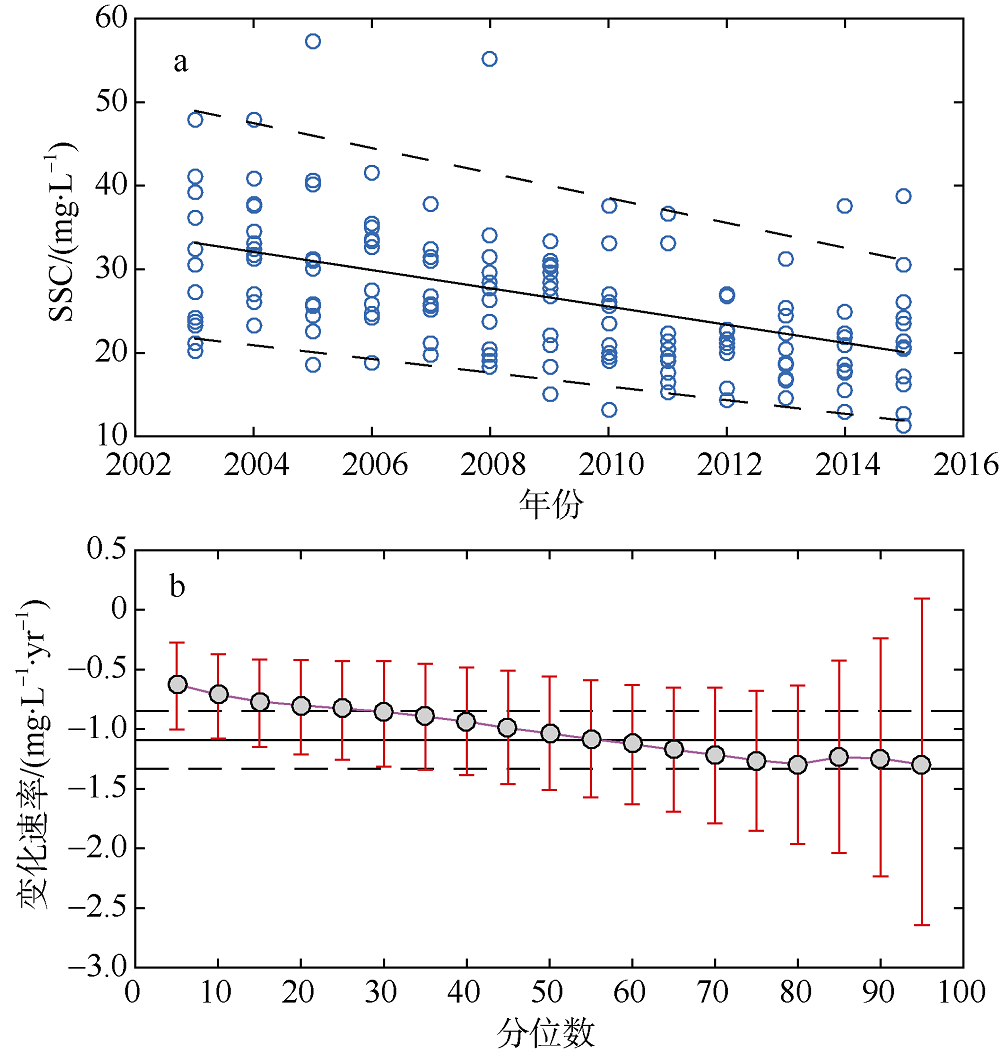
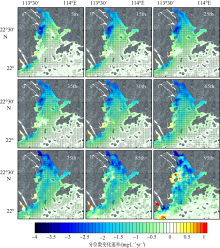
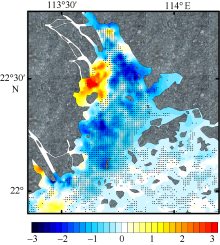
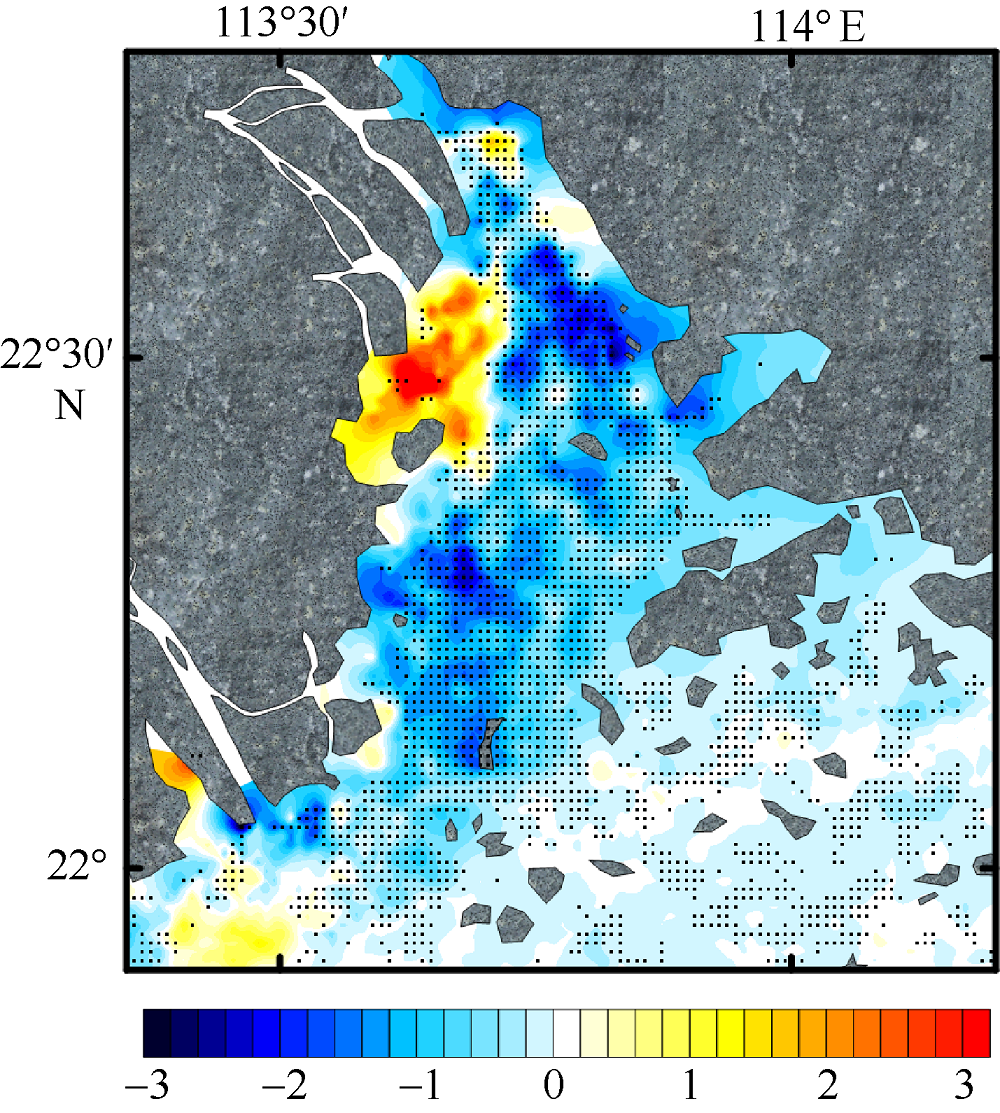
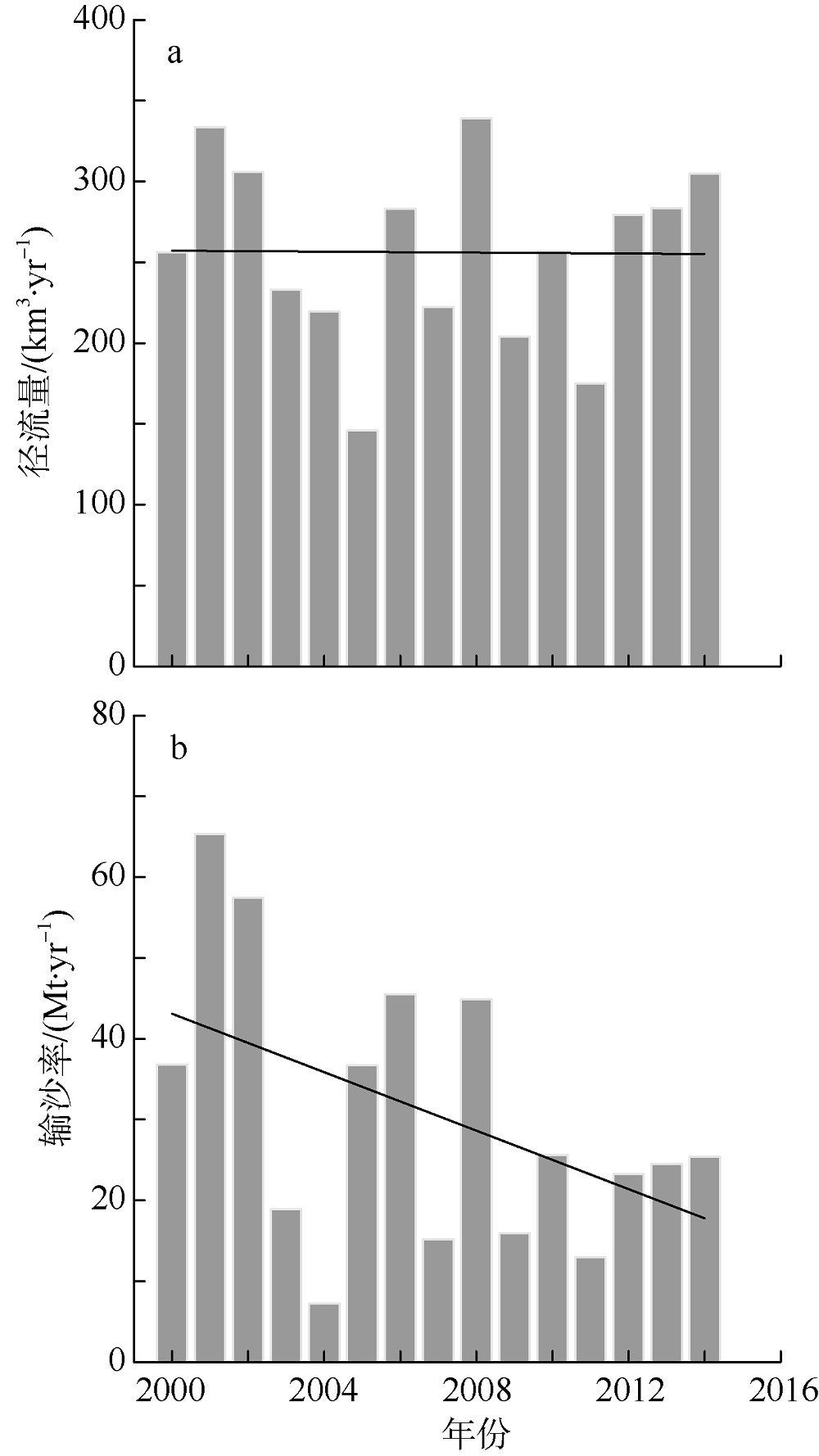
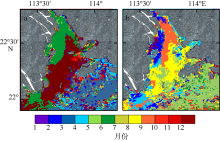
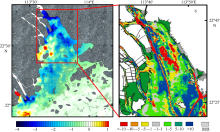
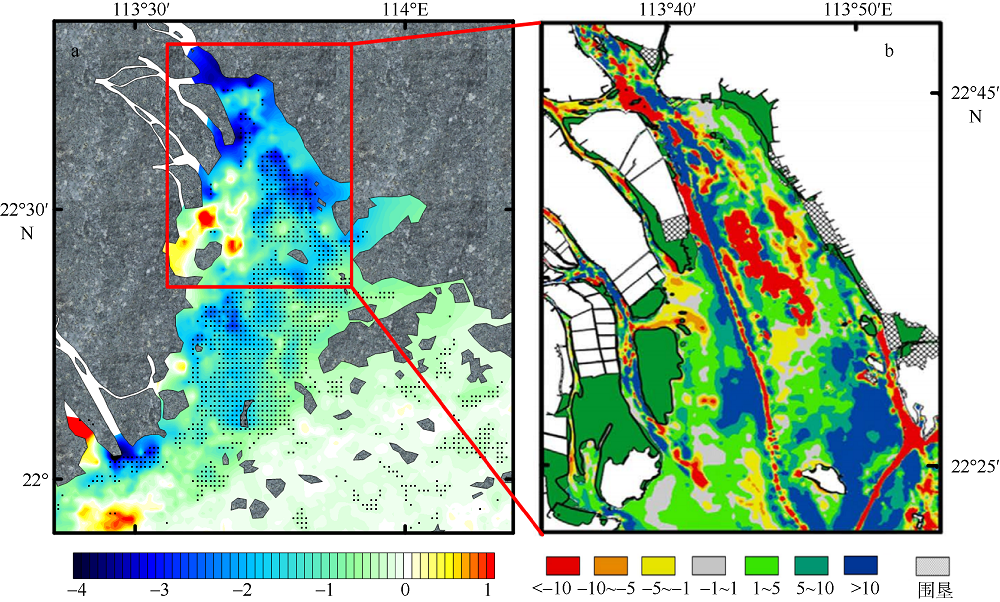
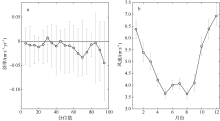
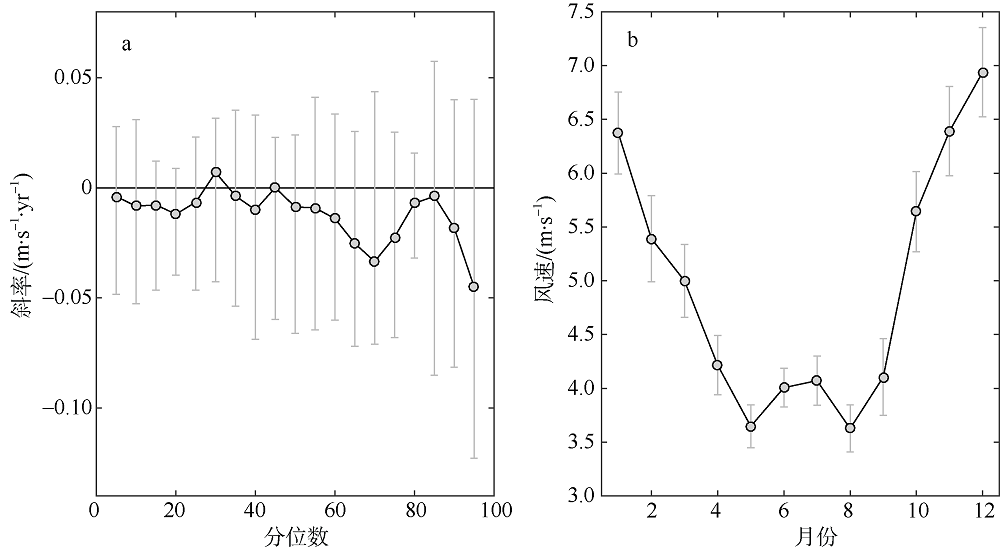
利用中分辨率成像光谱仪(moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer, MODIS)一级产品并结合航次数据, 反演2003—2015年间珠江河口表层悬浮泥沙浓度(suspended sediment concentration, SSC), 分析其分位数长期变化趋势并探讨其影响因素。结果表明, 珠江河口SSC呈总体下降趋势, 平均下降速率约为1.03mg·L -1·yr -1。口门外以及河口东北部区域平均SSC下降更快, 最高可达约4.0mg·L -1·yr -1。总体上, 珠江河口SSC高值下降速率大于低值, 且存在空间差异性。低值下降趋势显著地区主要分布在淇澳岛北部的口门外区域, 其SSC大小值之间的差异逐年增加; 而高值下降速率快的地区主要分布在虎门口、龙穴岛东南岸以及东航道附近水域, SSC每年大小值差异呈减小趋势。珠江河口SSC分位数趋势受径流输沙量、河口地形变化以及风的影响。由水库修建所致的上游输沙量减少导致淇澳岛北部口门外区域SSC的低值部分显著下降。虎门口、龙穴岛东南岸以及东航道附近水域的加深使得这些区域SSC高值部分下降显著, 而西滩区域的变浅使得冬季潮汐混合减弱, 导致SSC高值部分下降趋势显著。此外, 由风速下降引起的表层风混合减弱也是导致西滩南部SSC高值下降趋势显著的原因之一。
中图分类号:
- P333.4
引用本文
詹伟康,吴颉,韦惺,唐世林,詹海刚. 基于遥感反演的珠江河口表层悬沙浓度分位数趋势分析 *[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(3): 32-42.
Weikang ZHAN,Jie WU,Xing WEI,Shilin TANG,Haigang ZHAN. Quantile trend analysis for suspended sediment concentration in the Pearl River Estuary based on remote sensing[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 32-42.
| [1] | 何为 , 2001. 珠江口泥沙特点与控制因素[J]. 中山大学研究生学刊(自然科学), 22(1):84-89. |
| HE WEI , 2001. Characteristics and controlled factors of suspended sand in Pearl River estuary[J]. Journal of the Graduates Sun Yat-Sen University (Natural Sciences), 22(1):84-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 季荣耀, 陆永军, 王志力 , 等, 2015. 河口治理开发对伶仃洋滩槽演变影响分析[C]// 第十七届中国海洋(岸)工程学术讨论会论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社: 987-990. |
| [3] |
刘大召, 陈楚群, 刘汾汾 , 等, 2009. 利用混合光谱分解估测珠江口悬浮泥沙浓度[J]. 热带海洋学报, 28(5):43-48.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.05.007 |
|
LIU DAZHAO, CHEN CHUQUN, LIU FENFEN , et al, 2009. Estimation of suspended sediment concentration at Zhujiang River Mouth based on decomposition of mixing spectrum[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 28(5):43-48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.05.007 |
|
| [4] |
刘汾汾, 陈楚群, 唐世林 , 等, 2009. 基于现场光谱数据的珠江口MERIS悬浮泥沙分段算法[J]. 热带海洋学报, 28(1):9-14.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.01.002 |
|
LIU FENFEN, CHEN CHUQUN, TANG SHILIN , et al, 2009. A piecewise algorithm for retrieval of suspended sediment concentration based on in situ spectral data by MERIS in Zhujiang River estuary[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 28(1):9-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.01.002 |
|
| [5] | 栾虹, 付东洋, 李明杰 , 等, 2017. 基于Landsat 8珠江口悬浮泥沙四季遥感反演与分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 36(6):892-897. |
| LUAN HONG, FU DONGYANG, LI MINGJIE , et al, 2017. Based on Landsat 8 suspended sediment concentration of the Pearl River on each season inversion and analysis[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 36(6):892-897 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 倪培桐, 吴超羽, 陈卓英 , 2000. 应用数值模拟方法探讨河口最大浑浊带若干机理[J]. 热带海洋学报, 19(2):27-32. |
| NI PEITONG, WU CHAOYU, CHEN ZHUOYING , 2000. A discussion on some mechanisms of estuarine turbidity maximum zone by numerical models[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 19(2):27-32 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 倪培桐, 闻平, 刘剑宇 , 2016. 珠江三角洲水沙年际变化趋势分析[J]. 人民珠江, 37(1):19-24. |
| NI PEITONG, WEN PING, LIU JIANYU , 2016. Study on variation of annual water discharge and sediment load in Pearl River delta[J]. Pearl River, 37(1):19-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 唐兆民, 何志刚, 任杰 , 等, 2005. 珠江口虎门悬浮泥沙浓度的测量[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 44(4):124-128. |
| TANG ZHAOMIN, HE ZHIGANG, REN JIE , et al, 2005. Measurement on suspended sediment concentration at Humen Estuary of the Pearl River[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 44(4):124-128 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 田向平 , 1986. 珠江河口伶仃洋最大混浊带研究[J]. 热带海洋, 5(2):27-35. |
| TIAN XIANGPING , 1986. A study on turbidity maximum in Lingdingyang Estuary of the Pearl River[J]. Tropical Oceanology, 5(2):27-35 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 吴创收, 杨世伦, 黄世昌 , 等, 2014. 1954-2011年间珠江入海水沙通量变化的多尺度分析[J]. 地理学报, 69(3):422-432. |
| WU CHUANGSHOU, YANG SHILUN, HUANG SHICHANG , et al, 2014. Multi-scale variability of water discharge and sediment load in the Pearl River during 1954-2011[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 69(3):422-432 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 禹定峰, 邢前国, 陈楚群 , 等, 2010. 利用导数光谱估算珠江河口水体悬浮泥沙浓度[J]. 生态科学, 29(6):563-567. |
| YU DINGFENG, XING QIANGUO, CHEN CHUQUN , et al, 2010. Using derivative spectrum to estimate suspended sediment concentration of estuarine waters[J]. Ecological Science, 29(6):563-567 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 朱樊, 欧素英, 张铄涵 , 等, 2015. 基于MODIS影像的珠江口表层悬沙浓度反演及时空变化分析[J]. 泥沙研究, ( 2):67-73. |
| ZHU FAN, OU SUYING, ZHANG SHUOHAN , et al, 2015. MODIS images-based retrieval and analysis of spatial-temporal change of superficial suspended sediment concentration in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, ( 2):67-73 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | BAILEY S, WANG M H, 2001. Satellite aerosol optical thickness match-up procedures [C]//FARGION G S, BARNES R, MCCLAIN C. In situ aerosol optical thickness collected by the SIMBIOS program (1997-2000): protocols, and data QC and analysis. NASA technical memorandum 2001-209982. Greenbelt: Goddard Space Flight Center: 70-72. |
| [14] |
BARBOSA S M , 2008. Quantile trends in Baltic sea level[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(22):L22704.
doi: 10.1029/2008GL035182 |
| [15] |
BILOTTA G S, BRAZIER R E , 2008. Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota[J]. Water Research, 42(12):2849-2861.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.03.018 |
| [16] |
DOGLIOTTI A I, RUDDICK K, GUERRERO R , 2016. Seasonal and inter-annual turbidity variability in the Río de la Plata from 15 years of MODIS: El Niño dilution effect[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 182:27-39.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.09.013 |
| [17] |
DYER K R, CHRISTIE M C, FEATES N , et al, 2000. An investigation into processes influencing the Morphodynamics of an intertidal mudflat, the Dollard estuary, the Netherlands: I. hydrodynamics and suspended sediment[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 50(5):607-625.
doi: 10.1006/ecss.1999.0596 |
| [18] |
ELIAS E P L, VAN DER SPEK A J F, WANG Z B , et al, 2012. Morphodynamic development and sediment budget of the Dutch Wadden Sea over the last century[J]. Netherlands Journal of Geosciences, 91(3):293-310.
doi: 10.1017/S0016774600000457 |
| [19] |
FITZENBERGER B, HUJER R, MACURDY T E , et al, 2001. Testing for uniform wage trends in West-Germany: A cohort analysis using quantile regressions for censored data[J]. Empirical Economics, 26(1):41-86.
doi: 10.1007/s001810000048 |
| [20] |
FRANZKE C L E , 2015. Local trend disparities of European minimum and maximum temperature extremes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 42(15):6479-6484.
doi: 10.1002/2015GL065011 |
| [21] |
HE QUANJUN, CHEN CHUQUN , 2014. A new approach for atmospheric correction of MODIS imagery in turbid coastal waters: a case study for the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 5(3):249-257.
doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2014.898192 |
| [22] |
LI MING, ZHONG LIEJUN, BOICOURT W C , et al, 2007. Hurricane-induced destratification and restratification in a partially-mixed estuary[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 65(2):169-192.
doi: 10.1357/002224007780882550 |
| [23] |
LI XUEJIE, DAMEN M C J , 2010. Coastline change detection with satellite remote sensing for environmental management of the Pearl River Estuary, China[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 82 Suppl: S54-S61.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.02.005 |
| [24] | LIU RUNQI, WANG YAPING, GAO JIANHUA , et al, 2016. Turbidity maximum formation and its seasonal variations in the Zhujiang (Pearl River) Estuary, southern China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(8):22-31. |
| [25] |
MOREIRA D, SIMIONATO C G, GOHIN F , et al, 2013. Suspended matter mean distribution and seasonal cycle in the Río de La Plata estuary and the adjacent shelf from ocean color satellite (MODIS) and in-situ observations[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 68:51-66.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.08.015 |
| [26] |
PARTAL T, KAHYA E , 2006. Trend analysis in Turkish precipitation data[J]. Hydrological Processes, 20(9):2011-2026.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1085 |
| [27] |
PETUS C, MARIEU V, NOVOA S , et al, 2014. Monitoring spatio-temporal variability of the Adour River turbid plume (Bay of Biscay, France) with MODIS 250-m imagery[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 74:35-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.11.011 |
| [28] |
RHINES A, MCKINNON K A, TINGLEY M P , et al, 2017. Seasonally resolved distributional trends of North American temperatures show contraction of winter variability[J]. Journal of Climate, 30(3):1139-1157.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0363.1 |
| [29] | RUFF T W, NEELIN J D , 2012. Long tails in regional surface temperature probability distributions with implications for extremes under global warming[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(4):L04704. |
| [30] |
SCULLY M E, FRIEDRICHS C, BRUBAKER J , 2005. Control of estuarine stratification and mixing by wind-induced straining of the estuarine density field[J]. Estuaries, 28(3):321-326.
doi: 10.1007/BF02693915 |
| [31] |
SEN P K , 1968. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall's Tau[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 63(324):1379-1389.
doi: 10.1080/01621459.1968.10480934 |
| [32] |
SHI ZHEN, XU JIE, HUANG XIAOPING , et al, 2017. Relationship between nutrients and plankton biomass in the turbidity maximum zone of the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 57:72-84.
doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.11.013 |
| [33] |
TABARI H, MAROFI S, AEINI A , et al, 2011. Trend analysis of reference evapotranspiration in the western half of Iran[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 151(2):128-136.
doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.09.009 |
| [34] |
VAN MAREN D S, VAN KESSEL T, CRONIN K , et al, 2015. The impact of channel deepening and dredging on estuarine sediment concentration[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 95:1-14.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.12.010 |
| [35] |
VAN MAREN D S, OOST A P, WANG Z B , et al, 2016. The effect of land reclamations and sediment extraction on the suspended sediment concentration in the Ems Estuary[J]. Marine Geology, 376:147-157.
doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.03.007 |
| [36] |
WANG CHONGYANG, LI WEIJIAO, CHEN SHUISEN , et al, 2018. The spatial and temporal variation of total suspended solid concentration in Pearl River Estuary during 1987-2015 based on remote sensing[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 618:1125-1138.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.196 |
| [37] |
WANG HONGQING, HLADIK C M, HUANG WENRUI , et al, 2010. Detecting the spatial and temporal variability of chlorophyll-a concentration and total suspended solids in Apalachicola Bay, Florida using MODIS imagery[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 31(2):439-453.
doi: 10.1080/01431160902893485 |
| [38] |
WANG HOUJIE, YANG ZUOSHENG, SAITO Y , et al, 2007. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950-2005): Impacts of climate change and human activities[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 57(3-4):331-354.
doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.01.003 |
| [39] |
WANG MENGHUA, GORDON H R , 1994. A simple, moderately accurate, atmospheric correction algorithm for SeaWiFS[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 50(3):231-239.
doi: 10.1016/0034-4257(94)90073-6 |
| [40] | WANG SHUAI, FU BOJIE, PIAO SHILONG , et al, 2016. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes[J]. Nature Geoscience, 9(1):38-41. |
| [41] |
WONG L A, CHEN J C, XUE H , et al, 2003. A model study of the circulation in the Pearl River Estuary (PRE) and its adjacent coastal waters: 1. Simulations and comparison with observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 108(C5):3156.
doi: 10.1029/2002JC001451 |
| [42] |
WU C S, YANG S L, LEI YAPING , 2012. Quantifying the anthropogenic and climatic impacts on water discharge and sediment load in the Pearl River (Zhujiang), China (1954-2009)[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 452-453:190-204.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.05.064 |
| [43] |
WU Z Y, SAITO Y, ZHAO D N , et al, 2016. Impact of human activities on subaqueous topographic change in Lingding Bay of the Pearl River estuary, China, during 1955-2013[J]. Scientific Reports, 6:37742.
doi: 10.1038/srep37742 |
| [44] | XU KEHUI, MILLIMAN J D, YANG ZUOSHENG , et al, 2006. Yangtze sediment decline partly from Three Gorges Dam[J]. Eos Transactions American Geophysical Union, 87(19):185-190. |
| [45] |
YANG S L, ZHANG J, ZHU J , et al, 2005. Impact of dams on Yangtze River sediment supply to the sea and delta intertidal wetland response[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 110(E3):F03006.
doi: 10.1029/2004JF000271 |
| [46] | YE HAIBIN, CHEN CHUQUN, TANG SHILIN , et al, 2014. Remote sensing assessment of sediment variation in the Pearl River Estuary induced by Typhoon Vicente[J]. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 17(3):271-279. |
| [47] |
YUE S, HASHINO M , 2003. Temperature trends in Japan: 1900-1996[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 75(1-2):15-27.
doi: 10.1007/s00704-002-0717-1 |
| [48] |
ZHANG WEI, MU SHOUSHENG, ZHANG YANJING , et al, 2011. Temporal variation of suspended sediment load in the Pearl River due to human activities[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 26(4):487-497.
doi: 10.1016/S1001-6279(12)60007-9 |
| [49] |
ZHANG XINFENG, TANG DANLING, LI ZIZHEN , et al, 2009. The effects of wind and rainfall on suspended sediment concentration related to the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(9):1367-1373.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.04.023 pmid: 19476959 |
| [1] | 王钰, 胡晨悦, 丘仲锋, 赵冬至, 吴到懋, 廖廓. 基于云特性的多源卫星日间海雾探测技术研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 15-28. |
| [2] | 李为华, 李九发, 张文祥. 水体悬沙浓度连续测量技术研究综述[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 20-30. |
| [3] | 黄祖明, 周晓妍, 戴志军, 车志伟. 桐花树红树林潮滩近底层悬沙浓度垂向剖面变化特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 38-50. |
| [4] | 曾滇婷, 李君益, 谢玲玲, 叶小敏, 周达. 伶仃洋夏季叶绿素a时间变化特征及分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 16-25. |
| [5] | 蓝璇, 利锋, 张超, 董汉英, 杨清书, 余明辉, 文汝兵, 杨玉洁. 基于SOM模型的珠江河口河网铊生态风险评估[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 132-142. |
| [6] | 杨威, 董园, 俎婷婷, 刘长建, 修鹏. 南海北部夏季叶绿素a分布规律及影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(6): 9-20. |
| [7] | 欧素英. 华南不同类型热带风暴驱动下珠江口表层悬沙分布趋势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(3): 22-31. |
| [8] | 尹小青, 杨顶田, 周立柱. 黄、东海边界悬浮物输运量的卫星遥感估算[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(2): 10-16. |
| [9] | 郭甜甜, 陈圣波, 陆天启. 基于MODIS数据的多时相海表温度反演——以海南岛西南部近海海域为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(1): 9-14. |
| [10] | 裴木凤, 李适宇, 胡嘉镗, 胡希声. 丰、枯水期珠江河口水体交换的数值模拟[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(6): 28-35. |
| [11] | 王彪, 朱建荣. 基于FVCOM模型的珠江河口及其邻近海域的潮汐模拟*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(4): 17-27. |
| [12] | 姚月,许惠平. 福建围填海及其对海洋环境影响的遥感初探 [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(1): 72-78. |
| [13] | 肖志建,李团结,廖世智 . 伶仃洋表层沉积物特征及其泥沙运移趋势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(4): 58-65. |
| [14] | 刘欢 ,吴超羽 ,包芸 . 珠江河口的能量传播和能量耗散[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(3): 16-23. |
| [15] | 李开枝,黄良民,张建林,尹健强,罗琳. 珠江河口咸潮期间浮游植物的群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(1): 62-68. |
|
||