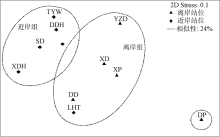
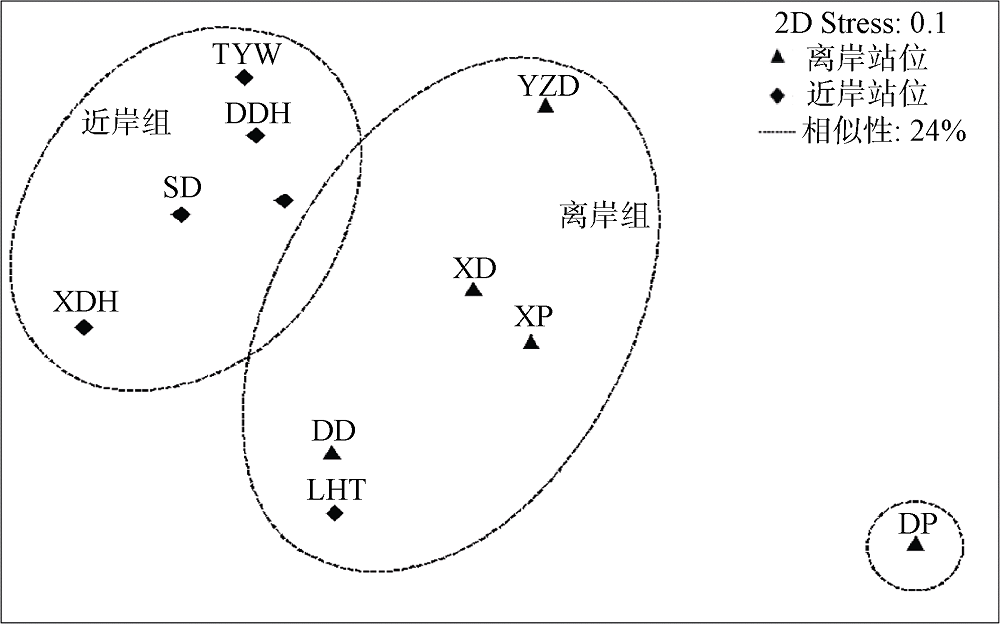
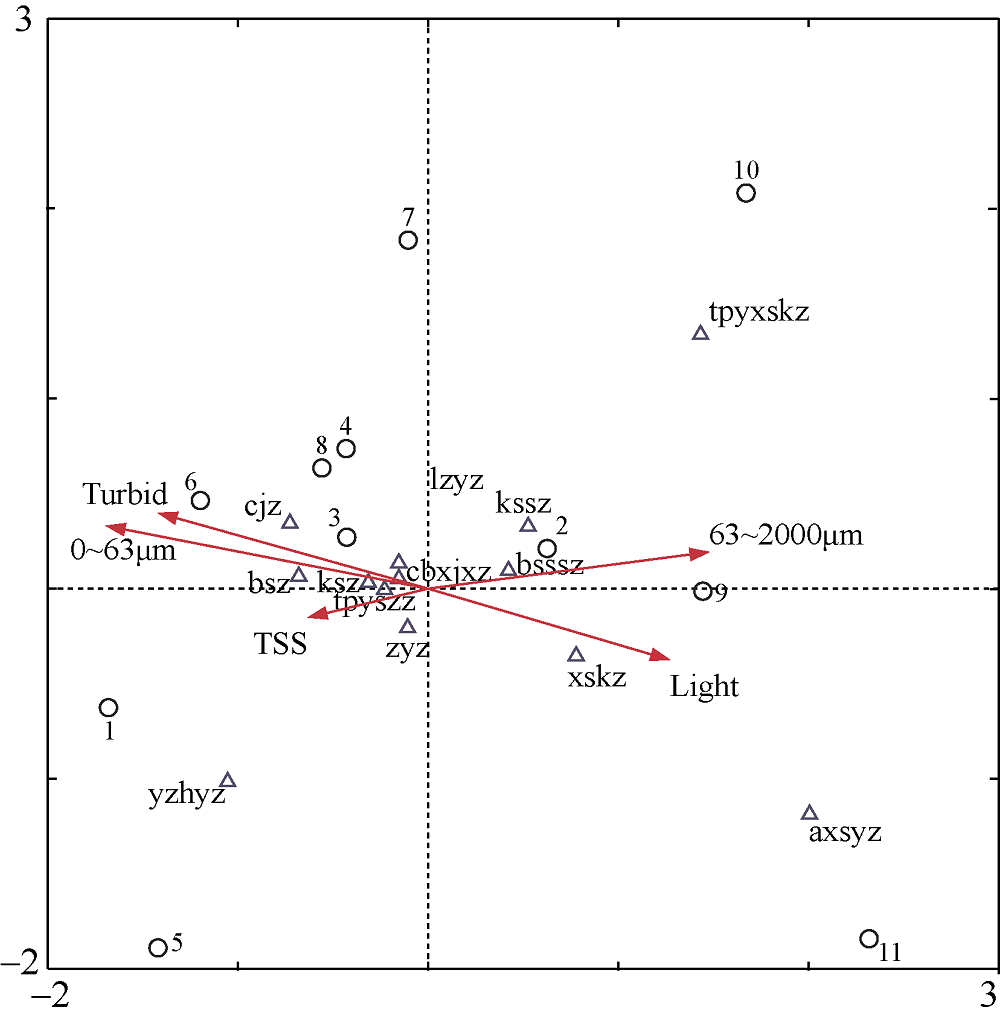
| [1] |
李秀保 , 2011. 三亚造礁石珊瑚群落组成、时空分布及主要影响因子识别研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院: 1-115.
|
|
LI XIUBAO . 2011. Identification of major factors influencing the composition, spatial and temporal variation of scleractinian coral community in Sanya China[D]. Beijing: Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: 1-115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
练健生, 黄晖, 黄良民 , 等, 2010. 三亚珊瑚礁及其生物多样性[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-106.
|
|
LIAN JIANSHENG, HUANG HUI, HUANG LIANGMIN , et al, 2010. Coral reef and its biodiversity of Sanya[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press: 1-106(in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
邢帅, 谭烨辉, 周林滨 , 等, 2012. 水体浑浊度对不同造礁石珊瑚种类共生虫黄藻的影响[J]. 科学通报, 57(5):348-354.
doi: 10.1360/972011-1184
|
|
XING SHUAI, TAN YEHUI, ZHOU LINBIN , et al, 2012. Effects of water turbidity on the symbiotic zooxanthella of hermatypic corals[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(5):348-354 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.1360/972011-1184
|
| [4] |
徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿 , 1989. 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 8(4):13-15.
|
|
Xu ZHAOLI, CHEN YAQU , 1989. Aggregated intensity of dominant species of Zooplankton in Autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Ecology, 8(4):13-15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
张德瑞, 周锦华 , 1978. 西沙群岛珊瑚藻科的研究Ⅰ[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 12:17-23.
|
|
ZHANG DERUI, ZHOU JINHUA , 1978. Studies on the Corallinaceae of the Xisha islands, Guangdong Province, China. Ⅰ[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 12:17-23 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
ADEY W H, TOWNSEND R A, BOYKINS W T , 1982. The crustose coralline algae (Rhodophyta: Corallinaceae) of the Hawaiian Islands[M]. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press: 1-74.
|
| [7] |
ANTHONY K R N, KLINE D I, DIAZ-PULIDO G , et al, 2008. Ocean acidification causes bleaching and productivity loss in coral reef builders[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(45):17442-17446.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804478105
|
| [8] |
BARNES D J, CHALKER B E , 1990. Calcification and photosynbook in reef-building corals and algae[M] // DUBINSKY Z. Ecosystems of the world. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier.
|
| [9] |
BRAGA J C, BOSENCE D W J, STENECK R S , 1993. New anatomical characters in fossil coralline algae and their taxonomic implications[J]. Palaeontology, 36:535-547.
|
| [10] |
BRODIE J, ZUCCARELLO G C , 2007. Systematics of the species-rich algae: Red algal classification, phylogeny and speciation[M] //HODKINSON R T, PARNELL J, WALDREN S. The taxonomy and systematics of large and species-rich taxa: building and using the tree of life. Boca Raton: CRC Press: 323-336.
|
| [11] |
CARAGNANO A, COLOMBO F, RODONDI G , et al, 2009. 3-D distribution of nongeniculate corallinales: a case study from a reef crest of South Sinai (Red Sea, Egypt)[J]. Coral Reefs, 28(4):881-891.
doi: 10.1007/s00338-009-0524-6
|
| [12] |
CLARKE K R, GORLEY R N , 2006a. Primer V6: user manual/tutorial[M]. Plymouth: Primer-E :1-126.
|
| [13] |
CLARKE K R, WARWICK R M , 2006b. Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation[M]. Plymouth: PRIMER-E.
|
| [14] |
FABRICIUS K, DE’ATH G , 2001. Environmental factors associated with the spatial distribution of crustose coralline algae on the Great Barrier Reef[J]. Coral Reefs, 19(4):303-309.
doi: 10.1007/s003380000120
|
| [15] |
FARR T, BROOM J, HART D , et al, 2009. Common coralline algae of northern New Zealand: an identification guide[M]. Wellington: NIWA:1-125.
|
| [16] |
GARBARY D J, JOHANSEN H W , 1982. Scanning electron microscopy of Corallina and Haliptilon (Corallinaceae, Rhodophyta): surface features and their taxonomic implications[J]. Journal of Phycology, 18(2):211-219.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.1982.18.issue-2
|
| [17] |
HARVEY A S, WOELKERLING W J , 2007. A guide to nongeniculate coralline red algal (Corallinales, Rhodophyta) rhodolith identification[J]. Ciencias Marinas, 33(4):411-426.
doi: 10.7773/cm
|
| [18] |
HEYWARD A J, NEGRI A P , 1999. Natural inducers for coral larval metamorphosis[J]. Coral Reefs, 18(3):273-279.
doi: 10.1007/s003380050193
|
| [19] |
HUANG LIANGMIN, TAN YEHUI, SONG XINGYU , et al, 2003. The status of the ecological environment and a proposed protection strategy in Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 47(1-6):180-186.
doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00070-5
|
| [20] |
IRYU Y, MATSUDA S, 1988. Depth distribution, abundance and species assemblages of nonarticulated coralline algae in the Ryukyu Islands, southwestern Japan [C]//Proceedings of the 6th international coral reef symposium. Townsville, Sixth International Coral Reef Symposium Executive Committee, 3:101-106.
|
| [21] |
KLUMPP D W, MCKINNON A D , 1992. Community structure, biomass and productivity of epilithic algal communities on the great barrier reef: dynamics at different spatial scales[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 86:77-89.
doi: 10.3354/meps086077
|
| [22] |
KUFFNER I B, ANDERSSON A J, JOKIEL P L , et al, 2008. Decreased abundance of crustose coralline algae due to ocean acidification[J]. Nature Geoscience, 1(2):114-117.
|
| [23] |
LASKER H R, KIM K , 1996. Larval development and settlement behavior of the gorgonian coral Plexaura kuna (Lasker, Kim and Coffroth)[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 207(1-2):161-175.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(96)02625-1
|
| [24] |
LITTLER D S, LITTLER M M , 2003. South Pacific reef plants: a divers' guide to the plant life of South Pacific coral reefs[M]. Washington, D.C.: Offshore Graphics: 1-331.
|
| [25] |
LITTLER M M, LITTLER D S , 1984. Models of tropical reef biogenesis: the contribution of algae[M] //ROUND F E, CHAPMAN D J. Progress in phycological research. Amsterdam: Elsevier Biomedical Press, 3:323-364.
|
| [26] |
MAUDSLEY B , 1990. Defenders of the reef[J]. New Scientist, 126(1714):52-56.
|
| [27] |
MINTON D, CONKLIN E, COUCH C S , et al, 2011. Survey of the coral reefs of Pelekane Bay[R]. Honolulu: The Nature Conservancy: 1-69.
|
| [28] |
OLIVER R L, MITROVIC S M, REES C , 2010. Influence of salinity on light conditions and phytoplankton growth in a turbid river[J]. River Research and Applications, 26(7):894-903.
doi: 10.1002/rra.v26:7
|
| [29] |
STELLER D L, FOSTER M S . 1995. Environmental factors influencing distribution and morphology of rhodoliths in Bahía Concepción, B.C.S., México[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 194(2):201-212.
doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(95)00086-0
|
| [30] |
STENECK R S, TESTA V, 1997. Are calcareous algae important to reefs today or in the past? [C]// Proceedings of 8th International coral reef symposium. Panama: Balboa, 1:685-688.
|
| [31] |
SZMANT A M , 2001. Introduction to the special issue of Coral Reefs on “Coral Reef Algal Community Dynamics” - Why are coral reefs world-wide becoming overgrown by algae? ‘Algae, algae everywhere, and nowhere a bite to eat!’[J]. Coral Reefs, 19(4):299-302.
doi: 10.1007/s003380000130
|
| [32] |
TSENG C K , 1983. Common seaweeds of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-316.
|
| [33] |
VAN DER MEIJ S E T, SUHAR SONO, HOEKSEMA B W , 2010. Long-term changes in coral assemblages under natural and anthropogenic stress in Jakarta Bay (1920-2005)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60(9):1442-1454.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.05.011
|
| [34] |
VIDAL R, MENESES I, SMITH M , 2003. Molecular genetic identification of crustose representatives of the order Corallinales (Rhodophyta) in Chile[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 28(3):404-419.
doi: 10.1016/S1055-7903(03)00123-4
|
| [35] |
WALKER D I, ORMOND R F G , 1982. Coral Death from Sewage and Phosphate Pollution at Aqaba, Red Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 13(1):21-25.
doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(82)90492-1
|
| [36] |
WILLIAMS E A, CRAIGIE A, YEATES A , et al, 2008. Articulated coralline algae of the genus Amphiroa are highly effective natural inducers of settlement in the tropical abalone Haliotis asinina[J]. Biological Bulletin, 215(1):98-107.
doi: 10.2307/25470687
|
| [37] |
WILSON S, BLAKE C, BERGES J A , et al, 2004. Environmental tolerances of free-living coralline algae (maerl): implications for European marine conservation[J]. Biological Conservation, 120(2):279-289.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2004.03.001
|
| [38] |
WOELKERLING W J , 1988. The coralline red algae: an analysis of the genera and subfamilies of nongeniculate corallinaceae[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press: 1-127.
|
| [39] |
WOELKERLING W J, HARVEY A , 1993. An account of southern Australian species of Mesophyllum (Corallinaceae, Rhodophyta)[J]. Australian Systematic Botany, 6(6):571-673.
doi: 10.1071/sb9930571
|
 ),练健生1,2,张浴阳1,2,杨剑辉1
),练健生1,2,张浴阳1,2,杨剑辉1
 ),Jiansheng LIAN1,2,Yuyang ZHANG1,2,Jianhui YANG1
),Jiansheng LIAN1,2,Yuyang ZHANG1,2,Jianhui YANG1