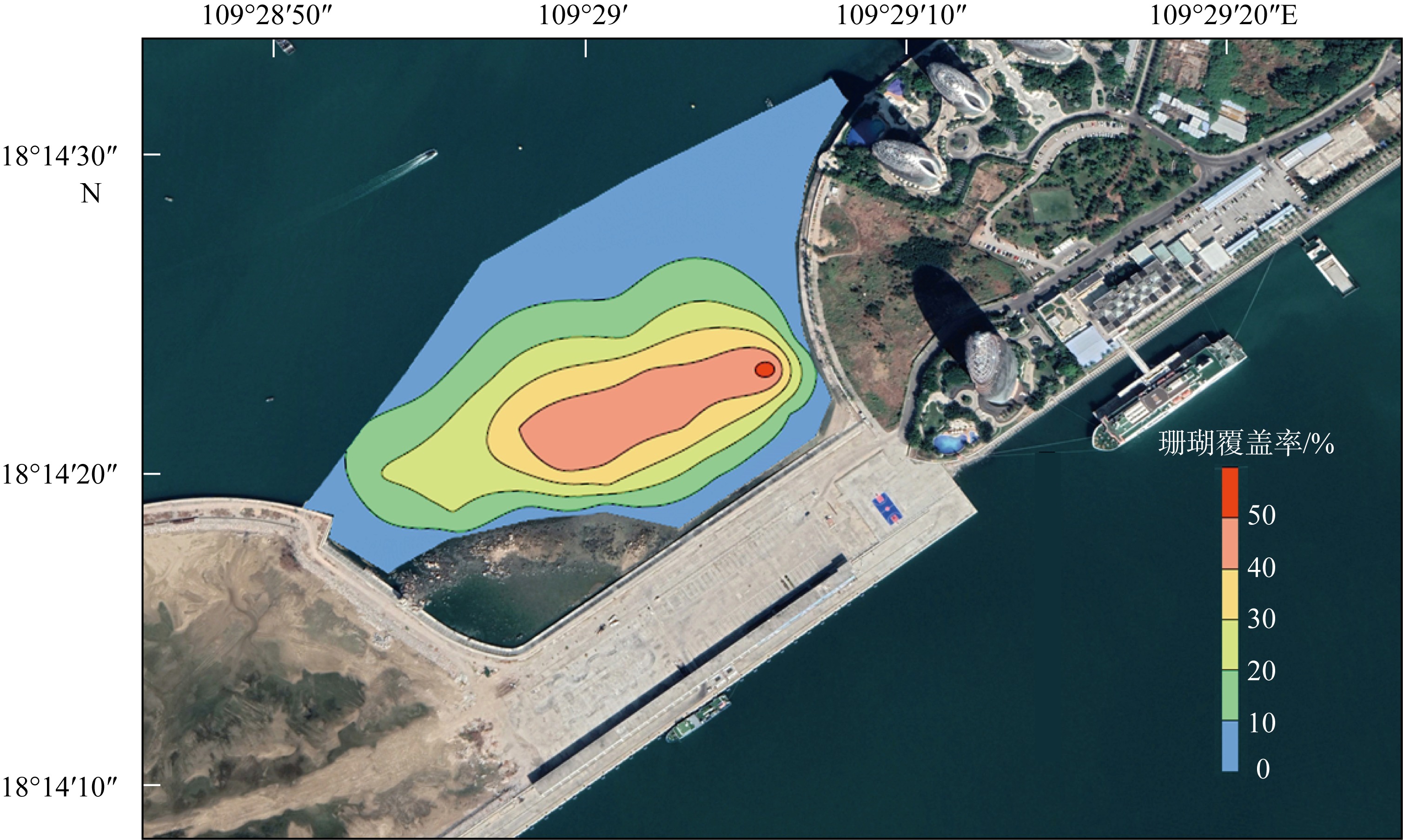
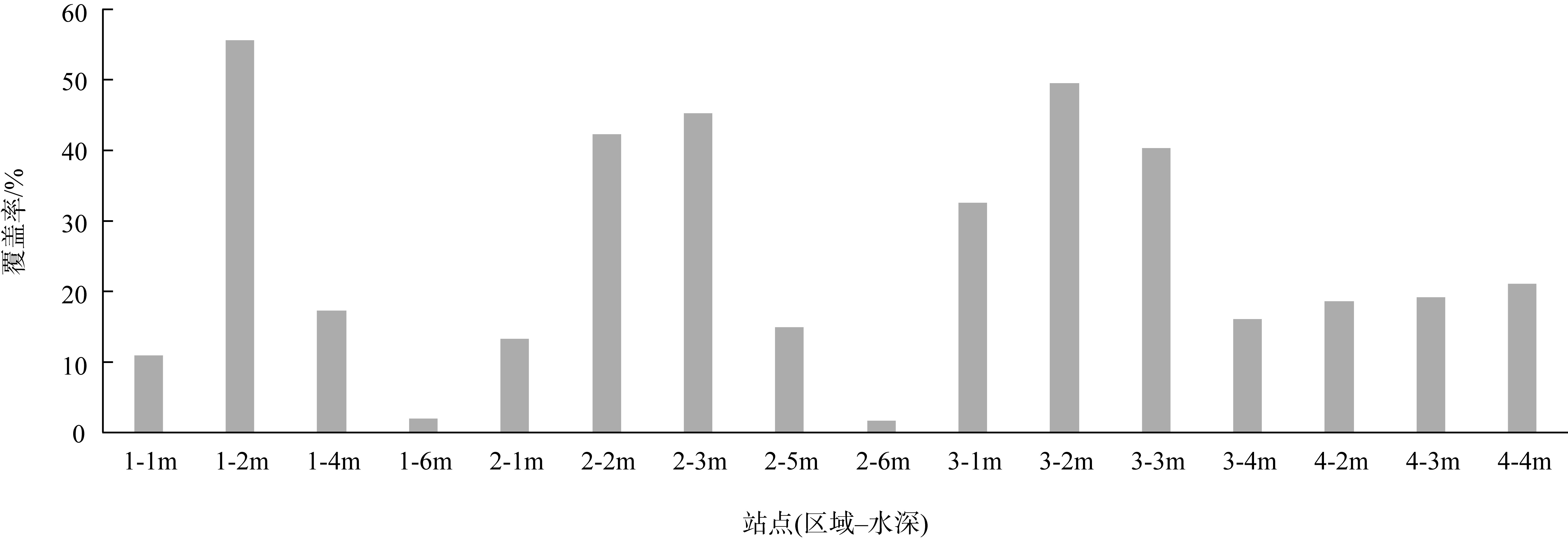
| [1] |
高永利, 黄晖, 练健生, 等, 2013. 大亚湾造礁石珊瑚移植迁入地的选择及移植存活率监测[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 32(2): 243-249.
|
|
GAO YONGLI, HUANG HUI, LIAN JIANSHENG, et al, 2013. Recipient site selection and hermatypic corals' survival rate in Daya Bay, China[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 32(2): 243-249 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
黄晖, 陈竹, 黄林韬, 2021. 中国珊瑚礁状况报告(2010-2019)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社.
|
|
HUANG HUI, CHEN ZHU, HUANG LINTAO, et al, 2021. Status of coral reefs in China (2010-2019)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
李长青, 夏利栋, 沈贝祺, 等, 2022. 海南三亚珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区珊瑚群落近年的动态变化[J]. 海南热带海洋学院学报, 29(5): 61-72.
|
|
LI CHANGQING, XIA LIDONG, SHEN BEIQI, et al, 2022. Dynamic changes of coral community in Sanya coral reef national nature reserve in recent years[J]. Journal of Hainan Tropical Ocean University, 29(5): 61-72 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
孙有方, 雷新明, 练健生, 等, 2018. 三亚珊瑚礁保护区珊瑚礁生态系统现状及其健康状况评价[J]. 生物多样性, 26(3): 258-265.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2017312
|
|
SUN YOUFANG, LEI XINMING, LIAN JIANSHENG, et al, 2018. Ecosystem status and health assessment of Sanya coral reef national nature reserve[J]. Biodiversity Science, 26(3): 258-265 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.17520/biods.2017312
|
| [5] |
张浴阳, 刘骋跃, 王丰国, 等, 2021. 典型近岸退化珊瑚礁的成功修复案例——蜈支洲珊瑚覆盖率的恢复[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 40(1): 26-33.
|
|
ZHANG YUYANG, LIU CHENGYUE, WANG FENGGUO, et al, 2021. Successful restoration of typical degraded coastal coral reefs--a restoration of coral coverage at Wuzhizhou Island[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 40(1): 26-33 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 2021. 三亚珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告[R]. 广州: 中国科学院南海海洋研究所 (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
自然资源部第三海洋研究所, 2021. 三亚凤凰岛二期项目拆除工程环境影响报告书[R]. 厦门: 自然资源部第三海洋研究所 (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
AJDARI D, MOTALLEBI A A, SHARIFROHANI M, et al, 2013. Coral relocation in Chabahar Bay, the North-east of Oman Sea[J]. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences, 12(1): 241-247.
|
| [9] |
BELLWOOD D R, HUGHES T P, FOLKE C, et al, 2004. Confronting the coral reef crisis[J]. Nature, 429(6994): 827-833.
|
| [10] |
BOSTRÖM-EINARSSON L, BABCOCK R C, BAYRAKTAROV E, et al, 2020. Coral restoration-A systematic review of current methods, successes, failures and future directions[J]. PLoS One, 15(1): e0226631.
|
| [11] |
ERFTEMEIJER P L A, RIEGL B, HOEKSEMA B W, et al, 2012. Environmental impacts of dredging and other sediment disturbances on corals: a review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(9): 1737-1765.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.05.008
pmid: 22682583
|
| [12] |
GALEWSKY J, STARK C P, DADSON S, et al, 2006. Tropical cyclone triggering of sediment discharge in Taiwan[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 111(F3): F03014.
|
| [13] |
HOFSTEDE R T, FINNEY C, MILLER A, et al, 2016. Monitoring and evaluation of coral transplantation to mitigate the impact of dredging works[C]. Proceedings of the 13th International Coral Reef Symposium. Honolulu: ICRS: 330-341.
|
| [14] |
HUGHES T P, HUANG H, YOUNG M A L, 2013. The wicked problem of China's disappearing coral reefs[J]. Conservation Biology, 27(2): 261-269.
doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2012.01957.x
pmid: 23140101
|
| [15] |
ISHIDA-CASTAÑEDA J, PIZARRO V, LÓPEZ-VICTORIA M, et al, 2020. Coral reef restoration in the Eastern Tropical Pacific: feasibility of the coral nursery approach[J]. Restoration Ecology, 28(1): 22-28.
|
| [16] |
KENNY I, KRAMER A, WILSON K P W, et al, 2012. Coral Relocation: A mitigation tool for dredging works in Jamaica[C/OL]. Cairns, Australia:ICRS [2023-06-25]. https://www.icrs2012.com/proceedings/manuscripts/ICRS2012_20A_4.pdf
|
| [17] |
LI XIUBAO, HUANG HUI, LIAN JIANSHENG, et al, 2013. Spatial and temporal variations in sediment accumulation and their impacts on coral communities in the Sanya Coral Reef Reserve, Hainan, China[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 96: 88-96.
|
| [18] |
MARAGOS J E, 1993. Impact of coastal construction on coral reefs in the U. S. ‐affiliated pacific Islands[J]. Coastal Management, 21(4): 235-269.
|
| [19] |
POPE E L, TALLING P J, CARTER L, et al, 2017. Damaging sediment density flows triggered by tropical cyclones[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 458: 161-169.
|
| [20] |
RAYMUNDO L J, MAYPA A P, 2004. Getting bigger faster: Mediation of size-specific mortality via fusion in juvenile coral transplants[J]. Ecological Applications, 14(1): 281-295.
|
| [21] |
RODGERS K S, LORANCE K, RICHARDS D A, et al, 2017. Effectiveness of coral relocation as a mitigation strategy in Kāne‘ohe Bay, Hawai‘i[J]. PeerJ, 5: e3346.
|
| [22] |
ROGERS C S, 1990. Responses of coral reefs and reef organisms to sedimentation[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 62(1-2): 185-202.
|
| [23] |
STENDER Y, JOKIEL P L, RODGERS K S, 2014. Thirty years of coral reef change in relation to coastal construction and increased sedimentation at Pelekane Bay, Hawaiʻi[J]. PeerJ, 2: e300.
|
| [24] |
WILKINSON C, 2004. Status of coral reefs of the world: 2004[M]. Townsville: Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS).
|
| [25] |
WILLIAMS S L, SU R C, JANETSKI N, et al, 2019. Large-scale coral reef rehabilitation after blast fishing in Indonesia[J]. Restoration Ecology, 27(2): 447-456.
doi: 10.1111/rec.12866
|
| [26] |
ZHANG YUYANG, HUANG HUI, HUANG JIEYING, et al, 2016. The effects of four transplantation methods on five coral species at the Sanya Bay[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(10): 88-95.
|
 ), 刘骋跃1,2,3, 俞晓磊1,2,3, 罗勇1,2,3, 周天成1,2,3,4, 练健生1,2,3, 黄晖1,2,3(
), 刘骋跃1,2,3, 俞晓磊1,2,3, 罗勇1,2,3, 周天成1,2,3,4, 练健生1,2,3, 黄晖1,2,3( )
)
 ), LIU Chengyue1,2,3, YU Xiaolei1,2,3, LUO Yong1,2,3, ZHOU Tiancheng1,2,3,4, LIAN Jiansheng1,2,3, HUANG Hui1,2,3(
), LIU Chengyue1,2,3, YU Xiaolei1,2,3, LUO Yong1,2,3, ZHOU Tiancheng1,2,3,4, LIAN Jiansheng1,2,3, HUANG Hui1,2,3( )
)