| [1] |
陈宝红, 谢尔艺, 高亚辉, 等, 2015. 米氏凯伦藻对海洋生物致毒作用的研究进展[J]. 福建水产, 37(3): 241-249.
|
|
CHEN BAOHONG, XIE ERYI, GAO YAHUI, et al, 2015. Toxic effects of red tide caused by Karenia mikimotoi on marine organisms[J]. Journal of Fujian Fisheries, 37(3): 241-249. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
陈旭阳, 刘保良, 2018. 海洋在线监测浮标在赤潮监测中的应用研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(5): 20-24.
|
|
CHEN XUYANG, LIU BAOLIANG, 2018. Application of Real-time monitoring buoy in monitoring red tide[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(5): 20-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [3] |
赫芬·I·里斯. 2020. 机器学习实战: 使用R、tidyverse和mlr[M]. 但波, 高山, 韩建立, 译. 北京: 清华大学出版社: 1-536.
|
|
RHYS H I. 2020. Machine learning: with R, the tidyverse, and mlr[M]. DAN BO, GAO SHAN, HAN JIANLI, trans. Beijing: Tsinghua University Publishing House: 1-536. (in Chinese)
|
| [4] |
蓝虹, 卢君峰, 曹宇峰, 等, 2014. 浅析平潭岛主要海洋灾害及防治对策[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 31(2): 55-58. (in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
李冬梅, 高永利, 田甜, 等, 2010. 水体扰动对多种赤潮藻生长的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(6): 65-70.
|
|
LI DONGMEI, GAO YONGLI, et al, 2010. Effects of turbulence on phytoplankton: species differences[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 29(6): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
林森杰, 姬南京, 罗昊, 2019. 海洋有害藻华研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 50(3): 495-510.
|
|
LIN SENJIE, JI NANJING, LUO HAO, 2019. Recent progress in marine harmful algal bloom research[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 50(3): 495-510. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [7] |
洛昊, 马明辉, 梁斌, 等, 2013. 中国近海赤潮基本特征与减灾对策[J]. 海洋通报, 32(5): 595-600.
|
|
LUO HAO, MA MINGHUI, LIANG BIN, et al, 2013. Basic characteristics and mitigation countermeasures of red tides in China seas[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 32(5): 595-600. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [8] |
马毅, 吴瑞贞, 李华建, 等, 2008. 有利于赤潮消亡的水文气象条件[J]. 海洋预报, 25(3): 1-6.
|
|
MA YI, WU RUIZHEN, LI HUAJIAN, et al, 2008. The hydrological-meteorological conditions conducive to the attenuation of red tide[J]. Marine Forecasts, 25(3): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [9] |
芮政, 杨桂军, 刘玉, 等, 2019. 扰动方式对水华微囊藻(Microcystis flos-aquae)群体大小的影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 31(2): 355-364.
doi: 10.18307/2019.0205
|
|
RUI ZHENG, YANG GUIJUN, LIU YU, et al, 2019. Effects of disturbance modes on the size of Microcystis flos-aquae colonies[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31(2): 355-364. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.18307/2019.0205
|
| [10] |
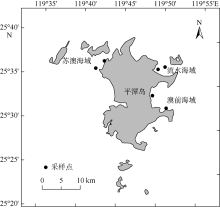
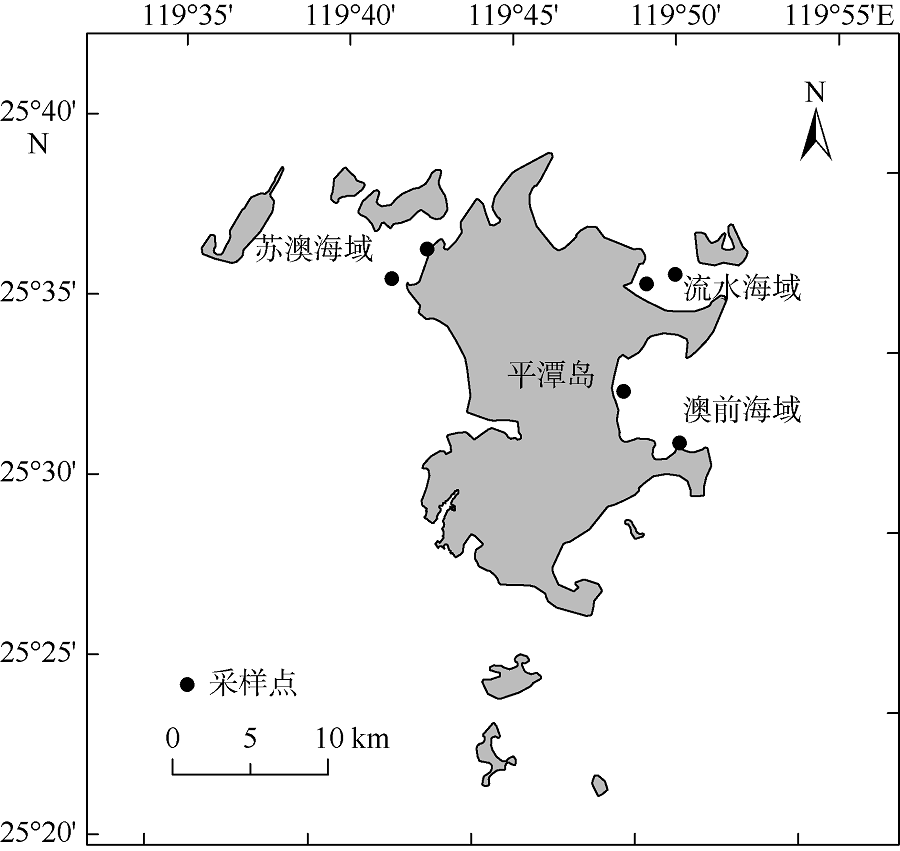
苏金洙, 高佳, 苏玉萍, 等, 2020. 福建平潭海域米氏凯伦藻(Karenia mikimotoi)增殖影响因子研究[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 36(4): 43-49, 56.
|
|
SU JINZHU, GAO JIA, SU YUPING, et al, 2020. Study on the factors affecting the proliferation of Karenia mikimotoi in Pingtan coastal area of Fujian province[J]. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 36(4): 43-49, 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [11] |
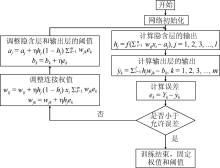
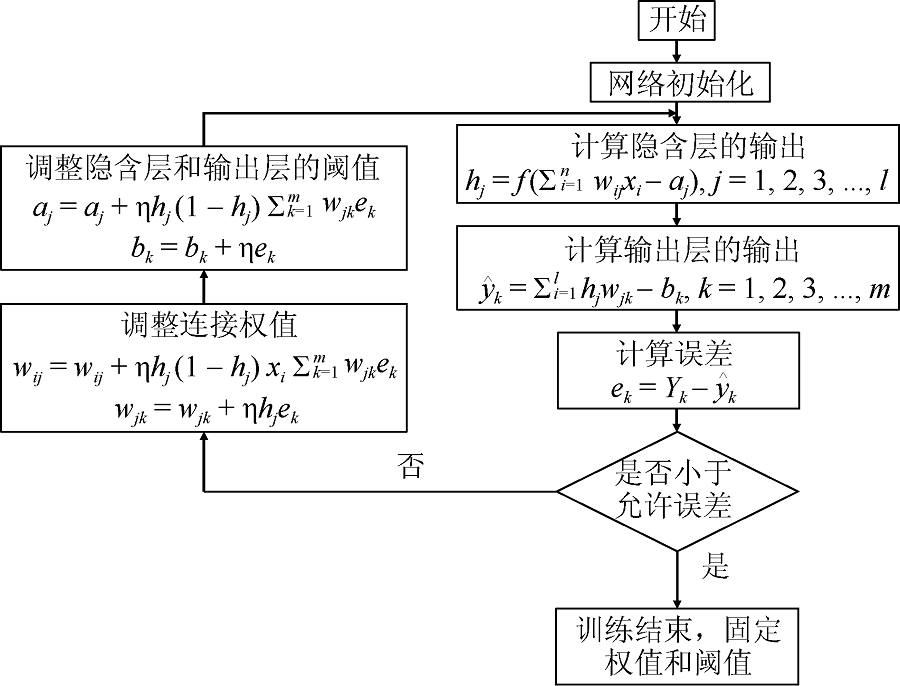
苏新红, 金丰军, 杨奇志, 等, 2017. 基于BP神经网络模型的福建海域赤潮预报方法研究[J]. 水产学报, 41(11): 1744-1755. (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
小沃尔特·J·韦伯, 1980. 水质控制物理化学方法[M]. 上海市政工程设计院, 译. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社: 510-511.
|
|
WEBER W J, 1980. Physicochemical processes for water quality control[M]. Shanghai Municipal Engineering Design Institute, trans. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press: 510-511. (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
许昆灿, 暨卫东, 周秋麟, 等, 2004. 表观增氧量在近岸海域赤潮快速评价与预警中的应用[J]. 台湾海峡, 23(4): 417-422.
|
|
XU KUNCAN, JI WEIDONG, ZHOU QIULIN, et al, 2004. Apparent oxygen increase (AOI) and its application in rapid assessment and prewarning of red tide in coastal waters[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 23(4): 417-422. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [14] |
许阳春, 张明峰, 苏玉萍, 等, 2020. 基于BP人工神经网络平潭海域赤潮叶绿素a浓度模型演算研究[J]. 海洋科学, 44(3): 34-41.
|
|
XU YANGCHUN, ZHANG MINGFENG, SU YUPING, et al, 2020. Calculation of the Chlorophyll-a concentration of red tide in the Pingtan Coastal Zone by a BP artificial neural network model[J]. Marine Sciences, 44(3): 34-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [15] |
俞志明, 陈楠生, 2019. 国内外赤潮的发展趋势与研究热点[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 50(3): 474-486.
|
|
YU ZHIMING, CHENG NANSHENG, 2019. Emerging trends in red tide and major research progresses[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 50(3): 474-486. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [16] |
张海涵, 王娜, 宗容容, 等, 2022. 水动力条件对藻类生理生态学影响的研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 35(1): 181-190.
|
|
ZHANG HAIHAN, WANG NA, ZONG RONGRONG, et al, 2022. Research progress on influence of hydrodynamic conditions on algal physiology and ecology[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 35(1): 181-190. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [17] |
赵聪蛟, 刘希真, 付声景, 等, 2020. 基于水质浮标在线监测的米氏凯伦藻赤潮过程及环境因子变化特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(2): 88-97.
|
|
ZHAO CONGJIAO, LIU XIZHEN, FU SHENGJING, et al, 2020. Variation characteristics of the evolution of Karenia mikimotoi bloom and environmental factors based on online monitoring buoy data[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(2): 88-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [18] |
赵雪, 杨凡, 郭娜, 等, 2009. 2007年2月汕头赤潮事件水文气象及海水理化因子影响分析[J]. 海洋预报, 26(1): 43-51. (in Chinese)
|
| [19] |
ANDERSON D M, 2009. Approaches to monitoring, control and management of harmful algal blooms (HABs)[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 52(7): 342-347.
|
| [20] |
AZANZA R V, FUKUYO Y, YAP L G, et al, 2005. Prorocentrum minimum bloom and its possible link to a massive fish kill in Bolinao, Pangasinan, Northern Philippines[J]. Harmful Algae, 4(3): 519-524.
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2004.08.006
|
| [21] |
BREIMAN L, 2001. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 45(1): 5-32.
doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324
|
| [22] |
DENG LEI, YANG WENYI, LIU HUI, 2019. PredPRBA: Prediction of protein-RNA binding affinity using gradient boosted regression trees[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 10: 637.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00637
|
| [23] |
ELITH J, LEATHWICK J R, HASTIE T, 2008. A working guide to boosted regression trees[J]. Journal of Animal Ecology, 77(4): 802-813.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2656.2008.01390.x
|
| [24] |
JIMÉNEZ-CARVELO A M, GONZÁLEZ-CASADO A, BAGUR- GONZÁLEZ M G, et al, 2019. Alternative data mining/ machine learning methods for the analytical evaluation of food quality and authenticity - A review[J]. Food Research International, 122: 25-39.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.03.063
|
| [25] |
KARKI S, SULTAN M, ELKADIRI R, et al, 2018. Mapping and forecasting onsets of harmful algal blooms using MODIS data over coastal waters surrounding Charlotte County, Florida[J]. Remote Sensing, 10(10): 1656.
doi: 10.3390/rs10101656
|
| [26] |
LIN H T, LIANG T J, CHEN S M, 2013. Estimation of battery state of health using probabilistic neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 9(2): 679-685.
doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2222650
|
| [27] |
LIU RUONAN, YANG BOYUAN, ZIO E, et al, 2018. Artificial intelligence for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: A review[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 108: 33-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.02.016
|
| [28] |
LYU JUNCHENG, ZHANG JIE, 2019. BP neural network prediction model for suicide attempt among Chinese rural residents[J]. Journal of Affective Disorders, 246: 465-473.
doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.12.111
|
| [29] |
NABIPOUR M, NAYYERI P, JABANI H, et al, 2020. Deep learning for stock market prediction[J]. Entropy, 22(8): 840.
doi: 10.3390/e22080840
|
| [30] |
PRASAD A M, IVERSON L R, LIAW A, 2006. Newer classification and regression tree techniques: Bagging and random forests for ecological prediction[J]. Ecosystems, 9(2): 181-199.
doi: 10.1007/s10021-005-0054-1
|
| [31] |
QIN MENGJIAO, LI ZHIHANG, DU ZHENHONG, 2017. Red tide time series forecasting by combining ARIMA and deep belief network[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 125: 39-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2017.03.027
|
| [32] |
RECKNAGEL F, 1997. ANNA-Artificial Neural Network model for predicting species abundance and succession of blue-green algae[J]. Hydrobiologia, 349(1): 47-57.
doi: 10.1023/A:1003041427672
|
| [33] |
SAN DIEGO-MCGLONE M L, AZANZA R V, VILLANOY C L, et al, 2008. Eutrophic waters, algal bloom and fish kill in fish farming areas in Bolinao, Pangasinan, Philippines[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 57(6-12): 295-301.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.03.028
|
| [34] |
TIAN WENCHONG, LIAO ZHENLIANG, ZHANG JIN, 2017. An optimization of artificial neural network model for predicting chlorophyll dynamics[J]. Ecological Modelling, 364: 42-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.09.013
|
| [35] |
WU DANNI, CHEN JUNHUI, HE XIUPING, et al, 2019. Distribution, partitioning, and seasonal variation of lipophilic marine algal toxins in aquatic environments of a typical semi-closed mariculture bay[J]. Environmental Pollution, 255: 113299.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113299
|
| [36] |
ZHOU BINGYIN, LU MING, WANG YONGGANG, 2016. Counting people using gradient boosted trees[C]// 2016 IEEE Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference. Chongqing, China: IEEE: 391-395.
|
| [37] |
ZOHDI E, ABBASPOUR M, 2019. Harmful algal blooms (red tide): a review of causes, impacts and approaches to monitoring and prediction[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16(3): 1789-1806.
doi: 10.1007/s13762-018-2108-x
|
 ), 邹嘉澍1, 苏玉萍1,2(
), 邹嘉澍1, 苏玉萍1,2( ), 张明峰3, 翁蓁洲4, 杨小强4
), 张明峰3, 翁蓁洲4, 杨小强4
 ), ZOU Jiashu1, SU Yuping1,2(
), ZOU Jiashu1, SU Yuping1,2( ), ZHANG Mingfeng3, WENG Zhenzhou4, Yang Xiaoqiang4
), ZHANG Mingfeng3, WENG Zhenzhou4, Yang Xiaoqiang4