热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 34-44.doi: 10.11978/2022105CSTR: 32234.14.2022105
所属专题: 全球变化专题
热带大洋春季海气耦合模态及其与ENSO的关系*
- 1.热带海洋环境国家重点实验室, 广东省海洋遥感重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
-
收稿日期:2022-05-10修回日期:2022-07-14出版日期:2023-03-10发布日期:2022-08-02 -
通讯作者:张玉红。email:zhangyuhong@scsio.ac.cn -
作者简介:张玉红 (1984—), 女, 副研究员, 主要从事海洋动力过程与海气相互作用研究。email: zhangyuhong@scsio.ac.cn
*感谢ERA5再分析资料提供海表气压、风场数据, 感谢美国国家气候中心提供SST数据下载, 感谢NOAA气候记录计划提供降水, 感谢哥白尼海洋环境监测服务中心提供海表面高度数据下载。
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41976024); 国家自然科学基金项目(41830538); 国家自然科学基金项目(42090042); 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)项目(2019BT02H594); 热带海洋环境国家重点实验室自主研究项目(LTOZZ2101)
Tropical ocean-atmosphere coupling modes and their relationship with ENSO during spring*
ZHANG Yuhong1,2,3( ), ZHANG Lianyi1,3, DU Yan1,2,3
), ZHANG Lianyi1,3, DU Yan1,2,3
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography, Guangdong Key Lab of Ocean Remote Sensing, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
-
Received:2022-05-10Revised:2022-07-14Online:2023-03-10Published:2022-08-02 -
Contact:ZHANG Yuhong. email:zhangyuhong@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976024); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41830538); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42090042); Southern Marine Science, Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(2019BT02H594); Independent Research Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography(LTOZZ2101)
摘要:
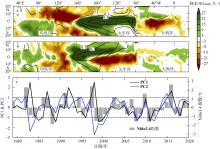
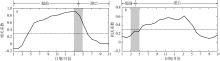
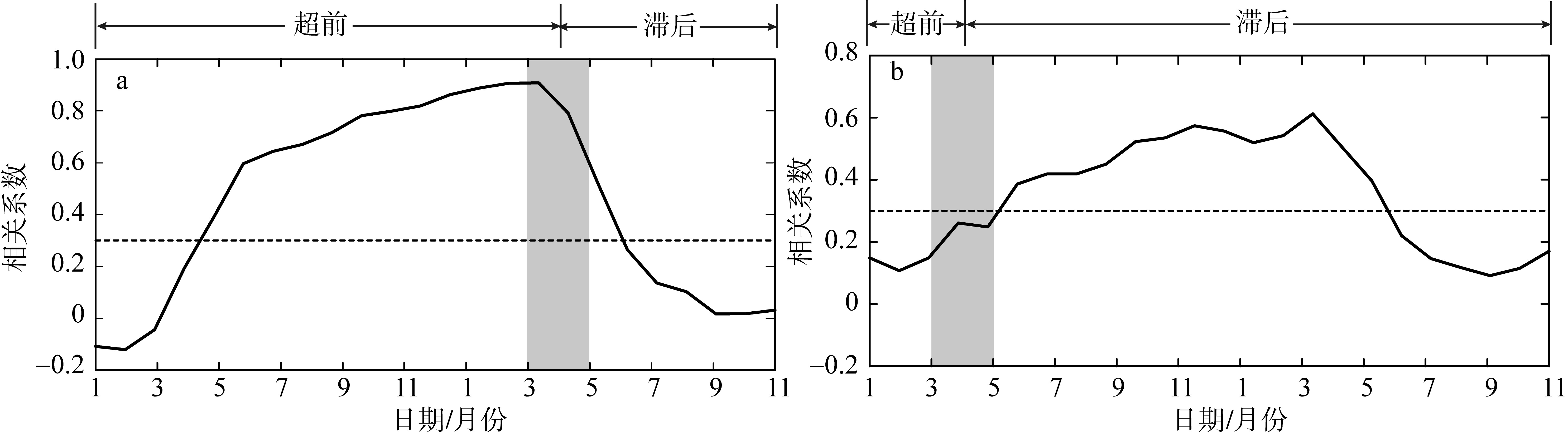
在北半球的春季, 热带三大洋的海洋-大气系统年际变化会对同期太平洋厄尔尼诺-南方涛动(El Niño-Southern oscillation, ENSO)产生响应, 同时也能通过区域海洋-大气耦合过程影响ENSO的发展。基于国际公开使用的海表温度资料和降水资料, 通过联合正交经验分解方法分析, 可以发现全球大洋春季存在两种显著的海气耦合模态。第一模态表现为: 在热带中东太平洋, 海表温度增暖、降水增多; 在热带大西洋和热带印度洋, 降水呈现经向偶极型分布以及跨赤道的海表温度梯度异常; 即伴随ENSO在春季消亡期的空间型态, 大西洋出现经向模态, 印度洋出现反对称模态。第二模态表现为: 太平洋经向海表温度和降水模态, 即太平洋经向模态。回归分析结果表明, ENSO盛期的大气环流调整引起了热带大西洋和印度洋降水辐合带异常, 并通过海面风场异常激发海盆内部的海洋-大气反馈, 引起春季经向模态。进一步研究发现, 冬、春季大西洋和印度洋热带辐合带分别位于赤道以北和以南, 导致两个海盆经向模态的降水异常相对赤道呈反对称分布。在春季, 太平洋经向模态的暖中心延伸到赤道上, 引起西风异常, 为后续El Niño的发展提供了有利条件。文章揭示了太平洋ENSO与春季热带三大洋经向模态之间的关系, 这有助于更好地理解热带气候模态的季节性“足迹”的发展过程。
引用本文
张玉红, 张涟漪, 杜岩. 热带大洋春季海气耦合模态及其与ENSO的关系*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 34-44.
ZHANG Yuhong, ZHANG Lianyi, DU Yan. Tropical ocean-atmosphere coupling modes and their relationship with ENSO during spring*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 34-44.
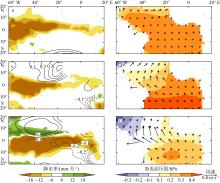
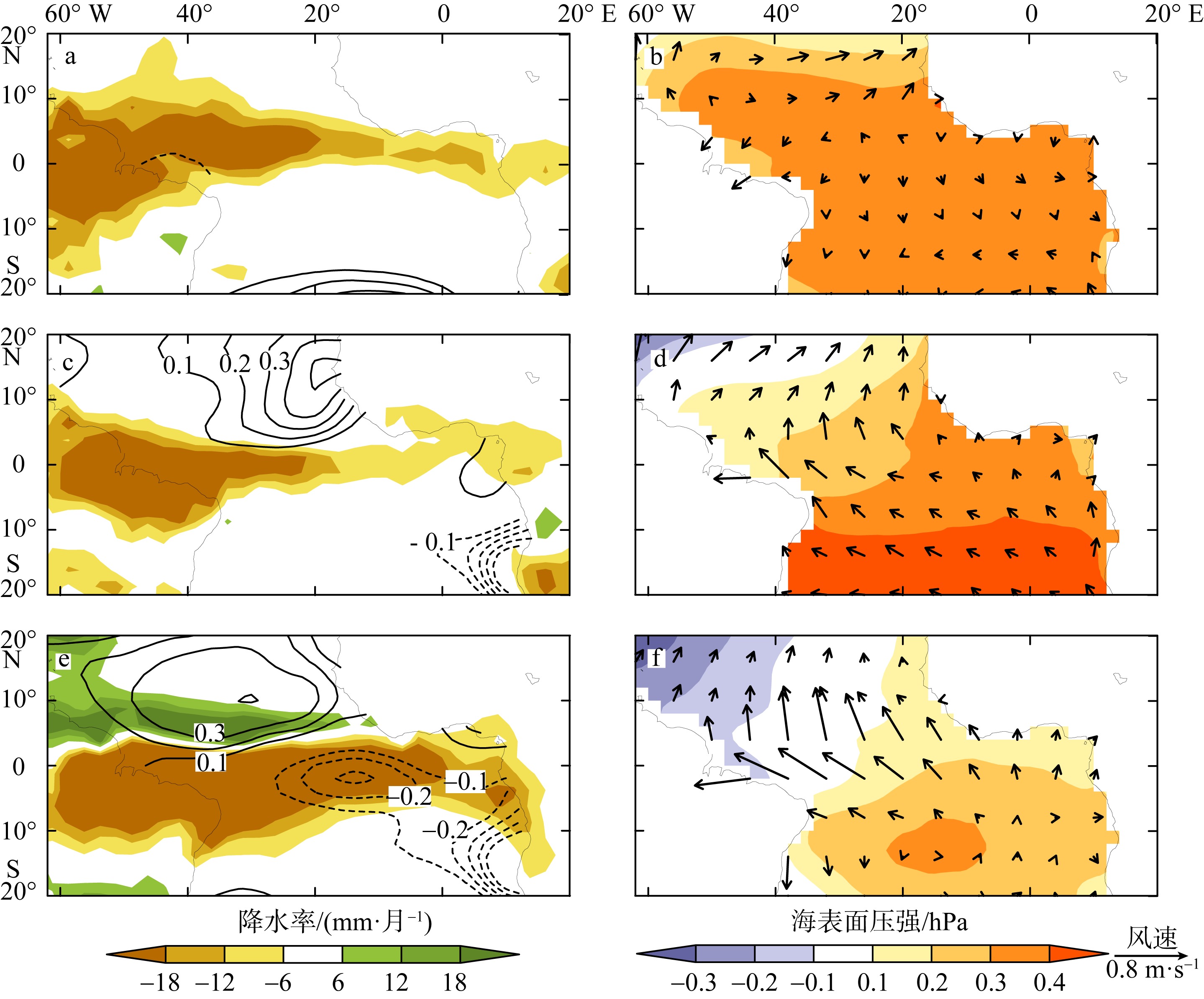
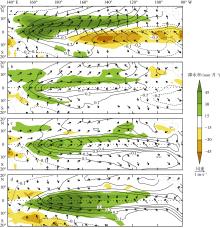
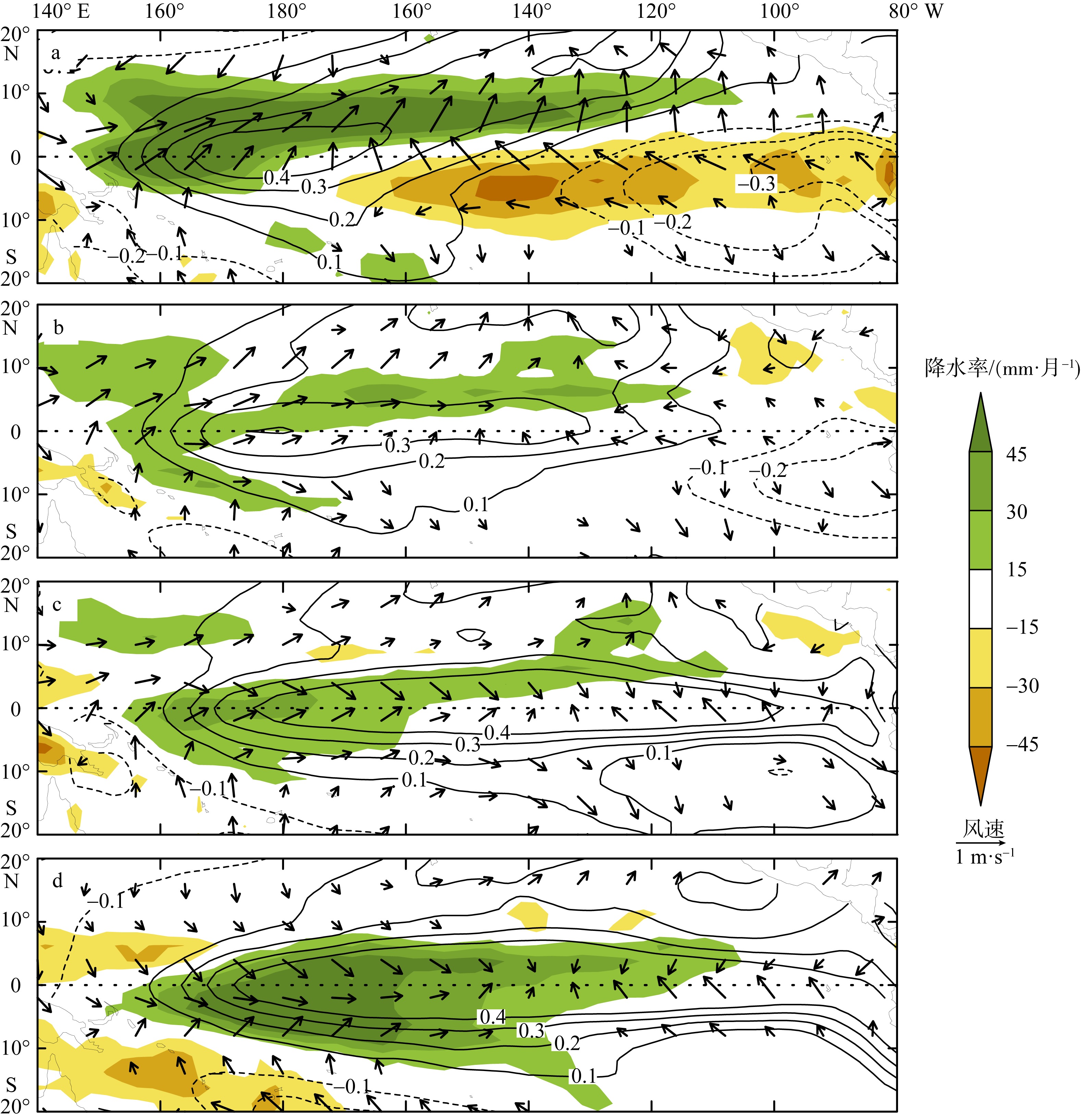
图6
热带印度洋、大西洋和太平洋降水率、海表温度、海表面压强(hPa)和风场异常回归到海表温度和降水联合EOF分析第一和第二模态时间序列上的超前滞后回归系数和气候态降水和风场的纬向平均的纬度-时间变化图 a, d, g: 印度洋(50°—90°E); b, e, h: 大西洋(60°W—20°E); c, f, i: 太平洋(140°E—80°W)。a, b, c: 降水(填色)和海表温度(等值线, 单位: ℃)的回归系数; d, e, f: 海表面压强(填色)和风场(矢量)的回归系数; g, h, i: 气候态降水(填色)和风场(矢量), 图中白色粗实线标注了气候态降水量为130 mm·月-1 的等值线(强降水中心)。印度洋和大西洋的各变量回归到第一模态; 太平洋的变量回归到第二模态。图中回归系数只展示了超过t检验95%置信度的结果"

| [1] |
doi: 10.1175/1525-7541(2003)004<1147:TVGPCP>2.0.CO;2 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<2205:TABTIO>2.0.CO;2 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI3797.1 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1969)097<0163:ATFTEP>2.3.CO;2 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1038/385516a0 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1007/s00382-017-3899-z |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1029/2000JD000307 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI4953.1 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1029/95JC01502 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<3280:ADSOTR>2.0.CO;2 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2590.1 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<0297:IVOCRE>2.0.CO;2 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0836.1 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1029/2001JC001278 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1029/2009GL040000 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1029/2019GL085205 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1029/2000JD900610 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012<0917:RSSTVD>2.0.CO;2 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00055.1 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1029/97JC03413 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<4287:IOEOTV>2.0.CO;2 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1029/2008GL034734 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1002/2014JC010429 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1175/2009JCLI3104.1 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00448.1 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1007/s00382-019-04851-9 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI4152.1 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0063.1 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-20-0122.1 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2464:VOSSTW>2.0.CO;2 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2004.10.014 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1982)110<0354:VITSST>2.0.CO;2 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<1606:GARSPP>2.0.CO;2 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1002/grl.v44.5 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0090.1 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078<2771:TDOENO>2.0.CO;2 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<2668:TSFMIT>2.0.CO;2 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1517:PEATHD>2.0.CO;2 |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1002/joc.2014.34.issue-8 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1029/97JC02719 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1477-870X |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1029/2019GL085840 |
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<0864:SAMOSI>2.0.CO;2 |
| [52] |
doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2544.1 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1007/s00376-015-5192-6 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.3402/tellusa.v46i4.15484 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0866.1 |
| [56] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-10-05001.1 |
| [57] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0860.1 |
| [58] |
doi: 10.1029/2005GL024327 |
| [59] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00082.1 |
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-21-0426.1 |
| [1] | 袁钰, 徐海明, 马静, 张彤. AMO对ENSO与初夏西太平洋海洋热浪年际关系的年代际调制作用*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 1-16. |
| [2] | 张琪, 连涛. 低频风应力强迫减弱数值模式中厄尔尼诺多样性[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 1-9. |
| [3] | 郑依玲,陈泽生,王海,杜岩. 2015/2016年超强厄尔尼诺事件基本特征及生成和消亡机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(4): 10-19. |
| [4] | 王闵杨, 罗义勇, 杜岩. 太平洋赤道不稳定波强度变化及其与ENSO的关系*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(3): 41-47. |
| [5] | 杨亚力, 杜岩. ENSO及印度洋海盆模态关联的南海SST异常年代际变化及海洋平流输送的贡献[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(1): 72-81. |
| [6] | 杜美芳, 徐海明, 周超. 基于CMIP5资料的热带大洋非均匀增暖及其成因的分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(3): 1-12. |
| [7] | 宋少华, 周卫健, 熊晓虎, 彭子成, 刘卫国, 陈特固. 对近183年我国南海冬季风变率的探讨: 来自珊瑚氧同位素的证据*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(1): 18-25. |
| [8] | 杜娟,郑飞,朱江. 一个重构的 153 年热带太平洋次表层上卷海温资料[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(1): 1-9. |
|
||