热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 169-173.doi: 10.11978/2022107CSTR: 32234.14.2022107
深海放线菌Streptomyces koyangensis SCSIO 5802中次级代谢产物neoabyssomicin H的分离鉴定*
宋永相1,2,3,4( ), 李晓悦1,3, 鞠建华1,2,3,4
), 李晓悦1,3, 鞠建华1,2,3,4
- 1.中国科学院热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东省海洋药物重点实验室, 广东 广州 510301
2.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
3.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
4.三亚中科海洋研究院, 海南 三亚, 572000
The isolation and identification of neoabyssomicin H from the deep-sea derived Streptomyces koyangensis SCSIO 5802*
SONG Yongxiang1,2,3,4( ), LI Xiaoyue1,3, JU Jianhua1,2,3,4
), LI Xiaoyue1,3, JU Jianhua1,2,3,4
- 1. CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511453, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4. Sanya Institute of Oceanology, SCSIO, Sanya 572000, China
摘要:
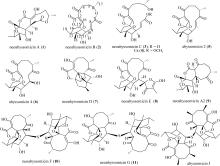
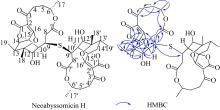
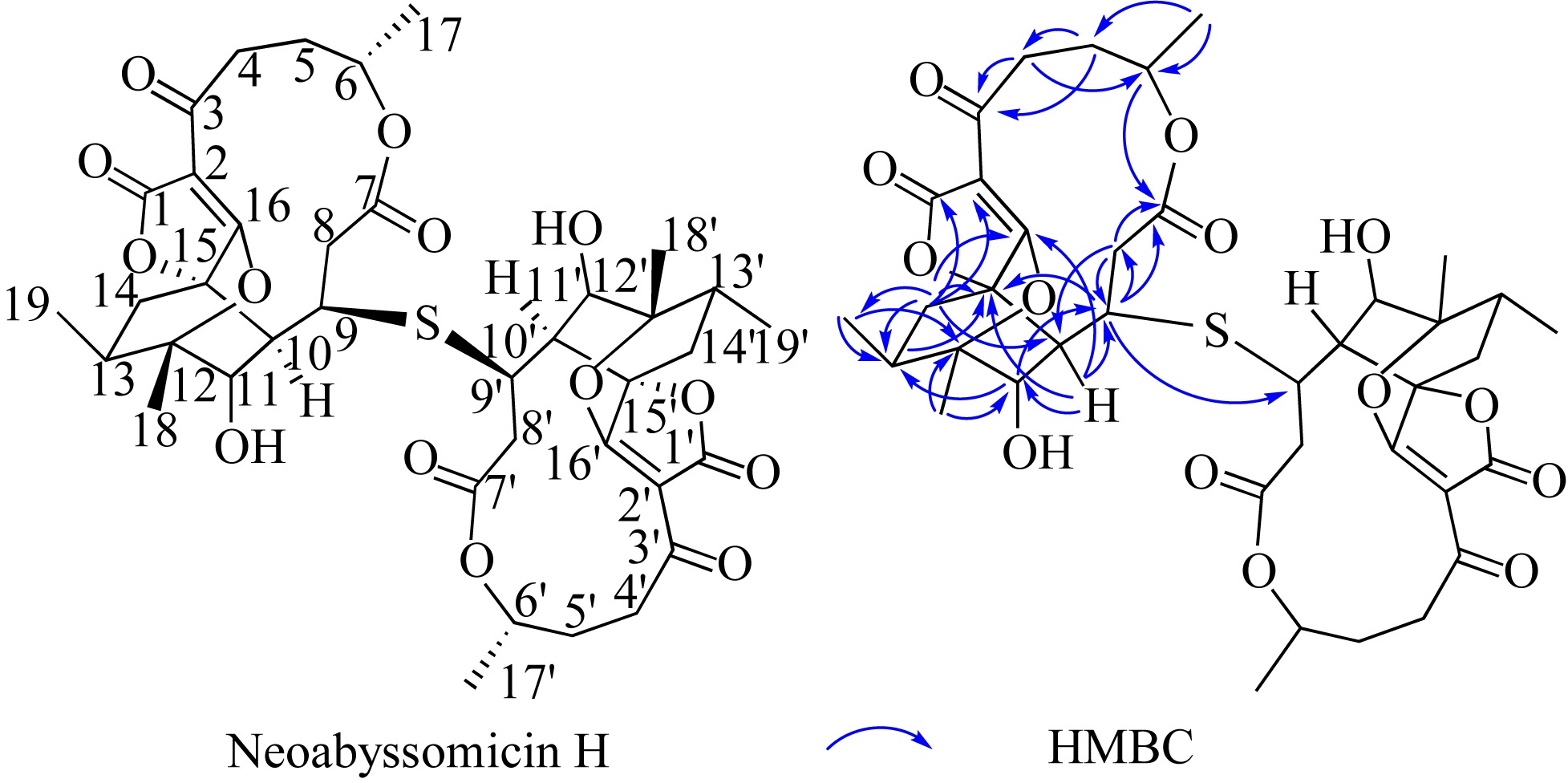
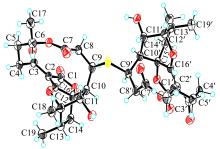
深渊霉素类化合物具有抗结核分枝杆菌、抗MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus)、选择性激活潜伏HIV病毒等生物活性, 具有显著的开发利用潜力。本文在前期研究基础上, 进一步对深海链霉菌Streptomyces koyangensis SCSIO 5802新型深渊霉素类化合物的生产潜力进行发掘, 综合利用多种色谱分离手段, 获得一个结构新颖的深渊霉素硫醚二聚体化合物, 命名为neoabyssomicin H。该化合物的结构通过UV、IR、HR-ESI-MS, 1D和2D NMR及X-Ray单晶铜靶衍射等进行了鉴定。活性测试结果表明, neoabyssomicin H对金黄色葡萄球菌和系列临床MRSA的MIC(minimum inhibitory concentration)值大于128μg·mL-1。该研究进一步丰富了深渊霉素类化合物, 为硫醚二聚体类深渊霉素活性化合物的研究提供了新的分子实体。