热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 158-168.doi: 10.11978/2022142CSTR: 32234.14.2022142
广西北部湾可培养黏细菌资源初探及其抗菌活性研究
卢天梅1( ), 官佳松1,2, 覃诗敬1, 刘永宏1,3, 苏志维1(
), 官佳松1,2, 覃诗敬1, 刘永宏1,3, 苏志维1( )
)
- 1.广西中医药大学海洋药物研究院, 广西 南宁 530200
2.广西大学农学院, 广西 南宁 530004
3.热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东省海洋药物重点实验室, 广东 广州 510301
-
收稿日期:2022-06-23修回日期:2022-08-24出版日期:2023-05-10发布日期:2022-09-01 -
作者简介:卢天梅(1994—), 女, 广西壮族自治区桂平市人, 硕士研究生, 从事海洋药用微生物资源挖掘与利用研究。email: 2646013152@qq.com
-
基金资助:广西中医药大学海洋药物研究院团队科研专项经费(2018ZD005-A08); 国家自然科学基金(32060098); 广西八桂学者专项经费(05019055); 广西中医药大学研究生教育创新计划项目(YCSZ2022024); 大学生创新项目(S202110600122); 广西科技计划项目(桂科AB19259010)
Preliminary study on the culturable myxobacteria resources from the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi and their antibacterial activity
LU Tianmei1( ), GUAN jiasong1,2, QIN Shijing1, LIU Yonghong1,3, SU Zhiwei1(
), GUAN jiasong1,2, QIN Shijing1, LIU Yonghong1,3, SU Zhiwei1( )
)
- 1. Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
2. College of Agriculture, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China
3. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, Guangzhou 510301, China
-
Received:2022-06-23Revised:2022-08-24Online:2023-05-10Published:2022-09-01 -
Supported by:Scientific Research Foundation of Institute of Marine Drugs, GUCM(2018ZD005-A08); National Natural Science Foundation of China(32060098); Special Fund for Bagui Scholars to Yonghong Liu(05019055); Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education of GXUCM(YCSZ2022024); University Student Innovation Project(S202110600122); Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region(AB19259010)
摘要:
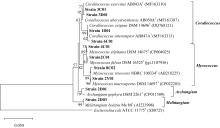
采用大肠杆菌诱导法和滤纸诱导法对广西北部湾不同海洋生境采集的样品进行黏细菌的分离纯化, 基于菌落形态特征结合16S rRNA基因序列分析对黏细菌纯培养物进行初步鉴定。从21份海洋生境样品中共分离纯化得到38株黏细菌, 隶属于4属10种, 其中黏球菌属和珊瑚球菌属分别占菌株总数的63.16%和26.32%, 属于优势菌属。采用VY/2培养基进行固体培养发酵, 利用丙酮提取浓缩获得提取物, 进一步利用滤纸片琼脂扩散法对菌株粗提物进行抗菌活性初步筛选。结果发现24株黏细菌提取物对9种指示菌具有不同程度的抑制作用, 抗菌阳性率达63.16%, 其中Myxococcus macrosporus (1H01)的提取物对肺炎克雷伯菌的抑制活性显著, 优于阳性药(氨苄青霉素钠, 1mg·mL-1)。研究结果表明广西北部湾特殊海洋生境黏细菌多样性丰富, 分离出的黏细菌具有良好的抗菌活性, 为新型抗生素应用研究奠定了物质基础。
引用本文
卢天梅, 官佳松, 覃诗敬, 刘永宏, 苏志维. 广西北部湾可培养黏细菌资源初探及其抗菌活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 158-168.
LU Tianmei, GUAN jiasong, QIN Shijing, LIU Yonghong, SU Zhiwei. Preliminary study on the culturable myxobacteria resources from the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi and their antibacterial activity[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 158-168.
表1
样品信息表"
| 样品编号 | 样品名称 | 采样区域 | 经纬度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1H | 木榄根际沉积物 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 2H | 木榄腐木 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 3H | 木榄胚轴 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 4H | 木榄树皮 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 5H | 木榄根际沉积物 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 6H | 白骨壤根际沉积物 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 1D | 海蚀坑沉积物 | 涠洲岛 | 109°05′52″E, 21°00′04″N |
| 2D | 滩岩老鼠簕根际沉积物 | 涠洲岛 | 109°05′58″E, 21°00′42″N |
| 3D | 礁石地衣 | 涠洲岛 | 109°05′56″E, 21°00′39″N |
| 4D | 滩岩仙人掌根际沉积物 | 涠洲岛 | 109°05′55″E, 21°00′15″N |
| 1Y | 盐田淤泥 | 银海区 | 109°16′39″E, 21°26′35″N |
| 2Y | 盐田淤泥 | 银海区 | 109°16′22″E, 21°26′35″N |
| 3Y | 盐田淤泥 | 银海区 | 109°16′23″E, 21°26′35″N |
| 1C | 海草床沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°12′06″E, 21°34′14″N |
| 2C | 互花米草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′10″E, 21°35′11″N |
| 3C | 互花米草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°10′57″E, 21°34′33″N |
| 4C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′29″E, 21°34′59″N |
| 5C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′21″E, 21°34′53″N |
| 6C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′20″E, 21°34′51″N |
| 7C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′36″E, 21°34′58″N |
| 8C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′24″E, 21°34′51″N |
表3
菌株的相关信息及耐盐能力"
| 种名 | 菌株编号 | 相似度/% | 耐盐能力/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corallococcus aberystwythensis | 3C01 | 99.61 | 1 |
| Corallococcus exercitus | 3D01 | 98.97 | 1 |
| Corallococcus exiguus | 6C01 | 98.85 | 1 |
| Melittangium boletus | 2D03 | 99.49 | <1 |
| Archangium gephyra | 2D01 | 100.00 | 1 |
| 1Y01 | 99.74 | 2 | |
| 4D01 | 99.15 | 1 | |
| Corallococcus interemptor | 1C01 | 100.00 | 1 |
| 1D01 | 100.00 | 1 | |
| 2D02 | 100.00 | 1 | |
| 6C02 | 99.87 | 1 | |
| 8C01 | 99.87 | 1.5 | |
| 1C02 | 99.74 | 1 | |
| 4H01 | 99.35 | 1 | |
| Myxococcus fulvus | 2C01 | 99.87 | 1 |
| 1H02 | 99.74 | <1 | |
| 5C01 | 99.36 | 1 | |
| 6H01 | 99.36 | 1 | |
| 1C04 | 98.85 | 1 | |
| 1D02 | 98.59 | 1 | |
| Myxococcus macrosporus | 2Y01 | 100.00 | 1.5 |
| 5H01 | 99.87 | 1.5 | |
| 1H01 | 99.74 | 1 | |
| 4H02 | 99.36 | <1 | |
| 3Y01 | 99.10 | 2 | |
| 3H01 | 98.97 | 2 | |
| 1C03 | 98.87 | 1 | |
| Myxococcus stipitatus | 4C01 | 99.87 | 1 |
| 7C01 | 99.74 | <1 | |
| 1C06 | 99.74 | <1 | |
| 3D02 | 99.62 | 1 | |
| 1H03 | 99.50 | 1 | |
| 5H02 | 99.49 | 1 | |
| 1C05 | 99.49 | 1 | |
| Myxococcus virescens | 8C02 | 99.49 | 2 |
| 1Y02 | 99.36 | 2 | |
| 2H01 | 99.36 | 2 | |
| 1C07 | 99.10 | 1.5 |
表5
黏细菌发酵提取物的抑菌活性"
| 菌种 | 编号 | 抑菌圈直径/mm | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G+ | G- | |||||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | ||
| C. aberystwythensis | 3C01 | - | - | - | - | 12.03±0.32 | 12.58±0.44 | - | - | - |
| C. exiguus | 6C01 | - | - | - | - | - | 9.28±0.14 | - | - | - |
| A. gephyra | 1Y01 | - | - | - | - | 12.07±0.04 | - | - | - | - |
| C. interemptor | 1C01 | - | - | - | - | 11.95±0.01 | - | - | - | - |
| 1D01 | - | - | - | - | 13.43±0.40 | 8.64±0.09 | 12.25±0.29 | - | - | |
| 2D02 | - | - | 9.53±0.25 | - | 11.83±0.25 | 11.10±0.16 | - | - | - | |
| 6C02 | - | - | - | - | - | 9.97±0.05 | - | - | - | |
| 1C02 | - | - | - | 10.57±0.05 | 15.97±0.06 | - | - | - | - | |
| M. fulvus | 2C01 | - | - | - | 10.33±0.32 | 14.93±0.11 | 11.54±0.44 | - | - | - |
| 5C01 | - | 7.67±0.42 | - | - | - | 12.79±0.18 | - | - | - | |
| 1C04 | 10.82±0.04 | 7.34±0.02 | 12.03±0.65 | 12.23±0.24 | 15.79±0.05 | 14.05±0.20 | 10.91±0.17 | 11.14±0.07 | 13.78±0.06 | |
| 1D02 | - | - | 8.40±0.30 | - | - | 13.76±0.08 | - | - | - | |
| M. macrosporus | 1H01 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 18.16±0.24 | - | 9.65±0.03 |
| 4H02 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10.39±0.51 | |
| 1C03 | - | - | - | - | 14.19±0.05 | - | - | - | - | |
| M. stipitatus | 7C01 | - | - | - | 14.77±0.15 | - | 9.89±0.62 | - | - | - |
| 1C06 | 9.76±0.47 | 9.14±0.03 | - | 13.70±0.02 | 12.24±0.04 | 10.22±0.05 | 9.75±0.08 | 8.01±0.04 | - | |
| 3D02 | 14.33±0.14 | 13.87±0.12 | 11.90±0.10 | 14.57±0.60 | 19.74±0.29 | 16.61±0.04 | 13.74±0.08 | 8.43±0.08 | - | |
| 1H03 | 11.22±0.05 | 12.15±0.18 | 11.86±0.09 | 10.75±0.02 | 17.36±0.07 | 8.65±0.06 | 12.94±0.09 | - | - | |
| 1C05 | 12.90±0.36 | - | - | - | - | 15.99±0.27 | 12.38±0.22 | - | - | |
| M. virescens | 8C02 | - | - | - | - | - | 14.00±0.26 | - | - | - |
| 1Y02 | 13.90±0.36 | 8.72±0.08 | 10.50±0.30 | 13.10±0.44 | 11.31±0.27 | 15.66±0.47 | - | - | - | |
| 2H01 | 10.03±0.09 | 7.54±0.13 | 10.15±0.13 | 11.59±0.03 | 12.25±0.03 | 10.09±0.12 | - | - | - | |
| 1C07 | - | - | - | - | 15.59±0.03 | - | - | - | - | |
| 氨苄青霉素钠 | - | 19.46±0.30 | 10.40±0.15 | 14.33±0.38 | 20.17±0.23 | 22.10±0.19 | 17.11±0.56 | 17.02±0.03 | 15.72±0.02 | 18.39±0.12 |
| 空白对照 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [1] |
韩敏敏, 李蜜, 刘昕明, 等, 2020. Khai岛和Pathiu岛珊瑚礁沉积物细菌多样性及细菌粗提物延缓秀丽隐杆线虫衰老活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(5): 19-29.
doi: 10.11978/2019126 |
|
|
|
| [2] |
蒋莲秀, 吴越, 陈建宏, 等, 2017. 具有广谱抗菌活性的红树林稀有放线菌的分离及鉴定[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 42(4): 311-317.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
鞠建华, 杨镇业, 李青连, 等, 2021. 微生物药物研究开发现状与思考[J]. 山东大学学报, 59(9): 43-50+63.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
李艳群, 陈柔雯, 林宗豪, 等, 2021. 一株群体感应抑制活性海洋放线菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(1): 75-81.
doi: 10.11978/2020011 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2020011 |
|
| [5] |
骆宁宁, 2015. 粘球菌通过mts基因簇调控社会性细胞行为以适应海水生境的分子机制[D]. 济南: 山东大学: 1-123.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
马丽丽, 田新朋, 李桂菊, 等, 2021. 海洋微生物来源天然产物研究现状与态势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(5): 134-146.
doi: 10.11978/2020104 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2020104 |
|
| [7] |
邱智军, 李越中, 张勇, 等, 2003. 海水盐离子对耐盐粘球菌生长和发育的影响[J]. 微生物学杂志, (3): 8-11.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
沙国萌, 陈冠军, 陈彤, 等, 2020. 抗生素耐药性的研究进展与控制策略[J]. 微生物学通报, 47(10): 3369-3379.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
宋腾飞, 2019. 海洋青霉菌(Penicillium sp. ZZ380)的代谢产物及其生物活性的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学: 1-116.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
王春玲, 冯广达, 姚青, 等, 2019. 粘细菌基因组学研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 46(9): 2394-2403.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
王春玲, 吕颖颖, 姚青, 等, 2021. 粘细菌资源挖掘与多相分类研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 48(8): 2870-2880.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
王聪, 王坤, 姜明国, 等, 2019. 广西北部湾放线菌的分离筛选及活性产物的鉴定[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 31(7): 1170-1176.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
王婷, 2018. 新型生防粘细菌Myxococcus sp. BS的分离及粘细菌对细菌性软腐病菌的捕食机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学: 1-85.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
王雪寒, 2019. 内蒙古东部地区的可培养粘细菌及其抗菌活性的初步检测[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学: 1-79.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
吴姝鸽, 2021. 湖泊沉积物微生物的多样性、分离培养及四株新菌的分类鉴定[D]. 济南: 山东大学: 1-105.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
杨少娟, 陈雪梅, 沈锐, 等, 2021. 广西北部湾局部海域海洋沉积物细菌多样性及生物活性评估[J]. 广西科学, 28(5): 460-472.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
蚁烁星, 周杨, 张鲜姣, 等, 2020. 不同分离方法对子实体形成和粘细菌分离的影响[J]. 微生物学报, 61(4): 923-934.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
周秀文, 2013. 土壤中粘细菌群落的调查及领地性行为的分子机制的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学: 1-183.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.3390/md16060209 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.3390/md16090314 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1007/s10482-010-9460-2 pmid: 20582471 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020196 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.040501-0 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1007/s10295-009-0683-z pmid: 20033830 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1102-1108.1991 pmid: 2059035 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.2471/BLT.16.181743 pmid: 27516629 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00194.x |
| [28] |
pmid: 11997170 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00424-7 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000250 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms6030084 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms6030073 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.09.010 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8843-6 pmid: 29455386 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.3390/v10070374 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1007/s00248-006-9169-y |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238769 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00012-21 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.3390/md17120698 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.6.3331-3336.2005 |
| [1] | 孙曼曼, 曾艳波, 许含, 姚励功, 郭跃伟, 苏明智. 中国南海豆荚软珊瑚Lobophytum sp. 的化学成分及其抗菌活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 189-197. |
| [2] | 叶禹秀, 罗小卫, 杨斌, 林秀萍, 刘永宏, 周雪峰. 南海礁栖海藻共附生真菌Pestalotiopsis neglecta SCSIO41 403次级代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 186-190. |
| [3] | 徐轶肖, 何喜林, 张腾, 蓝文陆. 北部湾棕囊藻藻华原因种分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(6): 122-130. |
| [4] | 王言丰,余景,陈丕茂,于杰,刘祝楠. 北部湾灯光罩网渔场时空分布与海洋环境关系分析 *[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(5): 68-76. |
| [5] | 黄向青, 崔振昂, 梁开, 甘华阳, 夏真, 霍振海. 北部湾暖池水域表层沉积特征及其环境指示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(1): 72-89. |
| [6] | 孙建男, 刘影, 谢为天, 徐春厚. 雷州半岛近岸海域海洋红酵母的分离鉴定[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(4): 87-92. |
| [7] | 张魁, 陈作志, 王跃中, 孙典荣, 邱永松. 北部湾短尾大眼鲷群体结构及生长、死亡和性成熟参数估计[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(5): 20-28. |
| [8] | 孙龙启, 林元烧, 陈俐骁, 曹文清, 郑连明. 北部湾北部生态系统结构与功能研究Ⅶ: 基于Ecopath模型的营养结构构建和关键种筛选[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(4): 51-62. |
| [9] | 李自立, 曹红燕, 贾春洋. 北部湾海面基于地波雷达观测“天兔”台风风场[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(4): 31-34. |
| [10] | 杨璐, 曹文清, 林元烧, 陈颖涵, 林昭进, 王雪辉. 夏季北部湾九种经济鱼类的食性类型及营养生态位初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(2): 66-75. |
| [11] | 王符菁, 林元烧, 曹文清, 张文静, 郑连明, 杨位迪, 王宇杰. 北部湾北部浮游植物群落结构及其与营养盐的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(6): 73-85. |
| [12] | 唐博, 龙江平, 金路, 许冬, 李团结. 珠江口和北部湾附近海域沉积物重金属生态风险比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(3): 75-81. |
| [13] | 龙超, 陈宪云, 陈波, 何碧娟, 高程海, 王一兵. 北部湾三角棘原甲藻(甲藻门原甲藻目)的形态观察和18S rDNA序列分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2014, 33(2): 66-71. |
| [14] | 于莹, 张武昌, 蔡昱明, 丰美萍, 李海波, 肖天. 2009年夏季北部湾浮游纤毛虫的丰度和生物量*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2014, 33(2): 60-65. |
| [15] | 李恒翔,严岩,何伟宏,邹晓理. 北部湾白龙半岛邻近海域污损生物生态研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(3): 108-113. |
|
||