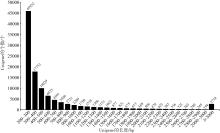
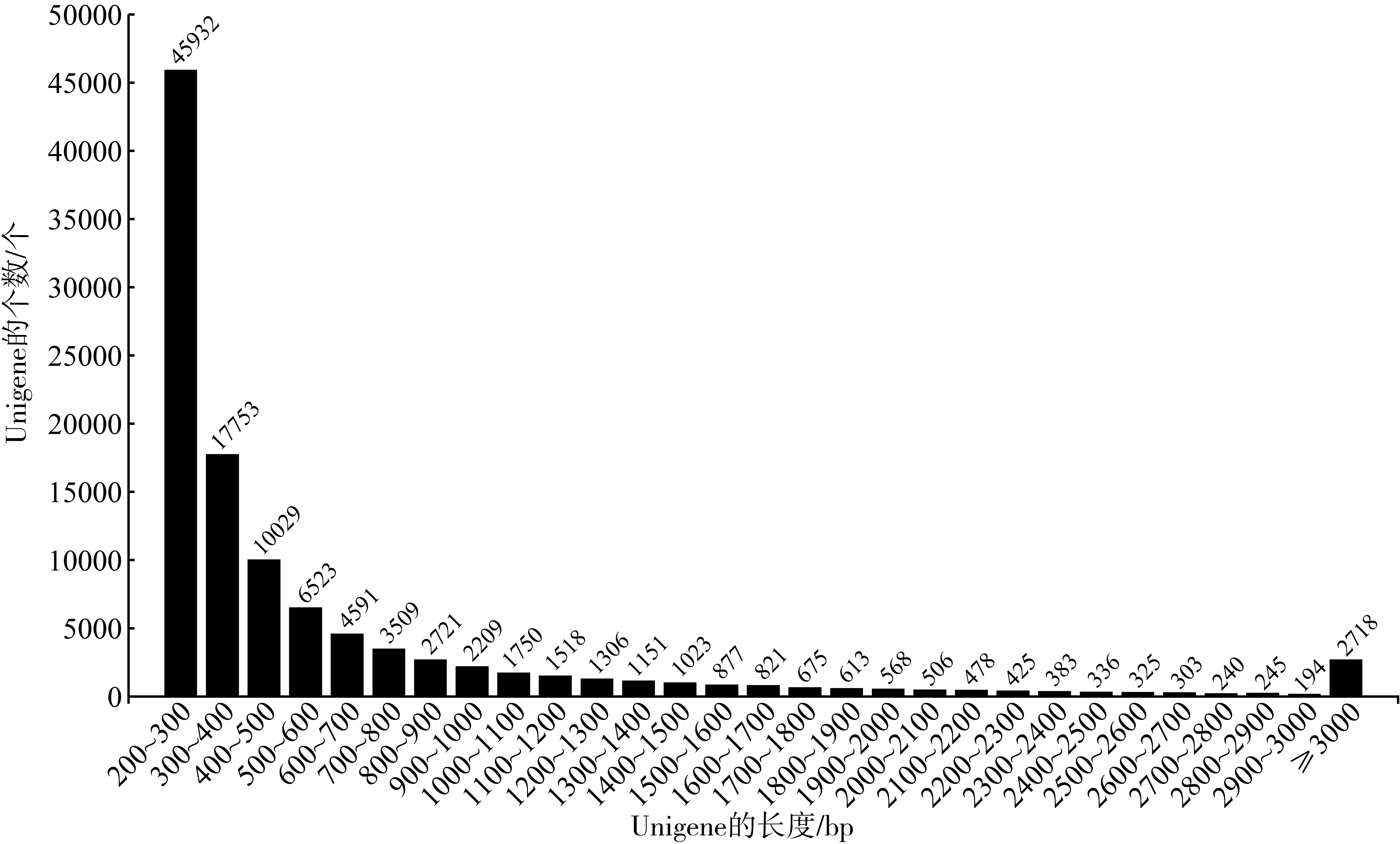
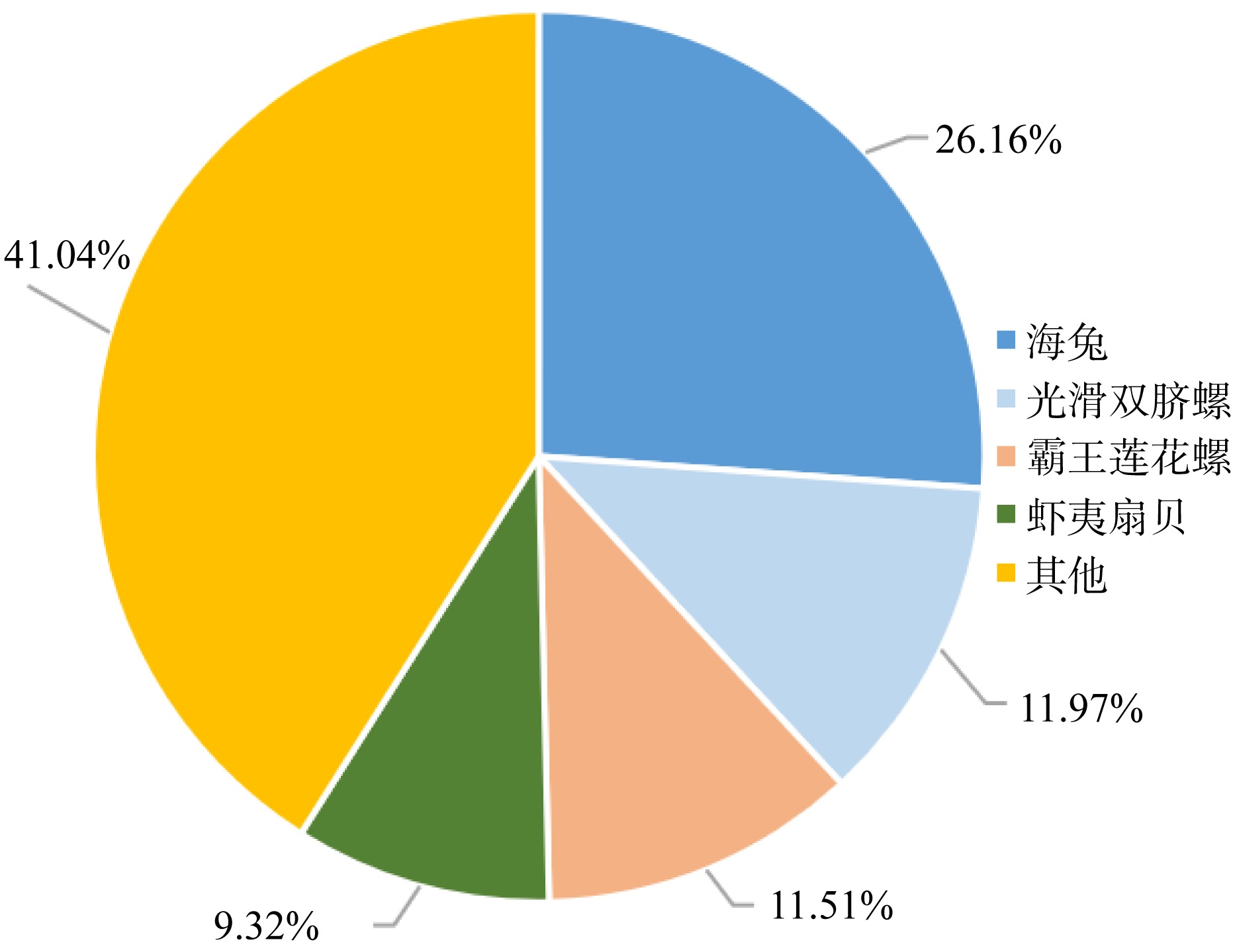
| [1] |
姜铁民, 张勇, 黄洁, 等, 2003. 合浦珠母贝26S蛋白酶体S4, S7亚基基因片段的分离与分析[J]. 海洋科学, 27(4): 28-34.
|
|
JIANG TIEMIN, ZHANG YONG, HUANG JIE, et al, 2003. Isolating and analyzing the Gene Fragements of S4 and S7 subunit of 26s proteasome from Pinctada fucata[J]. Marine Sciences, 27(4): 28-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
李琛, 郝瑞娟, 王庆恒, 等, 2017. 马氏珠母贝磺基转移酶PmCHST11基因的分子特征与表达分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 36(1): 150-157.
|
|
LI CHEN, HAO RUIJUAN, WANG QINGHENG, et al, 2017. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of pmCHST11 gene from sulfotransferase of Pinctada martensii[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 36(1): 160-167 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
潘肖兰, 刘惠茹, 许濛, 等, 2020. 马氏珠母贝水通道蛋白基因AQP4 cDNA 克隆和表达分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(3): 66-75.
doi: 10.11978/2019074
|
|
PAN XIAOLAN, LIU HUIRU, XU MENG, et al, 2020. Cloning and expression analysis of aquaporin gene AQP4 cDNA from Pinctada fucata martensii[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(3): 66-75 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
王庆恒, 郝瑞娟, 郑哲, 等, 2017. 马氏珠母贝磺基转移酶基因的克隆及功能[J]. 水产学报, 41(5): 669-677.
|
|
WANG QINGHENG, HAO RUIJUAN, ZHENG ZHE, et al, 2017. Cloning and function of sulfotransferase gene PmCHST1a in Pinctada martensii[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 41(5): 669-677 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
张格格, 2021. 法螺的遗传多样性分析及转录组测序[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学.
|
|
ZHANG GEGE, 2021. Analysis of genetic diversity of Charonia tritonis based on mtDNA COI gene sequences and transcriptome[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
BOSE U, SUWANSA-ARD S, MAIKAEO L, et al, 2017a. Neuropeptides encoded within a neural transcriptome of the giant triton snail Charonia tritonis, a crown-of-Thorns Starfish predator[J]. Peptides, 98: 3-14.
doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2017.01.004
|
| [7] |
BOSE U, WANG T, ZHAO M, et al, 2017b. Multiomics analysis of the giant triton snail salivary gland, a crown-of-thorns starfish predator[J]. Sci Rep, 7(1): 6000.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05974-x
|
| [8] |
CLAVERIE S A-M, AUDIC S, 1997. The significance of digital gene expression profiles[J]. Genome Res, 7(10): 986-995
doi: 10.1101/gr.7.10.986
|
| [9] |
GHISELLI F, IANNELLO M, PUCCIO G, et al, 2018. Comparative transcriptomics in two bivalve species offers different perspectives on the Evolution of sex-Biased genes[J]. Genome Biol Evol, 10(6): 1389-1402.
doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy082
pmid: 29897459
|
| [10] |
JOZEF K, STEPHAN K, BARBARA K, 2013. Calcium in the early evolution of living systems: a biohistorical Approach[J]. Current Organic Chemistry, 17(16): 1738-1750.
doi: 10.2174/13852728113179990081
|
| [11] |
KIM M A, RHEE J S, KIM T H, et al, 2017. Alternative splicing profile and sex-Preferential gene expression in the Female and Male pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai[J]. Genes (Basel), 8(3): 99.
doi: 10.3390/genes8030099
|
| [12] |
KLEIN A H, MOTTI C A, HILLBERG A K, et al, 2021. Development and interrogation of a transcriptomic resource for the Giant Triton Snail (Charonia tritonis)[J]. Mar Biotechnol (NY), 23(3): 501-515.
doi: 10.1007/s10126-021-10042-7
|
| [13] |
LANGMEAD B, SALZBERG S L, 2012. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2[J]. Nat Methods, 9(4): 357-359.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923
pmid: 22388286
|
| [14] |
LAVELLE C, SMITH L C, BISESI J H, J R, et al, 2018. Tissue-Based mapping of the Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas) transcriptome and proteome[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 9: 611.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00611
|
| [15] |
LI B, DEWEY C N, 2011. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome[J]. BMC Bioinform, 12: 323.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-323
|
| [16] |
LI YANGPING, ZHANG LINGLING, SUN YAN, et al, 2016. Transcriptome sequencing and comparative analysis of ovary and testis identifies potential key sex-Related genes and pathways in Scallop Patinopecten yessoensis[J]. Mar Biotechnol (NY), 18(4): 453-465.
doi: 10.1007/s10126-016-9706-8
|
| [17] |
LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D, 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method[J]. Methods, 25(4): 402-408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
pmid: 11846609
|
| [18] |
MA BIN, RAN ZHAOSHOU, XU XIAORONG, et al, 2019. Comparative transcriptome analyses provide insights into the adaptation mechanisms to acute salt stresses in juvenile Sinonovacula constricta[J]. Genes Genomics, 41(5): 599-612.
doi: 10.1007/s13258-019-00805-x
|
| [19] |
MALACHOWICZ M, WENNE R, 2019. Mantle transcriptome sequencing of Mytilus spp. and identification of putative biomineralization genes[J]. PeerJ, 6: e6245.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.6245
|
| [20] |
MOREIRA R, PEREIRO P, CANCHAYA C, et al, 2015. RNA-Seq in Mytilus galloprovincialis: comparative transcriptomics and expression profiles among different tissues[J]. Bmc Genomics, 16(1): 728.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1817-5
|
| [21] |
NIE HONGTAO, JIANG KUNYIN, JIANG LIWEN, et al, 2020. Transcriptome analysis reveals the pigmentation related genes in four different shell color strains of the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum[J]. Genomics, 112(2): 2011-2020.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2019.11.013
|
| [22] |
SHI YU, XU MENG, HUANG JING, et al, 2019. Transcriptome analysis of mantle tissues reveals potential biomineralization-related genes in Tectus pyramis Born[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics, 29: 131-144.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2018.11.010
|
| [23] |
WANG HONGDAN, PAN LUQING, XU RUIYI, et al, 2018. Comparative transcriptome analysis between the short-term stress and long-term adaptation of the Ruditapes philippinarum in response to benzo[a]pyrene[J]. Aquat Toxicol, 204: 59-69.
doi: S0166-445X(18)30636-2
pmid: 30189351
|
| [24] |
XU MENG, HUANG JING, SHI YU, et al, 2019. Comparative transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of yellow shell and black shell pearl oysters, Pinctada fucata martensii[J]. Bmc Genomics, 20(1): 469.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5807-x
|
| [25] |
YAN XIWU, NIE HONGTAO, HUO ZHONGMING, et al, 2019. Clam genome sequence clarifies the Molecular Basis of its benthic adaptation and extraordinary shell color diversity[J]. iScience, 19: 1225-1237.
doi: S2589-0042(19)30328-1
pmid: 31574780
|
| [26] |
YUEN B, POLZIN J, PETERSEN J M, 2019. Organ transcriptomes of the lucinid clam Loripes orbiculatus (Poli, 1791) provide insights into their specialised roles in the biology of a chemosymbiotic bivalve[J]. Bmc Genomics, 20(1): 820.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6177-0
pmid: 31699041
|
| [27] |
ZHANG GEGE, XU MENG, ZHANG CHENGLONG, et al, 2021. Comparative transcriptomic and expression profiles between the Foot Muscle and Mantle Tissues in the Giant Triton Snail Charonia tritonis[J]. Front Physiol, 12: 632518.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.632518
|
| [28] |
ZHANG HUA, YI XUEJIE, GUAN YUNYAN, et al, 2020. The role of the chondroitin sulfate synthase-1 gene in the immune response of the pearl oyster Pinctada fucata[J]. Fisheries Science, 86: 487-494.
doi: 10.1007/s12562-020-01420-6
|
| [29] |
ZHANG LÜ-PING, XIA JIANJUN, PENG PENGFEI, et al, 2013. Characterization of embryogenesis and early larval development in the Pacific triton, Charonia tritonis (Gastropoda: Caenogastropoda)[J]. Invertebrate Reproduction & Development, 57(3): 237-246.
|
 ), 张格格1,2, 岑希彤1,2, 何毛贤1(
), 张格格1,2, 岑希彤1,2, 何毛贤1( )
)
 ), ZHANG Gege1,2, CEN Xitong1,2, HE Maoxian1(
), ZHANG Gege1,2, CEN Xitong1,2, HE Maoxian1( )
)