| [1] |
曹西华, 俞志明, 邱丽霞, 2017. 改性黏土法消除球形棕囊藻赤潮的现场实验与效果评估[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 48(4): 753-759.
|
|
CAO XIHUA, YU ZHIMING, QIU LIXIA, 2017. Field experiment and emergent application of modified clays for Phaeocystis globosa blooms mitigation[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 48(4): 753-759 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
胡晓坤, 张清春, 陈振帆, 等, 2019. 北部湾海域球形棕囊藻遗传多样性分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 50(3): 601-610.
|
|
HU XIAOKUN, ZHANG QINGCHUN, CHEN ZHENFAN, et al, 2019. Genetic diversity of Phaeocystis globosa strains isolated from the Beibu Gulf, the South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 50(3): 601-610 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
胡晓燕, 殷明焱, 夏娃, 等, 2006. 中国金色藻属四个新记录种的超微结构研究[J]. 植物分类学报, 44(1): 64-71.
|
|
HU XIAOYAN, YIN MINGYAN, XIA WA, et al, 2006. Ultrastructure studies on four newly recorded species of Chrysochromulina (Haptophyta) in China[J]. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 44(1): 64-71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
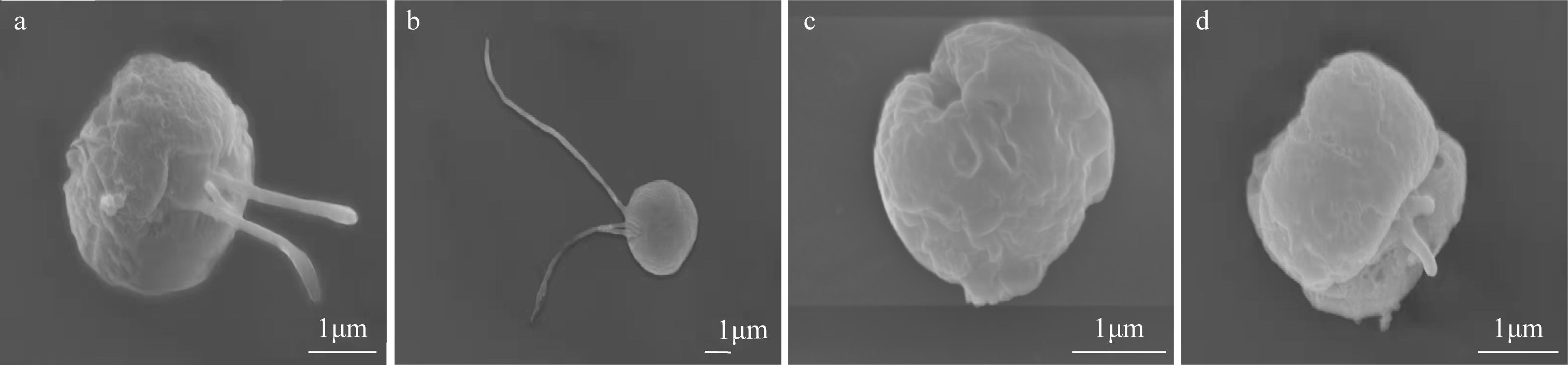
胡章喜, 邓蕴彦, 唐赢中, 2019. 我国北部湾球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)的表面形态和细胞超微结构的电镜观察[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 50(3): 621-629.
|
|
HU ZHANGXI, DENG YUNYAN, TANG YINGZHONG, 2019. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy observation on morphology and ultrastructure of Phaeocystis globosa from Beibu Gulf, China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 50(3): 621-629 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
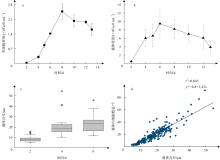
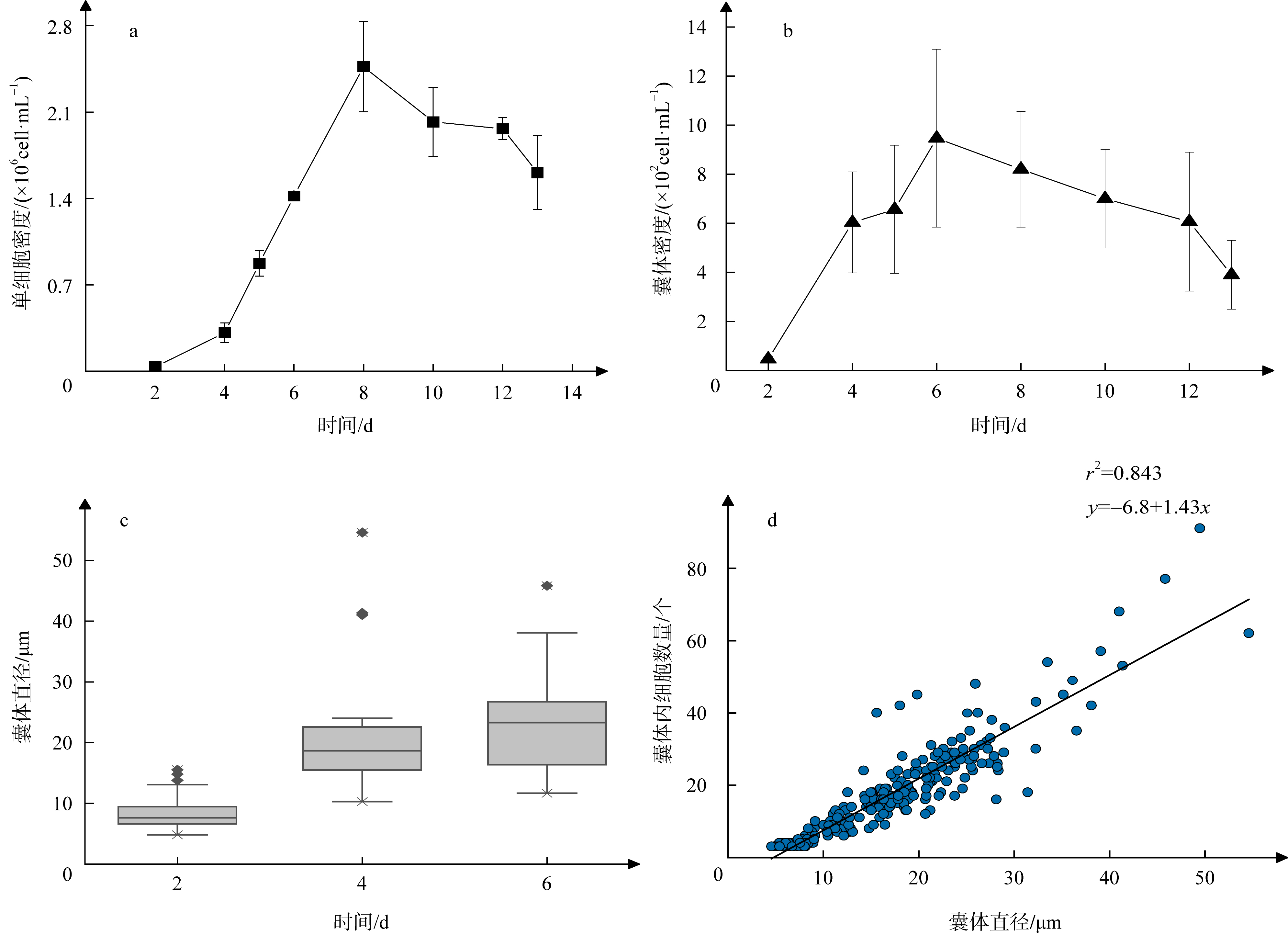
李杰, 陆家昌, 赖俊翔, 等, 2022. 球形棕囊藻游离单细胞的密度与囊体形成的关系研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 40(1): 84-95.
|
|
LI JIE, LU JIACHANG, LAI JUNXIANG, et al, 2022. Study on the relationship between solitary cell density and colony formation of Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel[J]. Plant Science Journal, 40(1): 84-95 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
刘洁生, 彭喜春, 杨维东, 2007. 球形棕囊藻溶血毒素对兔红细胞作用的AFM观察[J]. 热带海洋学报, 26(2): 55-58.
|
|
LIU JIESHENG, PENG XICHUN, YANG WEIDONG, 2007. AFM observation of hemolytic extracts from Phaeocystis globosa on rabbit erythrocytes[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 26(2): 55-58 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
刘悦, 李丽, 翟晓辉, 等, 2022. 深圳大鹏湾一次球形棕囊藻藻华的发生过程及成因分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(3): 164-171.
doi: 10.11978/2021148
|
|
LIU YUE, ZHAI XIAOHUI, et al, 2022. Analysis of the bloom caused by colonial Phaeocystis globosa in Mirs Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 41(3): 164-171 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
覃仙玲, 赖俊翔, 陈波, 等, 2016. 棕囊藻北部湾株的18S rDNA分子鉴定[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 24(2): 176-181.
|
|
QIN XIANLING, LAI JUNXIANG, CHEN BO, et al, 2016. Molecular Identification of Phaeocystis from Beibu Gulf based on 18S rDNA sequences[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 24(2): 176-181 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
曲凌云, 吕颂辉, 高春蕾, 等, 2008. 棕囊藻渤海株核糖体18S rDNA和ITS基因结构序列分析[J]. 海洋科学进展, 26(2): 200-206.
|
|
QU LINGYUN, LYU SONGHUI, GAO CHUNLEI, et al, 2008. Structure and sequence analysis of 18S rDNA and ITS gene of Phaeocystis isolate from the Bohai Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 26(2): 200-206 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
沈萍萍, 齐雨藻, 2021. 棕囊藻属(Phaeocystis)的种类多样性及地理分布特征研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 52(1): 1-15.
|
|
SHEN PINGPING, QI YUZAO, 2021. Research progress on species diversity and distribution of the genus Phaeocystis[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 52(1): 1-15 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
沈萍萍, 齐雨藻, 欧林坚, 2018. 中国沿海球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)的分类、分布及其藻华[J]. 海洋科学, 42(10): 146-162.
|
|
SHEN PINGPING, QI YUZAO, OU LINJIAN, 2018. Phaeocystis globosa in coastal China: taxonomy, distribution, and its blooms[J]. Marine Sciences, 42(10): 146-162 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
沈萍萍, 王艳, 齐雨藻, 等, 2000. 球形棕囊藻的生长特性及生活史研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 24(6): 635-643.
|
|
SHEN PINGPING, WANG YAN, QI YUZAO, et al, 2000. Growth characteristics and life cycle of Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 24(6): 635-643 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
王一奇, 丁翔翔, 宋会银, 等, 2023. 青岛近海球形棕囊藻的宏条形码分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 54(5): 1351-1362.
|
|
WANG YIQI, DING XIANGXIANG, SONG HUIYIN, et al, 2023. Metabarcoding analysis of Phaeocystis globosa in Qingdao coastal regions[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 54(5): 1351-1362 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
厦门大学, 2012-03-28. 球形棕囊藻培养液的除菌方法.中国: CN201110329306.8[P](in Chinese).
|
| [15] |
徐轶肖, 何喜林, 张腾, 等, 2020. 北部湾棕囊藻藻华原因种分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(6): 122-130.
doi: 10.11978/2020030
|
|
XU YIXIAO, HE XILIN, ZHANG TENG, et al, 2020. Causative species of Phaeocystis blooms in Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(6): 122-130 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
薛玥, 2023. 中国沿海球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel)遗传多样性研究[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学.
|
|
XUE YUE, 2023. Genetic diversity of Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel in the Chinese seas[D]. Yantai: Yantai University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
晏荣军, 尹平河, 潘剑宇, 等, 2006. 棕囊藻囊泡的培养与去除研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 25(3): 69-71.
|
|
YAN RONGJUN, YIN PINGHE, PAN JIANYU, et al, 2006. Studies on cultivation and removal of colonies of Phaeocytstis globosa[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 25(3): 69-71 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
杨和福, 2004. 棕囊藻的生物学概述Ⅰ. 形态分类和生理生态学[J]. 东海海洋, 22(1): 49-63.
|
|
YANG HEFU, 2004. The biology of Phaeocystis Ⅰ. the morphology, physiology and ecology of Phaeocystis[J]. Donghai Marine Science, 22(1): 49-63 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
张昆, 2020. 球形棕囊藻囊体形成的分子机制[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
ZHANG KUN, 2020. Molecular mechanism involved in the colony formation of Phaeocystis globosa[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [20] |
BAI LIN, LI HUILIN, 2019. Cryo-EM is uncovering the mechanism of eukaryotic protein N-glycosylation[J]. The FEBS Journal, 286(9): 1638-1644.
|
| [21] |
BAR-PELED M, GRIFFITH C L, ORY J J, et al, 2004. Biosynthesis of UDP-GlcA, a key metabolite for capsular polysaccharide synthesis in the pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans[J]. Biochemical Journal, 381: 131-136.
|
| [22] |
BAUMANN M E M, BRANDINI F P, STAUBES R, 1994. The influence of light and temperature on carbon-specific DMS release by cultures of Phaeocystis antarctica and three antarctic diatoms[J]. Marine Chemistry, 45(1-2): 129-136.
|
| [23] |
GAEBLER-SCHWARZ S, DAVIDSON A, ASSMY P, et al, 2010. A new cell stage in the haploid-diploid life cycle of the colony-forming haptophyte Phaeocystis antarctica and its ecological implications[J]. Journal of Phycology, 46(5): 1006-1016.
|
| [24] |
GUISELIN N, COURCOT L, ARTIGAS L F, et al, 2009. An optimised protocol to prepare Phaeocystis globosa morphotypes for scanning electron microscopy observation[J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 77(1): 119-123.
|
| [25] |
GÜGI B, LE COSTAOUEC T, BUREL C, et al, 2015. Diatom-specific oligosaccharide and polysaccharide structures help to unravel biosynthetic capabilities in diatoms[J]. Marine Drugs, 13(9): 5993-6018.
doi: 10.3390/md13095993
pmid: 26393622
|
| [26] |
HAMM C E, SIMSON D A, MERKEL R, et al, 1999. Colonies of Phaeocystis globosa are protected by a thin but tough skin[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 187: 101-111.
|
| [27] |
LIANG DAYONG, WANG XIAODONG, HUO YIPING, et al, 2021. Differences between solitary cells and colonial cells in the heteromorphic life cycle of Phaeocystis globosa: Morphology, physiology, and transcriptome[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 20(4): 939-948.
|
| [28] |
LIANG DAYONG, XIANG HUA, JIN PENG, et al, 2023. Response mechanism of harmful algae Phaeocystis globosa to ocean warming and acidification[J]. Environmental Pollution, 320: 121008.
|
| [29] |
NIU ZHUANG, LIU CHAO, ZHANG QINGCHUN, et al, 2022. Development of sensitive genotype-specific quantitative polymerase chain reaction methods for detection of Phaeocystis globosa in the South China Sea[J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 20(3): 131-145.
|
| [30] |
ROUSSEAU V, CHRÉTIENNOT-DINET M J, JACOBSEN A, et al, 2007. The life cycle of Phaeocystis: state of knowledge and presumptive role in ecology[J]. Biogeochemistry, 83(1-3): 29-47.
|
| [31] |
SHEN PINGPING, VAN RIJSSEL M, WANG YAN, et al, 2004. Toxic Phaeocystis globosa strains from China grow at remarkably high temperatures[C]// Harmful algae 2002. Florida, USA: Florida Marine Research Institute: 396-398.
|
| [32] |
SONG HUIYIN, LIU FENG, LI ZELIN, et al, 2020. Development of a high-resolution molecular marker for tracking Phaeocystis globosa genetic diversity through comparative analysis of chloroplast genomes[J]. Harmful Algae, 99: 101911.
|
| [33] |
VALLET S D, BERTHOLLIER C, RICARD-BLUM S, 2022. The glycosaminoglycan interactome 2.0[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, 322(6): C1271-C1278.
|
| [34] |
VAN RIJSSEL M, HAMM C, GIESKES W, 1997. Phaeocystis globosa (Prymnesiophyceae) colonies: hollow structures built with small amounts of polysaccharides[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 32(2): 185-192.
|
| [35] |
WANG XIAODONG, WANG YAN, OU LINJIAN, et al, 2015. Allocation Costs Associated with Induced Defense in Phaeocystis globosa (Prymnesiophyceae): the Effects of Nutrient Availability[J]. Scientific Reports, 5(1): 10850.
|
| [36] |
ZHANG QINGCHUN, NIU ZHUANG, WANG JINXIU, et al, 2021. Development of high-resolution chloroplast markers for intraspecific phylogeographic studies of Phaeocystis globosa[J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 39(2): 508-524.
|
| [37] |
ZHANG SHUFENG, ZHANG KUN, CHENG HUAMIN, et al, 2020. Comparative transcriptomics reveals colony formation mechanism of a harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 719: 137454.
|
| [38] |
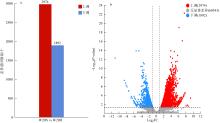
ZHU JIANAN, YU ZHIMING, HE LIYAN, et al, 2023. Mechanisms of Phaeocystis globosa blooms in the Beibu Gulf revealed by metatranscriptome analysis[J]. Harmful Algae, 124: 102407.
|
 ), XUE Yue, MENG Bufan, FU Feng, SHEN Pingping(
), XUE Yue, MENG Bufan, FU Feng, SHEN Pingping( )
)