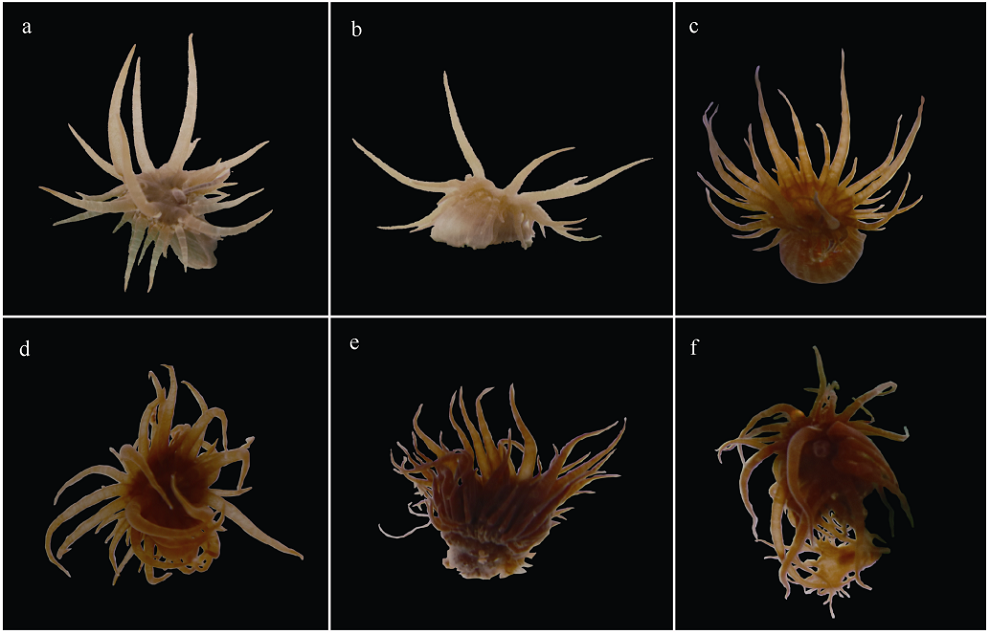
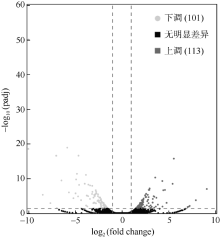
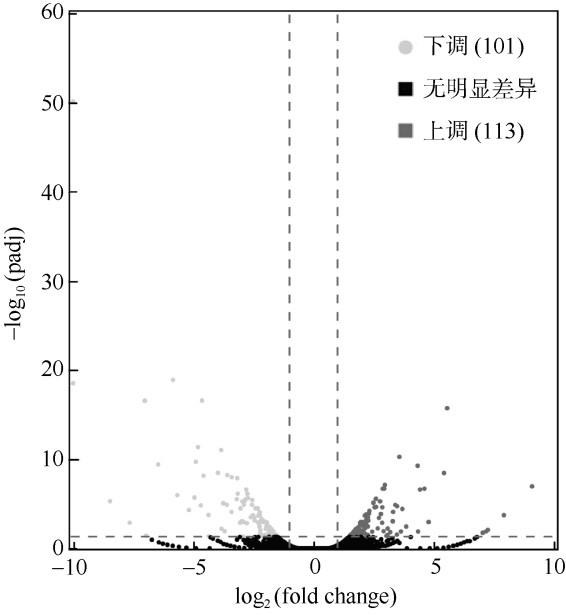
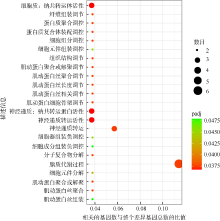
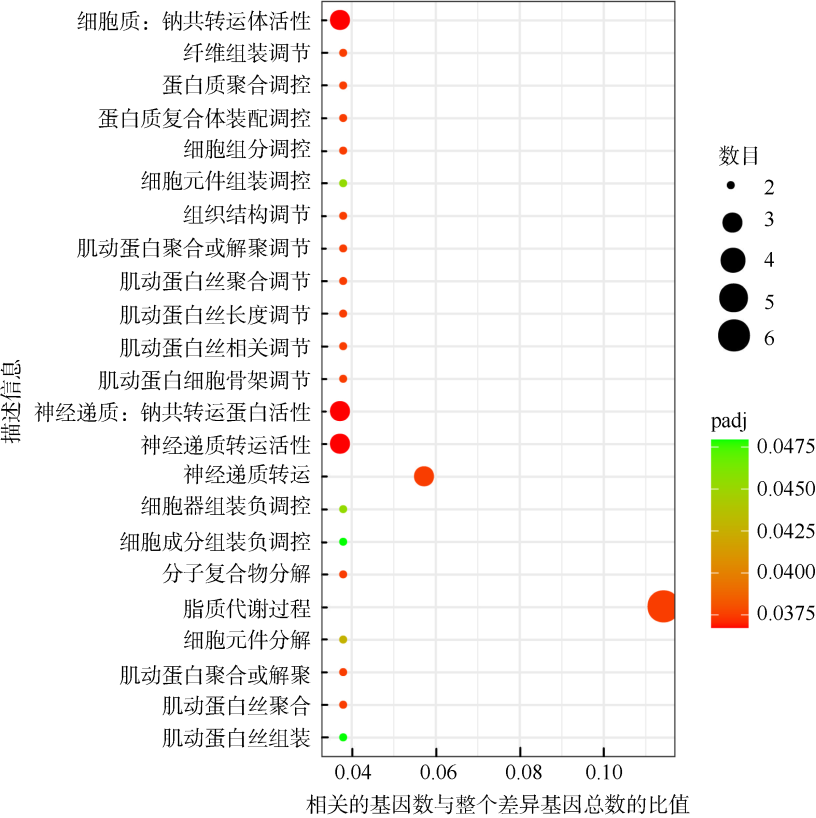
| [1] |
黄晖, 许昌有, 袁涛, 2013. 造礁石珊瑚白化相关功能基因的研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(4):43-50.
|
|
HUANG HUI, XU CHANGYOU, YUAN TAO, 2013. Research progress on functional genes involved in coral bleaching[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 32(4):43-50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
李新正, 寇琦, 王金宝, 等, 2020. 中国海洋无脊椎动物分类学与系统演化研究进展与展望[J]. 海洋科学, 44(7):26-70.
|
|
LI XINZHENG, KOU QI, WANG JINBAO, et al, 2020. Advances and perspectives of researches on taxonomy and phylogeny of marine invertebrates in China[J]. Marine Sciences, 44(7):26-70 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
李秀保, 黄晖, 练健生, 等, 2007. 珊瑚及共生藻在白化过程中的适应机制研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 27(3):1217-1225.
|
|
LI XIUBAO, HUANG HUI, LIAN JIANSHENG, et al, 2007. Progress of adaptive mechanism of coral and symbiotic algae during bleaching[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27(3):1217-1225 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
BARUCH R, AVISHAI N, RABINOWITZ C, 2005. UV incites diverse levels of DNA breaks in different cellular compartments of a branching coral species[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 208(5):843-848.
doi: 10.1242/jeb.01496
|
| [5] |
BAUMGARTEN S, SIMAKOV O, ESHERICK L Y, et al, 2015. The genome of Aiptasia, a sea anemone model for coral symbiosis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(38):11893-11898.
|
| [6] |
BIERI T, ONISHI M, XIANG TINGTING, et al, 2016. Relative contributions of various cellular mechanisms to loss of algae during Cnidarian bleaching[J]. PLoS One, 11(4):e0152693.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152693
|
| [7] |
BUDDEMEIER R W, FAUTIN D G, 1993. Coral bleaching as an adaptive mechanism: A testable hypojournal[J]. BioScience, 43(5):320-326.
doi: 10.2307/1312064
|
| [8] |
DE ORTE M R, CLOWEZ S, CALDEIRA K, 2019. Response of bleached and symbiotic sea anemones to plastic microfiber exposure[J]. Environmental Pollution, 249:512-517.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.100
|
| [9] |
DESALVO M K, VOOLSTRA C R, SUNAGAWA S, et al, 2008. Differential gene expression during thermal stress and bleaching in the Caribbean coral Montastraea faveolata[J]. Molecular Ecology, 17(17):3952-3971.
doi: 10.1111/mec.2008.17.issue-17
|
| [10] |
DOUGLAS A E, 2003. Coral bleaching--how and why?[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46(4):385-392.
doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00037-7
|
| [11] |
DUNN S R, BYTHELL J C, TISSIER M D A, et al, 2002. Programmed cell death and cell necrosis activity during hyperthermic stress-induced bleaching of the symbiotic sea anemone Aiptasia sp.[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 272(1):29-53.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00036-9
|
| [12] |
FREUDENTHAL H D, 1962. Symbiodinium gen. nov. and Symbiodinium microadriaticum sp. nov., a Zooxanthella: Taxonomy, Life Cycle, and Morphology[J]. Journal of Protozoology, 9(1):45-52.
doi: 10.1111/jeu.1962.9.issue-1
|
| [13] |
HOU JING, XU TAO, SU DINGJIA, et al, 2018. RNA-Seq reveals extensive transcriptional response to heat stress in the stony coral Galaxea fascicularis[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 9:37.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00037
|
| [14] |
HOWE P L, REICHELT-BRUSHETT A J, CLARK M W, 2012. Aiptasia pulchella: a tropical cnidarian representative for laboratory ecotoxicological research[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 31(11):2653-2662.
doi: 10.1002/etc.v31.11
|
| [15] |
HOWE P L, REICHELT-BRUSHETT A J, CLARK M W, 2014. Development of a chronic, early life-stage sub-lethal toxicity test and recovery assessment for the tropical zooxanthellate sea anemone Aiptasia pulchella[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 100:138-147.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.10.024
|
| [16] |
HU MINJIE, ZHENG XIAOBIN, FAN CHENMING, et al, 2020. Lineage dynamics of the endosymbiotic cell type in the soft coral Xenia[J]. Nature, 582(7813):534-538.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2385-7
|
| [17] |
KOCH J C, VERDE E A, WEIS V M, 2020. Carbonic anhydrases are influenced by the size and symbiont identity of the aggregating sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 223(13): jeb221424.
|
| [18] |
LESSER M P, 2011. Coral bleaching: causes and mechanisms[M]// DUBINSKY Z, STAMBLER N. Coral Reefs: An Ecosystem in Transition. Berlin: Springer: 405-419.
|
| [19] |
MORGAN M B, PARKER C C, ROBINSON J W, et al, 2012. Using Representational Difference Analysis to detect changes in transcript expression of Aiptasia genes after laboratory exposure to lindane[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 110- 111:66-73.
|
| [20] |
NII C M, MUSCATINE L, 1997. Oxidative stress in the symbiotic sea anemone Aiptasia pulchella (Carlgren, 1943): Contribution of the animal to superoxide ion production at elevated temperature[J]. Biological Bulletin, 192(3):444-456.
doi: 10.2307/1542753
|
| [21] |
PINZÓN J H, KAMEL B, BURGE C A, et al, 2015. Whole transcriptome analysis reveals changes in expression of immune-related genes during and after bleaching in a reef-building coral[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2(4):140214.
doi: 10.1098/rsos.140214
|
| [22] |
SAWYER S J, MUSCATINE L, 2001. Cellular mechanisms underlying temperature-induced bleaching in the tropical sea anemone Aiptasia pulchella[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 204(20):3443-3456.
doi: 10.1242/jeb.204.20.3443
|
| [23] |
SONG P C, WU T M, HONG MINGCHANG, et al, 2015. Elevated temperature inhibits recruitment of transferrin-positive vesicles and induces iron-deficiency genes expression in Aiptasia pulchella host-harbored Symbiodinium[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 188:1-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2015.05.005
|
| [24] |
SUBRAMANIAN A, TAMAYO P, MOOTHA V K, et al, 2005. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(43):15545-15550.
|
| [25] |
TRAPNELL C, WILLIAMS B A, PERTEA G, et al, 2010. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 28(5):511-515.
doi: 10.1038/nbt.1621
|
| [26] |
VAN TREUREN W, BROWER K K, LABANIEH L, et al, 2019. Live imaging of Aiptasia larvae, a model system for coral and anemone bleaching, using a simple microfluidic device[J]. Scientific Reports, 9(1):9275.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45167-2
|
| [27] |
WENG LICHI, PASARIBU B, LIN I P, et al, 2014. Nitrogen deprivation induces lipid droplet accumulation and alters fatty acid metabolism in symbiotic dinoflagellates isolated from Aiptasia pulchella[J]. Scientific Reports, 4(1):5777.
doi: 10.1038/srep05777
|
| [28] |
ZHU BAOHUA, WANG GUANGCE, HUANG BO, 2004. Effects of temperature, hypoxia, ammonia and nitrate on the bleaching among three coral species[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(18):1923-1928.
doi: 10.1007/BF03184283
|
 ), YAN Hao, WANG Lu(
), YAN Hao, WANG Lu( )
)