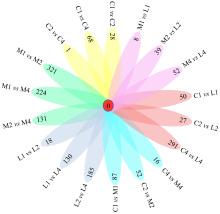
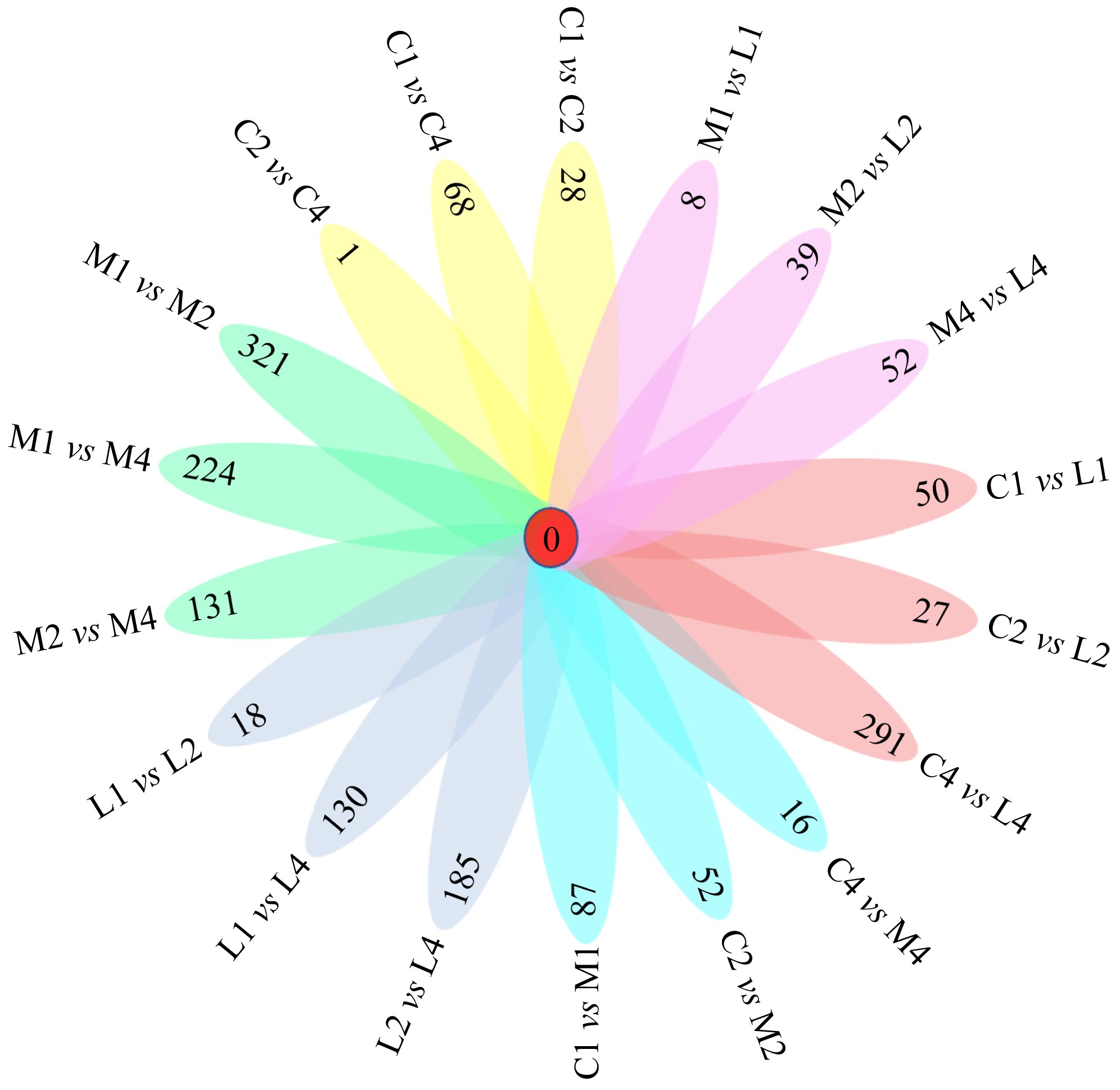
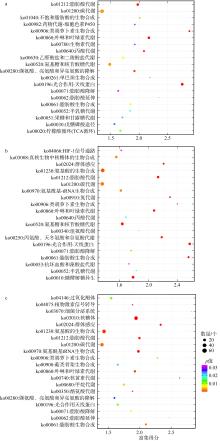
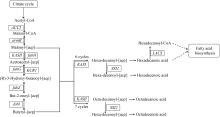
| [1] |
曹月蕾, 2021. 集胞藻PCC6803类胡萝卜素和脂肪酸代谢途径关键基因功能研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学.
|
|
CAO YUELEI, 2021. Research on the function of key genes in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 carotenoid and fatty acid metabolism pathway[D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
高彦龙, 吴玉霞, 张仲兴, 等, 2022. 苹果ELO家族基因鉴定及其在低温胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 49(8): 1621-1636.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0545
|
|
GAO YANLONG, WU YUXIA, ZHANG ZHONGXING, et al, 2022. Bioinformatics analysis of apple ELO gene family and its expression analysis under low temperature stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 49(8): 1621-1636 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
高羽荞, 闫博巍, 赵莹, 等, 2018. 碱蓬转录组分析及油脂合成相关基因表达模式[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 40(6): 801-811.
doi: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2018.06.009
|
|
GAO YUQIAO, YAN BOWEI, ZHAO YING, et al, 2018. Transcriptome analysis of Suaeda salsa and expression profiles of genes related to oil synthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 40(6): 801-811 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
黄璐, 2020. 海洋硅藻假微型海链藻休眠细胞形成过程的应激响应与长期适应机制[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
HUANG LU, 2020. Stress response and long-term acclimation mechanisms involves in the formation of resting cells of the marine diatom Thalassiosira pseuodnana[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
刘淑雅, 陈楠生, 2021. 胶州湾海域浮游植物和赤潮物种的生物多样性研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 45(4): 170-188.
|
|
CHEN SHUYA, CHEN NANSHENG, 2021. Advances in biodiversity analysis of phytoplankton and harmful algal bloom species in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 45(4): 170-188 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
刘璇, 张莹, 李爱芬, 2022. 活性氧介导微藻脂质积累的研究现状及进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 58(7): 1201-1211.
|
|
LIU XUAN, ZHANG YING, LI AIFEN, 2022. Research progress on reactive oxygen species-mediated lipid accumulation in microalgae[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 58(7): 1201-1211 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
聂煜东, 耿媛媛, 张贤明, 等, 2021. 产油微藻胁迫培养策略研究综述[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(8): 3853-3866.
|
|
NIE YUDONG, GENG YUANYUAN, ZHANG XIANMING, et al, 2021. A review on stress cultivation strategies of oleginous microalgae[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(8): 3853-3866 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
王延莉, 曹阳, 梁祎凡, 等, 2022. 绵羊ACAA1基因多态性及其与肉质性状的关联性分析[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 44(2): 204-209.
|
|
WANG YANLI, CAO YANG, LIAN YIFAN, et al, 2022. Polymorphism of ACAA1 gene and its association with meat quality traits in sheep[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 44(2): 204-209 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
位文倩, 孙昕, 黄峰, 等, 2022. 转录组揭示自养和混合培养栅藻油脂代谢途径差异[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 44(1): 130-137.
doi: 10.19802/j.issn.1007-9084.2020325
|
|
WEI WENQIAN, SUN XIN, HUANG FENG, et al, 2022. Transcriptome reveals differences in lipid metabolism pathways between autotrophic and mixotrophic Desmodesmus sp.[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 44(1): 130-137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
于仁成, 吕颂辉, 齐雨藻, 等, 2020. 中国近海有害藻华研究现状与展望[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(4): 768-788.
|
|
YU RENCHENG, LYU SONGHUI, QI YUZAO, et al, 2020. Progress and perspectives of harmful algal bloom studies in China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 51(4): 768-788 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
张梅, 米铁柱, 甄毓, 等, 2018. 基于玛氏骨条藻转录组的脂肪酸合成途径分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 48(4): 81-93.
|
|
ZHANG MEI, MI TIEZHU, ZHEN YU, et al, 2018. Description of fatty acid synthesis pathway based on Skeletonema marinoi transcriptome[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 48(4): 81-93 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
周婧雯, 丁玉娇, 曾晓蓉, 等, 2020. 生菜种子低温处理后耐冻性和脂肪酸合成代谢的关系研究[J]. 亚热带植物科学, 49(1): 9-14.
|
|
ZHOU JINGWEN, DING YUJIAO, ZENG XIAORONG, et al, 2020. Relationship between freezing tolerance and fatty acid biosynthesis in lettuce seeds after low temperature treatment[J]. Subtropical Plant Science, 49(1): 9-14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
庄珊珊, 2019. 海洋硅藻假微型海链藻休眠细胞形成过程的相关代谢调控[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
ZHAUNG SHANSAHN, 2019. Cellular metabolic modulation during the resting cells formation in marine diatom Thalassiosira pseuodnana[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
ABOMOHRA A E, SHANG H, EL-SHEEKH M, et al, 2019. Night illumination using monochromatic light-emitting diodes for enhanced microalgal growth and biodiesel production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 288: 121514.
doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121514
|
| [15] |
ASLAN S, HOFVANDER P, DUTTA P, et al, 2015. Transient silencing of the KASⅡ genes is feasible in Nicotiana benthamiana for metabolic engineering of wax ester composition[J]. Scientific Reports, 5: 11213.
doi: 10.1038/srep11213
|
| [16] |
BENMOUSSA-DAHMEN I, CHTOUROU H, REZGUI F, et al, 2016. Salinity stress increases lipid, secondary metabolites and enzyme activity in Amphora subtropica and Dunaliella sp. for biodiesel production[J]. Bioresource Technology, 218: 816-825.
doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.022
|
| [17] |
BIDLE K D, 2016. Programmed cell death in Unicellular Phytoplankton[J]. Current Biology, 26(13): R594-R607.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.05.056
|
| [18] |
BOLGER A M, LOHSE M, USADEL B, 2014. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data[J]. Bioinformatics, 30(15): 2114-2120.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
pmid: 24695404
|
| [19] |
CHENG R, GE Y, YANG B, et al, 2013. Cloning and functional analysis of putative malonyl-CoA: acyl-carrier protein transacylase gene from the docosahexaenoic acid-producer Schizochytrium sp. TIO1101[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 29(6): 959-967.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-013-1253-0
|
| [20] |
FIELD C B, BEHRENFELD M J, RANDERSON J T, et al, 1998. Primary production of the biosphere: integrating terrestrial and oceanic components[J]. Science, 281(5374): 237-240.
doi: 10.1126/science.281.5374.237
|
| [21] |
GONG FAHUI, LI GUIHAO, WANG YAPING, et al, 2020. Spatial shifts in size structure, phylogenetic diversity, community composition and abundance of small eukaryotic plankton in a coastal upwelling area of the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 42(6): 650-667.
|
| [22] |
KHATOON H, ABDU RAHMAN N, BANERJEE S, et al, 2014. Effects of different salinities and pH on the growth and proximate composition of Nannochloropsis sp. and Tetraselmis sp. isolated from South China Sea cultured under control and natural condition[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 95: 11-18.
|
| [23] |
LOVIO-FRAGOSO J P, DE JESÚS-CAMPOS D, LÓPEZ-ELÍAS J A, et al, 2021. Biochemical and molecular aspects of phosphorus limitation in diatoms and their relationship with biomolecule accumulation[J]. Biology, 10(7): 565.
doi: 10.3390/biology10070565
|
| [24] |
MSANNE J, XU DI, KONDA A R, et al, 2012. Metabolic and gene expression changes triggered by nitrogen deprivation in the photoautotrophically grown microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Coccomyxa sp. C-169[J]. Phytochemistry, 75: 50-59.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.12.007
|
| [25] |
NAKANISHI K, NISHIJIMA M, NISHIMURA M, et al, 1996. Bacteria that induce morphogenesis in Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta) grown under axenic conditions[J]. Journal of Phycology, 32(3): 479-482.
doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3646.1996.00479.x
|
| [26] |
PIDKOWICH M S, NGUYEN H T, HEILMANN I, et al, 2007. Modulating seed beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase Ⅱ level converts the composition of a temperate seed oil to that of a palm-like tropical oil[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(11): 4742-4747.
|
| [27] |
RAY J L, HARAMATY L, THYRHAUG R, et al, 2014. Virus infection of Haptolina ericina and Phaeocystis pouchetii implicates evolutionary conservation of programmed cell death induction in marine haptophyte-virus interactions[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 36(4): 943-955.
doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbu029
|
| [28] |
ROESSLER P G, OHLROGGE J B, 1993. Cloning and characterization of the gene that encodes acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase in the alga Cyclotella cryptica[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 268(26): 19254-19259.
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)36507-X
|
| [29] |
SHARMA T, GOUR R S, KANT A, et al, 2015. Lipid content in Scenedesmus species correlates with multiple genes of fatty acid and triacylglycerol biosynthetic pathways[J]. Algal Research, 12: 341-349.
doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2015.09.006
|
| [30] |
SUN XIAOMAN, REN LUJING, ZHAO QUANYU, et al, 2019. Enhancement of lipid accumulation in microalgae by metabolic engineering[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 1864(4): 552-566.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.10.004
|
| [31] |
TONON T, QING RENWEI, HARVEY D, et al, 2005. Identification of a long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid acyl-coenzyme A synthetase from the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana[J]. Plant Physiology, 138(1): 402-408.
doi: 10.1104/pp.104.054528
|
| [32] |
YANG JIA, LI XIN, HU HONGYING, et al, 2011. Growth and lipid accumulation properties of a freshwater microalga, Chlorella ellipsoidea YJ1, in domestic secondary effluents[J]. Applied Energy, 88(10): 3295-3299.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.11.029
|
 ), 李佳岷1,2, 王华龙3, 米铁柱1,2,4(
), 李佳岷1,2, 王华龙3, 米铁柱1,2,4( ), 甄毓1,2,4
), 甄毓1,2,4
 ), LI Jiamin1,2, WANG Hualong3, MI Tiezhu1,2,4(
), LI Jiamin1,2, WANG Hualong3, MI Tiezhu1,2,4( ), ZHEN Yu1,2,4
), ZHEN Yu1,2,4