热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 140-153.doi: 10.11978/2023022CSTR: 32234.14.2023022
西沙群岛中新世藻礁白云岩植物格架、储层特征和成礁模式*
陈舒1,2( ), 许红2,3, 卢树参3,4, 张海洋5, 马亚增1,2, 罗进雄1(
), 许红2,3, 卢树参3,4, 张海洋5, 马亚增1,2, 罗进雄1( )
)
- 1.长江大学, 湖北 武汉 430100
2.自然资源部第一海洋研究所, 山东 青岛 266061
3.中国地质调查局青岛海洋地质研究所, 山东 青岛 266071
4.中国石油大学(华东), 山东 青岛 266580
5.河北省地震局保定中心台, 河北 保定 071000
-
收稿日期:2023-02-21修回日期:2023-05-25出版日期:2024-03-10发布日期:2024-03-26 -
作者简介:陈舒(1996—), 女, 山东省济宁市人, 硕士研究生, 从事沉积学研究。email: 1542866059@qq.com
*感谢青岛海洋地质研究所、中海石油湛江分公司提供样品支持。许红为共同第一作者。
-
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2017FY201407); 国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2012CB956004); 国家油气重大专项(2011ZX05025-002-04); 国家自然科学基金项目(41106064)
The framework, reservoir characteristics and reef formation model of Miocene algal reef dolomite in the Xisha Islands*
CHEN Shu1,2( ), XU Hong2,3, LU Shushen3,4, Zhang Haiyang5, MA Yazeng1,2, LUO Jinxiong1(
), XU Hong2,3, LU Shushen3,4, Zhang Haiyang5, MA Yazeng1,2, LUO Jinxiong1( )
)
- 1. Yangtze University, Wuhan 430100, China
2. The First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, Qingdao 266061, China
3. Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, China Geological Survey, Qingdao 266071, China
4. China University of Petroleum (East China), Qingdao 266580, China
5. Baoding Center Seismic Station, Hebei Earthquake Agency, Baoding 071000, China
-
Received:2023-02-21Revised:2023-05-25Online:2024-03-10Published:2024-03-26 -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program(2017FY201407); National Key Basic Research and Development Program(2012CB956004); National Key Oil and Gas Project(2011ZX05025-002-04); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41106064)
摘要:
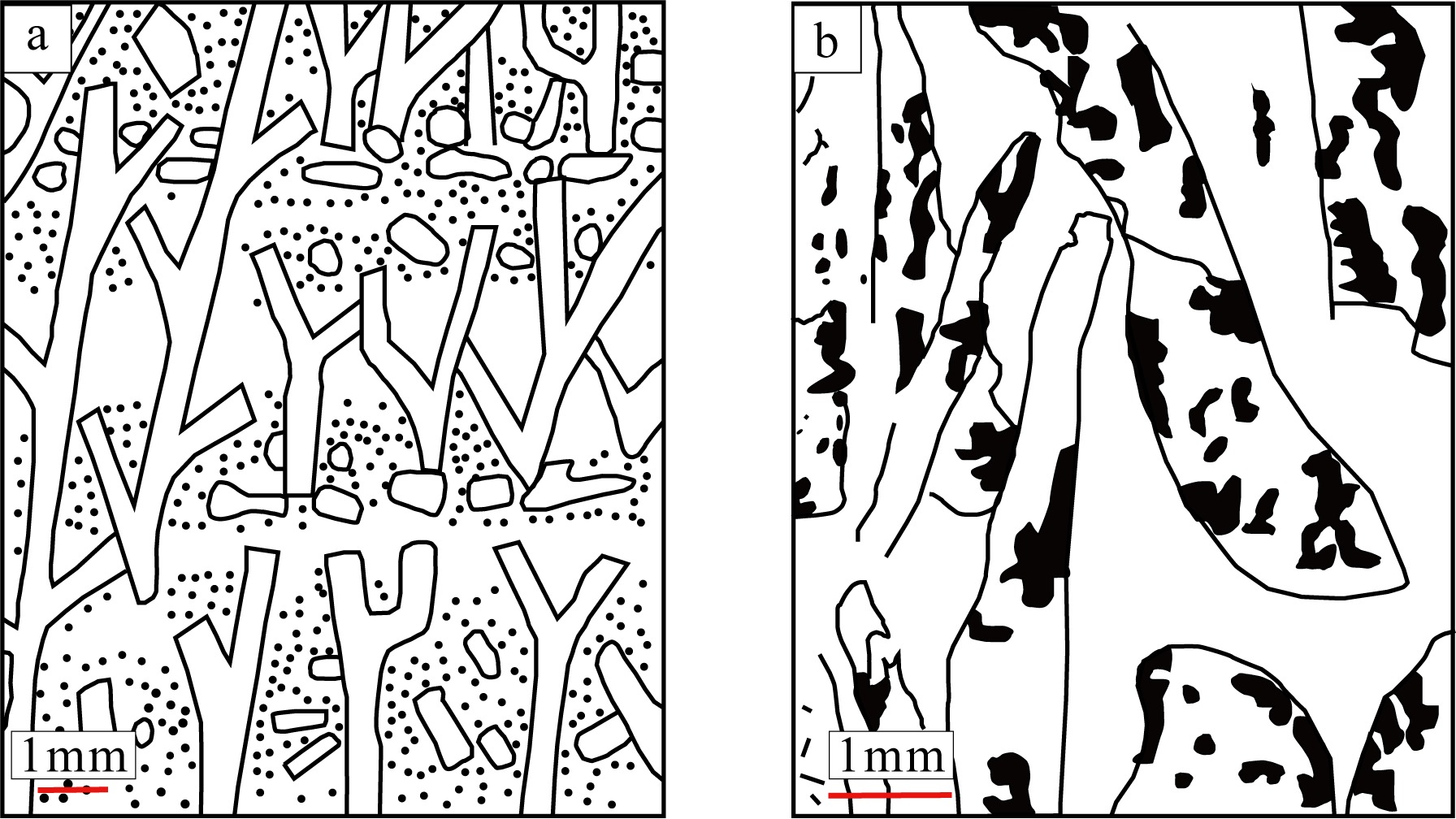
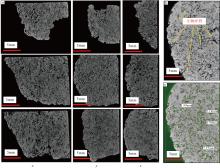
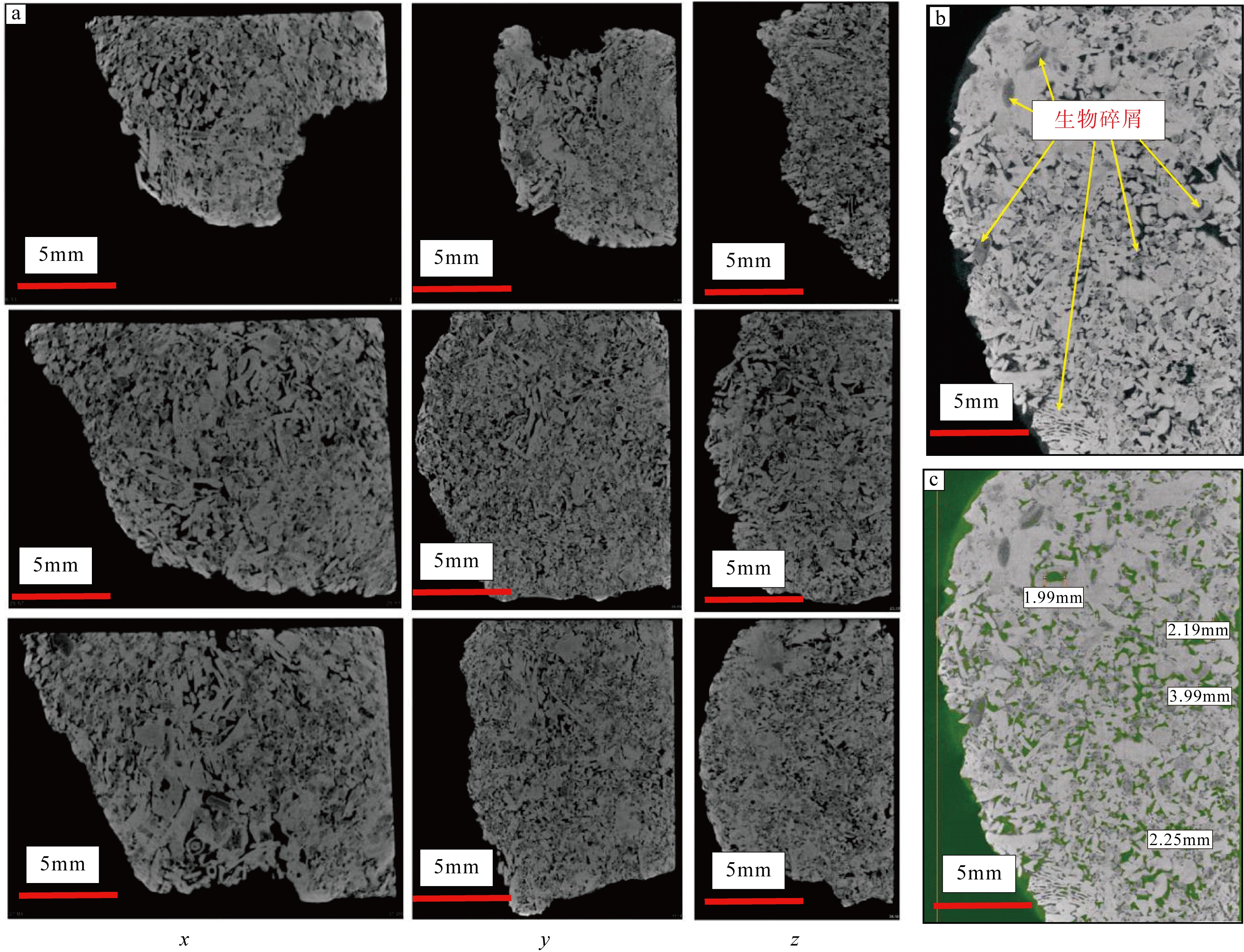
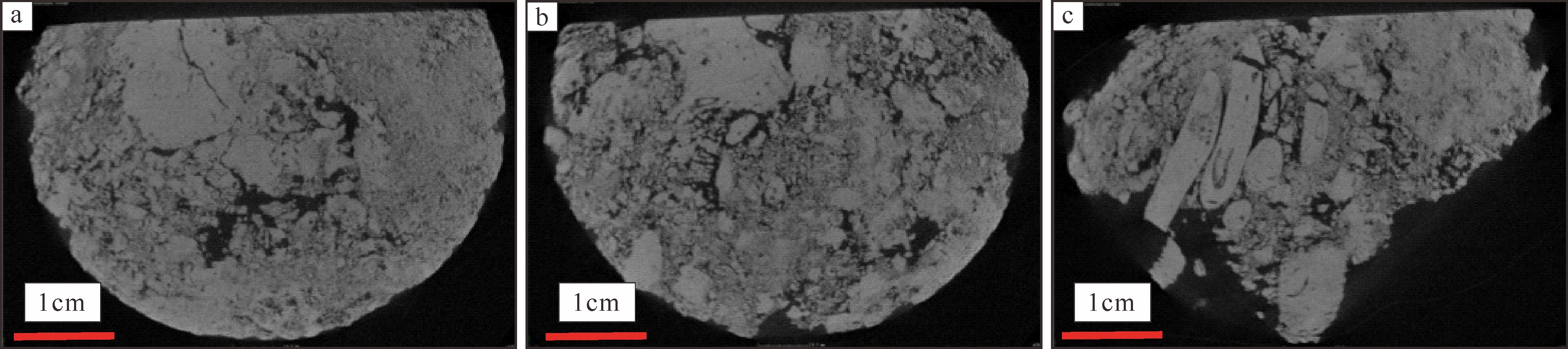
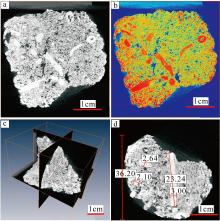
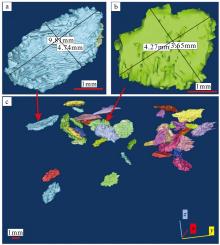
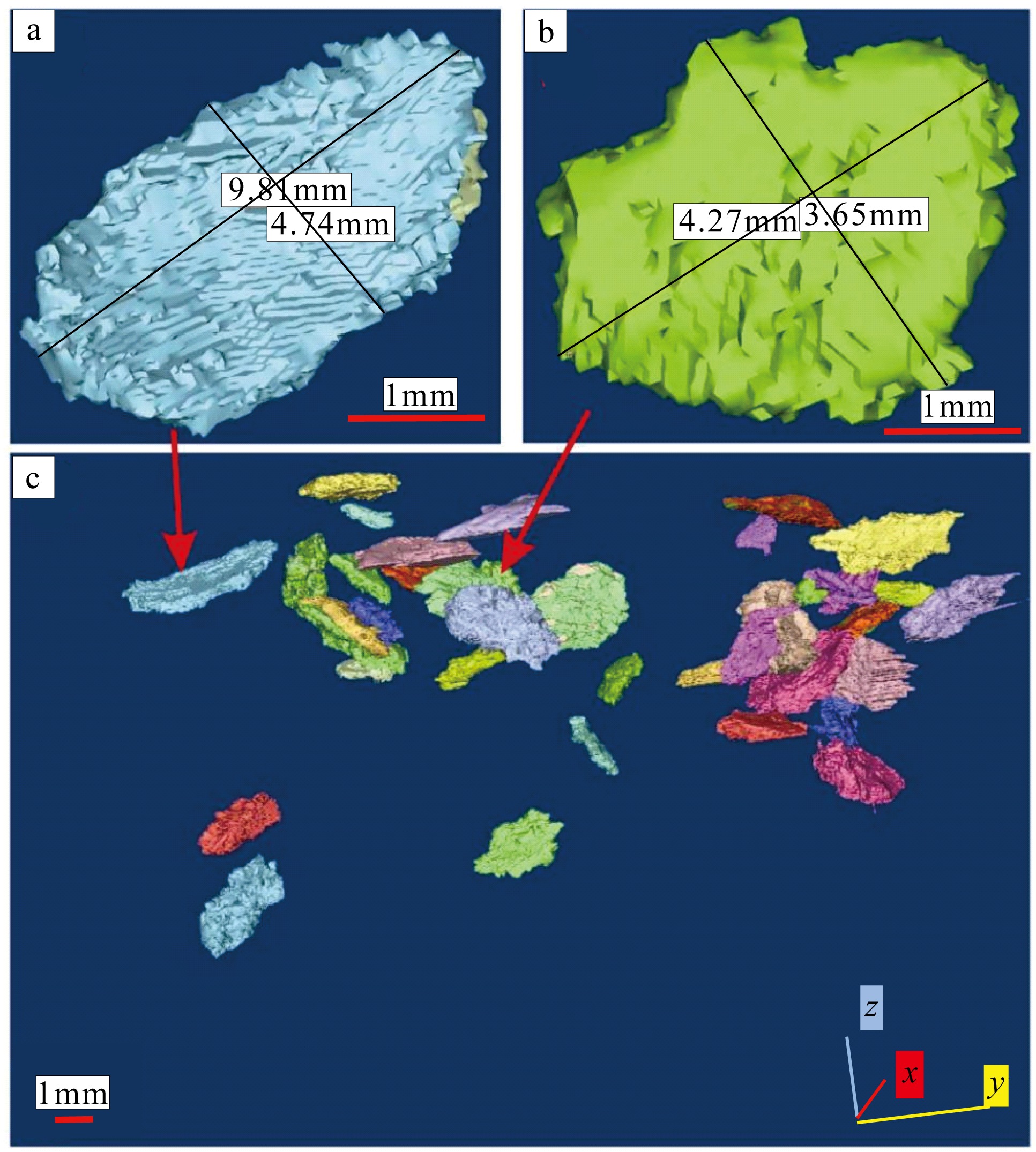
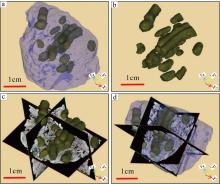
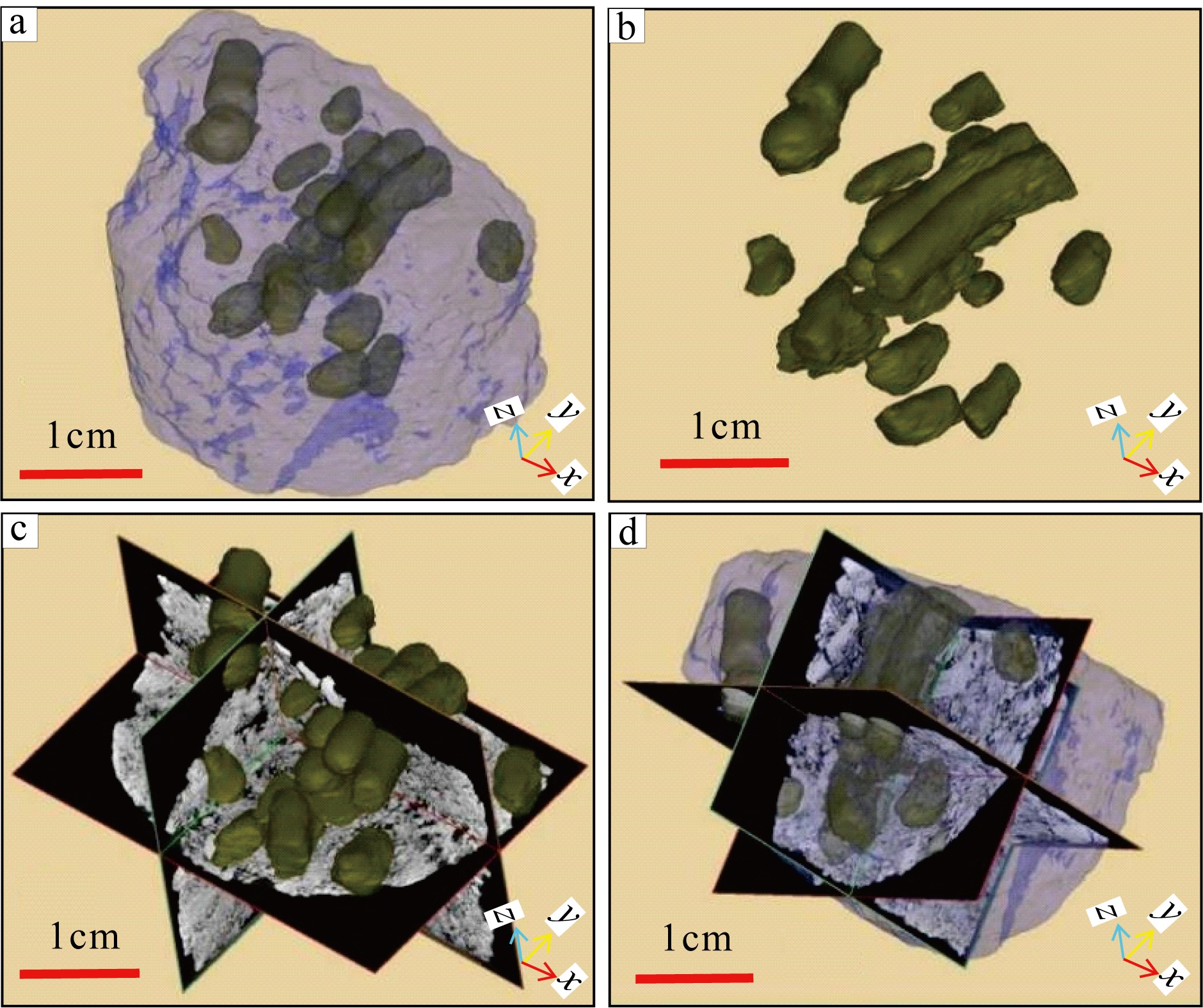
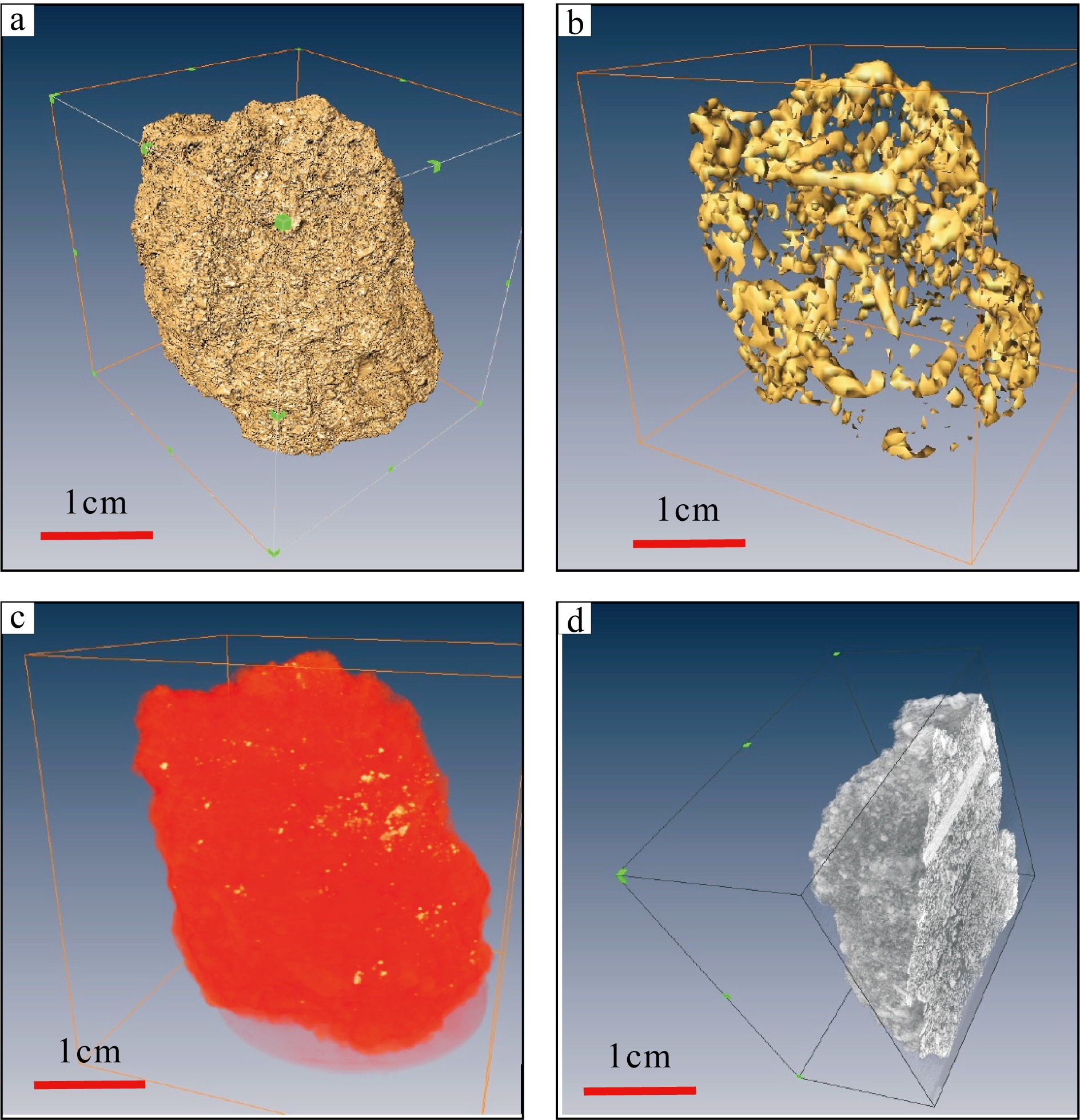
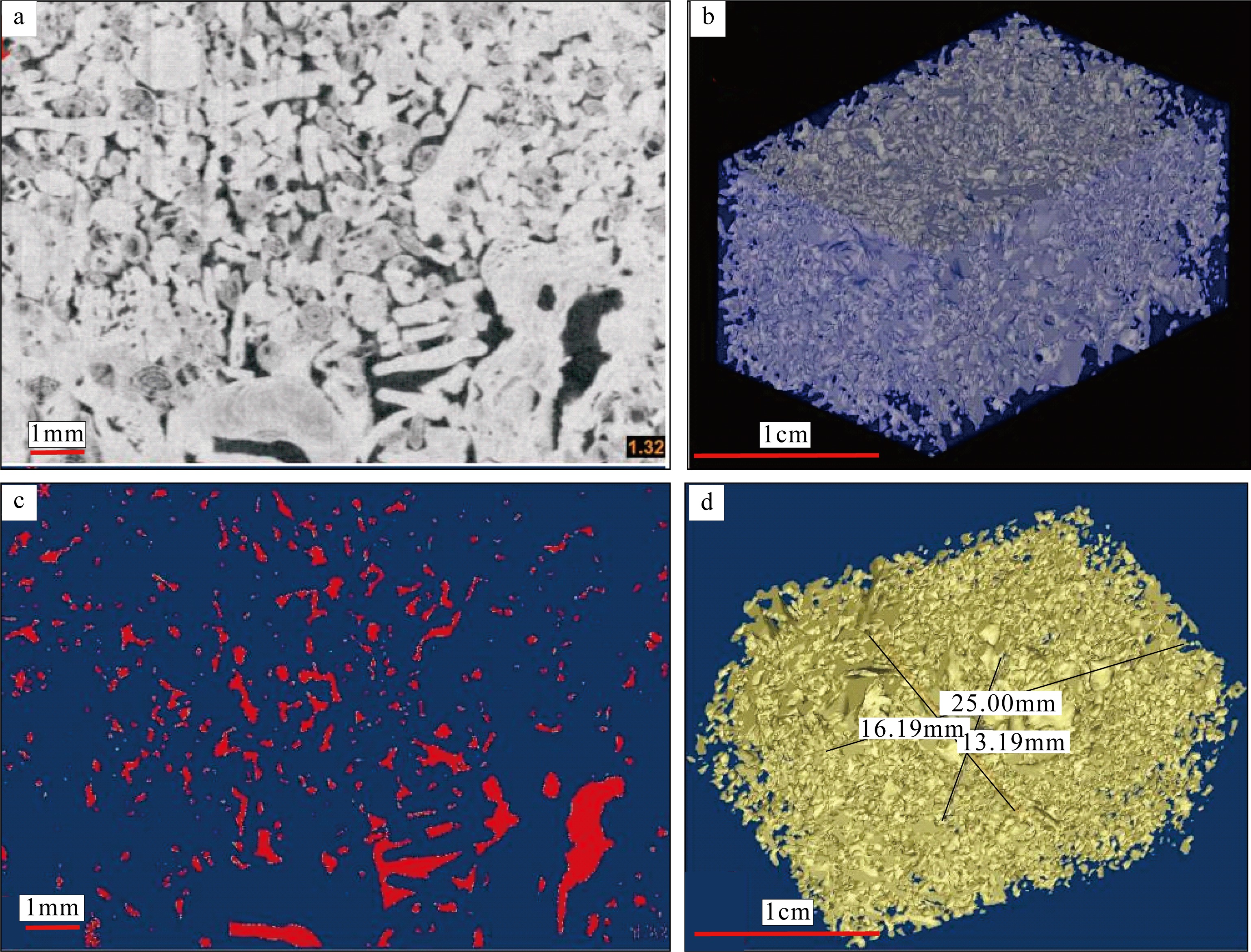
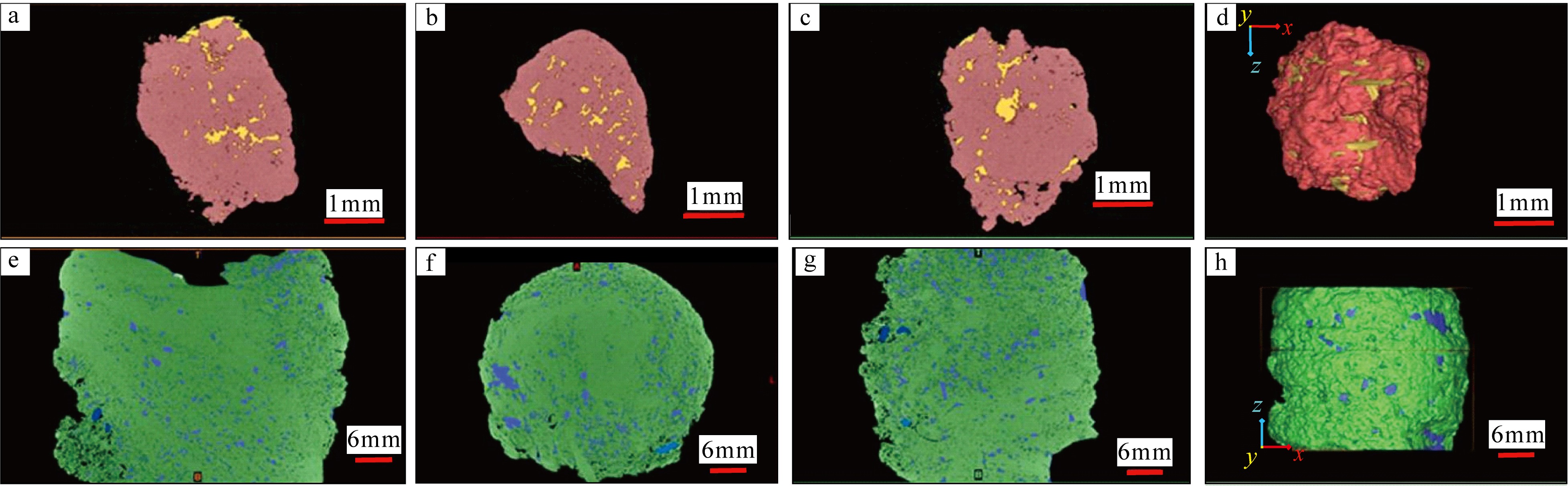
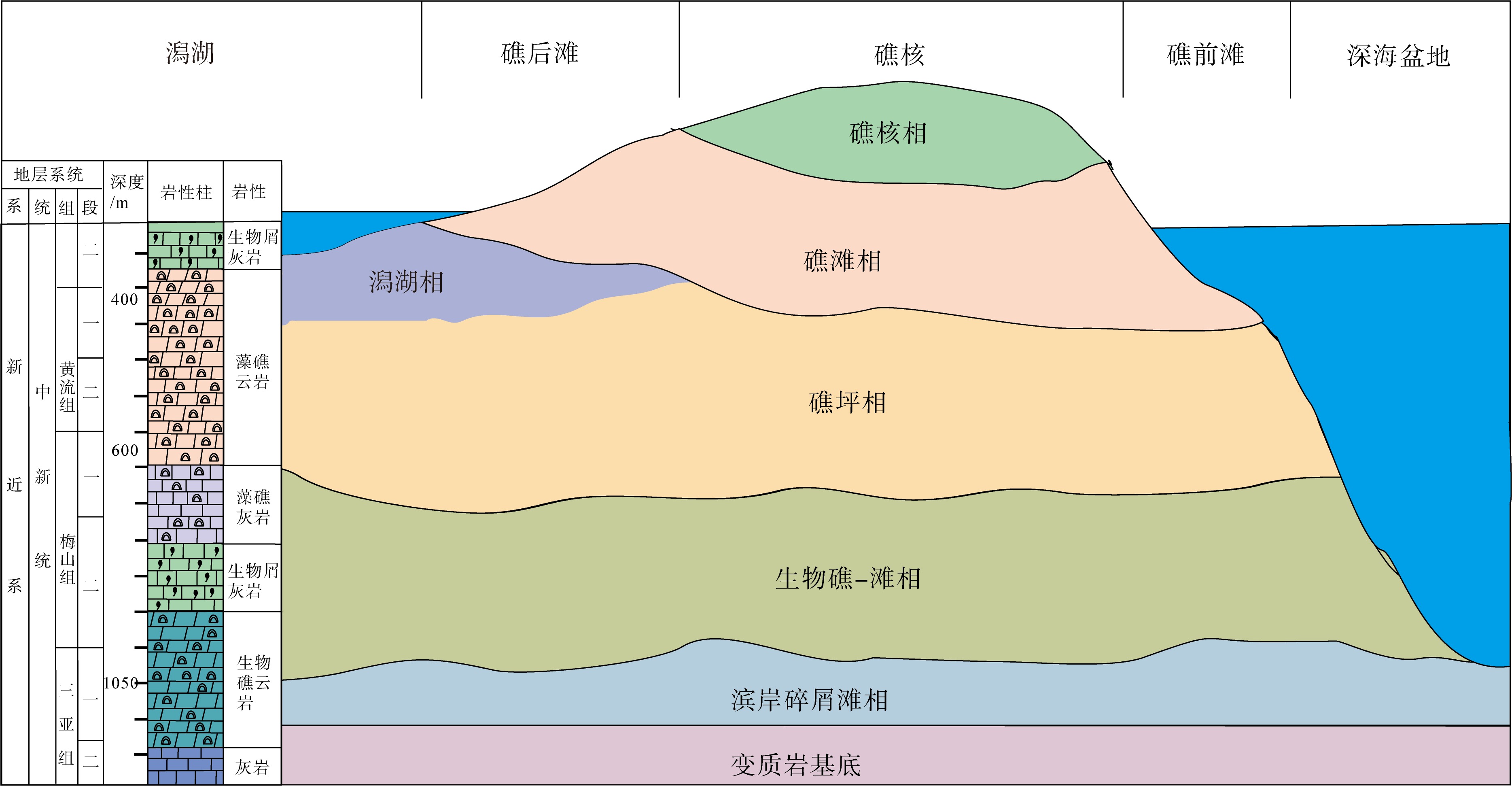
传统生物礁成因理论质疑钙藻形成坚固生物礁抗浪结构的能力, 将钙藻归类于附礁生物群落。文章利用微焦X射线扫描成像技术(X-CT), 研究“西科1井”、“西永2井”中新世红藻珊瑚藻科南海奇石藻(新种)格架岩和绿藻仙掌藻节片岩岩芯。通过三维层析成像直观透视图像, 发现钙藻生物营造的藻礁抗浪结构, 包括典型红藻柱状格架结构、障积结构和绿藻仙掌藻节片结构, 证实钙藻植物是主要的造礁造岩生物。通过三维孔隙重构, 获得总孔隙体积、面孔率、孔隙度的物性参数, 验证了藻礁是南海沉积盆地中新世重要的油气储集层。提出了藻礁成因模式: 造礁钙藻适应海面升降逐步演替-取代, 经过钙化-埋藏化石化-白云石化, 沉积生成藻礁云岩, 造成中新世西沙礁纵向序列的增长。
引用本文
陈舒, 许红, 卢树参, 张海洋, 马亚增, 罗进雄. 西沙群岛中新世藻礁白云岩植物格架、储层特征和成礁模式*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 140-153.
CHEN Shu, XU Hong, LU Shushen, Zhang Haiyang, MA Yazeng, LUO Jinxiong. The framework, reservoir characteristics and reef formation model of Miocene algal reef dolomite in the Xisha Islands*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 140-153.
| [1] |
白斌, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等, 2013. 利用多尺度CT成像表征致密砂岩微观孔喉结构[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 40(3): 329-333.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈斯忠, 胡平忠, 1987. 珠江口盆地第三纪生物礁及其找油意义[J]. 中国海上油气, 1(1): 3-10.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈浩, 黄继新, 常广发, 等, 2018. 基于全岩心CT的遗迹化石识别及沉积环境分析: 以加拿大麦凯Ⅲ油砂区块为例[J]. 古地理学报, 20(4): 703-712.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
范嘉松, 1996. 中国生物礁与油气[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
高林志, 邢裕盛, 刘桂芝, 1995. 吉林浑江地区新元古代微古植物群及其沉积环境[J]. 地层古生物论文集, (2): 1-23, 124-127.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
侯健, 李振泉, 张顺康, 等, 2008. 岩石三维网络模型构建的实验和模拟研究[J]. 中国科学, 8(11): 1563-1575.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
蒋观利, 吴青柏, 蒲毅彬, 等, 2005. 甲烷水合物形成过程的CT识别原理和成像特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 16(6): 814-817.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
李菊花, 郑斌, 2015. 微观孔隙分形表征新方法及其在页岩储层中的应用[J]. 天然气工业, 35(5): 52-59.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李玉彬, 李向良, 张奎祥, 等, 2000. 微焦点X射线计算机层析(CMT)及其在石油研究领域的应用[J]. CT理论与应用研究, 9(3): 35-40.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李越, 穆西南,
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
李越, 穆西南, 袁金良, 等, 2001. 山东中寒武世钙藻礁的层位拟定[C]. 中国古生物学会第21届学术年会论文摘要集: 20-21.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
廉培庆, 高文彬, 汤翔, 等, 2020. 基于CT扫描图像的碳酸盐岩油藏孔隙分类方法[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 41(4): 852-861.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
刘月田, 郭分乔, 涂彬, 等, 2005. 全岩心非均匀径向渗流各向异性渗透率测定方法[J]. 石油学报, 26(6): 66-68.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200506014 |
|
|
|
| [14] |
刘志礼, 1990. 化石藻类学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
马文国, 刘傲雄, 2011. CT扫描技术对岩石孔隙结构的研究[J]. 中外能源, 16(7): 54-56.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
马骁, 许红, 付和平, 等, 2021. 海洋造礁仙掌藻研究进展及西沙石岛仙掌藻[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 37(6): 77-83.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
穆西南, 1982. 西藏的一些钙藻化石. 青藏高原科学考察丛书, 西藏古生物(第五分册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:205-240.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
穆西南, 王玉净, 1985. 西藏定日始新世的一些钙藻化石[J]. 微体古生物学报, (3): 289- 299, 323-325.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
穆西南, 严惠君, 李越, 等, 2003b. 华北地台东部中寒武世微生物礁的时空分布[J]. 微体古生物学报, (3): 279-285.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
穆西南, 袁训来, 2003a. 绪论: 化石藻类和叠层石[J]. 微体古生物学报, (1): 1-2.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
彭瑞东, 杨彦从, 鞠杨, 等, 2011. 基于灰度CT图像的岩石孔隙分形维数计算[J]. 科学通报, 56(26): 2256-2266.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
钱凯, 王淑芬, 1986. 济阳坳陷下第三系礁灰岩及礁灰岩油气藏[J]. 石油勘探与开发, (5): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
钱凯, 王素民, 刘淑范, 等, 1980. 华东北部下第三系礁灰岩的发现及其石油地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 25(24): 1140-1142.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
孙海, 姚军, 张磊, 等, 2014. 基于孔隙结构的页岩渗透率计算方法[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 38(2): 92-98.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
孙建孟, 闫国亮, 姜黎明, 等, 2014. 基于数字岩心研究流体性质对裂缝性低渗透储层弹性参数的影响规律[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 38(3): 39-44.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
王玉净, 1976. 珠穆朗玛峰地区晚白垩世及早第三纪钙藻化石. 珠穆朗玛峰地区科学考察报告(1966—1968), 古生物(第二分册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:425-457.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
王玉净, 勾韵娴, 章炳高, 等, 1996. 西沙群岛西琛一井中新世地层、古生物群和古环境研究[J]. 微体古生物学报, (3): 215-223.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
吴洁, 刘成东, 张守鹏, 等, 2012. 显微CT技术在石油地质中的应用初探[J]. 江西科学, 30(5): 634-637.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
邢裕盛, 1987. 前寒武纪微古植物学在我国的发展和应用[J]. 地层古生物论文集, (1): 8-28 (in Chinese).
|
| [30] |
邢裕盛, 刘桂芝, 1973. 燕辽地区震旦纪微古植物群及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, (1): 1-64 (in Chinese).
|
| [31] |
邢裕盛, 刘桂芝, 1980. 鄂西震旦亚界微古植物群及其地层意义[J]. 地层古生物论文集, (1): 1-14, 91-96, 124.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
邢裕盛, 刘桂芝, 1982. 中国晚前寒武纪微古植物群及其地层意义[C]. 中国地质科学院文集, (4): 55-67.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
许红, 1992. 中国海域及邻区含油气盆地生物礁的对比研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 12(4): 41-52.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
许红, 蔡峰, 王玉净, 等, 1999. 西沙中新世生物礁演化与藻类的造礁作用[J]. 科学通报, 43(13): 1435-1439 (in Chinese).
|
| [35] |
姚艳斌, 刘大锰, 蔡益栋, 等, 2010. 基于NMR和X-CT的煤的孔裂隙精细定量表征[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 40(11): 1598-1607 (in Chinese).
|
| [36] |
曾鼎乾, 1981. 南海北部大陆架第三系[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
章海宁, 姜黎明, 张金功, 等, 2014. 岩石结构对碎屑岩储层弹性参数影响的数值研究[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 50(6): 773-778.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
张明书, 何起祥, 业治铮, 1989. 西沙生物礁碳酸盐沉积地质学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-117.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
赵永刚, 赵明华, 赵永鹏, 等, 2006. 一种分析碳酸盐岩孔隙系统数字图像的新方法[J]. 天然气工业, 26(12): 75-78.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
朱浩然, 1979. 山东滨县下第三系沙河街组的藻类化石[J]. 古生物学, 18(4): 327-346.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
朱袁智, 沙庆安, 郭丽芬, 等, 1997. 南沙群岛永暑礁新生代珊瑚礁地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.10.016 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.04.003 |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00302016 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00304068 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(03)00074-7 |
| [49] |
doi: 10.3354/meps09892 |
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
doi: 10.3354/meps09309 |
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2011.04.006 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.4236/msa.2013.48A003 |
| [56] |
doi: 10.1111/jpy.2007.43.issue-1 |
| [57] |
doi: 10.1023/A:1026287816324 |
| [58] |
|
| [1] | 雷明凤, 余克服, 廖芝衡, 陈飚, 黄学勇, 陈小燕. 西沙群岛银屿珊瑚礁的生态快速退化及其对鱼类的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 87-99. |
| [2] | 高洁, 余克服, 许慎栋, 黄学勇, 陈飚, 王永刚. 西沙群岛永乐环礁礁外坡沉积物中有机碳的含量与来源分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [3] | 赵金发, 刘永, 李纯厚, 王腾, 石娟, 肖雅元, 吴鹏, 宋晓宇. 应用高通量测序技术研究永乐环礁和东岛鱼卵种类组成和分布[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 127-136. |
| [4] | 黄海波, 丘学林, 龙根元, 矫东风, 韩孝辉. 利用接收函数方法约束西沙碳酸盐岩台地沉积厚度与速度结构[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 135-144. |
| [5] | 冯英辞, 詹文欢, 姚衍桃, 孙杰, 刘守金, 李健. 西沙群岛礁区的地质构造及其活动性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(3): 48-53. |
| [6] | 邓晓东, 刘军亮, 蔡树群. 南海西沙群岛陆架区的潮流特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(4): 8-12. |
| [7] | 晏宏,孙立广,刘晓东,邱世灿. 近50年来南海西沙群岛海域气候异常的ENSO效应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(5): 29-35. |
|
||