热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 81-91.doi: 10.11978/2023083CSTR: 32234.14.2023083
广西涠洲岛蛭态轮虫物种多样性及生境偏好研究
- 暨南大学生命科学技术学院, 人与自然生命共同体实验室, 广东 广州 510632
-
收稿日期:2023-06-19修回日期:2023-08-20出版日期:2024-03-10发布日期:2024-03-26 -
作者简介:陈俊强(1998—), 男, 广东省中山市人, 硕士研究生, 从事轮虫分类和生态学研究。email: 875218738@qq.com
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(41673080); 广东省基础研究与应用基础研究基金项目(2021A1515010814)
Species diversity and habitat preference of bdelloid rotifers in the Weizhou island, Guangxi
CHEN Junqiang( ), WANG Wenbo, WANG Qing, YANG Yufeng(
), WANG Wenbo, WANG Qing, YANG Yufeng( )
)
- College of Life Science and Technology, Key Laboratory of Philosophy and Social Science in Guangdong Province of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
-
Received:2023-06-19Revised:2023-08-20Online:2024-03-10Published:2024-03-26 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41673080); Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2021A1515010814)
摘要:
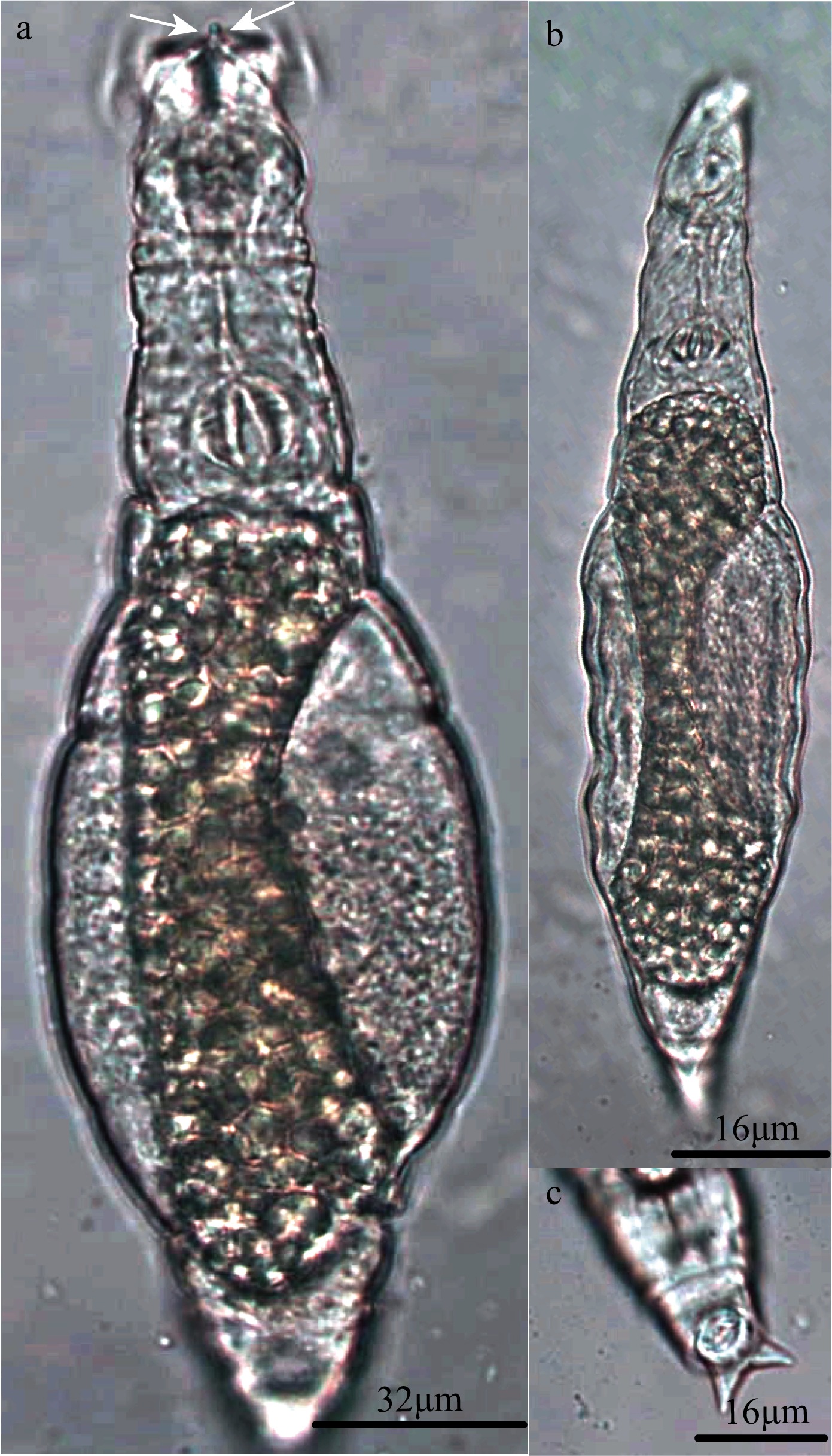
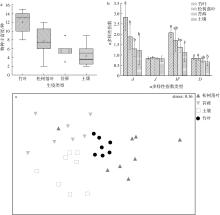
岛屿生境和生物群落组成独特, 但有关岛屿蛭态轮虫的研究报道较少。为研究岛屿环境蛭态轮虫的物种多样性, 于2021—2022年在广西涠洲岛苔藓、土壤、竹叶、松树落叶、其他落叶、带柄植物花瓣和燃烧后叶杆共7种生境进行调查, 共记录蛭态轮虫3科8属53种, 其中中国新记录种3种, 结果显示涠洲岛蛭态轮虫物种多样性高(占全球已报道蛭态轮虫物种数量10.6%)。前4种生境间物种丰富度差异显著(p<0.0001), 且不同生境间物种组成差异性显著大于同类生境内物种组成差异(p=0.001), 表明蛭态轮虫生境偏好明显; 指示种分析(IndVal)表明, 共有10种蛭态轮虫显著偏好某一生境。
引用本文
陈俊强, 汪文博, 王庆, 杨宇峰. 广西涠洲岛蛭态轮虫物种多样性及生境偏好研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 81-91.
CHEN Junqiang, WANG Wenbo, WANG Qing, YANG Yufeng. Species diversity and habitat preference of bdelloid rotifers in the Weizhou island, Guangxi[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 81-91.
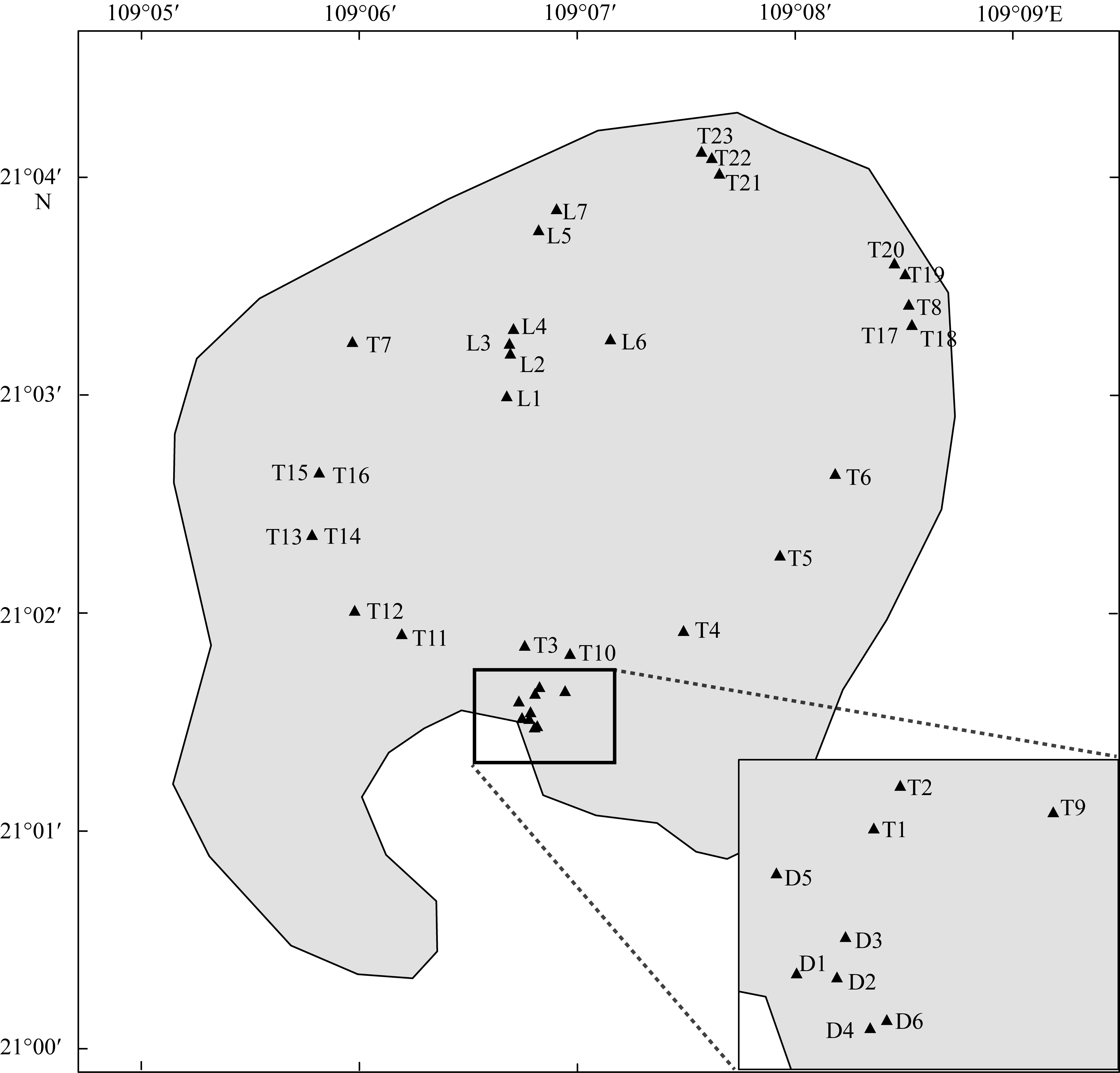
表1
涠洲岛采样点信息"
| 采样点编号 | 采样日期 | 生境类型 | 位置坐标 |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 2021.12.25 | 苔藓 | 21°01′31.18″N, 109°06′44.85″E |
| D2 | 2021.12.25 | 苔藓 | 21°01′30.99″N, 109°06′46.72″E |
| D3 | 2021.12.25 | 苔藓 | 21°01′32.86″N, 109°06′47.11″E |
| D4 | 2021.12.25 | 竹叶 | 21°01′28.66″N, 109°06′48.23″E |
| D5 | 2021.12.25 | 带柄植物花瓣 | 21°01′35.78″N, 109°06′43.92″E |
| D6 | 2021.12.25 | 其他落叶 | 21°01′29.04″N, 109°06′49.01″E |
| T1 | 2022.05.20 | 松树落叶 | 21°01′37.85″N, 109°06′48.41″E |
| T2 | 2022.05.20 | 松树落叶 | 21°01′39.81″N, 109°06′49.63″E |
| T3 | 2022.05.20 | 松树落叶 | 21°01′51.10″N, 109°06′45.49″E |
| T4 | 2022.05.20 | 松树落叶 | 21°01′55.18″N, 109°07′29.31″E |
| T5 | 2022.05.20 | 松树落叶 | 21°02′15.92″N, 109°07′55.89″E |
| T6 | 2022.05.20 | 松树落叶 | 21°02′38.42″N, 109°08′10.98″E |
| T7 | 2022.05.20 | 松树落叶 | 21°03′14.81″N, 109°05′58.09″E |
| T8 | 2022.05.20 | 松树落叶 | 21°03′25.02″N, 109°08′31.24″E |
| T9 | 2022.05.20 | 土壤 | 21°01′38.60″N, 109°06′56.67″E |
| T10 | 2022.05.20 | 土壤 | 21°01′48.87″N, 109°06′58.02″E |
| T11 | 2022.05.20 | 土壤 | 21°01′54.35″N, 109°06′11.71″E |
| T12 | 2022.05.20 | 苔藓 | 21°02′00.77″N, 109°05′58.72″E |
| T13 | 2022.05.20 | 土壤 | 21°02′21.57″N, 109°05′46.95″E |
| T14 | 2022.05.20 | 苔藓 | 21°02′21.57″N, 109°05′46.95″E |
| T15 | 2022.05.20 | 苔藓 | 21°02′38.85″N, 109°05′48.94″E |
| T16 | 2022.05.20 | 土壤 | 21°02′38.85″N, 109°05′48.94″E |
| T17 | 2022.05.20 | 土壤 | 21°03′19.43″N, 109°08′32.16″E |
| T18 | 2022.05.20 | 苔藓 | 21°03′19.43″N, 109°08′32.16″E |
| T19 | 2022.05.20 | 土壤 | 21°03′33.47″N, 109°08′30.27″E |
| T20 | 2022.05.20 | 其他落叶 | 21°03′36.33″N, 109°08′27.31″E |
| T21 | 2022.05.20 | 燃烧后的叶杆 | 21°04′01.04″N, 109°07′39.11″E |
| T22 | 2022.05.20 | 其他落叶 | 21°04′05.46″N, 109°07′37.01″E |
| T23 | 2022.05.20 | 土壤 | 21°04′07.17″N, 109°07′34.15″E |
| L1 | 2022.09.01 | 竹叶 | 21°02′59.77″N, 109°06′40.56″E |
| L2 | 2022.09.01 | 竹叶 | 21°03′11.56″N, 109°06′41.59″E |
| L3 | 2022.09.01 | 竹叶 | 21°03′14.23″N, 109°06′41.36″E |
| L4 | 2022.09.01 | 竹叶 | 21°03′18.36″N, 109°06′42.47″E |
| L5 | 2022.09.01 | 竹叶 | 21°03′45.55″N, 109°06′49.39″E |
| L6 | 2022.09.01 | 其他落叶 | 21°03′15.45″N, 109°07′09.17″E |
| L7 | 2022.09.01 | 竹叶 | 21°03′51.35″N, 109°06′54.29″E |
表2
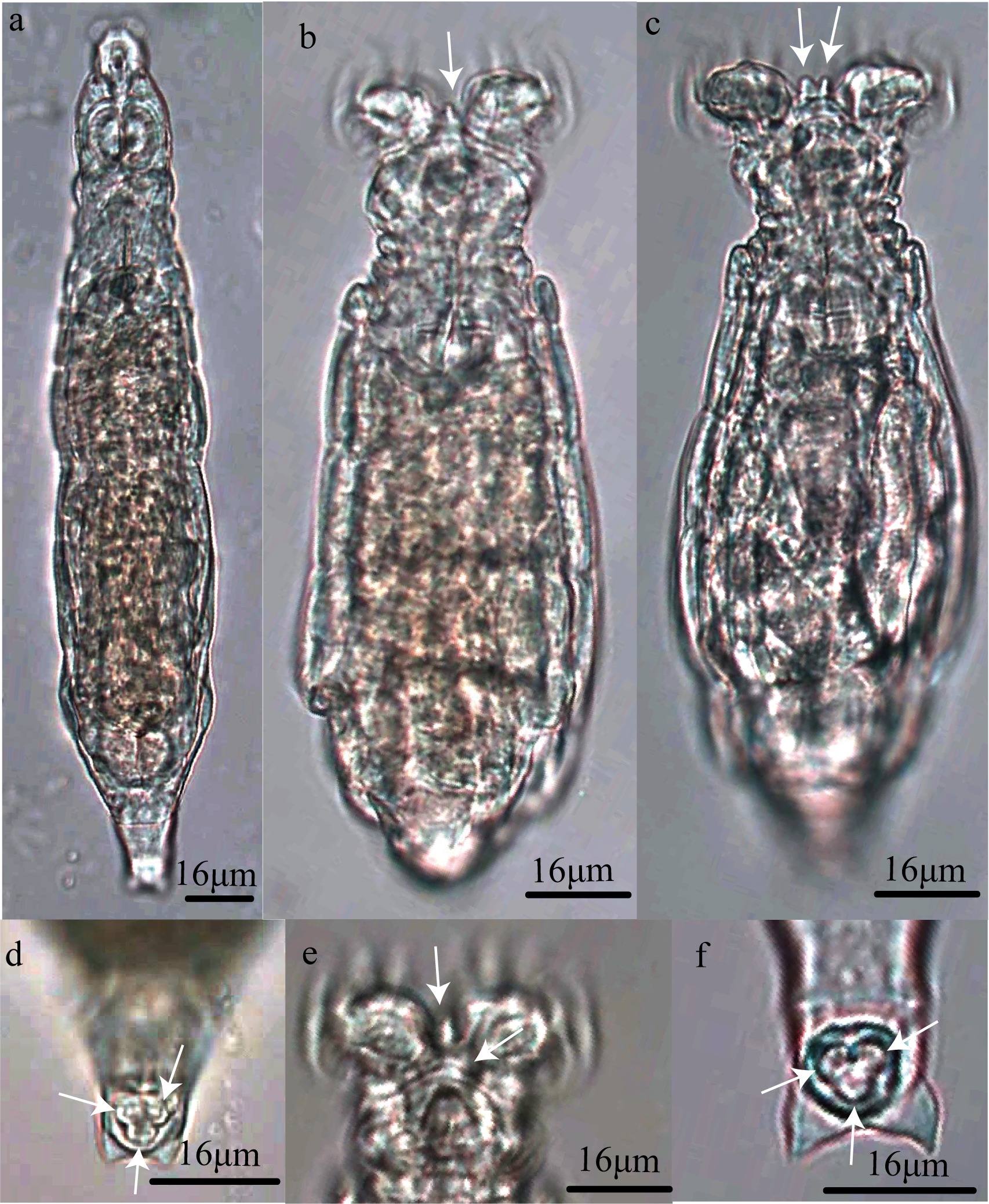
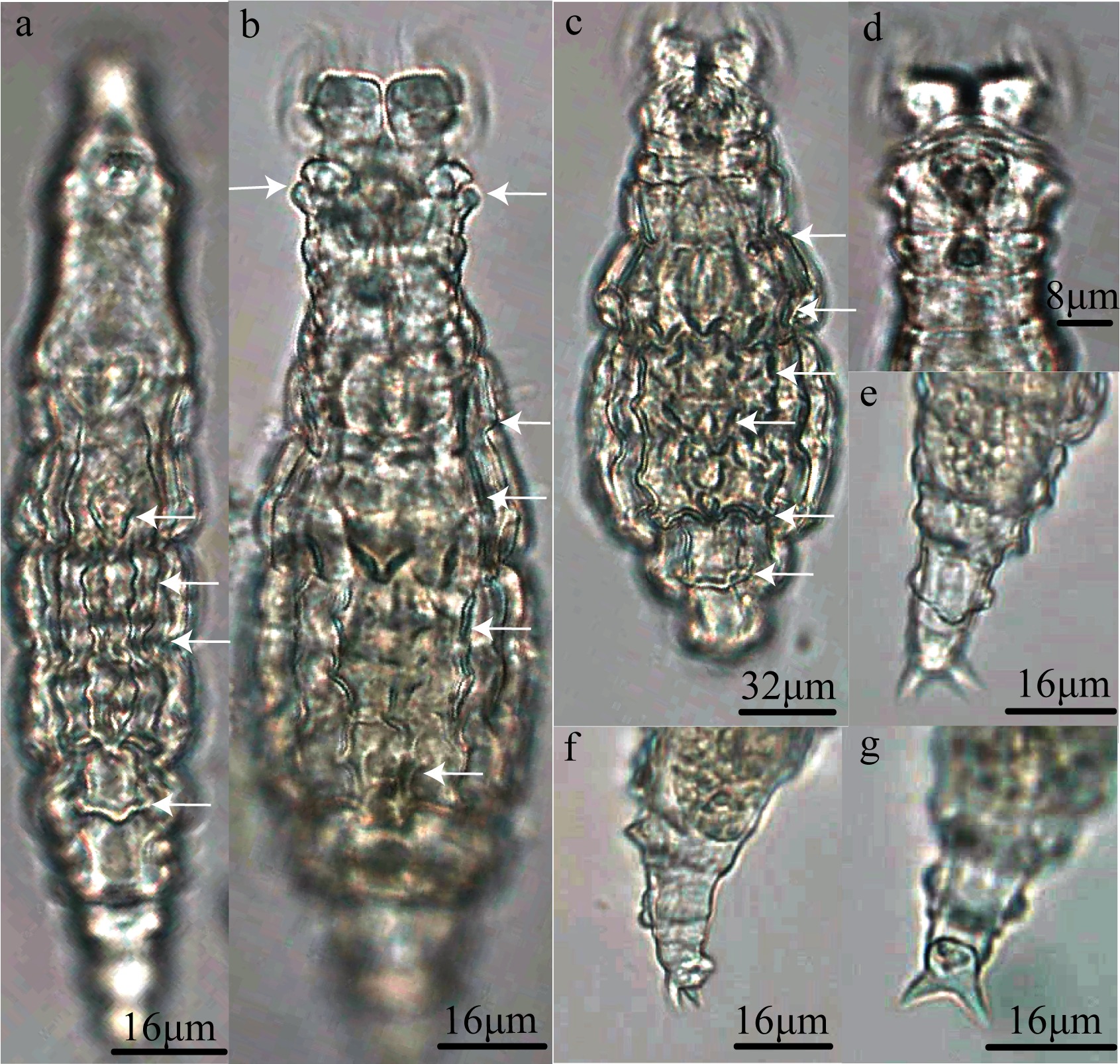
涠洲岛蛭态轮虫物种名录表"
| 科 | 属 | 种 | 生境类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 盘网轮科 Adinetidae | 盘网轮属Adineta | 急角盘网轮虫Adineta acuticornis Haigh, | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓, 燃烧后的叶杆 |
| 贝式盘网轮虫A. beysunae Örstan, | 竹叶, 松树落叶 | ||
| 楔足盘网轮虫A. cuneata Milne, 1916 | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓 | ||
| 游荡盘网轮虫A. vaga (Davis, 1873) | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓, 燃烧后的叶杆 | ||
| 突盘轮Bradyscela | 跛足突盘轮虫Bradyscela clauda (Bryce, 1893) | 竹叶, 其他落叶 | |
| 宿轮科Habrotrochidae | 宿轮属 Habrotrocha | 双齿宿轮虫H. bidens (Gosse, 1851) | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓 |
| 缢缩宿轮虫H. constricta (Dujardin, 1841) | 竹叶 | ||
| 领宿轮虫H. collaris Wulfert, 1965 | 竹叶, 苔藓 | ||
| 金色宿轮虫H. flava Bryce,1915 | 竹叶, 松树落叶 | ||
| 黄体宿轮虫H. flaviformis De Koning, 1947 | 竹叶, 其他落叶 | ||
| 舌凸宿轮虫H. ligula Bryce, 1913 | 松树落叶, 燃烧后的叶杆 | ||
| 罗莎宿轮虫H. rosa Donner, 1949 | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶 | ||
| 三趾宿轮虫H. tripus (Murray, | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶 | ||
| 弯唇宿轮虫H. thienemanni Hauer, 1924 | 竹叶 | ||
| 一种宿轮虫Habrotrocha sp.1 | 松树落叶 | ||
| 一种宿轮虫Habrotrocha sp.2 | 土壤 | ||
| 一种宿轮虫Habrotrocha sp.3 | 竹叶 | ||
| 一种宿轮虫Habrotrocha sp.4 | 竹叶 | ||
| 敖突轮属Otostephanos | 皇家敖突轮虫Otostephanos regalis Milne, 1916 | 其他落叶 | |
| 环颈敖突轮虫O. torquatus (Bryce, 1913) | 竹叶 | ||
| 旋轮科 Philodinidae | 粗颈轮属Macrotrachela | 短唇粗颈轮虫Macrotrachela brevilabris De Koning, 1947 | 松树落叶 |
| 精巧粗颈轮虫M. concinna (Bryce, | 竹叶, 苔藓 | ||
| 戈氏粗颈轮虫M. decora (Bryce, | 竹叶, 土壤, 燃烧后的叶杆 | ||
| 欧氏粗颈轮虫M. ehrenbergii (Janson, 1893) | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓 | ||
| 栖居粗颈轮虫M. habita (Bryce, 1894) | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓, 土壤, 燃烧后的叶杆 | ||
| 毛粗颈轮虫M. induta Donner, 1951 | 其他落叶, 苔藓 | ||
| 无刺粗颈轮虫M. inermis Donner, | 竹叶, 松树落叶 | ||
| 奇异粗颈轮虫M. insolita De Koning, 1947 | 松树落叶 | ||
| 圆腹粗颈轮虫M. kallosoma (Schulte, 1954) | 竹叶 | ||
| 游离粗颈轮虫M. libera Donner, 1949 | 松树落叶, 土壤 | ||
| 多刺粗颈轮虫M. multispinosa (Murray, 1908) | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓, 土壤, 带柄植物花瓣 | ||
| 舌凸矮小粗颈轮虫M. nana ligulata Schulte, 1954* | 竹叶 | ||
| 娜娜矮小粗颈轮虫M. nana nana (Bryce, | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 燃烧后的叶杆 | ||
| 四角粗颈轮虫M. quadricornifera Milne, 1886 | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓, 带柄植物花瓣 | ||
| 美丽粗颈轮虫M. speciosa (Murray, | 其他落叶 | ||
| 畏弱粗颈轮虫M. timida Milne, 1916 | 松树落叶 | ||
| 一种粗颈轮虫Macrotrachela sp.1 | 竹叶, 苔藓 | ||
| 一种粗颈轮虫Macrotrachela sp.2 | 竹叶 | ||
| 水蛭轮属Mniobia | 水蛭轮虫 Mniobia tentans Donner, 1949 | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓 | |
| 一种水蛭轮虫Mniobia sp. | 竹叶 | ||
| 旋轮属Philodina | 宽沟锐角旋轮虫Philodina acuticornis odiosa Milne, 1916 | 苔藓, 带柄植物花瓣 | |
| 南极旋轮虫P. antarctica Murray, 1910 | 带柄植物花瓣 | ||
| 双戟旋轮虫P. duplicalcar (De Koning, 1947) | 其他落叶 | ||
| 巨环旋轮虫P. megalotrocha Ehrenberg, 1832 | 松树落叶 | ||
| 微戟旋轮虫P. parvicalcar De Koning, 1947 | 松树落叶, 苔藓, 苔藓土壤, 土壤 | ||
| 宽体旋轮虫P. plena (Bryce, 1894) | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓, 土壤 | ||
| 迅捷旋轮虫P. rapida Milne, 1916 | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 燃烧后的叶杆 | ||
| 褶皱旋轮虫P. rugosa Bryce, 1903 | 竹叶, 土壤 | ||
| 宁静旋轮虫P. tranquilla Wulfert, 1942 | 带柄植物花瓣 | ||
| 凶猛旋轮虫P. vorax (Janson, 1893) | 竹叶, 苔藓, 土壤 | ||
| 旋轮科 Philodinidae | 轮虫属Rotaria | 转轮虫R. rotatoria (Pallas, 1766) | 松树落叶 |
| 污轮虫R. sordida (Western, 1893) | 竹叶, 松树落叶, 其他落叶, 苔藓, 土壤 | ||
| 懒轮虫R. tardigrada (Ehrenberg, 1830) | 松树落叶 |
表4
蛭态轮虫4种生境丰度、IndVal指数、p值和生境偏好"
| 物种 | 丰度 | IndVal/% | p 值 | 生境偏好 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 竹叶 | 松树落叶 | 苔藓 | 土壤 | ||||
| 游荡盘网轮虫(A. vaga) | 8 | 45 | 1 | 0 | 72.3 | 0.013 | 竹叶, 松树落叶 |
| 双齿宿轮虫(H. biddens) | 15 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 68.3 | 0.022 | 竹叶, 松树落叶 |
| 金色宿轮虫(H. flava) | 13 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 63.8 | 0.043 | 竹叶 |
| 罗莎宿轮虫(H. rosa) | 13 | 51 | 0 | 0 | 89.4 | 0.001 | 竹叶, 松树落叶 |
| 三趾宿轮虫(H. tripus) | 9 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 68.3 | 0.022 | 竹叶, 松树落叶 |
| 戈氏粗颈轮虫(M. decora) | 1 | 0 | 3 | 32 | 81.0 | 0.006 | 土壤 |
| 多刺粗颈轮虫(M. multispinosa) | 94 | 8 | 28 | 56 | 80.9 | 0.027 | 竹叶, 苔藓, 土壤 |
| 四角粗颈轮虫(M. quadricornifera) | 29 | 1 | 26 | 1 | 74.4 | 0.017 | 竹叶, 苔藓 |
| 宽体旋轮虫(P. plena) | 31 | 16 | 0 | 3 | 79.4 | 0.004 | 竹叶, 松树落叶 |
| 迅捷旋轮虫(P. rapida) | 8 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 68.3 | 0.023 | 竹叶, 松树落叶 |
表5
蛭态轮虫4种生境优势种及优势度"
| 种类组成 | 区域优势度 | 竹叶 | 松树落叶 | 苔藓 | 土壤 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 急角盘网轮虫(A. acuticornis) | / | 0.03 | / | 0.03 | / |
| 游荡盘网轮虫(A. vaga) | / | / | 0.06 | / | — |
| 双齿宿轮虫(H. bidens) | / | 0.03 | / | — | — |
| 金色宿轮虫(H. flava) | / | 0.02 | / | — | — |
| 罗莎宿轮虫(H. rosa) | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.13 | — | — |
| 三趾宿轮虫(H. tripus) | / | / | 0.02 | — | — |
| 戈氏粗颈轮虫(M. decora) | / | / | — | / | 0.11 |
| 栖居粗颈轮虫(M. habita) | 0.03 | / | / | 0.19 | 0.03 |
| 多刺粗颈轮虫(M. multispinosa) | 0.09 | 0.27 | / | 0.07 | 0.16 |
| 四角粗颈轮虫(M. quadricornifera) | / | 0.07 | / | 0.03 | / |
| 一种水蛭轮虫(Mniobia sp.) | / | — | / | 0.05 | — |
| 微戟旋轮虫(P. parvicalcar) | / | — | / | 0.02 | / |
| 宽体旋轮虫(P. plena) | / | 0.08 | / | — | / |
| 迅捷旋轮虫(P. rapida) | / | / | 0.02 | — | — |
| 凶猛旋轮虫(P. vorax) | / | / | — | — | 0.03 |
| 污轮虫(R. sordida) | 0.07 | 0.09 | / | 0.03 | 0.27 |
| [1] |
王庆, 李莹, 汪文博, 等, 2021. 广东省蛭态轮虫物种多样性及其系统发育研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(9): 4367-4377.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
汪文博, 李莹, 王晓妍, 等, 2022. 中国蛭态轮虫亚纲6种新记录种记述[J]. 动物学杂志, 57(4): 595-606.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
汪文博, 王庆, 李莹, 等, 2021. 落叶生境蛭态轮虫物种多样性及四种中国新记录种[J]. 水生生物学报, 45(2): 436-445.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
pmid: 3427163 |
| [7] |
pmid: 12004087 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1111/emi.2006.8.issue-4 |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1186/s40462-019-0155-7 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1089/ast.2012.0828 pmid: 22924877 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1111/jbi.2006.33.issue-7 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.2307/2657136 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(1997)078[0363:LDASNC]2.0.CO;2 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.3923/javaa.2010.2437.2444 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.3906/zoo-1410-46 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1086/278718 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4524.2.3 pmid: 30486120 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1086/278718 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1007/s10750-019-04144-6 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1093/icb/45.5.759 pmid: 21676827 |
| [29] |
pmid: 17957710 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1078/0044-5231-00101 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012678108 pmid: 21368117 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1146/annurev-environ-101718-033245 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1007/s10750-005-4111-8 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.17216/LimnoFish-5000151941 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.3897/zookeys.941.50465 pmid: 32595405 |
| [1] | 饶义勇, 赵美榕, 旷泽行, 黄洪辉, 谭萼辉. 浮筏式牡蛎养殖对大型底栖动物群落功能结构的影响——以大鹏澳为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 69-83. |
| [2] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [3] | 程夏雯, 张兰兰, 邱卓雅, 向荣, 常虎. 北印度洋—南海表层水体中浮游动物胶体虫(放射虫)的物种多样性、生物地理及其季节变化*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 97-112. |
| [4] | 陈志云, 郭翔, 刘毅, 尉鹏, 张素萍. 厦门近海尖梭螺属(软体动物门, 腹足纲, 梭螺科)一新记录种[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 189-192. |
| [5] | 李开枝, 柯志新, 王军星, 谭烨辉. 西沙群岛珊瑚礁海域浮游动物群落结构初步分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 121-131. |
| [6] | 苏芯莹, 钟瑜, 李尧, 谭美婷, 黄亚东, 刘珊, 徐向荣, 宋星宇. 珠江口典型海岛周边水域浮游植物分布特征及其影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 30-42. |
| [7] | 韩敏敏, 李蜜, 刘昕明, 刘永宏, 龙超, 钟振国, 易湘茜, 高程海. Khai岛和Pathiu岛珊瑚礁沉积物细菌多样性及细菌粗提物延缓秀丽隐杆线虫衰老活性研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 19-29. |
| [8] | 陈志云, 连喜平, 谭烨辉. 中国海塔螺科Turridae一新记录种 (软体动物门, 腹足纲, 新腹足目)[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(1): 92-94. |
| [9] | 陈志云, 谭烨辉, 连喜平. 中国海芋螺属一新记录(腹足纲, 芋螺科)[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(3): 99-100. |
|
||