热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 69-83.doi: 10.11978/2023146CSTR: 32234.14.2023146
浮筏式牡蛎养殖对大型底栖动物群落功能结构的影响——以大鹏澳为例*
饶义勇1,2( ), 赵美榕1, 旷泽行1, 黄洪辉1,2(
), 赵美榕1, 旷泽行1, 黄洪辉1,2( ), 谭萼辉3
), 谭萼辉3
- 1.中国水产科学研究院南海水产研究所, 广东 广州 510300
2.广东省渔业生态环境重点实验室, 广东 广州 510300
3.海南大学南海海洋资源利用国家重点实验室, 海南 海口 570228
-
收稿日期:2023-10-10修回日期:2023-10-31出版日期:2024-09-10发布日期:2024-10-10 -
作者简介:饶义勇(1989—), 男, 福建省南平市人, 博士, 从事海洋底栖动物群落生态学研究。email: raoyiyong@scsfri.ac.cn
*本研究的样品采集工作由周贤、覃晓青、杜胜奇、许明监、谭桢、谢东海协助完成, 特此感谢。
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42206119); 海南大学南海海洋资源利用国家重点实验室开放课题项目(MRUKF202101); 中国水产科学研究院南海水产研究所中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费专项(2020TS02); 福建省社会科学基金项目(FJ2021C083)
Influence of raft-string oyster culture on the functional structure of macrobenthic communities: a case study in the Dapeng Cove*
RAO Yiyong1,2( ), ZHAO Meirong1, KUANG Zexing1, HUANG Honghui1,2(
), ZHAO Meirong1, KUANG Zexing1, HUANG Honghui1,2( ), TAN Erhui3
), TAN Erhui3
- 1. South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Guangzhou 510300, China
2. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fishery Ecology and Environment, Guangzhou 510300, China
3. State Key Laboratory of Marine Resource Utilization in South China Sea, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
-
Received:2023-10-10Revised:2023-10-31Online:2024-09-10Published:2024-10-10 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42206119); Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Marine Resource Utilization in South China Sea, Hainan University(MRUKF202101); Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS(2020TS02); Fujian Provincial Social Science Foundation Youth Project(FJ2021C083)
摘要:
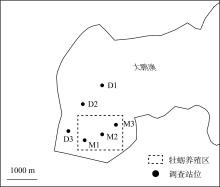
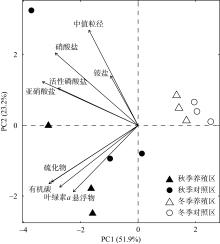
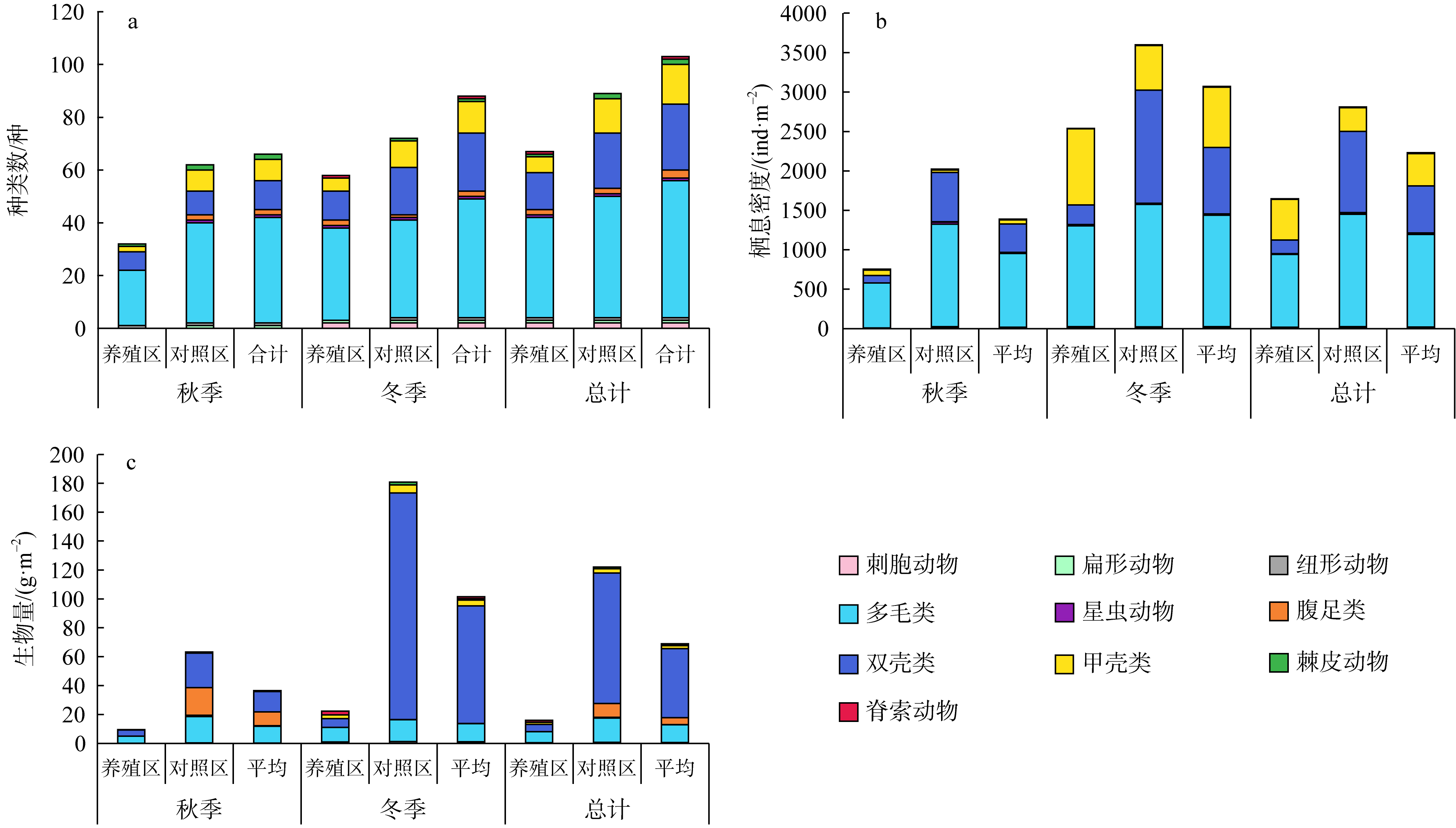
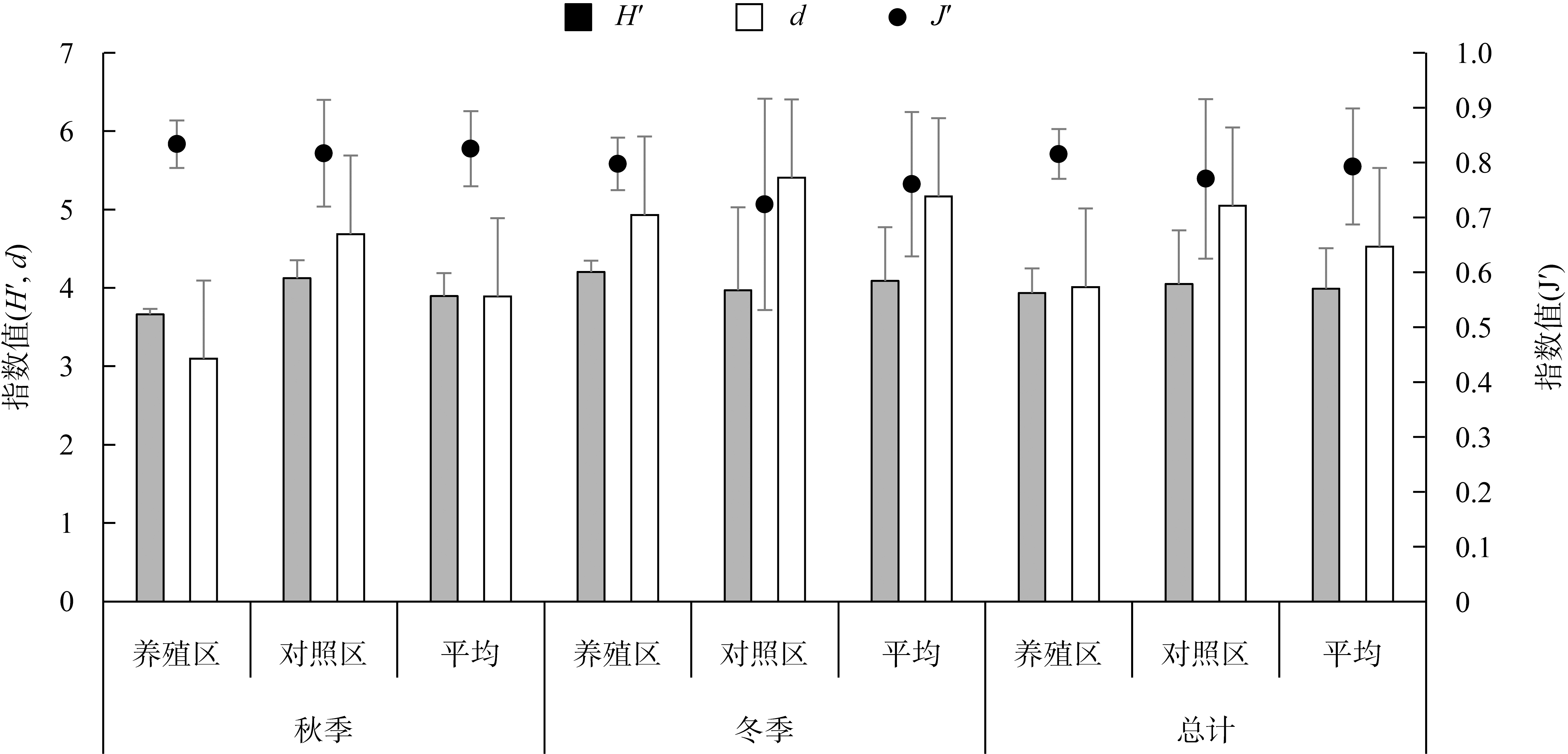
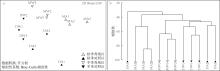
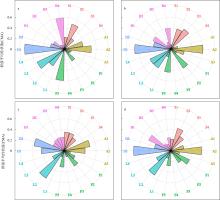
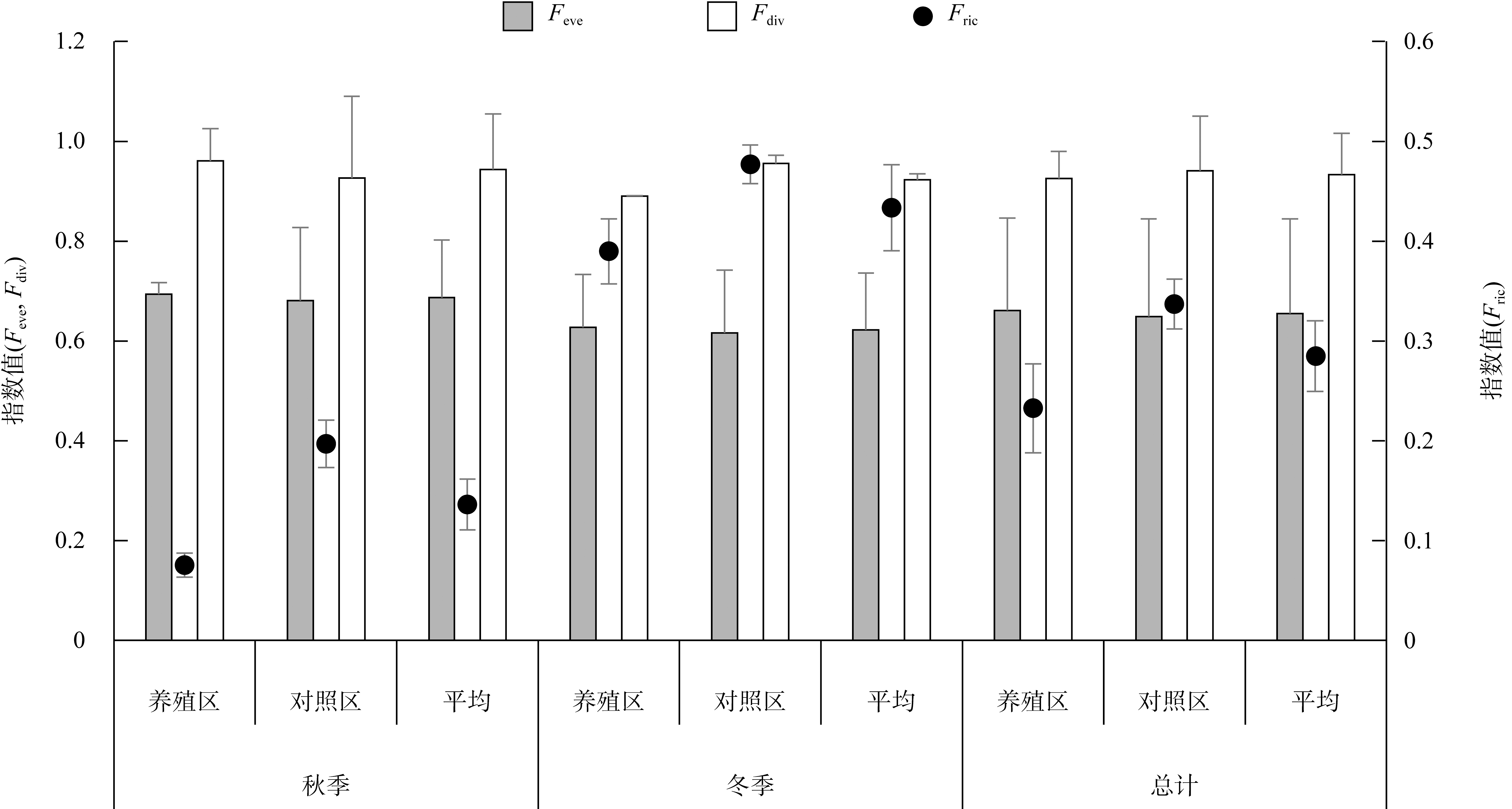
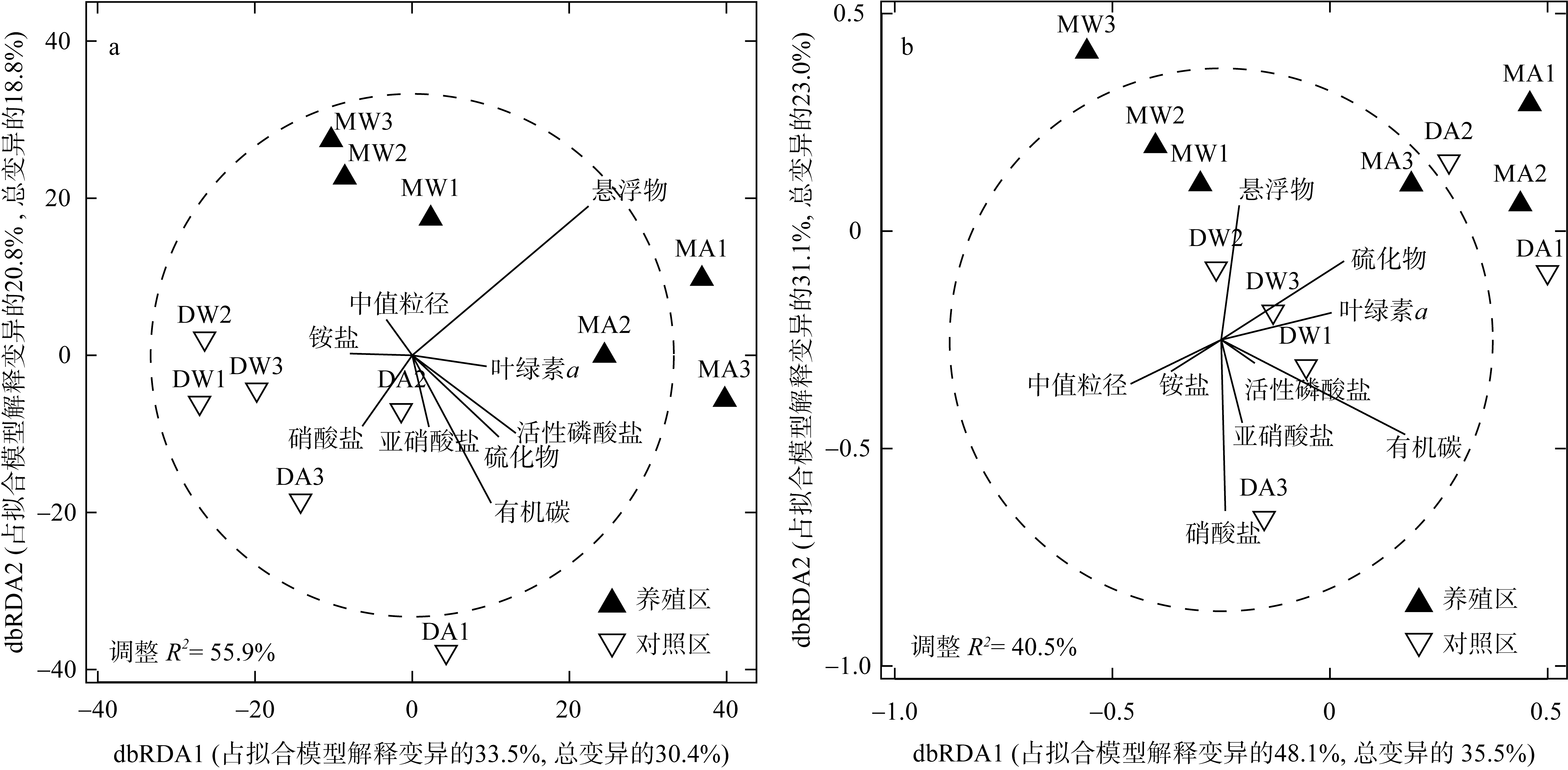
牡蛎养殖的环境生态效应存在争议, 其对大型底栖动物的影响机理缺乏清晰认识。本研究于2020年11月(秋季)和2021年1月(冬季)在大鹏澳浮筏式牡蛎养殖区及邻近海域进行了2个航次大型底栖动物和相关环境因子的调查监测。2个航次共获得大型底栖动物103种, 种类组成以多毛类、双壳类和甲壳类物种占优势。大型底栖动物群落的物种组成在季节间(秋季和冬季)和区域间(养殖区和对照区)具有显著差异。冬季大型底栖动物的种类数、栖息密度和生物量等群落参数高于秋季, 对照区高于养殖区。生物性状分析(biological traits analysis, BTA)结果显示, 大型底栖动物群落的性状组成仅在季节间具有显著差异。牡蛎养殖区和对照区大型底栖动物群落的性状组成差异不显著, 但生物扰动方式、个体大小、摄食类型等性状在区域间仍有一定的差别。牡蛎养殖区大型底栖动物群落的功能丰富度(functional richness, Fric)低于对照区, 但功能均匀度(functional evenness, Feve)和功能分散度(functional divergence, Fdiv)在区域之间的差异不大。表层水体的叶绿素a、悬浮物、营养盐以及沉积物的有机碳、硫化物和中值粒径是影响大型底栖动物物种组成和性状组成的重要环境因子。摄食类型、栖息方式以及幼体发育方式等性状与环境因子的关系比较密切, 物种丰富度(d)和功能丰富度指数具有较高的环境指示意义。
引用本文
饶义勇, 赵美榕, 旷泽行, 黄洪辉, 谭萼辉. 浮筏式牡蛎养殖对大型底栖动物群落功能结构的影响——以大鹏澳为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 69-83.
RAO Yiyong, ZHAO Meirong, KUANG Zexing, HUANG Honghui, TAN Erhui. Influence of raft-string oyster culture on the functional structure of macrobenthic communities: a case study in the Dapeng Cove*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 69-83.
表1
环境要素分析方法及检出限"
| 检测要素 | 检测标准(方法) | 检出限 | 仪器设备名称及型号 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 悬浮物 | 海洋监测规范 第4部分: 海水分析GB 17378.4-2007 (重量法) | 0.8mg·L-1 | 分析天平XS205 |
| 亚硝酸盐 | 海洋监测规范 第4部分: 海水分析GB 17378.4-2007 (萘乙二胺分光光度法) | 0.0003mg·L-1 | 紫外分光光度计UV-7504 |
| 硝酸盐 | 海洋监测规范 第4部分: 海水分析GB 17378.4-2007 (镉柱还原法) | 0.003mg·L-1 | 紫外分光光度计UV-7504 |
| 铵盐 | 海洋监测规范 第4部分: 海水分析GB 17378.4-2007 (靛酚蓝分光光度法) | 0.0009mg·L-1 | 紫外分光光度计UV-7504 |
| 活性磷酸盐 | 海洋监测规范 第4部分: 海水分析GB 17378.4-2007 (磷钼蓝分光光度法) | 0.0005mg·L-1 | 紫外分光光度计UV-7504 |
| 叶绿素a | 海洋监测规范 第7部分: 近海污染生态调查和生物监测GB 17378.7-2007 (荧光分光光度法) | / | TURNER10-AU现场荧光仪 |
| 中值粒径 | 激光衍射法 | 0.02μm | Mastersizer 2000G 激光粒度分析仪 |
| 有机碳 | 海洋监测规范 第5部分: 沉积物分析GB 17378.5-2007 (重铬酸钾氧化-还原容量法) | 0.3mg·kg-1 | 紫外分光光度计UV-7504 |
| 硫化物 | 海洋监测规范 第5部分: 沉积物分析GB 17378.5-2007 (亚甲基蓝分光光度法) | 0.01% | 滴定管 |
表2
大型底栖动物性状及其功能属性"
| 性状 | 性状类别 | 代码 | 功能属性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 个体大小 | 极小 (<1cm) | S1 | 个体大小对生产力、栖息地的结构和增益程度具有直接影响, 并对沉积物-水界面的氧气和养分通量产生重要影响。并与生态系统的食物网结构、营养级和能流有关(Bolam et al, |
| 小 (1~3cm) | S2 | ||
| 中 (3~10cm) | S3 | ||
| 大 (>10cm) | S4 | ||
| 个体寿命 | 短 (<1a) | A1 | 反映生物受到扰动的恢复力, 寿命长的生物需要更长的时间来恢复, 而寿命短的生物可以快速恢复, 并可能随着干扰的增加而增多(Bolam et al, |
| 中 (1~3a) | A2 | ||
| 长 (>3a) | A3 | ||
| 摄食类型 | 悬浮食性 | F1 | 指示水动力条件, 例如悬浮食性生物一般生活于急流中; 影响氧气的渗透、资源的利用、有机物的分解和养分的循环/再生; 对群落中其他物种的控制作用(Bremner, |
| 沉积食性 | F2 | ||
| 植食性 | F3 | ||
| 腐食性 | F4 | ||
| 捕食性 | F5 | ||
| 栖息习性 | 管栖 | L1 | 栖息习性对沉积物的生物地球化学循环具有直接影响, 同时, 栖息习性不同的生物对捕食和扰动具有不同的响应, 如附着生物易受捕食; 穴居和管栖的生物受缺氧环境影响较小(Bremner, |
| 穴居 | L2 | ||
| 自由生活 | L3 | ||
| 附着 | L4 | ||
| 幼体发育 | 营浮游发育 | D1 | 物种扩散、入侵或从种群减少中恢复的能力。通常营浮游发育的物种的扩散能力要高于底栖直接发育的物种(Bolam et al, |
| 底栖直接发育 | D2 | ||
| 生物扰动 | 底表沉积 | B1 | 影响沉积物的生物地球化学循环和理化性质(沉积物粒径、氧化还原电位等) (Queirós et al, |
| 向上传输 | B2 | ||
| 向下传输 | B3 | ||
| 扩散混合 | B4 |
表3
大鹏澳浮筏式牡蛎养殖区及邻近海域环境因子平均值和标准差"
| 环境因子 | 秋季 | 冬季 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 养殖区 | 对照区 | 养殖区 | 对照区 | ||
| 水环境 | 叶绿素a /(mg·m-3) | 2.98 (1.06) | 2.64 (0.14) | 0.88 (0.29) | 0.93 (0.15) |
| 悬浮物/(mg·L-1) | 16.3 (2.2) | 8.9 (2.2) | 8.7 (0.4) | 8.7 (0.5) | |
| 亚硝酸盐/(mg·L-1) | 0.0028 (0.0007) | 0.0027 (0.0025) | 0.0012 (0.0002) | 0.0003 (0.0004) | |
| 硝酸盐/(mg·L-1) | 0.097 (0.048) | 0.181 (0.192) | 0.033 (0.003) | 0.021 (0.012) | |
| 铵盐/(mg·L-1) | 0.020 (0.020) | 0.014 (0.009) | 0.026 (0.008) | 0.011 (0.003) | |
| 活性磷酸盐/(mg·L-1) | 0.0061 (0.0029) | 0.0055 (0.0013) | 0.0041 (0.0006) | 0.0039 (0.0010) | |
| 沉积环境 | 有机碳/% | 2.83 (0.18) | 2.19 (0.05) | 1.37 (0.11) | 0.67 (0.07) |
| 硫化物/(mg·kg-1) | 484.33 (73.11) | 461.67 (141.55) | 10.20 (10.53) | 7.41 (2.04) | |
| 中值粒径/μm | 10.44 (1.02) | 40.30 (37.75) | 11.48 (1.04) | 17.95 (2.65) | |
表4
大鹏澳浮筏式牡蛎养殖区及邻近海域大型底栖动物群落相异性的主要贡献种"
| 类群 | 种名 | 季节间 | 区域间 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 栖息密度/(ind·m-2) | 贡献度/% | 栖息密度/(ind·m-2) | 贡献度/% | ||||
| 秋季 | 冬季 | 养殖区 | 对照区 | ||||
| 多毛类 | 背褶沙蚕 Tambalagamia fauveli | 95 | 15 | 2.4 | 102 | 8 | 3.0 |
| 才女虫 Polydora sp. | 5 | 42 | 1.9 | 27 | 20 | 1.3 | |
| 寡节甘吻沙蚕 Glycinde gurjanovae | 75 | 158 | 2.2 | 62 | 172 | 2.4 | |
| 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕 Nephtys oligobranchia | 23 | 98 | 2.1 | 50 | 72 | 1.7 | |
| 花冈钩毛虫 Sigambra hanaokai | 158 | 158 | 2.0 | 143 | 173 | 2.3 | |
| 滑指矶沙蚕 Eunice indica | 62 | 67 | 1.5 | 38 | 90 | 1.7 | |
| 角海蛹 Ophelina acuminate | 10 | 55 | 2.0 | 38 | 27 | 1.4 | |
| 欧努菲虫 Onuphis eremita | 42 | 47 | 2.0 | 0 | 88 | 3.5 | |
| 蛇杂毛虫 Poecilochaetus serpens | 35 | 25 | 1.8 | 10 | 50 | 1.8 | |
| 梳鳃虫 Terebellides stroemii | 50 | 73 | 2.4 | 90 | 33 | 2.4 | |
| 树蛰虫 Pista cristata | 7 | 117 | 2.5 | 7 | 117 | 2.5 | |
| 细丝鳃虫 Cirratulus filiformis | 118 | 130 | 1.9 | 95 | 153 | 1.8 | |
| 持真节虫 Euclymene annandalei | 42 | 15 | 4.5 | 3 | 53 | 2.1 | |
| 稚齿虫 Prionospi sp. | 8 | 125 | 3.2 | 98 | 35 | 2.3 | |
| 双壳类 | 安汶圆蛤 Cycladicama amboinensis | 123 | 22 | 1.7 | 15 | 130 | 2.1 |
| 波纹螂斗蛤 Myadora fluctuosa | 3 | 42 | 2.0 | 17 | 28 | 1.5 | |
| 粗帝汶蛤 Timoclea scabra | 22 | 603 | 5.4 | 30 | 595 | 5.2 | |
| 虹光亮樱蛤 Nitidotellina iridella | 150 | 33 | 2.3 | 15 | 168 | 2.7 | |
| 理蛤 Theora lata | 27 | 27 | 1.5 | 43 | 10 | 2.2 | |
| 甲壳类 | 巴西地钩虾 Podocerus brasiliensis | 0 | 292 | 4.8 | 242 | 50 | 3.2 |
| 蜾蠃蜚 Corophium sp. | 0 | 47 | 1.7 | 47 | 0 | 1.4 | |
| 宽甲古涟虫 Eucoma lata | 2 | 67 | 1.9 | 0 | 68 | 2.0 | |
| 六齿拟钩虾 Gammaropsis sexdentata | 37 | 197 | 3.6 | 218 | 15 | 4.0 | |
| 双眼钩虾 Ampelisca sp. | 2 | 133 | 2.9 | 0 | 135 | 3.0 | |
| 平均相异性 /% | 61.6 | 62.0 | |||||
表5
大鹏澳浮筏式牡蛎养殖区及邻近海域大型底栖动物群落性状组成相异性的主要贡献性状类别"
| 性状 | 性状类别 | 季节间 | 区域间 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 群落加权平均性状值 | 贡献度/% | 群落加权平均性状值 | 贡献度/% | ||||
| 秋季 | 冬季 | 养殖区 | 对照区 | ||||
| 个体大小 | S1 (极小个体) | 0.15 | 0.29 | 5.2 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 5.6 |
| S2 (小个体) | 0.44 | 0.39 | 5.4 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 5.8 | |
| S3 (中等个体) | 0.35 | 0.31 | 4.4 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 5.5 | |
| S4 (大个体) | 0.05 | 0.02 | 1.2 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.9 | |
| 个体寿命 | A1 (短寿命) | 0.25 | 0.37 | 6.3 | 0.42 | 0.19 | 7.9 |
| A2 (中等寿命) | 0.56 | 0.49 | 5.1 | 0.45 | 0.59 | 5.7 | |
| A3 (长寿命) | 0.20 | 0.14 | 2.6 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 3.3 | |
| 摄食类型 | F1 (悬浮食性) | 0.12 | 0.31 | 6.2 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 5.7 |
| F2 (沉积食性) | 0.35 | 0.31 | 3.5 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 4.0 | |
| F3 (极小个体) | 0.01 | 0.09 | 2.3 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 2.0 | |
| F4 (腐食性) | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.2 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.2 | |
| F5 (捕食性) | 0.51 | 0.29 | 7.4 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 5.9 | |
| 栖息习性 | L1 (管栖) | 0.10 | 0.14 | 2.2 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 2.7 |
| L2 (穴居) | 0.40 | 0.58 | 6.9 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 6.6 | |
| L3 (自由生活) | 0.49 | 0.27 | 8.0 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 6.6 | |
| L4 (附着) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.4 | |
| 幼体发育 | D1 (营浮游发育) | 0.71 | 0.56 | 6.2 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 6.0 |
| D2 (底栖直接发育) | 0.29 | 0.44 | 6.2 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 6.0 | |
| 生物扰动 | B1 (底表沉积) | 0.30 | 0.34 | 5.3 | 0.23 | 0.41 | 6.6 |
| B2 (向上传输) | 0.10 | 0.21 | 3.6 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 2.8 | |
| B3 (向下传输) | 0.11 | 0.20 | 3.2 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 3.1 | |
| B4 (扩散混合) | 0.49 | 0.25 | 8.3 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 6.7 | |
| 平均相异性/% | 27.1 | 25.2 | |||||
| [1] |
白美娜, 江涛, 陈飞羽, 等, 2019. 大亚湾大鹏澳牡蛎养殖临近海域自养微微型浮游生物种群分布特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 50(1): 129-138.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
蔡立哲, 2003. 大型底栖动物污染指数(MPI)[J]. 环境科学学报, 23(5): 625-629.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
邓邦平, 杨宇峰, 2011. 大鹏澳养殖海域表底层水环境及浮游动物群落结构的比较研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 30(4): 492-495.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2007a. GB/T12963-2007海洋调查规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2007b. GB/T17378-2007海洋监测规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
齐占会, 王珺, 黄洪辉, 等, 2012. 广东省海水养殖贝藻类碳汇潜力评估[J]. 南方水产科学, 8(1): 30-35.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
于宗赫, 江涛, 夏建军, 等, 2014. 大鹏澳牡蛎养殖区生态服务价值评估[J]. 水产学报, 38(6): 853-860.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
张玲, 李政菊, 陈飞羽, 等, 2015. 大鹏澳牡蛎养殖对浮游植物种群结构的影响研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 46(3): 549-555.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
朱骅, 2019. 从碳汇渔业到蓝色粮仓的发展机制[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 28(6): 968-975.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
pmid: 16862294 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13263-w pmid: 29030563 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.07.024 pmid: 20825954 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
pmid: 24649641 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.2134/jeq2019.03.0099 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1038/s41597-019-0344-7 pmid: 31913312 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-020007 pmid: 25251269 |
| [31] |
doi: S0025-326X(19)30250-4 pmid: 31232327 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2009.04.001 pmid: 19409610 |
| [38] |
doi: S0025-326X(19)30526-0 pmid: 31426174 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1002/ece3.769 pmid: 24198953 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
pmid: 16038944 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1890/07-1206.1 pmid: 18724739 |
| [1] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [2] | 陈俊强, 汪文博, 王庆, 杨宇峰. 广西涠洲岛蛭态轮虫物种多样性及生境偏好研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 81-91. |
| [3] | 耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [4] | 程夏雯, 张兰兰, 邱卓雅, 向荣, 常虎. 北印度洋—南海表层水体中浮游动物胶体虫(放射虫)的物种多样性、生物地理及其季节变化*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 97-112. |
| [5] | 马文刚, 夏景全, 魏一凡, 尹洪洋, 覃乐政, 刘相波, 胡雪晴, 许强, 李秀保, 王爱民. 三亚蜈支洲岛海洋牧场近岛区底表大型底栖动物群落结构及评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [6] | 李开枝, 柯志新, 王军星, 谭烨辉. 西沙群岛珊瑚礁海域浮游动物群落结构初步分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 121-131. |
| [7] | 韩敏敏, 李蜜, 刘昕明, 刘永宏, 龙超, 钟振国, 易湘茜, 高程海. Khai岛和Pathiu岛珊瑚礁沉积物细菌多样性及细菌粗提物延缓秀丽隐杆线虫衰老活性研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 19-29. |
| [8] | 赖廷和, 何斌源, 黄中坚, 汤乔, 覃漉雁, 朱婷, 莫珍妮, 刘俐, 钟云旭. 防城河口湾潮间带大型底栖动物群落结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(2): 67-77. |
| [9] | 罗章凤, 方展强. 珠海横琴岛芒洲湿地红树林人工恢复期大型底栖动物群落结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(3): 61-72. |
|
||