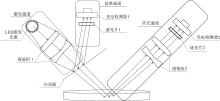
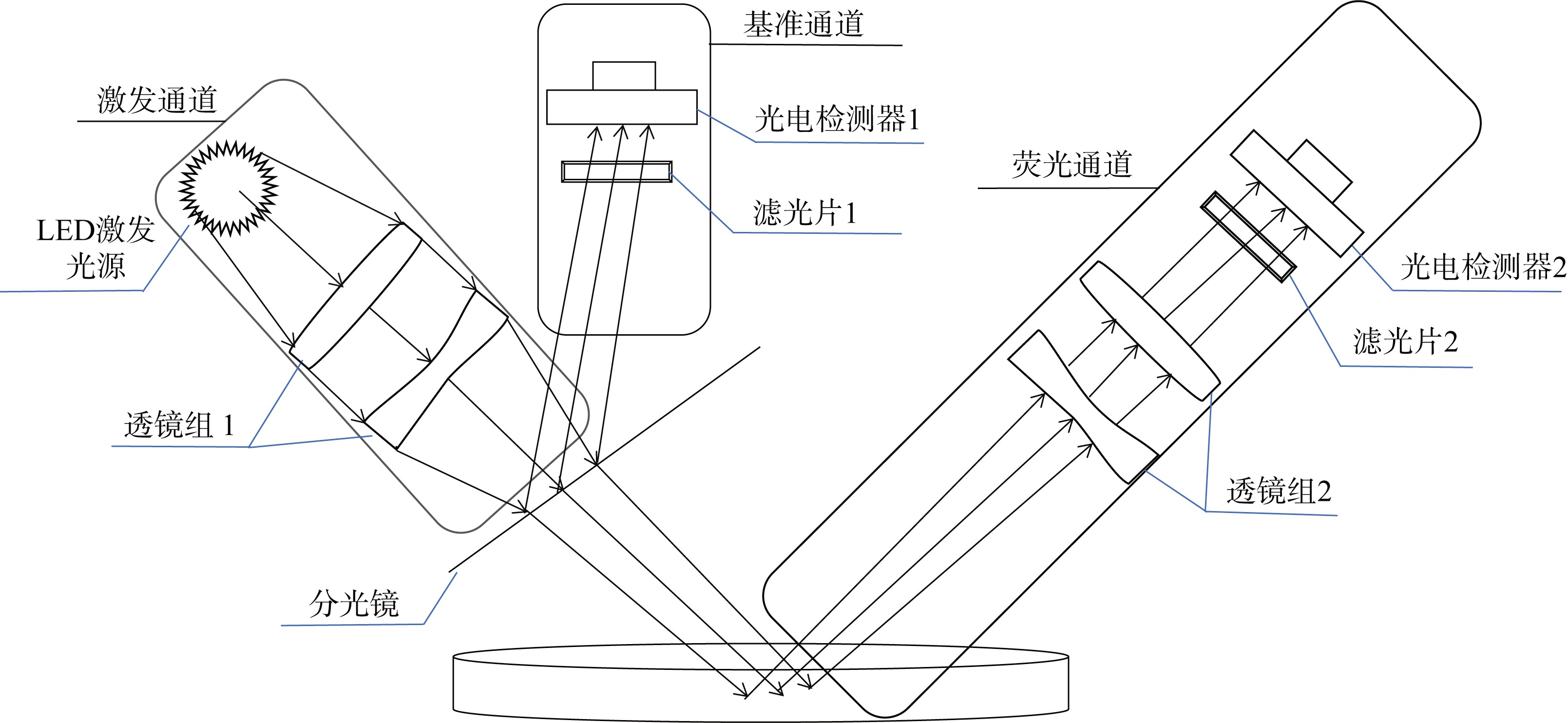
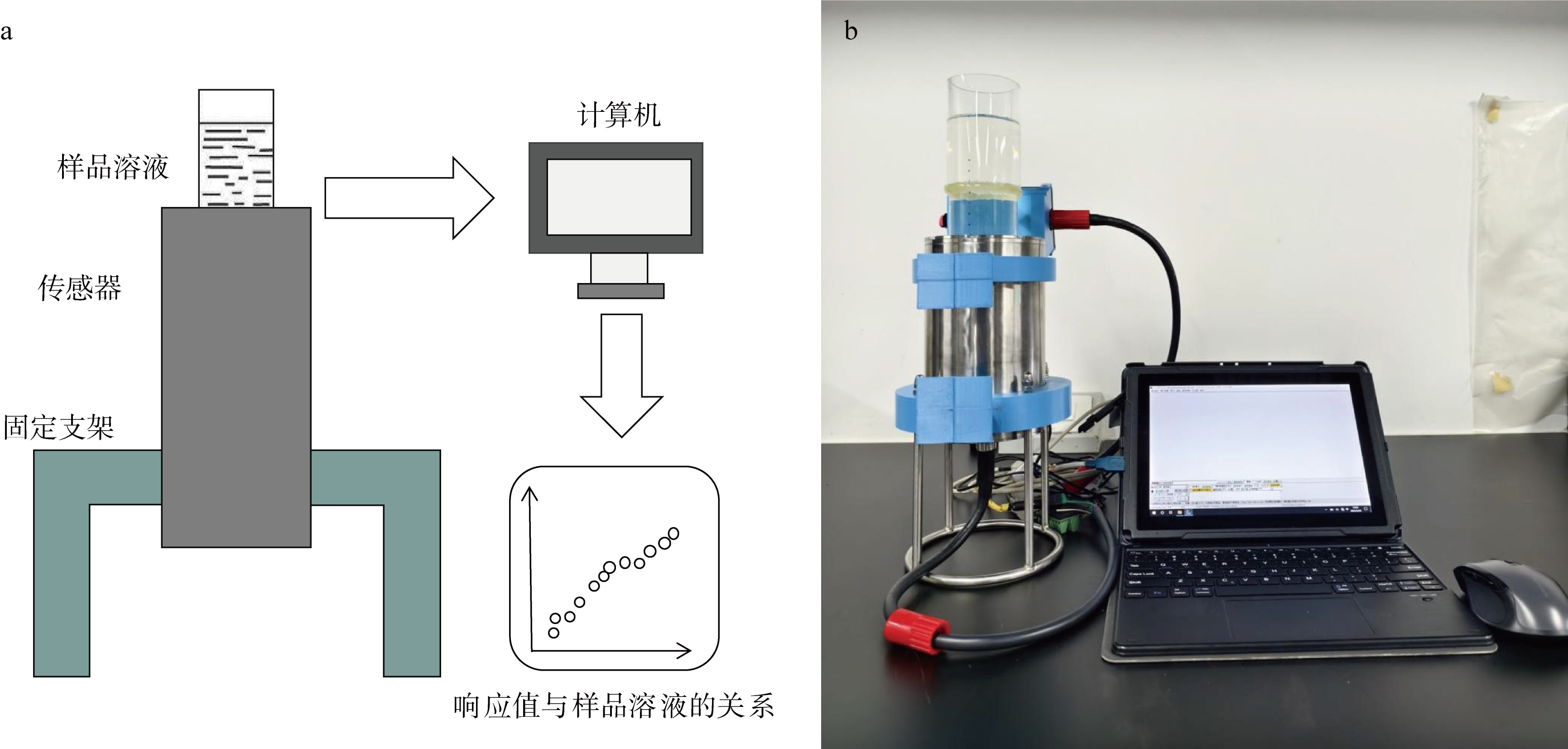
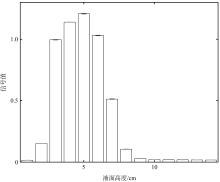
| [1] |
郭晶晶, 王岚云, 2015. 紫外法和荧光法测定海水油类质控指标研究[J]. 化学工程与装备, (11): 199-204, 228 (in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
黄宏新, 2011. 高压充油电缆检测基础问题的研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学.
|
|
HUANG HONGXIN, 2011. Research on fundamental issue of high-pressure[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
李建超, 邓琥, 武志翔, 等, 2012. 水中油在线荧光检测系统的标定研究[J]. 自动化与仪表, 27(4): 53-56.
|
|
LI JIANCHAO, DENG HU, WU ZHIXIANG, et al, 2012. Calibration of online system of examing oil-in-water using fluorescence[J]. Automation & Instrumentation, 27(4): 53-56 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
李义, 禹海清, 董建芳, 等, 2010. 加标回收在水质分析中的应用及回收率计算方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 29: 597-600.
|
|
LI YI, YU HAIQING, DONG JIANFANG, et al, 2010. Application of standard addition in water quality analysis and calculation methods for recovery rates[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 29: 597-600 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
梁树生, 朱志雄, 2024. 荧光法和紫外法测定海水中石油类的对比研究[J]. 广东化工, 51(20): 16-19.
|
|
LIANG SHUSHENG, ZHU ZHIXIONG, 2024. Comparative study on the determination of petroleum in seawater by fluorescence and ultraviolet methods[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 51(20): 16-19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
柳杰, 傅明利, 冯宾, 等, 2025. 基于荧光法的海底电缆绝缘油示踪检测装置[J]. 高电压技术: 1-11.
|
|
LIU JIE, FU MINGLI, FENG BIN, et al, 2025. The tracer detection device for insulating oil in submarine cables based on the fluorescence method[J]. High Voltage Technology: 1-11 [2025-09-03]. https://doi.org/10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20242082 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
栾晓宁, 王春艳, 李颖, 等, 2009. 从浓度定量分析探讨异丙醇作原油萃取剂的可行性[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 31(2): 151-156.
|
|
LUAN XIAONING, WANG CHUNYAN, LI YING, et al, 2009. Discussion on the feasibility of isopropanol as an extractant of crude oil on the basis of concentration quantitative analysis[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 31(2): 151-156 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
罗登林, 丘泰球, 卢群, 2005. 超声波技术及应用(Ⅱ): 声化学技术在日化工业中的应用[J]. 日用化学工业, 35(6): 393-395.
|
|
LUO DENGLIN, QIU TAIQIU, LU QUN, 2005. Ultrasound and its applications (Ⅱ): Applications of sonochemistry in daily chemical industry[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 35(6): 393-395 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
马国明, 秦炜淇, 王思涵, 等, 2025. 海底电缆状态分布式光纤监测技术研究综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 45(1): 370-388.
|
|
MA GUOMING, QIN WEIQI, WANG SIHAN, et al, 2025. Review of submarine cable condition monitoring based on distributed optical fiber sensing[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 45(1): 370-388 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
彭三兵, 张鹏, 何斌, 等, 2024. 基于紫外荧光法的海上平台钻井液含油率检测研究[J]. 山东化工, 53(23): 189-191, 197.
|
|
PENG SANBING, ZHANG PENG, HE BIN, et al, 2024. The test study of drilling fluid oil content in offshore platform based on ultraviolet fluorescence method[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 53(23): 189-191, 197 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
王赛男, 许赞, 刘亮, 等, 2023. 一种便携式荧光测油仪在海上溢油应急监测中的适用性研究[J]. 中国环境监测, 39(3): 190-196.
|
|
WANG SAINAN, XU ZAN, LIU LIANG, et al, 2023. Study on the applicability of a portable fluorescent oil-in-water analyzer to emergency monitoring of offshore oil spill[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 39(3): 190-196 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
新疆维吾尔自治区市场监督管理局, 2021. 水质石油类的测定荧光光度法(DB 65/T 4369—2021)[S].
|
|
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Market Supervision and Administration Bureau, 2021. Water quality-determination of petroleum-hydrocarbons-fluorescence spectrophotometric method (DB 65/T4369-2021)[S]. (in Chinese).
|
| [13] |
薛晓杰, 王诚熹, 姜巍巍, 2018. 正己烷紫外分光光度法测定地表水中石油类的方法改进[J]. 净水技术, 37(S1), 34-35, 60.
|
|
XUE XIAOJIE, WANG CHENGXI, JIANG WEIWEI, 2018. Improvement of determination of petroleum in surface water by ultraviolet spectrophotometry with n-hexane[J]. Water Purification Technology, 37(S1): 34-35, 60.
|
| [14] |
杨铨, 冯伟, 邢龙辉, 等, 2024. 油液监测黏度传感器标定方法优化研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 49(5): 171-176.
|
|
YANG QUAN, FENG WEI, XING LONGHUI, et al, 2024. Optimization of calibration method for viscosity sensor in oil monitoring[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 49(5): 171-176 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
杨书会, 王延圣, 王文亮, 等, 2024. 多糖乳液的制备、乳化特性的影响因素及其应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技, 45(14): 398-407.
|
|
YANG SHUHUI, WANG YANSHENG, WANG WENLIANG, et al, 2024. Research progress in preparation, influencing factors of emulsifying properties and application of polysaccharide emulsion[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 45(14): 398-407 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
叶欣, 张雪容, 王珏, 2010. 自动萃取仪对水中油类的萃取效率研究[J]. 福建分析测试, 19(3): 46-48.
|
|
YE XIN, ZHANG XUERONG, WANG YU, 2010. Study on the extraction efficiency of oils in water by automatic extraction equipment[J]. Fujian Analysis & Testing, 19(3): 46-48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
张飞, 2015. 水中石油类和动植物油类萃取方式的比对研究[J]. 环境与发展, 27(2): 95-97.
|
|
ZHANG FEI, 2015. Comparative studies of the methods to extract the amount of the petroleum oil and animal and plant oils contained in water[J]. Environment and Development, 27(2): 95-97 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2018.07.004
|
| [18] |
赵广立, 冯巍巍, 付龙文, 等, 2014. 基于紫外荧光法检测水中油含量的浸入式传感装置的研究[J]. 海洋通报, 33(1): 77-83.
|
|
ZHAO GUANGLI, FENG WEIWEI, FU LONGWEN, et al, 2014. Research on a submersible oil-in-water detection probe based on ultraviolet fluorescence analysis technique[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 33(1): 77-83 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2006. 荧光分光光度计( JJG 537-2006)[S].
|
|
General administration of quality supervision, inspection and quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2006. Fluorescence Spectrophotometer (JJG 537-2006)[S]. (in Chinese).
|
| [20] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2007. 海洋监测规范第4部分:海水分析(GB 17378. 4-2007)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社.
|
|
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, 2007. Specifications for marine monitoring-Part 4: seawater analysis (GB 17378. 4-2007)[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese).
|
| [21] |
ABOU SAMRA R M, ALI R R, 2024. Tracking the behavior of an accidental oil spill and its impacts on the marine environment in the Eastern Mediterranean[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 198: 115887.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115887
|
| [22] |
ALARURI S D, 2019. Multiwavelength laser induced fluorescence (LIF) LIDAR system for remote detection and identification of oil spills[J]. Optik, 181: 239-245.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.12.073
|
| [23] |
BOOTH A, FLECK J, PELLERIN B A, et al 2023. Field techniques for fluorescence measurements targeting dissolved organic matter, hydrocarbons, and wastewater in environmental waters: Principles and guidelines for instrument selection, operation and maintenance, quality assurance, and data reporting[R/OL]// CALIFORNIA WATER SCIENCE CENTER, NEW YORK WATER SCIENCE CENTER, OREGON WATER SCIENCE CENTER, CARIBBEAN-FLORIDA WATER SCIENCE CENTER. Collection of water data by direct measurement. techniques and methods. Reston: U.S. Geological Survey [2025-09-03]. https://doi.org/10.3133/tm1D11.
|
| [24] |
BUSTAMANTE S, MANANA M, ARROYO A, et al, 2024. Evolution of graphical methods for the identification of insulation faults in oil-immersed power transformers: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 199: 114473.
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2024.114473
|
| [25] |
DE CAROLIS G, ADAMO M, PASQUARIELLO G, 2014. On the estimation of thickness of marine oil slicks from sun-glittered, near-infrared MERIS and MODIS imagery: the Lebanon oil spill case study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 52(1): 559-573.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242476
|
| [26] |
EYKELBOSH A, 2014. Short- and long-term health impacts of marine and terrestrial oil spills[R/OL]. Vancouver, B C: Prepared for the Regional Health Protection Program, Office of the Chief Medical Health Officer, Vancouver Coastal Health Office of the Chief Medical Health Officer, Vancouver Coastal Health [2025-09-03]. https://www.vch.ca/media/VCH-health-impacts-oilspill.pdf.
|
| [27] |
GARCIA-PINEDA O, STAPLES G, JONES C E, et al, 2020. Classification of oil spill by thicknesses using multiple remote sensors[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 236: 111421.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111421
|
| [28] |
LEIFER I, LEHR W J, SIMECEK-BEATTY D, et al, 2012. State of the art satellite and airborne marine oil spill remote sensing: Application to the BP Deepwater Horizon oil spill[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 124: 185-209.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.03.024
|
| [29] |
LU YINGCHENG, SHI JING, HU CHUANMIN, et al, 2020. Optical interpretation of oil emulsions in the ocean-Part II: Applications to multi-band coarse-resolution imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 242: 111778.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111778
|
| [30] |
OTREMBA Z, PISKOZUB J, 2004. Modelling the bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) of seawater polluted by an oil film[J]. Optics Express, 12(8): 1671-1676.
pmid: 19474993
|
| [31] |
PAHLAVANZADEH F, KHALOOZADEH H, FOROUZANFAR M, 2025. Oil pipeline multiple leakage detection and localization based on sensor fusion[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 167: 109038.
doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2024.109038
|
| [32] |
RESCH-GENGER U, HOFFMANN K, HOFFMANN A, 2008. Standardization of fluorescence measurements: criteria for the choice of suitable standards and approaches to fit-for-purpose calibration tools[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1130: 35-43.
doi: 10.1196/nyas.2008.1130.issue-1
|
| [33] |
SINGH H, BHARDWAJ N, ARYA S K, et al, 2020. Environmental impacts of oil spills and their remediation by magnetic nanomaterials[J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 14: 100305.
|
| [34] |
TIANG S S L, LOW L E, ALI I, et al, 2024. Recent advances in ultrasonic cavitation technologies for emulsion preparation: a mini review. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering[J], 45: 101046.
|
| [35] |
UDEPURKAR A P, CLASEN C, KUHN S, 2023. Emulsification mechanism in an ultrasonic microreactor: Influence of surface roughness and ultrasound frequency[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 94: 106323.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106323
|
| [36] |
WU W H, ESKIN D G, PRIYADARSHI A, et al, 2021. New insights into the mechanisms of ultrasonic emulsification in the oil-water system and the role of gas bubbles[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 73: 105501.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105501
|
| [37] |
XIE BEIBEI, YUAN LI, KONG DEMING, et al, 2021. Analysis of fluorescence simulation and experiments for sea surface oil film based on LIF[J]. Applied Optics, 60(18): 5439-5450.
doi: 10.1364/AO.426451
|
| [38] |
ZAJAREVICH N, SLEZAK V, PEURIOT A, et al, 2013. Photoacoustic detection of perfluorocarbon tracers in air for application to leak detection in oil-filled cables[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 34(8): 1444-1450.
doi: 10.1007/s10765-013-1446-7
|
 ), 许占堂2, 施震2(
), 许占堂2, 施震2( ), 张军1, 谢梦圆1, 熊兰兰3, 胡鑫3, 赵科泉4
), 张军1, 谢梦圆1, 熊兰兰3, 胡鑫3, 赵科泉4
 ), XU Zhantang2, SHI Zhen2(
), XU Zhantang2, SHI Zhen2( ), ZHANG Jun1, XIE Mengyuan1, XIONG Lanlan3, HU Xin3, ZHAO Kequan4
), ZHANG Jun1, XIE Mengyuan1, XIONG Lanlan3, HU Xin3, ZHAO Kequan4