| [1] |
郭玉洁, 钱树本, 2003. 中国海藻志: 第五卷硅藻门第一册中心纲[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 379-380(in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
CHAMNANSINP A, LI YANG, LUNDHOLM N, et al, 2013. Global diversity of two widespread, colony-forming diatoms of the marine plankton, Chaetoceros socialis (syn. C. radians) and Chaetoceros gelidus sp. nov[J]. Journal of Phycology, 49(6):1128-1141.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.12121
|
| [3] |
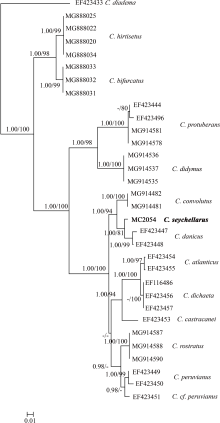
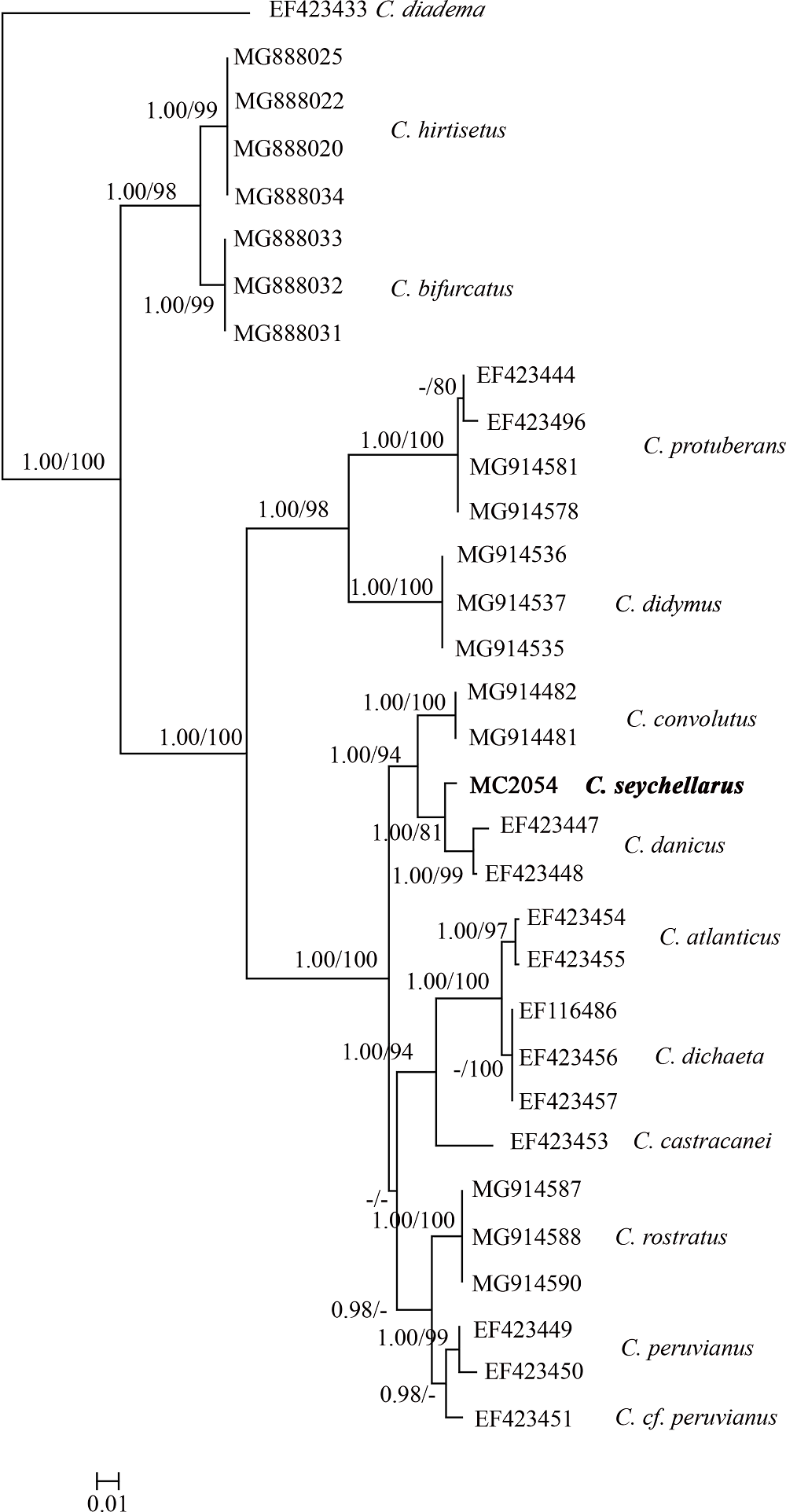
DE LUCA D, SARNO D, PIREDDA R, et al, 2019. A multigene phylogeny to infer the evolutionary history of chaetocerotaceae (bacillariophyta)[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 140:106575.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2019.106575
|
| [4] |
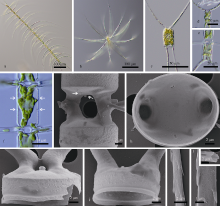
HERNÁNDEZ-BECERRIL D U, 1993. Note on the morphology of two planktonic diatoms: Chaetoceros bacteriastroides and C. seychellarus, with comments on their taxonomy and distribution[J]. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 111(2):117-128.
doi: 10.1006/bojl.1993.1010
|
| [5] |
HERNÁNDEZ-BECERRIL D U, 1996. A morphological study of Chaetoceros species (Bacillariophyta) from the plankton of the Pacific Ocean of Mexico[J]. Bulletin of the Natural History Museum, 26(1):1-73.
|
| [6] |
HERNÁNDEZ-BECERRIL D U, GRANADOS C F, 1998. Species of the diatom genus Chaetoceros (Bacillariophyceae) in the plankton from the southern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Botanica Marina, 41(1-6):505-519.
|
| [7] |
HERNÁNDEZ-BECERRIL D U, AKÉ-CASTILLO J A, 2001. New observations on the morphology of the marine planktonic diatom Chaetoceros seychellarus and taxonomic implications[J]. Nova Hedwigia, 72(3-4):399-408.
doi: 10.1127/nova.hedwigia/72/2001/399
|
| [8] |
KARSTEN G, 1907. Das indische phytoplankton[M]. Wiss ergebn: Deutsche tiefsee Exped. “Valdivia”: 1-389.
|
| [9] |
KOOISTRA W H C F, SARNO D, HERNÁNDEZ-BECERRIL D U, et al, 2010. Comparative molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses of taxa in the Chaetocerotaceae (Bacillariophyta)[J]. Phycologia, 49(5):471-500.
doi: 10.2216/09-59.1
|
| [10] |
LEE J H, 2011. Algal flora of Korea. Volume 3, Number 5. Chrysophyta: Bacillariophyceae: Centrales: Biddulphiineae: Centrales. Incheon: National Institute of Biological Resources: 1-94.
|
| [11] |
LUNDHOLM N, DAUGBJERG N, MOESTRUP Ø, 2002. Phylogeny of the Bacillariaceae with emphasis on the genus Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) based on partial LSU rDNA[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 37(1):115-134.
doi: 10.1017/S096702620100347X
|
| [12] |
MANGUIN E, 1957. Premier inventaire des Diatomées de la Terre Adélie Antarctique. Espèces nouvelles[J]. Revue Algologique, Nouvelle Série, 3(3):111-134.
|
| [13] |
MILLER M A, PFEIFFER W, SCHWARTZ T, 2010. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees [C]// Proceedings of 2010 Gateway computing environments workshop. New Orleans, LA, USA: IEEE: 1-8.
|
| [14] |
NYLANDER J A A, 2004. MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary biology Centre, Uppsala university[EB/OL]. https://www.oalib.com/references/12406599.
|
| [15] |
RONQUIST F, TESLENKO M, VAN DER MARK P, et al, 2012. MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space[J]. Systematic Biology, 61(3):539-542.
doi: 10.1093/sysbio/sys029
|
| [16] |
SHEVCHENKO O G, ORLOVA T Y, HERNÁNDEZ-BECERRIL D U, 2006. The genus Chaetoceros (Bacillariophyta) from Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan[J]. Botanica Marina, 49(3):236-258.
|
| [17] |
TAYLOR F J R, 1966. Phytoplankton of the south western Indian Ocean[J]. Nova Hedwigia, 12(3-4):433-476.
|
| [18] |
TOMAS C R, HASLE G R, 1997. Identifying marine phytoplankton[M]. San Diego: Academic Press: 469-475.
|
| [19] |
XU XIAOJING, LUNDHOLM N, LI YANG, 2020. A study of Chaetoceros debilis sensu lato species (Bacillariophyceae), with ememdation of C. debilis and description of C. galeatus sp. nov.[J]. Journal of Phycology, 56(3):784-797.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.v56.3
|
 ), ZHAI Mengyi, LI Yang(
), ZHAI Mengyi, LI Yang( )
)