热带海洋学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 106-115.doi: 10.11978/2019077CSTR: 32234.14.2019077
• 海洋生物学 • 上一篇
广西涠洲岛底栖甲藻前沟藻属(Amphidinium)种类的形态学和系统发育学研究
- 暨南大学生命科学技术学院, 水体富营养化与赤潮防治广东普通高校重点实验室, 广东 广州 510632
-
收稿日期:2019-08-24修回日期:2019-11-26出版日期:2020-05-10发布日期:2020-05-19 -
通讯作者:吕颂辉 -
作者简介:江丽春(1992—), 女, 江西省九江市人, 硕士研究生, 从事海洋底栖甲藻分类学 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(41576162);国家自然科学基金(41876173)
Morphology and Phylogenetics study on the species of Amphidinium (Gymnodinials, Dinophyceae) from Weizhou Island, Guangxi
Lichun JIANG, Qun LI, Songhui LÜ( )
)
- College of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, Key Laboratory of Aquatic Eutrophication and Control of Harmful Algae Blooms of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Guangzhou 510632, China
-
Received:2019-08-24Revised:2019-11-26Online:2020-05-10Published:2020-05-19 -
Contact:Songhui Lü -
Supported by:National Nature Science Foundation of China(41576162);National Nature Science Foundation of China(41876173)
摘要:
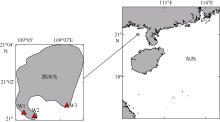
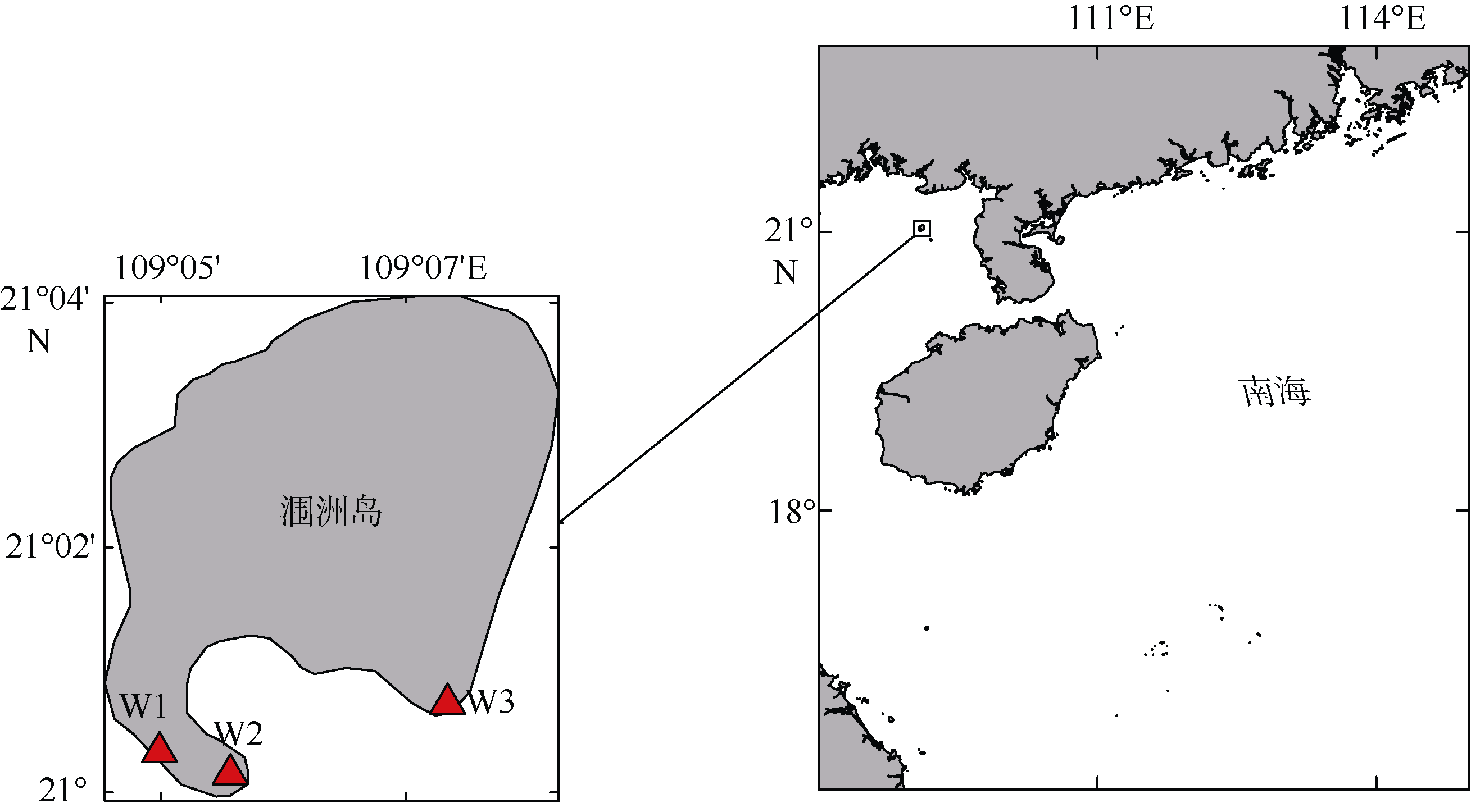
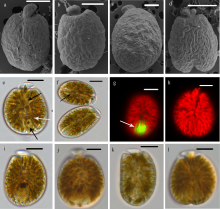
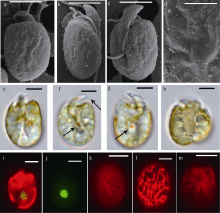
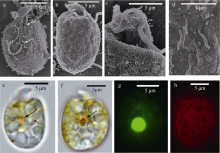
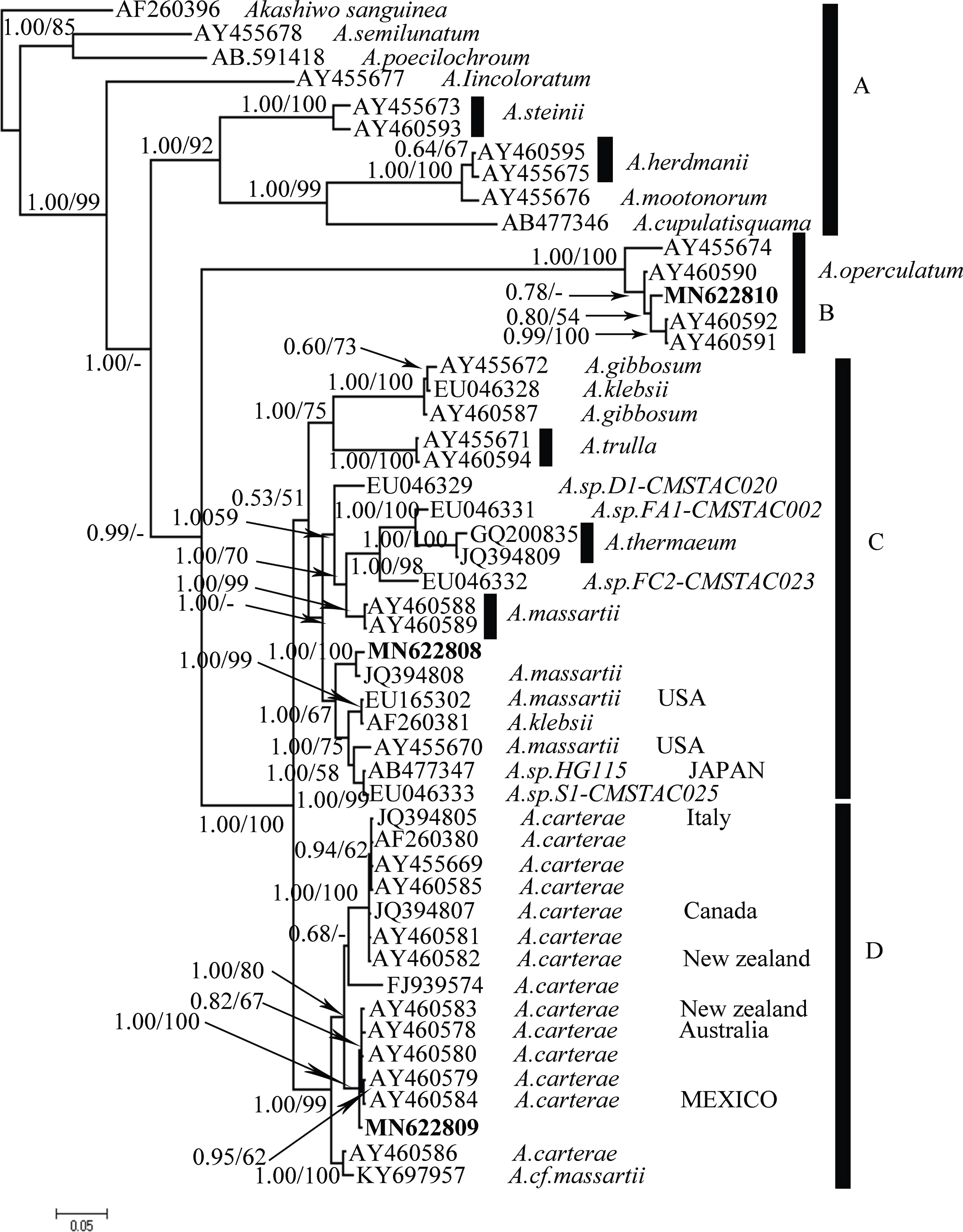
本文对采集自我国广西涠洲岛海域潮下带大型海藻及死珊瑚上的附着底栖甲藻样品进行了分析。利用毛细管单细胞分离方法成功分离并培养了多株前沟藻属种类, 运用光学显微镜、扫描电镜和分子生物学等技术, 对所获得的前沟藻株系进行形态学和系统发育分析, 鉴定出前沟藻属3个种, 分别为具盖前沟藻(Amphidinium operculatum)、玛氏前沟藻(Amphidinium massertii)和强壮前沟藻(Amphidinium caeterae), 其中具盖前沟藻和玛氏前沟藻为我国新纪录种。分析比较了不同种类间形态和系统发育的差异, 发现3种前沟藻的形态特征大体与相应模式种报道的一致。本研究丰富了我国前沟藻种类多样性和系统发育进化信息, 同时将两个新记录种具盖前沟藻和玛氏前沟藻的已知分布范围拓展到了我国南部沿海水域。
引用本文
江丽春, 李群, 吕颂辉. 广西涠洲岛底栖甲藻前沟藻属(Amphidinium)种类的形态学和系统发育学研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(3): 106-115.
Lichun JIANG, Qun LI, Songhui LÜ. Morphology and Phylogenetics study on the species of Amphidinium (Gymnodinials, Dinophyceae) from Weizhou Island, Guangxi[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(3): 106-115.
| 1 | 韩笑天, 颜天, 邹景忠 , 等, 2004. 强壮前沟藻(Amphidinium carterae Hulburt)形态特征及其生长特性研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 35(3):279-283. |
| HAN XIAOTIAN, YAN TIAN, ZOU JINGZHONG , et al, 2004. Morphological features and growth characteristics of the dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae Hulburt[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 35(3):279-283 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 2 | 张珍妮, 姜玥璐, 李曼璐 , 等, 2016. 强壮前沟藻(Amphidinium carterae Hulbert)在多重逆境条件下的生长和生理响应[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(5):982-989. |
| ZHANG ZHENNI, JIANG YUELU, LI MANLU , et al, 2016. The growth and physiological changes of Amphidinium carterae Hulbert under environmental stresses[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 47(5):982-989 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 3 |
BAIG H S, SAIFULLAH S M, DAR A , 2006. Occurrence and toxicity of Amphidinium carterae Hulburt in the North Arabian Sea[J]. Harmful Algae, 5(2):133-140.
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2005.06.010 |
| 4 |
BAUER I, MARANDA L, SHIMIZU Y , et al, 1994. The structures of amphidinolide B isomers: strongly cytotoxic macrolides produced by a free-swimming dinoflagellate, Amphidinium sp[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 116(6):2657-2658.
doi: 10.1021/ja00085a071 |
| 5 |
BAUER I, MARANDA L, YOUNG K A , et al, 1995a. Isolation and structure of Caribenolide I, a highly potent antitumor macrolide from a cultured free-swimming Caribbean dinoflagellate, Amphidinium sp. S1-36-5[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 60(4):1084-1086.
doi: 10.1021/jo00109a050 |
| 6 |
BAUER I, MARANDA L, YOUNG K A , et al, 1995b. The isolation and structures of unusual 1, 4-polyketides from the dinoflagellate, Amphidinium sp.[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 36(7):991-994.
doi: 10.1016/0040-4039(94)02423-9 |
| 7 | BIECHELER B , 1952. Recherches sur les Peridiniens[J]. Bulletin Biologique de la France et de la Belgique, 36(Suppl.):1-149. |
| 8 |
BOTES L, PRICE B, WALDRON M , et al, 2002. A simple and rapid scanning electron microscope preparative technique for delicate “Gymnodinioid” dinoflagellates[J]. Microscopy Research and Technique, 59(2):128-130.
doi: 10.1002/jemt.10184 pmid: 12373723 |
| 9 | CARTER N , 1937. New or interesting algae from brackish water[J]. Archives für Protistenkunde, 90:1-68. |
| 10 | CLAPARÈDE R É, LACHMANN J , 1859. Études sur les infusoires et les rhizopodes[J]. Mémoires de l'Institut National Genevois, 6:261-482. |
| 11 |
DAUGBJERG N, HANSEN G, LARSEN J , et al, 2000. Phylogeny of some of the major genera of dinoflagellates based on ultrastructure and partial LSU rDNA sequence data, including the erection of three new genera of unarmoured dinoflagellates[J]. Phycologia, 39(4):302-317.
doi: 10.2216/i0031-8884-39-4-302.1 |
| 12 | DODGE J D, CRAWFORD R M , 1968. Fine structure of the dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae Hulbert[J]. Protistologica, 4:231-242. |
| 13 | DOLAPSAKIS N P, ECONOMOU-AMILLI A , 2009. A new marine species of Amphidinium (Dinophyceae) from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece[J]. Acta Protozoologica, 48(2):153-170. |
| 14 | FENSOME R A, TAYLOR F J R, NORRIS G , et al, 1993. A classification of living and fossil dinoflagellates[J]. Micropaleontology, Special Publication, 7:1-351. |
| 15 |
FUKUYO Y , 1981. Taxonomical study on benthic dinoflagellates collected in coral reefs[J]. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 47(8):967-978.
doi: 10.2331/suisan.47.967 |
| 16 |
GARCÉS E, FERNANDEZ M, PENNA A , et al, 2006. Characterization of NW Mediterranean Karlodinium spp. (Dinophyceae) strains using morphological, molecular, chemical, and physiological methodologies[J]. Journal of Phycology, 42(5):1096-1112.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.2006.42.issue-5 |
| 17 | HALL T A , 1999. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT[J]. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41(41):95-98. |
| 18 | HULBURT E M , 1957. The taxonomy of unarmored Dinophyceae of shallow embayments on Cape Cod, Massachusetts[J]. The Biological Bulletin, 112(2):196-219. |
| 19 | JØRGENSEN M F, MURRAY S, DAUGBJERG N , 2004a. Amphidinium revisited. I. redefinition of Amphidinium (Dinophyceae) based on cladistic and molecular phylogenetic analyses[J]. Journal of Phycology, 40(2):351-365. |
| 20 | JØRGENSEN M F, MURRAY S, DAUGBJERG N , 2004b. A new genus of athecate interstitial dinoflagellates, Togula gen. nov., previously encompassed within Amphidinium sensu lato: inferred from light and electron microscopy and phylogenetic analyses of partial large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences[J]. Phycological Research, 52(3):284-299. |
| 21 | KARAFAS S, TENG S T, LEAW C P , et al, 2017. An evaluation of the genus Amphidinium (Dinophyceae) combining evidence from morphology, phylogenetics, and toxin production, with the introduction of six novel species[J]. Harmful Algae, 68:128-151. |
| 22 | KOBAYASHI J, SHIGEMORI H, ISHIBASHI M , et al, 1991. Amphidinolides G and H: new potent cytotoxic macrolides from the cultured symbiotic dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 56(17):5221-5224. |
| 23 | KOFOID C A, SWEZY O , 1921. The free-living unarmored dinoflagellata[M]. California: University of California Press. |
| 24 | KONG XIANYU, HAN XIURONG, GAO MIN , et al, 2016. Antialgal and antilarval activities of bioactive compounds extracted from the marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 15(6):1014-1020. |
| 25 | LEE K H, JEONG H J, PARK K , et al, 2013. Morphology and molecular characterization of the epiphytic dinoflagellate Amphidinium massartii, isolated from the temperate waters off Jeju Island, Korea[J]. Algae, 28(3):213-231. |
| 26 | MARANDA L, SHIMIZU Y , 1996. Amphidinium operculatum var. nov. gibbosum (Dinophyceae), a free-swimming marine species producing cytotoxic metabolites[J]. Journal of Phycology, 32(5):873-879. |
| 27 |
MORRILL L C, LOEBLICH III A R , 1981. A survey for body scales in dinoflagellates and a revision of Cachonina and Heterocapsa (Pyrrhophyta)[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 3(1):53-65.
doi: 10.1093/plankt/3.1.53 |
| 28 |
MURRAY S A, GARBY T, HOPPENRATH M , et al, 2012. Genetic diversity, morphological uniformity and polyketide production in dinoflagellates (Amphidinium, Dinoflagellata)[J]. PLoS One, 7(6):e38253.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038253 |
| 29 |
MURRAY S, JØRGENSEN M F, DAUGBJERG N , et al, 2004. Amphidinium revisited. II. Resolving species boundaries in the Amphidinium operculatum species complex (Dinophyceae), including the descriptions of Amphidinium trulla sp. nov. and Amphidinium gibbosum. comb. nov.[J]. Journal of Phycology, 40(2):366-382.
doi: 10.1046/j.1529-8817.2004.03132.x |
| 30 | MURRAY S, PATTERSON D J , 2002. The benthic dinoflagellate genus Amphidinium in south-eastern Australian waters, including three new species[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 37(2):279-298. |
| 31 | PAGE R D M . 1996. TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers[J]. Computer Applications in the Biosciences, 12(4):357-358. |
| 32 | REÑÉ A, CAMP J, GARCÉS E , 2015. Diversity and phylogeny of Gymnodiniales (Dinophyceae) from the NW Mediterranean Sea revealed by a morphological and molecular approach[J]. Protist, 166(2):234-263. |
| 33 | RHODES L L, SMITH K F, MUNDAY R , et al, 2010. Toxic dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) from Rarotonga, Cook Islands[J]. Toxicon, 56(5):751-758. |
| 34 | RONQUIST F, HUELSENBECK J P , 2003. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models[J]. Bioinformatics, 19(12):1572-1574. |
| 35 | SATAKE M, MURATA M, YASUMOTO T , et al, 1991. Amphidinol, a polyhydroxy-polyene antifungal agent with an unprecedented structure, from a marine dinoflagellate, Amphidinium klebsii[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 113(26):9859-9861. |
| 36 |
SEKIDA S, OKUDA K, KATSUMATA K , et al, 2003. A novel type of body scale found in two strains of Amphidinium species (Dinopbyceae)[J]. Phycologia, 42(6):661-666.
doi: 10.2216/i0031-8884-42-6-661.1 |
| 37 |
TAMURA K, PETERSON D, PETERSON N , et al, 2011. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28(10):2731-2739.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121 |
| 38 |
TAMURA M, TAKANO Y, HORIGUCHI T , 2009. Discovery of a novel type of body scale in the marine dinoflagellate, Amphidinium cupulatisquama sp. nov. (Dinophyceae)[J]. Phycological Research, 57(4):304-312.
doi: 10.1111/(ISSN)1440-1835 |
| 39 | TRUBY E W , 1997. Preparation of single-celled marine dinoflagellates for electron microscopy[J]. Microscopy Research and Technique, 36(4):337-340. |
| 40 |
VILA M, CAMP J, GARCÉS E , et al, 2001. High resolution spatio-temporal detection of potentially harmful dinoflagellates in confined waters of the NW Mediterranean[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 23(5):497-514.
doi: 10.1093/plankt/23.5.497 |
| 41 | WATANABE M M, SUDA S, INOUYA I , et al, 1990. Lepidodinium viride gen. et sp. nov. (Gymnodinaiales, Dinophyta), a green dinoflagellate with a chlorophyll A-containing and B-containing endosymbiont[J]. Journal of Phycology, 26(4):741-751. |
| 42 |
YASUMOTO T, SEINO N, MURAKAMI Y , et al, 1987. Toxins produced by benthic dinoflagellates[J]. The Biological Bulletin, 172(1):128-131.
doi: 10.2307/1541612 |
| [1] | 王佳熹, 卢护木, 齐鑫, 高程海, 刘永宏, 罗小卫. 涠洲岛鹿角珊瑚共附生真菌Arachniotus ruber GXIMD 02510的次级代谢产物及抑菌活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 174-180. |
| [2] | 李能辉, 黄庆, 李航, 曾俊, 吴科锋, 谭华强. 基于形态和分子数据对湛江海域4个江蓠物种(红藻门)的分类学研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 34-47. |
| [3] | 邢楠楠, 任润馨, 唐振洲, 罗志宏, 夏辰曦, 刘永宏, 彭亮, 陈显强. 涠洲岛海洋沉积物来源真菌Aspergillus sp. GXIMD02003的代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 154-160. |
| [4] | 郭键林, 孙显, 杨宇峰, 王庆. 广西涠洲岛大型海藻场及其邻近海域桡足类群落结构演替特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 155-165. |
| [5] | 韩通, 李晶晶, 刘正一, 刘凯, 张金浩, 秦松, 钟志海. 红纤维虾形草(Phyllospadix iwatensis)种子形态及内部特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 105-113. |
| [6] | 刘巍, 郭海朋, 董鹏生, 燕孟琛, 张德民. 别样玫瑰变色杆菌(Aliiroseovarius sp.)Z3基因组测序及比较基因组分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 52-61. |
| [7] | 刘金梅, 黄冰心, 丁兰平, 王雪聪, 闫璟, 闫盼竹, 张瑶. 我国海南省东南部台湾那屿藻的形态观察及系统发育分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 76-82. |
| [8] | 牛彪彪, 翟梦怡, 李扬. 塞舌尔角毛藻的形态学再描述和分子系统学分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(4): 44-49. |
| [9] | 龙超, 罗肇河, 韦章良, 杨芳芳, 李茹, 龙丽娟. 海南三亚鹿回头虫黄藻(Effrenium voratum)的形态学和系统发育学研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(4): 35-43. |
| [10] | 刘金梅, 姜晶晶, 马鑫, 黄冰心, 杨楠, 刘美媛, 丁兰平. 我国粤东沙菜属(红藻门 杉藻目)的分类鉴定 *[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(1): 99-110. |
| [11] | 徐轶肖, 何喜林, 张腾, 蓝文陆. 北部湾棕囊藻藻华原因种分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(6): 122-130. |
| [12] | 张婷, 胡敏航, 张文静, 陈天然, 刘猛. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁近千年的发育过程及其对气候变化的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(4): 70-79. |
| [13] | 黄丽芬, 李群, 吕颂辉, 张亮, 谢学东. 中国西沙群岛底栖甲藻热带库里亚藻(Coolia tropicalis)的形态学、系统发育及毒性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(3): 86-97. |
| [14] | 黄景, 潘肖兰, 许濛, 刘文广, 张华, 何毛贤. 形态学和SNP标记分析马氏珠母贝杂交子代及其亲本群体的遗传结构[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(6): 80-89. |
| [15] | 李永梅, 刘瑞, 杨楠, 丁兰平, 黄冰心, 王艺晓, 陈彦伟. 海南省4种江蓠属(红藻门)海藻的形态分类学研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(4): 29-37. |
|
||