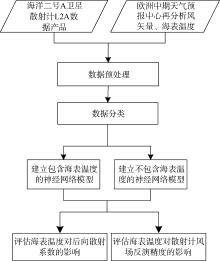
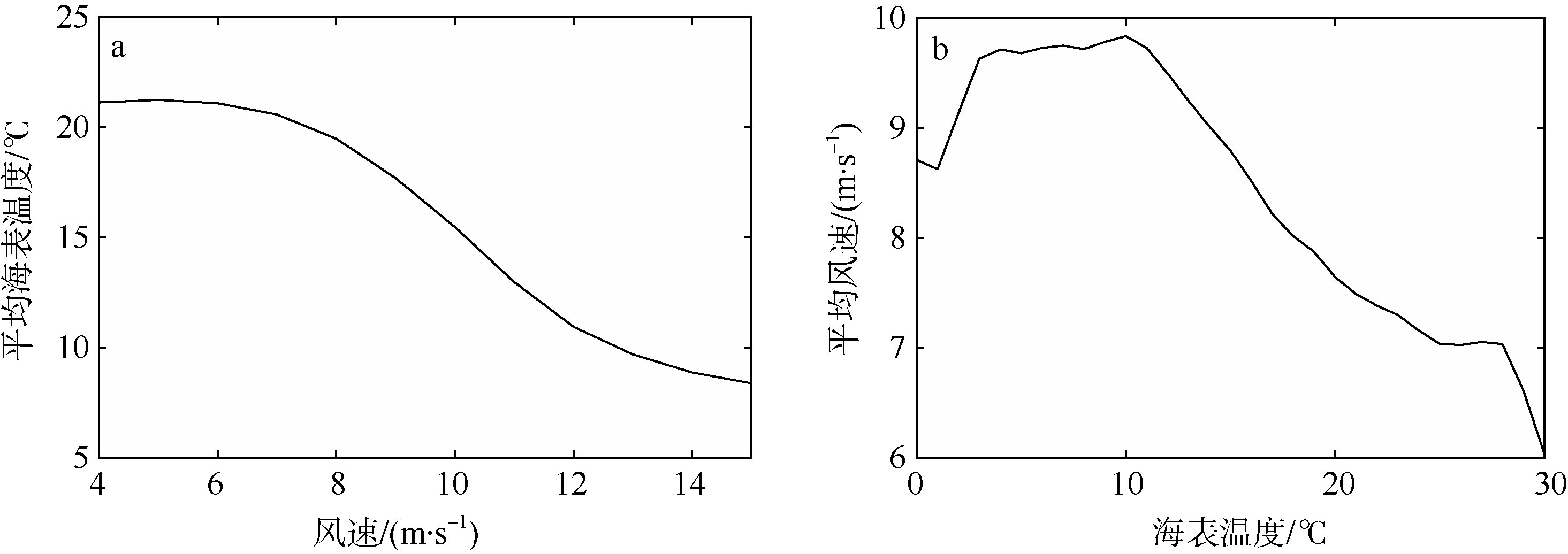
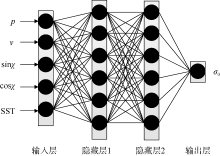
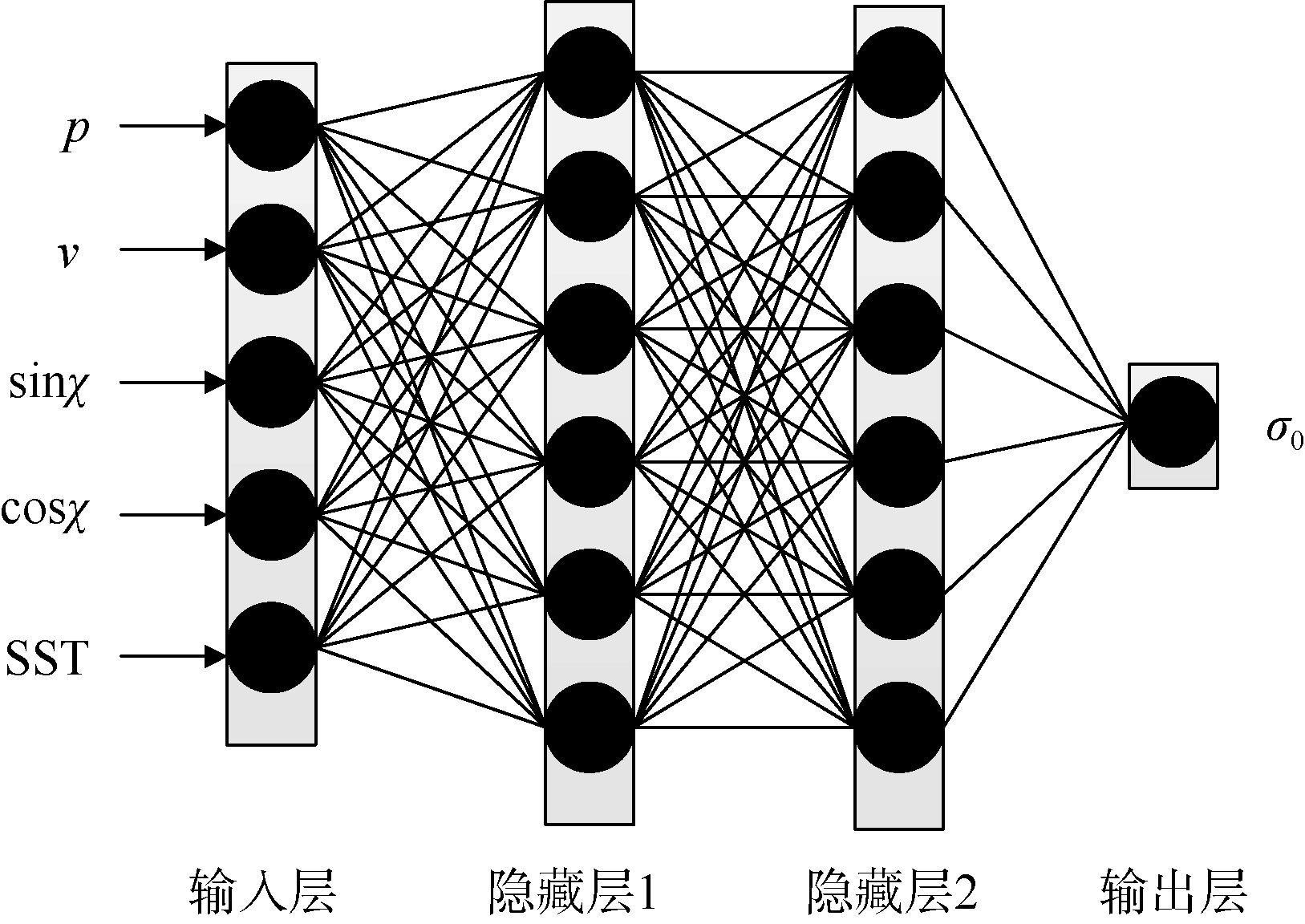
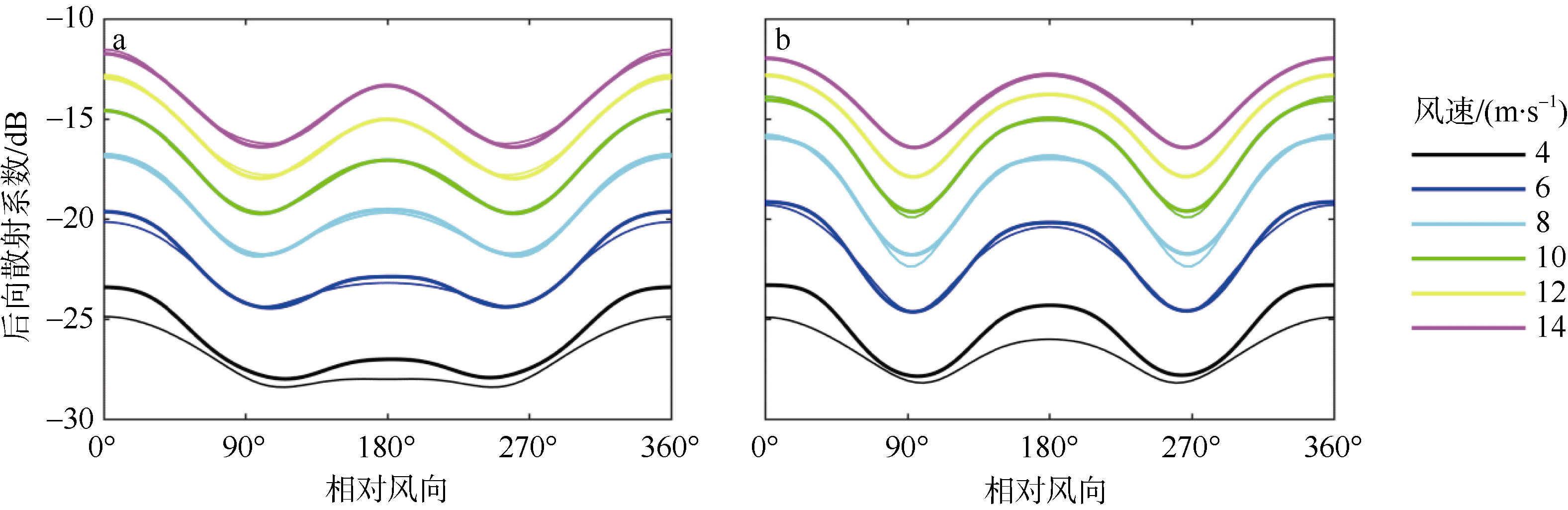
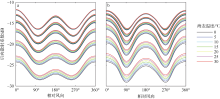
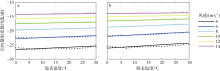
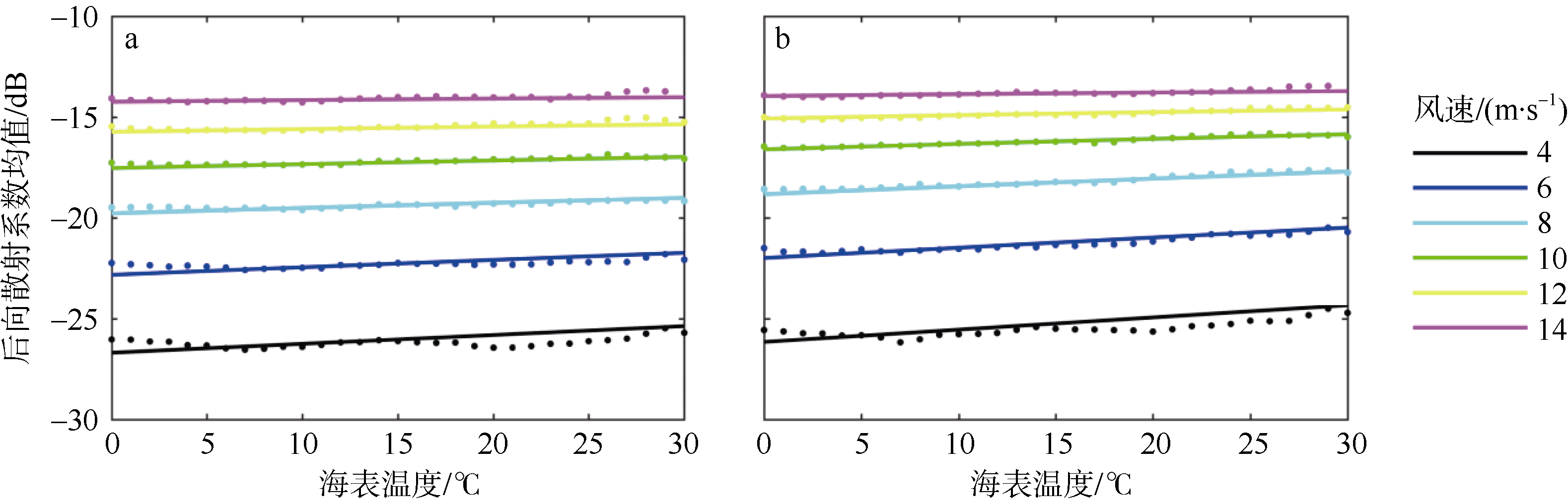
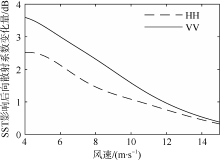
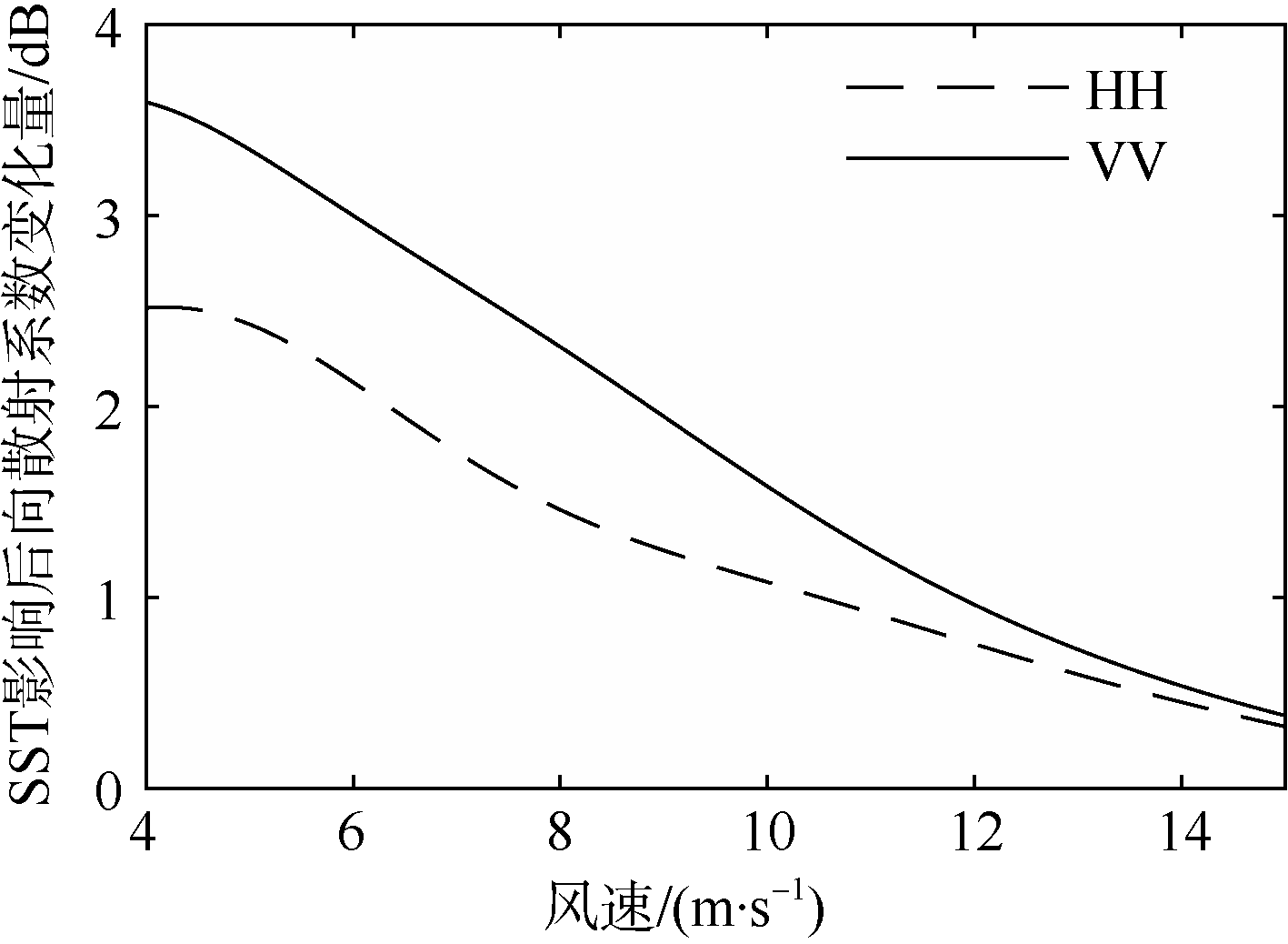
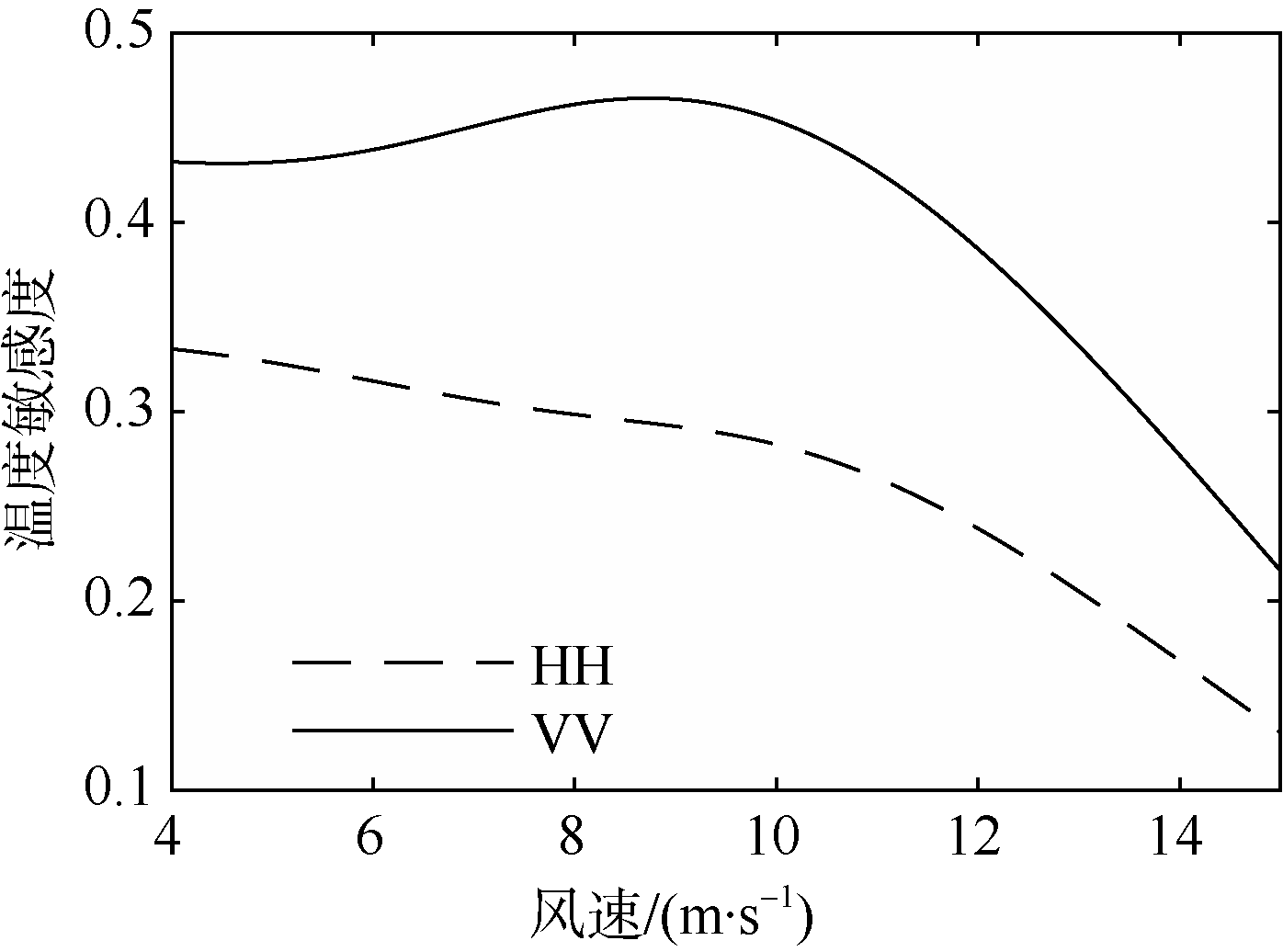
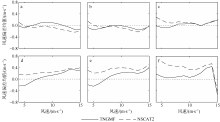
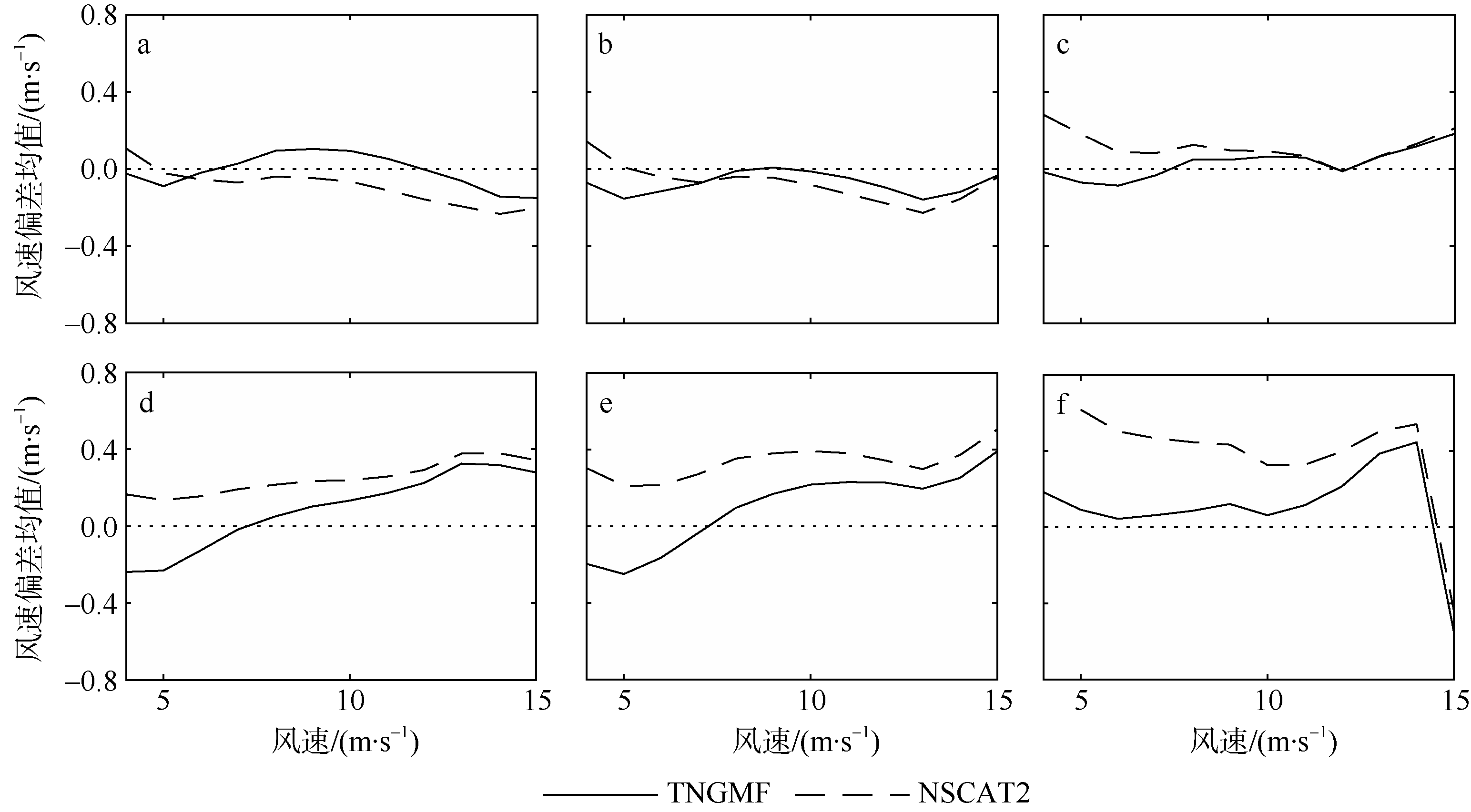
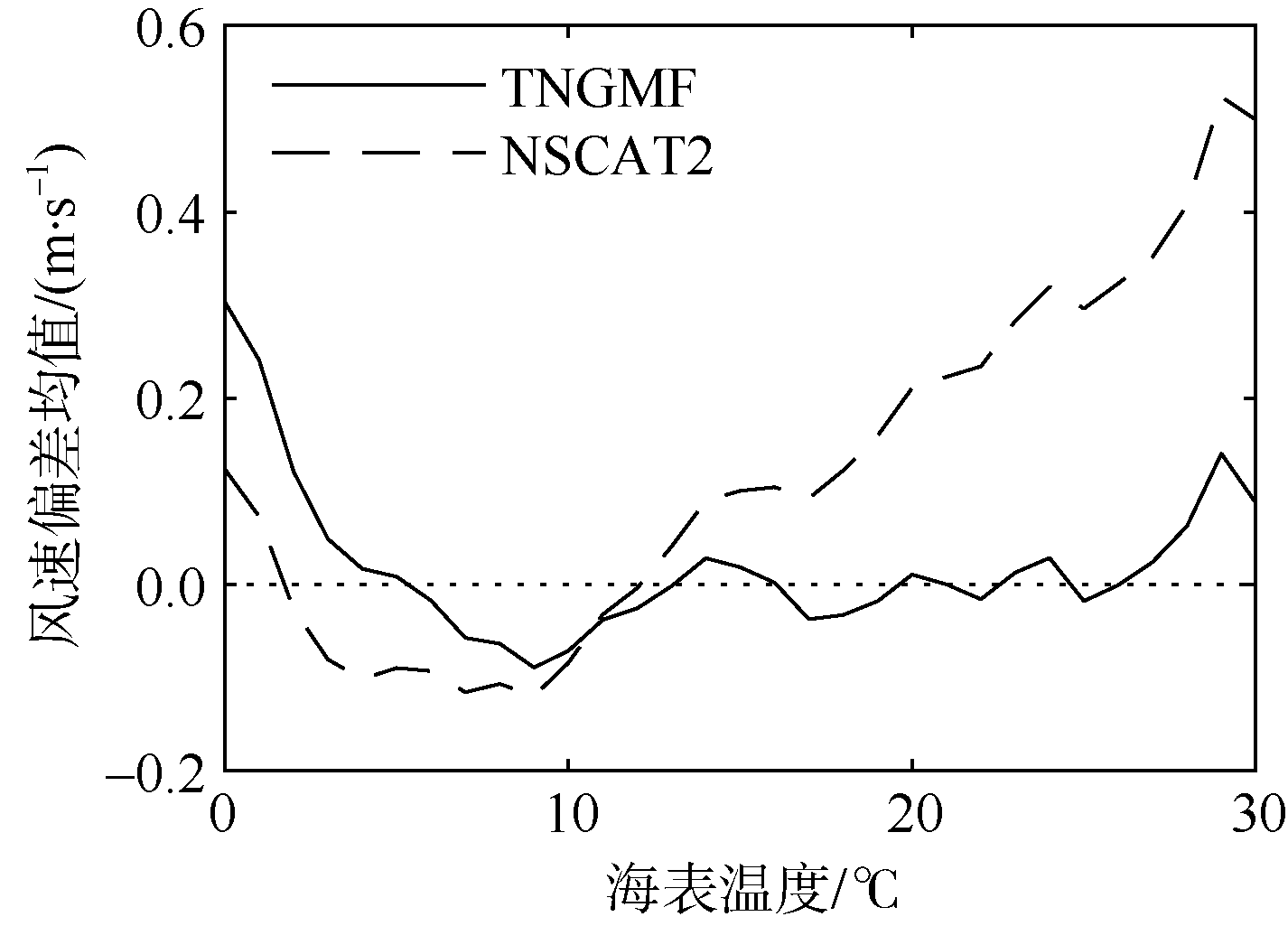
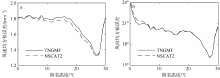
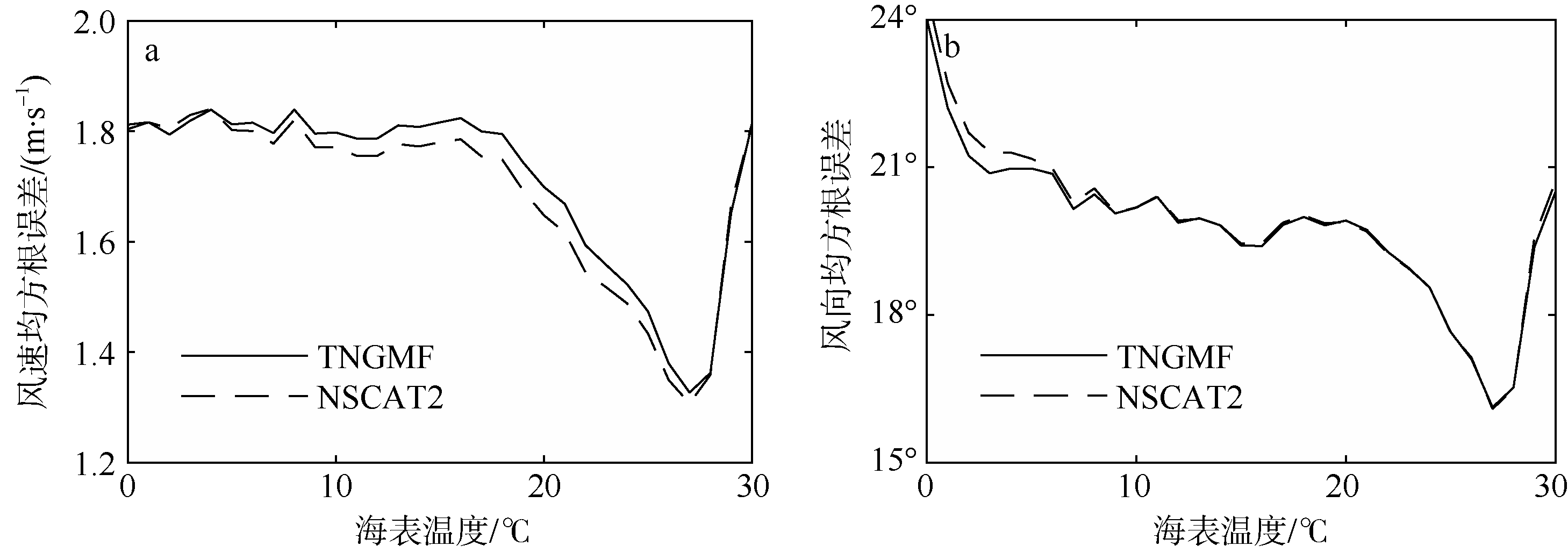
| [1] |
陈坤堂, 董晓龙, 徐星欧, 等, 2017. 微波散射计反演海面风场的神经网络方法研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 32(4): 683-690.
|
|
CHEN KUNTANG, DONG XIAOLONG, XU XING’OU, et al, 2017. The study on oceanic vector wind field retrieve technique based on neural networks of microwave scatterometer[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 32(4): 683-690. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
李燕初, 孙瀛, 林明森, 等, 1999. 用圆中数滤波器排除卫星散射计风场反演中的风向模糊[J]. 台湾海峡, 18(1): 42-48.
|
|
LI YANCHU, SUN YING, LIN MINGSEN, et al, 1999. Resolving directional ambiguities for scatterometer derived winds by a circular median filter algorithm[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 18(1): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [3] |
林明森, 宋新改, 彭海龙, 等, 2006. 散射计资料的风场神经网络反演算法研究[J]. 国土资源遥感, (2): 8-11.
|
|
LIN MINGSEN, SONG XIN’GAI, PENG HAILONG, et al, 2006. Neural network wind retrieval from scatterometer data[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, (2): 8-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
王婷, 江文辉, 肖南峰, 2011. 基于改进BP神经网络的数字识别[J]. 电子设计工程, 19(3): 108-112.
|
|
WANG TING, JIANG WENHUI, XIAO NANFENG, 2011. Numerical recognition based on improved BP neural network[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 19(3): 108-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
解学通, 方裕, 陈晓翔, 等, 2005. 基于最大似然估计的海面风场反演算法研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 21(1): 30-33.
|
|
XIE XUETONG, FANG YU, CHEN XIAOXIANG, et al, 2005. Research on numerical wind vector retrieval algorithm based on maximum likelihood estimation[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 21(1): 30-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
解学通, 陈克海, 郭丽青, 等, 2007. 包含温度因子的海水地球物理模型函数建模研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 26(6): 14-20.
|
|
XIE XUETONG, CHEN KEHAI, GUO LIQING, et al, 2007. Research on modeling of ocean water geophysical model function including ocean surface temperature[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 26(6): 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [7] |
BENTAMY A, GRODSKY S A, CARTON J A, et al, 2012. Matching ASCAT and QuikSCAT winds[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117(C2): C02011.
|
| [8] |
BOURASSA M A, RODRIGUEZ E, GASTON R, 2010. NASA’s ocean vector winds science team workshops[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 91(7): 925-928.
doi: 10.1175/2010BAMS2880.1
|
| [9] |
DEE D P, UPPALA S M, SIMMONS A J, et al, 2011. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 137(656): 553-597.
|
| [10] |
DONELAN M A, PIERSON JR W J, 1987. Radar scattering and equilibrium ranges in wind-generated waves with application to scatterometry[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 92(C5): 4971-5029.
|
| [11] |
DU YANLEI, YANG XIAOFENG, YANG JIAN, et al, 2021. Effects of temperature on sea surface radar backscattering under neutral and nonneutral atmospheric conditions for wind retrieval applications: a numerical study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 59(4): 2727-2743.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3013980
|
| [12] |
EBUCHI N, 2000. Evaluation of NSCAT-2 wind vectors by using statistical distributions of wind speeds and directions[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 56(2): 161-172.
doi: 10.1023/A:1011183029009
|
| [13] |
FREILICH M H, DUNBAR R S, 1999. The accuracy of the NSCAT 1 vector winds: comparisons with National Data Buoy Center buoys[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 104(C5): 11231-11246.
|
| [14] |
GRODSKY S A, KUDRYAVTSEV V N, BENTAMY A, et al, 2012. Does direct impact of SST on short wind waves matter for scatterometry?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(12): L12602.
|
| [15] |
KIM T S, PARK K A, LI XIAOFENG, et al, 2017. Observation of wind direction change on the sea surface temperature front using high-resolution full polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 10(6): 2599-2607.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.4609443
|
| [16] |
KUDRYAVTSEV V N, MAKIN V K, CHAPRON B, 1999. Coupled sea surface-atmosphere model: 2. Spectrum of short wind waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 104(C4): 7625-7639.
|
| [17] |
LIN WENMING, DONG XIAOLONG, PORTABELLA M, et al, 2019. A perspective on the performance of the CFOSAT rotating fan-beam scatterometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 57(2): 627-639.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2858852
|
| [18] |
MEJIA C, THIRIA S, TRAN N, et al, 1998. Determination of the geophysical model function of the ERS-1 scatterometer by the use of neural networks[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 103(C6): 12853-12868.
|
| [19] |
NGHIEM S V, LI F K, WALSH E J, et al, 2000. Radar backscatter across the Gulf Stream sea surface temperature front[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 38(2): 926-941.
doi: 10.1109/36.841975
|
| [20] |
PENG YIHUAN, XIE XUETONG, LIN MINGSEN, et al, 2020. A modeling study of the impact of the sea surface temperature on the backscattering coefficient and wind field retrieval[J]. IEEE Access, 8: 78652-78662.
doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639
|
| [21] |
SCHULTZ H, 1990. A circular median filter approach for resolving directional ambiguities in wind fields retrieved from spaceborne scatterometer data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 95(C4): 5291-5303.
|
| [22] |
SOISUVARN S, JELENAK Z, CHANG P S, et al, 2013. CMOD5. H - a high wind geophysical model function for C-band vertically polarized satellite scatterometer measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 51(6): 3744-3760.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2219871
|
| [23] |
WANG ZHIXIONG, STOFFELEN A, VERHOEF A, 2016. Ku-band scatterometer SST sensitivity and geophysical model function[C]// Proceedings of 2016 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium. Beijing, China: IEEE.
|
| [24] |
WANG ZHIXIONG, STOFFELEN A, ZHAO CHAOFANG, et al, 2017. An SST‐dependent Ku‐band geophysical model function for RapidScat[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 122(4): 3461-3480.
doi: 10.1002/2016JC012619
|
| [25] |
XIE XUETONG, TIAN DONGXUAN, CHEN KEHAI, et al, 2019. A SST-dependent geophysical model function for HY-2A microwave scatterometer[C]// Proceedings of 2019 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium. Yokohama, Japan: IEEE.
|
| [26] |
XIE XUETONG, WANG JING, LIN MINGSEN, 2020. A neural network-based rain effect correction method for HY-2A scatterometer backscatter measurements[J]. Remote Sensing, 12(10): 1648.
doi: 10.3390/rs12101648
|
| [27] |
ZHENG QUANAN, YAN XIAOHAI, KLEMAS V, et al, 1995. Laboratory measurements of the effects of viscosity on short water wave spectra and implication for radar remote sensing of the ocean surface[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 13(3): 193-205.
doi: 10.1007/BF02850519
|
 ), XIE Xuetong2(
), XIE Xuetong2( ), ZHANG Jinlan1, ZHENG Yan1
), ZHANG Jinlan1, ZHENG Yan1