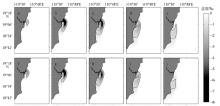
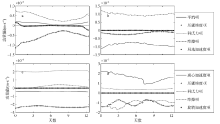
| [1] |
倪智慧, 陈辉, 董礼先, 等, 2012. 长江口外羽状流水体中的垂向混合与层化的观测与分析[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 46(11): 1862-1873.
|
|
NI ZHIHUI, CHEN HUI, DONG LIXIAN, et al, 2012. Measurement and analysis of vertical mixing and stratification within the plume outside the Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 46(11): 1862-1873 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
左浩, 高抒, 2005. 海南岛博鳌港洪水过程模拟[J]. 海洋通报, 24(1): 8-17.
|
|
ZUO HAO, GAO SHU, 2005. Simulation of flooding processes in Boao harbour, Hainan Island[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 24(1): 8-17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
AMANTE C, EAKINS B W, 2009. ETOPO1 1 arc-minute global relief model: procedures, data sources and analysis[R]. NOAA Technical Memorandum NESDIS NGDC-24, Boulder, Colorado: National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA.
|
| [4] |
CHAO S Y, 1988. River-forced estuarine plumes[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 18(1): 72-88.
|
| [5] |
CHAO S Y, BOICOURT W C, 1986. Onset of estuarine plumes[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 16(12): 2137-2149.
|
| [6] |
CHEN CHANGSHENG, LIU HEDONG, BEARDSLEY R C, 2003. An unstructured grid, finite-volume, three-dimensional, primitive equations ocean model: application to coastal ocean and estuaries[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 20(1): 159-186.
|
| [7] |
CHOI B J, WILKIN J L, 2007. The effect of wind on the dispersal of the Hudson River plume[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 37(7): 1878-1897.
|
| [8] |
EGBERT G D, EROFEEVA S Y, 2002. Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 19(2): 183-204.
|
| [9] |
FANG GUOHONG, WANG GANG, FANG YUE, et al, 2012. A review on the South China Sea western boundary current[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 31(5): 1-10.
|
| [10] |
GEYER W R, BEARDSLEY R C, LENTZ S J, et al, 1996. Physical oceanography of the Amazon shelf[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 16(5-6): 575-616.
|
| [11] |
HENCH J L, LUETTICH R A JR, 2003. Transient tidal circulation and momentum balances at a shallow inlet[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 33(4): 913-932.
|
| [12] |
HETLAND R D, 2005. Relating river plume structure to vertical mixing[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 35(9): 1667-1688.
|
| [13] |
HORNER-DEVINE A R, 2009. The bulge circulation in the Columbia River plume[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 29(1): 234-251.
|
| [14] |
HORNER-DEVINE A R, HETLAND R D, MACDONALD D G, 2015. Mixing and transport in coastal river plumes[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 47(1): 569-594.
|
| [15] |
LENTZ S J, LIMEBURNER R, 1995. The Amazon River Plume during AMASSEDS: spatial characteristics and salinity variability[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 100(C2): 2355-2375.
|
| [16] |
MCCABE R M, MACCREADY P, HICKEY B M, 2009. Ebb-tide dynamics and spreading of a large river plume[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 39(11): 2839-2856.
|
| [17] |
MELLOR G L, YAMADA T, 1982. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 20(4): 851-875.
|
| [18] |
SAHA S, MOORTHI S, WU XINGREN, et al, 2014. The NCEP climate forecast system version 2[J]. Journal of Climate, 27(6): 2185-2208.
|
| [19] |
SMAGORINSKY J, 1963. General circulation experiments with the primitive equations[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 91(3): 99-164.
|
| [20] |
TARYA A, VAN DER VEGT M, HOITINK A J F, 2015. Wind forcing controls on river plume spreading on a tropical continental shelf[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 120(1): 16-35.
|
| [21] |
UNCLES R J, LEWIS R E, 2001. The transport of fresh water from river to coastal zone through a temperate estuary[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 46(2): 161-175.
|
| [22] |
WHITNEY M M, GARVINE R W, 2006. Simulating the Delaware Bay buoyant outflow: comparison with observations[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 36(1): 3-21.
|
| [23] |
WU HUI, ZHU JIANRONG, SHEN JIAN, et al, 2011. Tidal modulation on the Changjiang River plume in summer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C8): C08017.
|
| [24] |
ZHAO JUNPENG, GONG WENPING, SHEN JIAN, 2017. The effect of wind on the dispersal of a tropical small river plume[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, doi: 10.1007/s11707-016-0628-6. (in Press)
|
 ), Yihan LI2, Wenping GONG1(
), Yihan LI2, Wenping GONG1( )
)