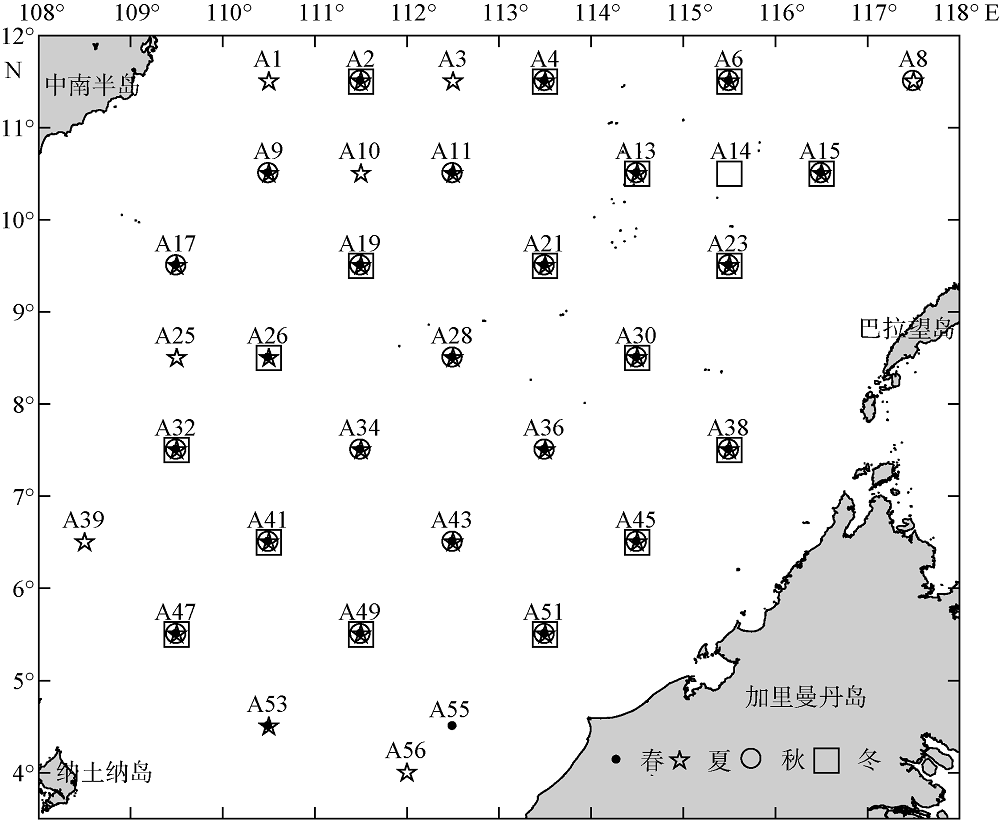
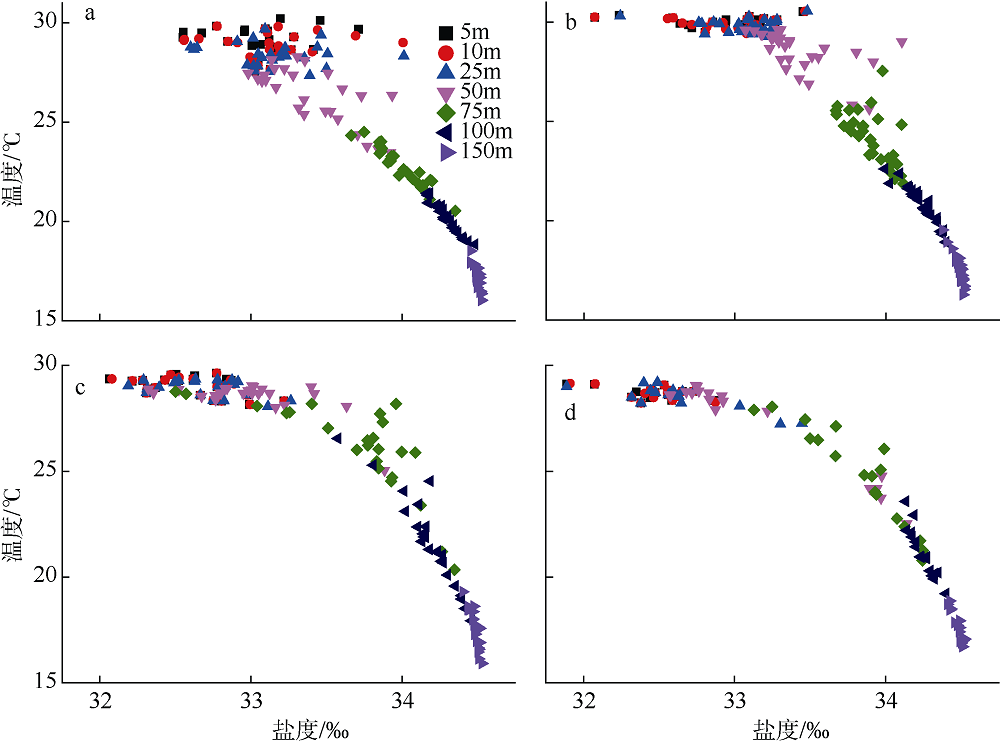
| [1] |
曹文熙, 杨跃忠, 2002. 海洋光合有效辐射分布的计算模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 21(3): 47-54.
|
|
CAO WENXI, YANG YUEZHONG, 2002. A bio-optical model for ocean photosynthetic available radiation[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 21(3): 47-54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
陈楚群, 施平, 毛庆文, 2001. 南海海域叶绿素浓度分布特征的卫星遥感分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 20(2): 66-70.
|
|
CHEN CHUQUN, SHI PING, MAO QINGWEN, 2001. Satellite remotely-sensed analysis of distribution characters of chlorophyll concentration in South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 20(2): 66-70 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
陈小燕, 2013. 基于遥感的长时间序列浮游植物的多尺度变化研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
CHEN XIAOYAN, 2013. Multi-scale variations in the long time series of phytoplankton from satellite data[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
方文东, 郭忠信, 黄羽庭, 1997. 南海南部海区的环流观测研究[J]. 科学通报, 42(21): 2264-2271.
|
|
FANG WENDONG, GUO ZHONGXIN, HUANG YUTING, 1998. Observational study of the circulation in the southern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 43(11): 898-905 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
高姗, 王辉, 刘桂梅, 等, 2010. 南海叶绿素a浓度垂直分布的统计估算[J]. 海洋学报, 32(4): 168-176.
|
|
GAO SHAN, WANG HUI, LIU GUIMEI, et al, 2010. The statistical estimation of the vertical distribution of chlorophyll a concentration in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 32(4): 168-176 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
高姗, 2011. 南海低营养级生态要素时空分布特征及模型研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
GAO SHAN, 2011. The study of lower trophic level ecosystem in the South China Sea: observation and modeling investigation[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
宫响, 2012. 南海北部次表层叶绿素最大值特征的理论分析及数值模拟研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
GONG XIANG, 2012. Analytical and numerical study on subsurface chlorophyll maximum in the northern South China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
黄良民, 1991. 南沙群岛海区的光合色素和初级生产力的分布特征初探[M]//中国科学院南沙综合科学考察队. 南沙群岛及其邻近海区海洋生物研究论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社: 66-88. (in Chinese).
|
| [9] |
黄良民, 1992. 南海不同海区叶绿素a和海水荧光值的垂向变化[J]. 热带海洋, 11(4): 89-95.
|
|
HUANG LIANGMIN, 1992. Vertical variations of chlorophyll a and fluorescence values of different areas in South China Sea[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 11(4): 89-95 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
柯志新, 黄良民, 谭烨辉, 等, 2013. 2008年夏末南海北部叶绿素a的空间分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(4): 51-57.
|
|
KE ZHIXIN, HUANG LIANGMIN, TAN YEHUI, et al, 2013. Spatial distribution of chlorophyll a and its relationships with environmental factors in northern South China Sea in late summer 2008[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 32(4): 51-57 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
李宝华, 傅克忖, 1999. 南黄海浮游植物与水色透明度之间相关关系的研究[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 17(3): 73-79.
|
|
LI BAOHUA, FU KECUN, 1999. The study of correlations between phytoplankton and the transparency, water color in Southern Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 17(3): 73-79 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
李纯厚, 齐占会, 黄洪辉, 等, 2010. 海洋碳汇研究进展及南海碳汇渔业发展方向探讨[J]. 南方水产, 6(6): 81-86.
|
|
LI CHUNHOU, QI ZHANHUI, HUANG HONGHUI, et al, 2010. Review on marine carbon sink and development of carbon sink fisheries in South China Sea[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 6(6): 81-86 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
李敏, 2009. 南海海洋叶绿素a时空分布及对季风变动响应的研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院.
|
|
LI MIN, 2009. A study on the spatial and temporal Chl-a distribution in the South China Sea and a response to the South China Sea monsoon[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
廖秀丽, 黄洪辉, 巩秀玉, 等, 2015. 2013年南沙海域混合层深度的季节变化特征[J]. 南方水产科学, 11(5): 67-75.
|
|
LIAO XIULI, HUANG HONGHUI, GONG XIUYU, et al, 2015. Seasonal variability in mixed layer depth in Nansha area in 2013[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 11(5): 67-75 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
林丽茹, 赵辉, 2012. 南海海域浮游植物叶绿素与海表温度季节变化特征分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 30(4): 46-54.
|
|
LIN LIRU, ZHAO HUI, 2012. Analysis on the relations between sea surface temperature and phytoplankton Chlorophyll-a in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 30(4): 46-54 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [16] |
林学举, 2001. 南海北部微微型浮游生物结构及叶绿素α最大值的形成机制[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
LIN XUEJU, 2001. Picoplankton composition and mechanisms of formation of subsurface chlorophyll maxima in the northern South China Sea[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [17] |
刘昕, 王静, 程旭华, 等, 2012. 南海叶绿素浓度的时空变化特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 31(4): 42-48.
|
|
LIU XIN, WANG JING, CHENG XUHUA, et al, 2012. The temporal and spatial evolution of chlorophyll-a concentration in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 31(4): 42-48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [18] |
沈新强, 王云龙, 袁骐, 等, 2004. 北太平洋鱿鱼渔场叶绿素a分布特点及其与渔场的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 26(6): 118-123.
|
|
SHEN XINQIANG, WANG YUNLONG, YUAN QI, et al, 2004. Distributional characteristics of chlorophyll a and relation to the fishing ground in the squid fishing ground of the northern Pacific Ocean[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 26(6): 118-123 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [19] |
唐峰华, 崔雪森, 杨胜龙, 等, 2014. 海洋环境对中西太平洋金枪鱼围网渔场影响的GIS时空分析[J]. 南方水产科学, 10(2): 18-26.
|
|
TANG FENGHUA, CUI XUESEN, YANG SHENGLONG, et al, 2014. GIS analysis on effect of temporal and spatial patterns of marine environment on purse seine fishery in the western and central Pacific[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 10(2): 18-26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [20] |
于杰, 陈国宝, 张魁, 等, 2016. 南海中部海域夏季叶绿素a浓度垂向分布特征[J]. 南方水产科学, 12(4): 1-8.
|
|
YU JIE, CHEN GUOBAO, ZHANG KUI, et al, 2016. Vertical distribution of summer chlorophyll a concentration in the middle South China Sea[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 12(4): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [21] |
张清凌, 陈楚群, 施平, 2003. 南沙群岛海域水体漫衰减系数Kd(490) 的特性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 22(1): 9-16.
|
|
ZHANG QINGLING, CHEN CHUQUN, SHI PING, 2003. Characteristics of Kd(490) around Nansha Islands in South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 22(1): 9-16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [22] |
赵辉, 齐义泉, 王东晓, 等, 2005a. 南海叶绿素浓度季节变化及空间分布特征研究[J]. 海洋学报, 27(4): 45-52.
|
|
ZHAO HUI, QI YIQUAN, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2005a. Study on the features of chlorophyll-a derived from SeaWiFS in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 27(4): 45-52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [23] |
赵辉, 唐丹玲, 王素芬, 2005b. 南海西北部夏季叶绿素a浓度的分布特征及其对海洋环境的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 24(6): 31-37.
|
|
ZHAO HUI, TANG DANLING, WANG SUFEN, 2005b. Spatial distribution of chlorophyll a concentration in summer in Western South China Sea and its response to oceanographic environmental factors[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 24(6): 31-37 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [24] |
DANDONNEAU Y, 1979. Concentrations en chlorophylle dans le Pacifique tropical sud-ouest: comparaison avec d'autres aires océaniques tropicales[J]. Oceanologica Acta, 2(2): 133-142.
|
| [25] |
HANSON C E, PESANT S, WAITE A M, et al, 2007. Assessing the magnitude and significance of deep chlorophyll maxima of the coastal eastern Indian Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 54(8/9/10): 884-901.
|
| [26] |
HOLD N, MURRAY L G, HINZ H, et al, 2013. Environmental drivers of small scale spatial variation in the reproductive schedule of a commercially important bivalve mollusc[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 92: 144-153.
|
| [27] |
LIN JINGROU, TANG DANLING, ALPERS W, et al, 2014. Response of dissolved oxygen and related marine ecological parameters to a tropical cyclone in the South China Sea[J]. Advances in Space Research, 53(7): 1081-1091.
|
| [28] |
LIU HUAXUE, SONG XINGYU, HUANG LIANGMIN, et al, 2011. Phytoplankton biomass and production in northern South China Sea during summer: influenced by Pearl River discharge and coastal upwelling[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(3): 133-136.
|
| [29] |
LIU MEILING, LIU XIANGNAN, MA AOHUI, et al, 2014. Spatio-temporal stability and abnormality of chlorophyll-a in the Northern South China Sea during 2002-2012 from MODIS images using wavelet analysis[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 75: 15-27.
|
| [30] |
MOREL A, BERTHON J F, 1989. Surface pigments, algal biomass profiles, and potential production of the euphotic layer: relationships reinvestigated in view of remote‐sensing applications[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 34(8): 1545-1562.
|
| [31] |
SISWANTO E, ISHIZAKA J, YOKOUCHI K, 2005. Estimating chlorophyll-a vertical profiles from satellite data and the implication for primary production in the Kuroshio front of the East China Sea[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 61(3): 575-589.
|
| [32] |
SONG XINGYU, LAI ZHIGANG, JI RUBAO, et al, 2012. Summertime primary production in northwest South China Sea: interaction of coastal eddy, upwelling and biological processes[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 48: 110-121.
|
| [33] |
TAKAHASHI M, HORI T, 1984. Abundance of picophytoplankton in the subsurface chlorophyll maximum layer in subtropical and tropical waters[J]. Marine Biology, 79(2): 177-186.
|
| [34] |
WANG JIUJUAN, TANG DANLING, 2014. Phytoplankton patchiness during spring intermonsoon in western coast of South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 101: 120-128.
|
| [35] |
YE H J, SUI Y, TANG D L, et al, 2013. A subsurface chlorophyll a bloom induced by typhoon in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 128: 138-145.
|
 ), Ming DAI, Xiuyu GONG, Huaxue LIU, Honghui HUANG(
), Ming DAI, Xiuyu GONG, Huaxue LIU, Honghui HUANG( )
)