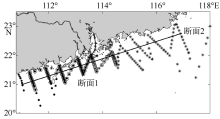
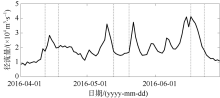
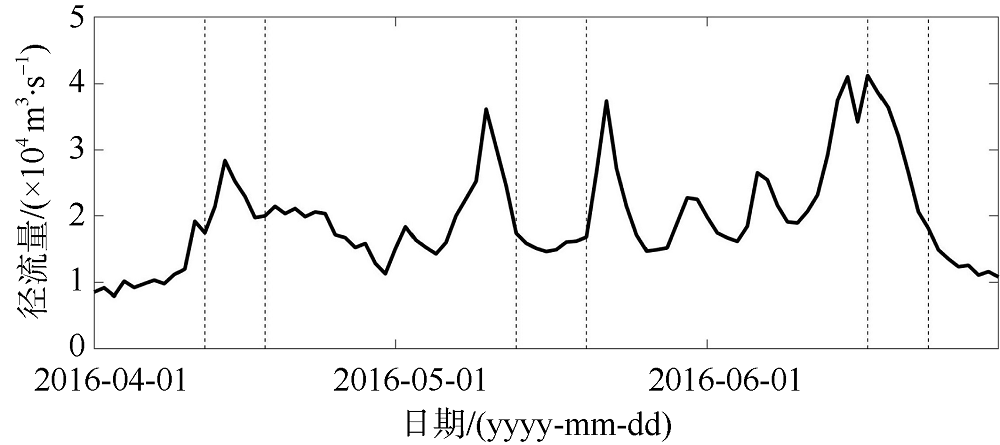
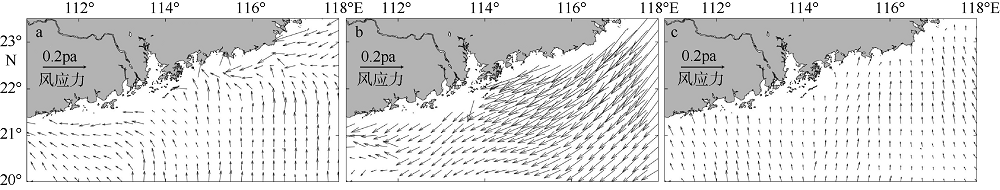
| [1] |
胡辉, 胡方西, 1995. 长江口的水系和锋面[J]. 中国水产科学, 2(1):81-90.
|
|
HU HUI, HU FANGXI, 1995. Water types and frontal surface in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2(1):81-90 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
贾国东, 彭平安, 傅家谟, 2002. 珠江口近百年来富营养化加剧的沉积记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 22(2):158-165.
|
|
JIA GUODONG, PENG PING’AN, FU JIAMO, 2002. Sedimentary records of accelerated eutrophication for the last 100 years at the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 22(2):158-165 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
罗琳, 李适宇, 王东晓, 2008. 珠江河口夏季缺氧现象的模拟[J]. 水科学进展, 19(5):729-735.
|
|
LUO LIN, LI SHIYU, WANG DONGXIAO, 2008. Modelling of hypoxia in the Pearl River Estuary in summer[J]. Advances in Water Science, 19(5):729-735 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
毛汉礼, 甘子钧, 蓝淑芳, 1963. 长江冲淡水及其混合问题的初步探讨[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 5(3):183-206.
|
|
MAO HANLEE, KAN TZECHUN, LAN SHUFANG, 1963. A preliminary study of the Yangtze diluted water and its mixing processes[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 5(3):183-206 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
宁修仁, 刘子琳, 蔡昱明, 2000. 我国海洋初级生产力研究二十年[J]. 东海海洋, 18(3):13-20.
|
|
NING XIUREN, LIU ZILIN, CAI YUMING, 2000. A review on primary production studies for China seas in the past 20 years[J]. Donghai Marine Science, 18(3):13-20 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
薛惠洁, 柴扉, 徐丹亚, 等, 2001. 南海沿岸流特征及其季节变化[G]//中国海洋学文集. 北京: 海洋出版社, 13:64-75.
|
|
XUE HUIJIE, CHAI FEI, XU DANYA, et al, 2001. Characteristics and seasonal variation of the coastal currents in the South China Sea[G]//Oceanography in China. Beijing: Ocean Press: 13:64-75(in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
叶安乐, 李凤岐, 1992. 物理海洋学[M]. 青岛: 青岛海洋大学出版社: 251-259(in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
叶丰, 2011. 珠江河口溶解氧的关键控制因素及底层缺氧的历史记录[D]. 广州: 中国科学院南海海洋研究所: 1-106.
|
|
YE FENG, 2011. Indentification of key factors controlling dissolved oxygen and sedimentary record of low oxygen events in the Pearl River Estuary[D]. Guangzhou: South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: 1-106 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
赵焕庭, 1990. 珠江河口演变[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 357-360(in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
CAI WEIJUN, DAI MINHAN, WANG YONGCHEN, et al, 2004. The biogeochemistry of inorganic carbon and nutrients in the Pearl River Estuary and the adjacent Northern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 24(12):1301-1319.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.04.005
|
| [11] |
DAI MINHAN, ZHAI WEIDONG, CAI WEIJUN, et al, 2008. Effects of an estuarine plume-associated bloom on the carbonate system in the lower reaches of the Pearl River Estuary and the coastal zone of the northern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 28(12):1416-1423.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2007.04.018
|
| [12] |
GAO NA, MA YI, ZHAO MINGLI, et al, 2020. Quantile analysis of long-term trends of near-surface chlorophyll-a in the Pearl River Plume[J]. Water, 12(6):1662.
doi: 10.3390/w12061662
|
| [13] |
HU JIANFANG, ZHANG GAN, LI KECHANG, et al, 2008. Increased eutrophication offshore Hong Kong, China during the past 75 years: Evidence from high-resolution sedimentary records[J]. Marine Chemistry, 110(1-2):7-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2008.02.001
|
| [14] |
HUANG X P, HUANG L M, YUE W Z, 2003. The characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication in the Pearl River Estuary, South China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 47(1-6):30-36.
doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00474-5
|
| [15] |
LI DOU, GAN JIANPING, HUI R, et al, 2020. Vortex and biogeochemical dynamics for the hypoxia formation within the coastal transition zone off the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 125(8): e2020JC016178.
|
| [16] |
LI Q P, ZHOU WEIWEN, CHEN YINCHAO, et al, 2018. Phytoplankton response to a plume front in the northern South China Sea[J]. Biogeosciences, 15(8):2551-2563.
doi: 10.5194/bg-15-2551-2018
|
| [17] |
LIU GUANGPING, HE WEIHONG, CAI SHUQUN, 2020. Seasonal variation of dissolved oxygen in the southeast of the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Water, 12(9):2475.
doi: 10.3390/w12092475
|
| [18] |
LU ZHONGMING, GAN JIANPING, DAI MINHAN, et al, 2018. Joint effects of extrinsic biophysical fluxes and intrinsic hydrodynamics on the formation of hypoxia west off the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(9):6241-6259.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014199
|
| [19] |
LUO L, ZHOU W, WANG D, 2012. Responses of the river plume to the external forcing in Pearl River Estuary[J]. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 15(1):62-69.
|
| [20] |
MEYBECK M, 1982. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus transport by world rivers[J]. American Journal of Science, 282(4):401-450.
doi: 10.2475/ajs.282.4.401
|
| [21] |
OU SUYING, ZHANG HONG, WANG DONGXIAO, 2009. Dynamics of the buoyant plume off the Pearl River Estuary in summer[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 9(5):471-492.
doi: 10.1007/s10652-009-9146-3
|
| [22] |
RABOUILLE C, CONLEY D J, DAI M H, et al, 2008. Comparison of hypoxia among four river-dominated ocean margins: The Changjiang (Yangtze), Mississippi, Pearl, and Rhône rivers[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 28(12):1527-1537.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2008.01.020
|
| [23] |
SHI ZHEN, XU JIE, HUANG XIAOPING, et al, 2017. Relationship between nutrients and plankton biomass in the turbidity maximum zone of the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 57:72-84.
doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.11.013
|
| [24] |
SIMPSON J H, SHARPLES J, RIPPETH T P, 1991. A prescriptive model of stratification induced by freshwater runoff[J]. Estuarine, Coastal & Shelf Science, 33(1):23-35.
|
| [25] |
WONG L A, CHEN J C, XUE H, et al, 2003. A model study of the circulation in the Pearl River Estuary (PRE) and its adjacent coastal waters: 2. Sensitivity experiments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 108(C5):3157.
|
| [26] |
XIA X M, LI Y, YANG H, et al, 2004. Observations on the size and settling velocity distributions of suspended sediment in the Pearl River Estuary, China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 24(16):1809-1826.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.06.009
|
| [27] |
YIN KEDONG, LIN ZHIFENG, KE ZHIYUAN, 2004. Temporal and spatial distribution of dissolved oxygen in the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent coastal waters[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 24(16):1935-1948.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.06.017
|
| [28] |
ZHANG HENG, LI SHIYU, 2010. Effects of physical and biochemical processes on the dissolved oxygen budget for the Pearl River Estuary during summer[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 79(1-2):65-88.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2009.07.002
|
| [29] |
ZHANG LING, YIN KEDONG, WANG LU, et al, 2009. The sources and accumulation rate of sedimentary organic matter in the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent coastal area, Southern China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 85(2):190-196.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.07.035
|
 ), 陈寅超1,2, 刘子嘉1,2, 葛在名1,2, 马梦真1,2, 张苑芳1,2, 李芊1,2,3(
), 陈寅超1,2, 刘子嘉1,2, 葛在名1,2, 马梦真1,2, 张苑芳1,2, 李芊1,2,3( )
)
 ), CHEN Yinchao1,2, LIU Zijia1,2, GE Zaiming1,2, MA Mengzhen1,2, ZHANG Yuanfang1,2, LI Qian1,2,3(
), CHEN Yinchao1,2, LIU Zijia1,2, GE Zaiming1,2, MA Mengzhen1,2, ZHANG Yuanfang1,2, LI Qian1,2,3( )
)