热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 32-42.doi: 10.11978/2021145CSTR: 32234.14.2021145
所属专题: 全球变化专题
台风对珠江口风暴增水的影响分析
高娜1( ), 赵明利1, 马毅1, 徐婉明1, 詹海刚2,3, 蔡树群2,3,4,5
), 赵明利1, 马毅1, 徐婉明1, 詹海刚2,3, 蔡树群2,3,4,5
- 1.国家海洋局南海规划与环境研究院, 广东 广州 510310
2.热带海洋环境国家重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
3.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
4.中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 广东 广州 510301
5.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2021-10-27修回日期:2022-03-15出版日期:2023-01-10发布日期:2022-03-03 -
通讯作者:赵明利。email:zhaomingli@126.com -
作者简介:高娜(1988—), 女, 山东省新泰市人, 博士研究生, 从事海洋防灾减灾研究。email: gaona12@mails.ucas.ac.cn -
基金资助:家重点研发计划(2017YFC1405300); 国家自然科学基金(41890851); 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(GML2019ZD0305)
Effect of typhoon on storm surge in the Pearl River Estuary
GAO Na1( ), ZHAO Mingli1, MA Yi1, XU Wanming1, ZHAN Haigang2,3, CAI Shuqun2,3,4,5
), ZHAO Mingli1, MA Yi1, XU Wanming1, ZHAN Haigang2,3, CAI Shuqun2,3,4,5
- 1. South China Sea Institute of Planning and Environmental Research, State Oceanic Administration, Guangzhou 510310, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography of the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
4. Institution of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
5. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2021-10-27Revised:2022-03-15Online:2023-01-10Published:2022-03-03 -
Contact:ZHAO Mingli. email:zhaomingli@126.com -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2017YFC1405300); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41890851); Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0305)
摘要:
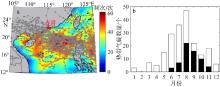
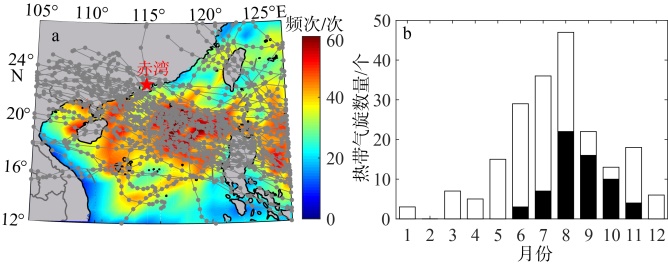
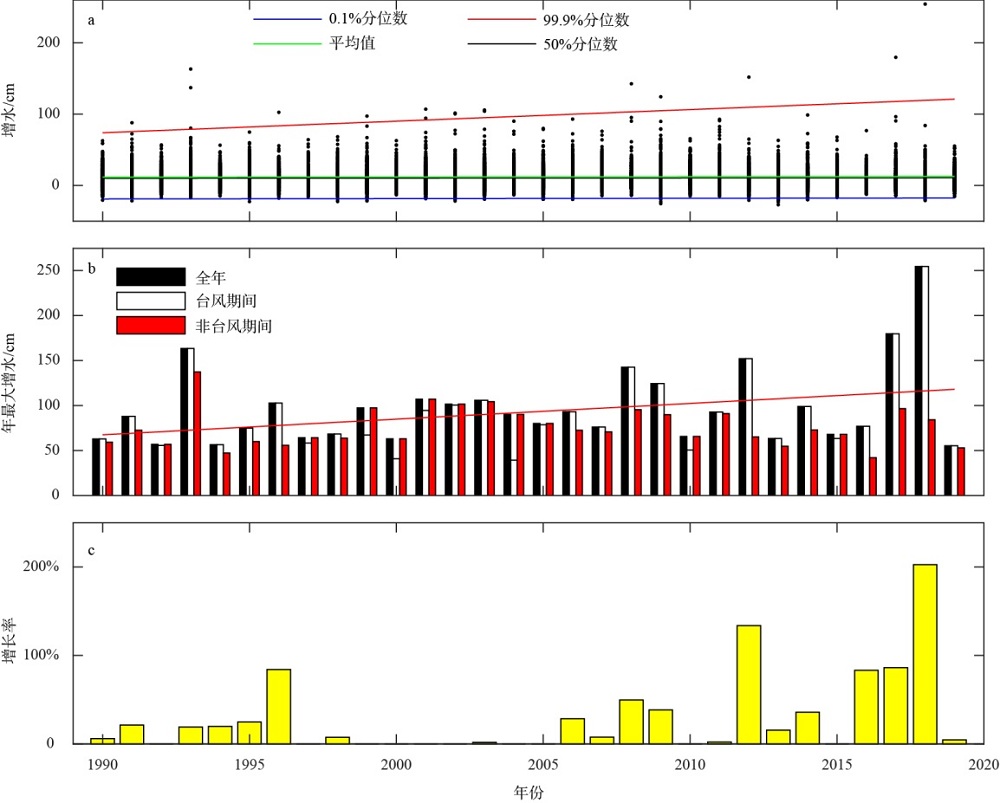
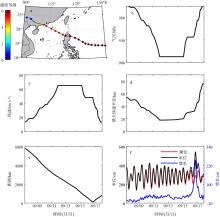
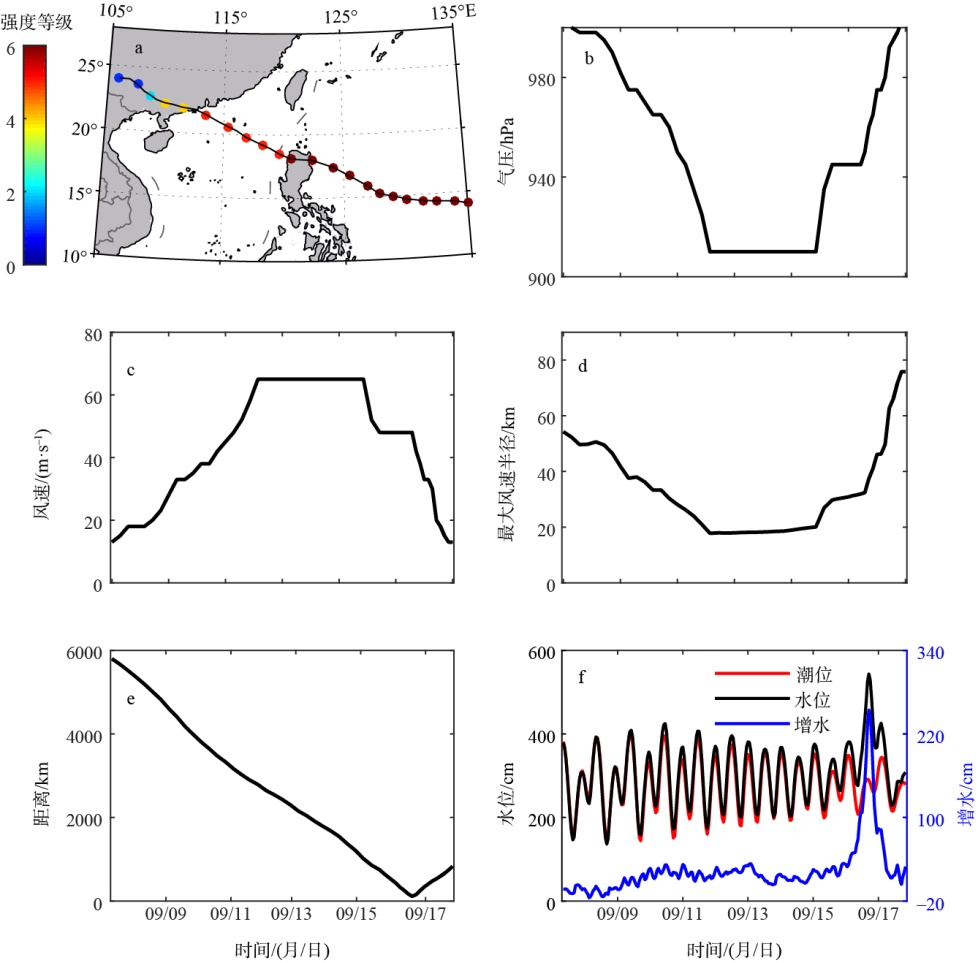
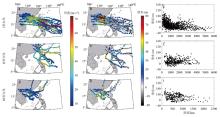
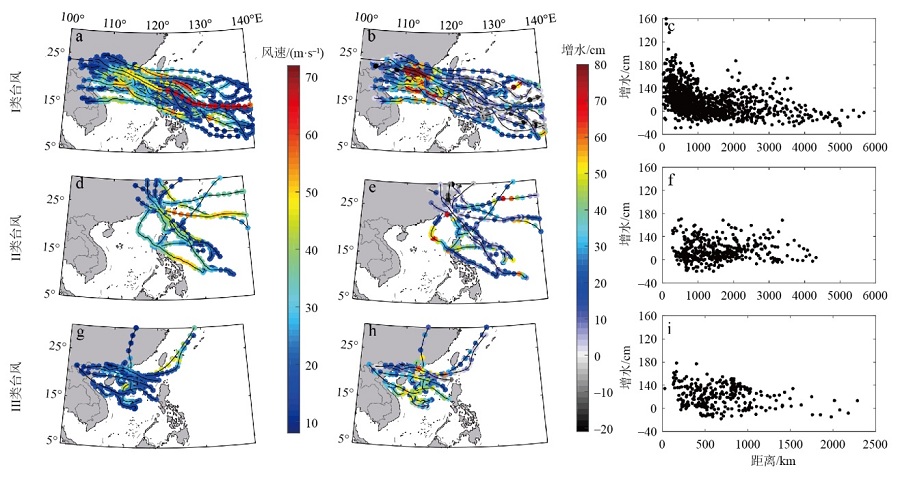
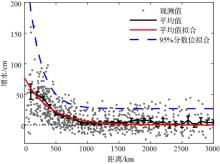
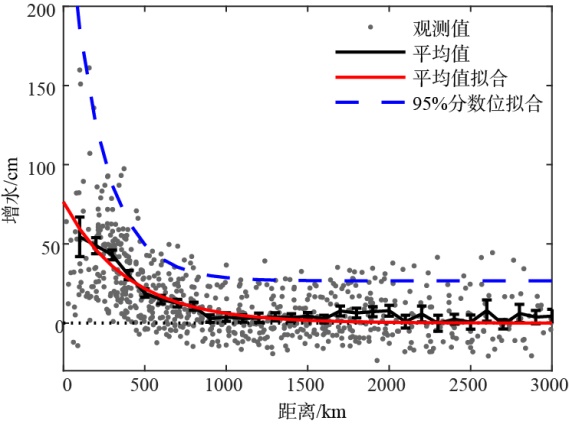
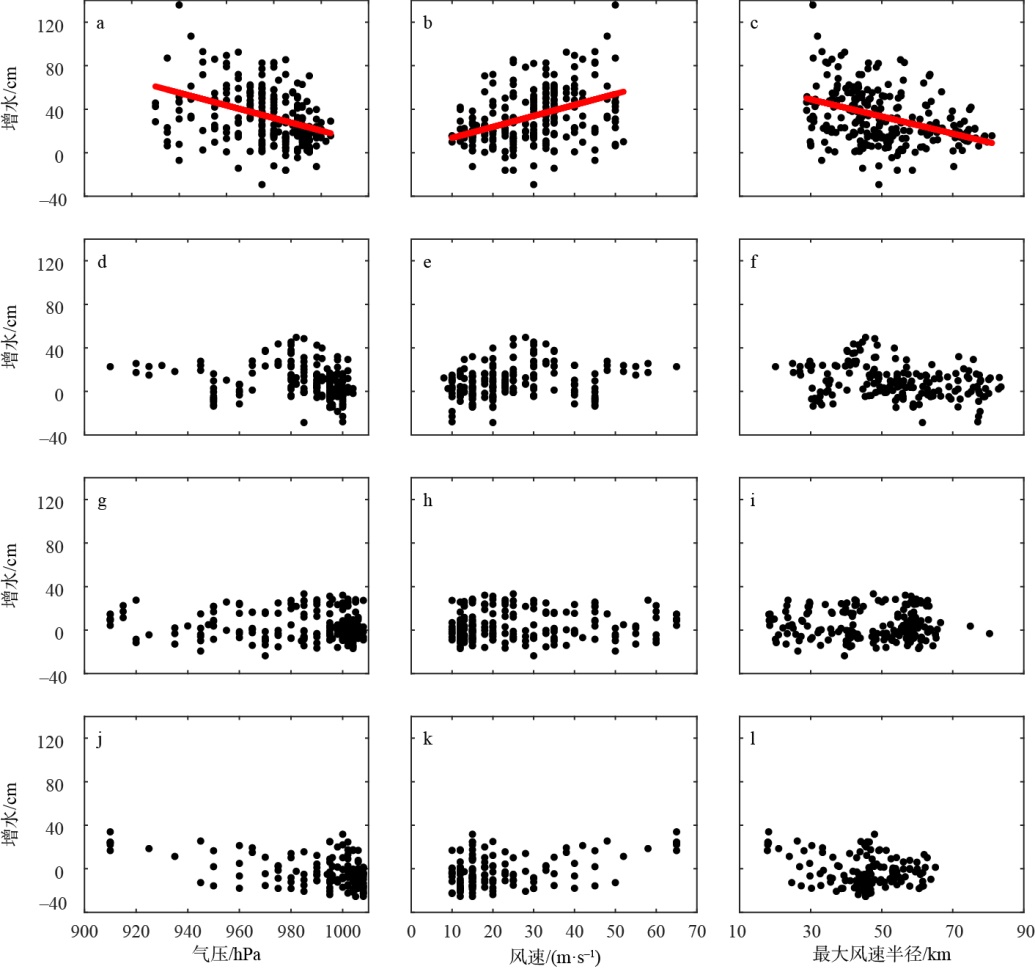
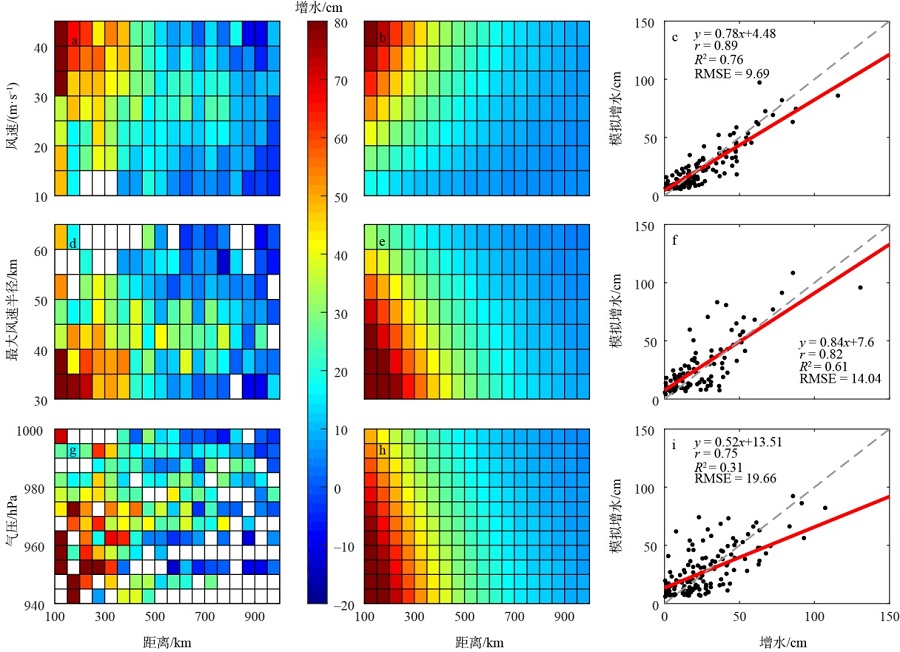
珠江口沿岸风暴潮灾害频发, 且受台风影响显著。本研究对珠江口赤湾站近30 a(1990—2019)的极端增水进行了分析。结果显示: 近年来该区域年平均增水没有显著变化, 但极端风暴增水( 99.9%分位数)强度显著增强(1.62cm·a-1), 意味着极端风暴潮灾害强度不断变大; 在这30a里, 有20a的年最大增水发生于台风期间(占66.7%), 2018年超强台风“山竹”引起的增水峰值达254cm, 为近30a最大的风暴潮灾害事件; 增水对台风的最大响应距离约为500~800km。在台风影响范围内, 增水强度与台风强度呈近似的线性关系, 与距台风中心距离则呈指数关系。分别利用台风强度的不同指标(台风中心最低气压、最大风速和最大风速半径), 结合观测站距台风中心的距离, 对增水进行拟合, 发现风速与距离组合对风暴增水的刻画效果最好[Sw=3.23e-0.0036D×(Γw-3.90)+4.48, R2=0.78, RMSE=9.69cm]。这些研究结果可提升对珠江口风暴潮灾害的认识, 为台风风暴潮模拟提供验证资料, 并为风暴潮灾害风险评估与应对决策提供参考依据。
引用本文
高娜, 赵明利, 马毅, 徐婉明, 詹海刚, 蔡树群. 台风对珠江口风暴增水的影响分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 32-42.
GAO Na, ZHAO Mingli, MA Yi, XU Wanming, ZHAN Haigang, CAI Shuqun. Effect of typhoon on storm surge in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 32-42.
| [1] |
陈波, 邱绍芳, 2000. 广西沿海港湾风暴潮增减水与台风路径和地形效应的关系[J]. 广西科学, 7(4): 282-285.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈波, 董德信, 陈宪云, 等, 2017. 南海北部台风引起的广西近岸增减水研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (2): 1-11.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
董剑希, 李涛, 侯京明, 等, 2014. 广东省风暴潮时空分布特征及重点城市风暴潮风险研究[J]. 海洋学报, 36(3): 83-93.
|
|
doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1062-7 |
|
| [4] |
广东省海洋与渔业厅, (2017-03-22). 广东省海洋灾害公报2016[EB/OL]. http://nr.gd.gov.cn/zwgknew/tzgg/gg/content/post_3186916.html. in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
广东省海洋与渔业厅, (2018-04-23). 广东省海洋灾害公报2017[EB/OL]. http://nr.gd.gov.cn/zwgknew/sjfb/tjsj/content/post_3186924.html. in Chinese)
|
| [6] |
郭洪寿, 1991. 我国潮灾灾度评估初探[J]. 南京大学学报, (5): 18-22. (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
韩晶, 2019. 台风山竹和天鸽对珠海沿海风暴潮增水影响[J]. 吉林水利, (8): 47-49, 53.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
韩树宗, 潘嵩, 2013. 杭州湾台风风暴潮增水过程的数值分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 43(7): 1-6.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
黄世昌, 李玉成, 赵鑫, 等, 2008. 浙江沿海超强台风作用下风暴潮增水数值分析[J]. 海洋工程, 26(3): 58-64.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
梁连松, 张钊, 顾冬明, 等, 2020. 典型路径下台风移速调整对鳌江站增水的数值分析[J]. 海洋预报, 37(5): 59-66.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
刘秋兴, 傅赐福, 李明杰, 等, 2018. “天鸽”台风风暴潮预报及数值研究[J]. 海洋预报, 35(1): 29-36.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
刘士诚, 陈永平, 谭亚, 等, 2021. 珠江河网1822号台风“山竹”期间风暴增水模拟及特性分析[J]. 海洋预报, 38(2): 12-20.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
牛海燕, 刘敏, 陆敏, 等, 2011. 中国沿海地区台风致灾因子危险性评估[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (6): 20-25, 35.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
潘明婕, 孔俊, 杨芳, 等, 2019. 台风路径对磨刀门水道咸潮上溯动力过程的影响机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(3): 53-67.
doi: 10.11978/2018081 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2018081 |
|
| [15] |
王康发生, 尹占娥, 殷杰, 2011. 海平面上升背景下中国沿海台风风暴潮脆弱性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(6): 31-36.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.06.031 |
|
|
|
| [16] |
王敏, 尹义星, 陈晓旸, 等, 2020. 异常北折台风“洛坦”与异常西折台风“奥玛”路径的对比及预报[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(1): 53-65.
doi: 10.11978/2019042 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2019042 |
|
| [17] |
王培涛, 于福江, 刘秋兴, 等, 2010. 福建沿海精细化台风风暴潮集合数值预报技术研究及应用[J]. 海洋预报, 27(5): 7-15.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
魏晓宇, 刘雪峰, 2010. 闸坡站风暴潮增水与热带气旋登陆点及路径的关系[J]. 台湾海峡, 29(1): 122-127.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
吴海军, 相海波, 谢巨伦, 2012. 永暑礁风暴潮增水极值预报初探[J]. 科技信息, (9): 41-42.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
谢亚力, 黄世昌, 王瑞锋, 等, 2007. 钱塘江河口围涂对杭州湾风暴潮影响数值模拟[J]. 海洋工程, 25(3): 61-67.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
杨玄阁, 朱良生, 2017. 琼州海峡台风风暴潮增水过程的数值分析[J]. 人民珠江, 38(1): 43-47.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
尹宝树, 王涛, 侯一筠, 等, 2001. 渤海波浪和潮汐风暴潮相互作用对波浪影响的数值研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 32(1): 109-116.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
殷成团, 张金善, 熊梦婕, 等, 2019. 我国南海沿海台风及暴潮灾害趋势分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(1): 35-42.
doi: 10.11978/2018037 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2018037 |
|
| [24] |
尹尽勇, 徐晶, 曹越男, 等, 2012. 我国海洋气象预报业务现状与发展[J]. 气象科技进展, 2(6): 17-26.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
于福江, 董剑希, 叶琳, 2015. 中国风暴潮灾害史料集: 1949-2009[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
张敏, 罗军, 胡金磊, 等, 2019. 雷州市沿海风暴潮淹没危险性评估[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(2): 1-12.
doi: 10.11978/2018067 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2018067 |
|
| [27] |
自然资源部, 海洋预警监测司, (2019-04-28). 中国海洋灾害公报2018[EB/OL]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/201905/t20190510_2411197.html.
|
|
Natural Resources Ministry, Marine Early Warning and Monitoring Division, (2019-04-28). Bulletin of China marine disaster 2018[EB/OL]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/201905/t20190510_2411197.html.
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1977)105<0421:TCMSLP>2.0.CO;2 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2005.12.015 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2011.11.001 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2011.11446946 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.3390/w12061662 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1002/2017GL073680 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1029/2008GL033564 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1257/jep.15.4.143 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-0211-7 |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1126/science.abb9038 pmid: 33510027 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2019.01.024 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-12-00119.1 |
| [1] | 孙泽铭, 韩树宗, 王明杰, 苏翰祥. 不同路径台风对中国近海海温的影响特征统计分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 17-31. |
| [2] | 商洁, 吴莹, 邹依珂, 马靖雯. FY-3D卫星MWRI资料反演洋面台风降雨率*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 32-40. |
| [3] | 张哲然, 胡俊洋, 周凯, 张鹏晖, 邢久星, 陈胜利. 不同类型台风气象场对深圳近海海域风暴潮模拟的比较研究—以台风“山竹”为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. |
| [4] | 李骏旻, 李博, 陈武阳, 刘军亮. 三亚近岸海浪观测特征及其对台风过程的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 25-35. |
| [5] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [6] | 赵中贤, 孙珍, 毛云华, 张伙带. 南海北部陆缘不均匀伸展及脉动式构造升降史*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 96-115. |
| [7] | 唐灵, 聂宇华, 王平, 汤超莲. 1974—2020年珠江口外海海洋热浪变化趋势分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 143-150. |
| [8] | 束艾青, 许冬梅, 李泓, 吴海英, 沈菲菲, 邓华, 白亚雯. FY-3D卫星MWHS-2辐射率资料直接同化对台风“米娜”预报的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 17-28. |
| [9] | 郭俊丽, 时连强, 陈沈良, 张敏, 常洋, 张达恒. 台风季节朱家尖岛砂、砾质岬湾海滩的不同沉积地貌动态变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 82-96. |
| [10] | 喜扬洋, 王日明, 冯炳斌, 陈波. 北海银滩响应台风作用的动力地貌过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 97-104. |
| [11] | 商博文, 吴云超, 江志坚, 刘松林, 黄小平. 珠江口沉积物有机质特征、来源及其对碳存储的意义[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 16-28. |
| [12] | 尹天齐, 王庆, 杨宇峰, 岑竞仪. 基于形态学和DNA分子鉴定的珠江口浮游动物群落结构比较研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 172-185. |
| [13] | 陈琼, 唐世林, 吴颉. 基于GF-4卫星反演的珠江口水体表层悬浮泥沙时空变化特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 65-76. |
| [14] | 李卓, 黎伟标, 张奡褀. 台风登陆前华南地区降水日变化特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 26-37. |
| [15] | 帅义萍, 陈寅超, 刘子嘉, 葛在名, 马梦真, 张苑芳, 李芊. 2016年春季季风转换期的珠江冲淡水分布与生态特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 63-71. |
|
||