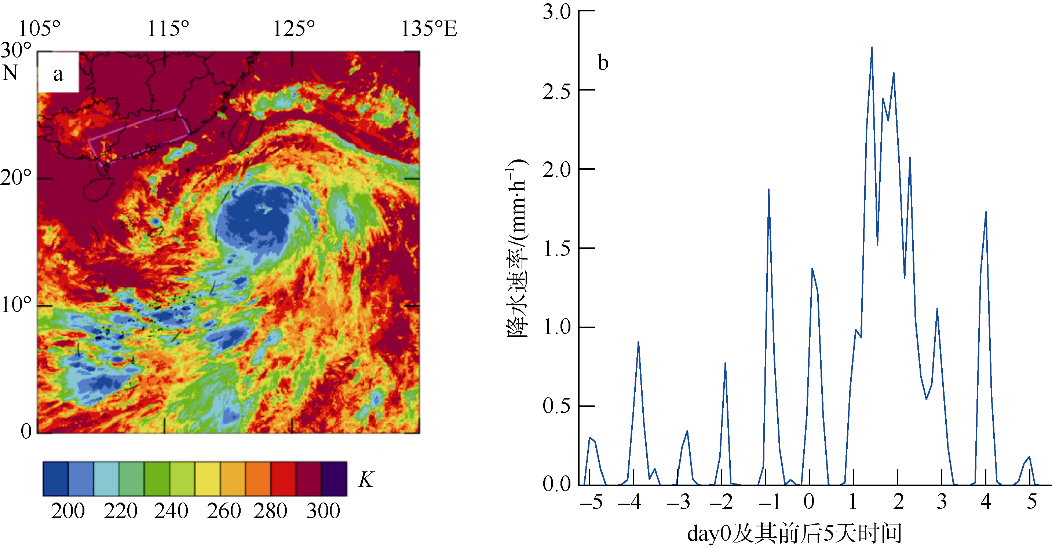
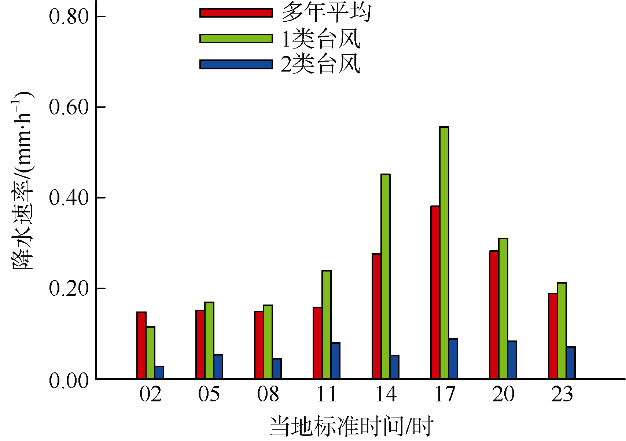
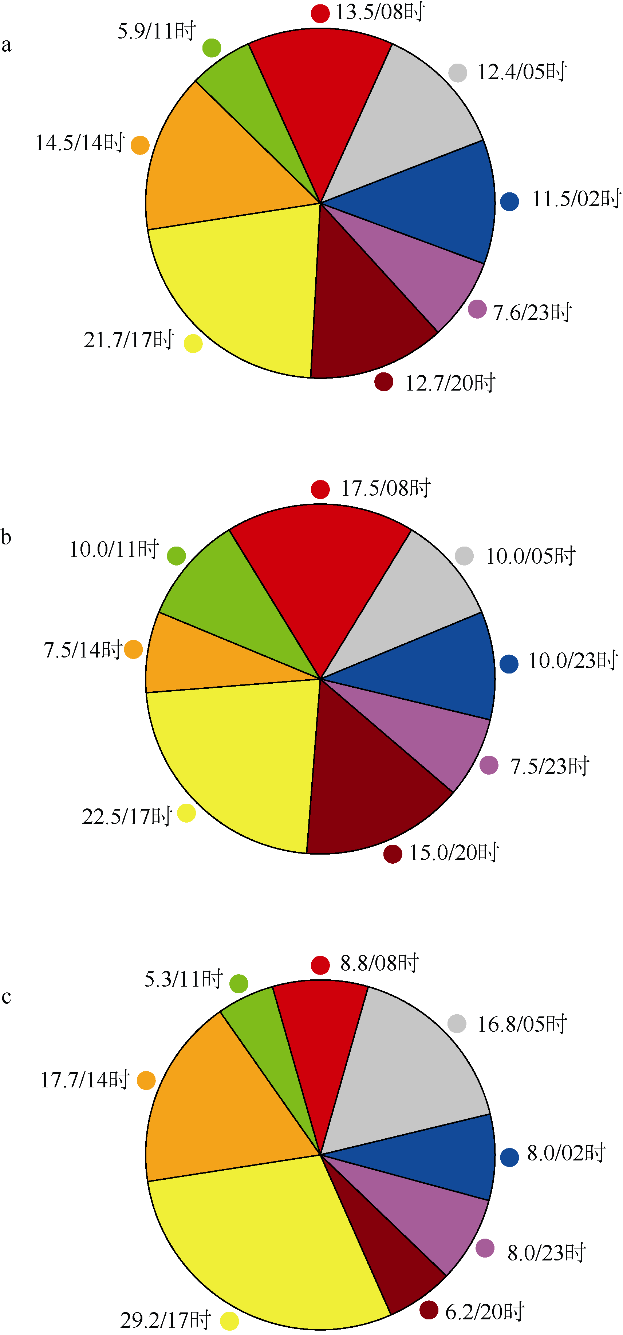
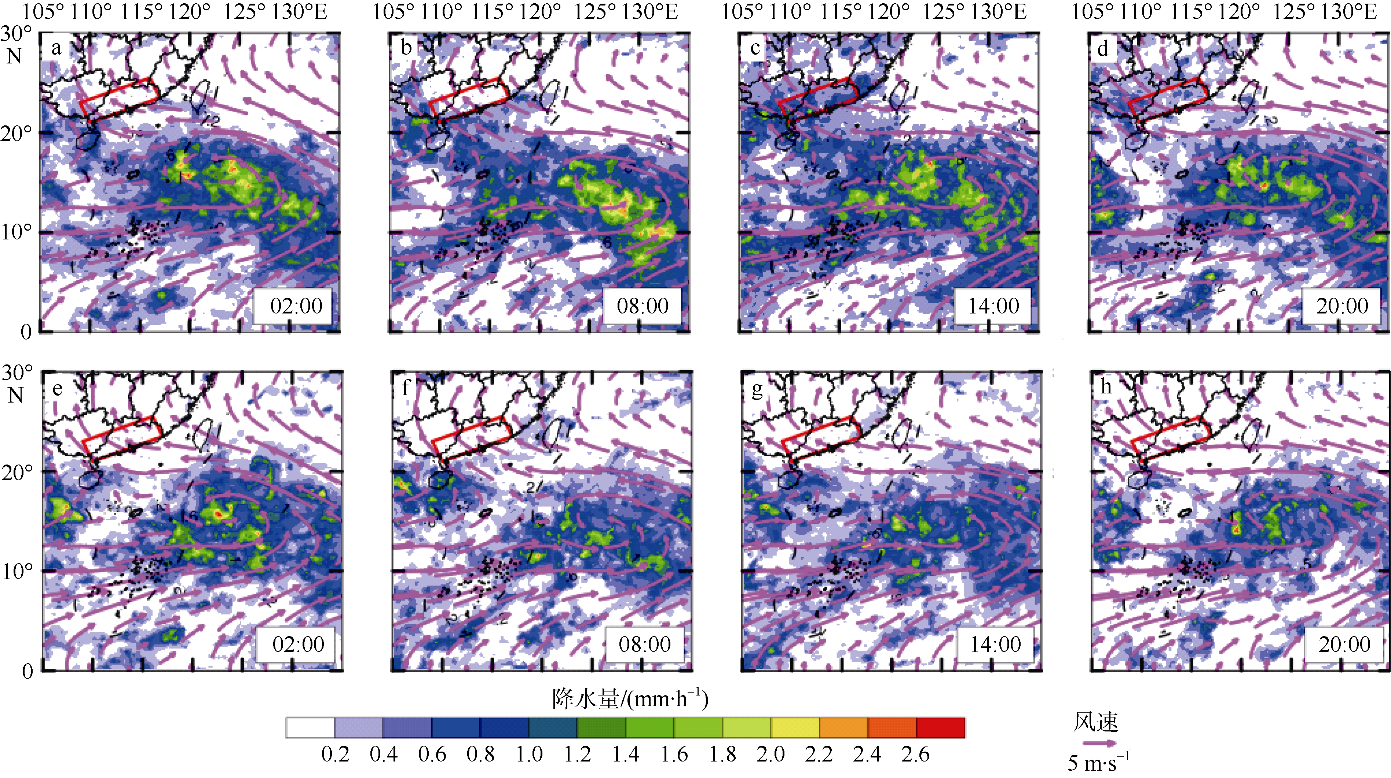
| [1] |
陈炯, 郑永光, 张小玲, 等, 2013. 中国暖季短时强降水分布和日变化特征及其与中尺度对流系统日变化关系分析[J]. 气象学报, 71(3). 367-382.
|
|
CHEN JIONG, ZHENG YONGGUANG, ZHANG XIAOLING, et al, 2013. Analysis of the climatological distribution and diurnal variations of the short-duration heavy rain and its ralation with diurnal variations of the MCSs over China during the warm season[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 71(3): 367-382. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
黄天福, 谢佳君, 刘鹏, 2013. 基于多卫星资料的全国夏秋季节降水日变化特征研究[J]. 贵州气象, 37(6): 30-33. (in Chinese)
|
| [3] |
李传祥, 王咏青, 夏华弟, 等, 2013. “海棠”、“罗莎”和“莫拉克”登陆前降水量差异分析[J]. 浙江气象, 34(2): 32-39. (in Chinese)
|
| [4] |
李德帅, 2013. 基于逐小时资料的华南地区汛期降水时空变化特征及其成因研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学: 1-151.
|
|
LI DESHUAI, 2013. Research on the spatiotemporal characteristics of hourly precipitation over South China during the warm season and its possible causes[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University: 1-151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
吕翔, 徐海明, 2007. 中南半岛地区夏季降水日变化特征[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 30(5): 632-642.
|
|
LÜ XIANG, XU HAIMING, 2007. Diurnal variations of rainfall in summer over the Indo-China peninsula[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 30(5): 632-642. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
莫志祥, 1983. 从两次暴雨过程看热力条件分析的重要性[J]. 广西气象, (3): 21-24. (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
唐红玉, 顾建峰, 俞胜宾, 等, 2011. 西南地区降水日变化特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 30(2): 376-384.
|
|
TANG HONGYU, GU JIANFENG, YU SHENGBIN, et al, 2011. Analysis on diurnal variation of precipitation in Southwest China[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 30(2): 376-384. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [8] |
唐晓春, 刘会平, 潘安定, 等, 2003. 广东沿海地区近50年登陆台风灾害特征分析[J]. 地理科学, 23(2): 182-187.
|
|
TANG XIAOCHUN, LIU HUIPING, PAN ANDING, et al, 2003. Analysis of disastrous features of landing Typhoo in coastal regions of Guangdong province in recent 50 years[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 23(2): 182-187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [9] |
王美蓉, 郭栋, 钟珊珊, 2019. 多源资料在青藏高原大气热源计算中的适用性分析[J]. 气象, 45(12): 1718-1726.
|
|
WANG MEIRONG, GUO DONG, ZHONG SHANSHAN, 2019. Comparision of the multi-source datasets in calculation of the atmospheric heat sources over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 45(12): 1718-1726. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [10] |
王文秀, 郭汝凤, 陈世发, 等, 2018. 1951-2016年登陆我国华南地区台风的时空分布特征分析[J]. 防护林科技, (6): 16-18.
|
|
WANG WENXIU, GUO RUFENG, CHEN SHIFA, et al, 2018. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of Typhoons in Southern China from 1951 to 2016[J]. Protection Forest Science and Technology, (6): 16-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [11] |
夏静雯, 傅云飞, 2016. 东亚与南亚雨季对流和层云降水云内的温湿结构特征分析[J]. 大气科学, 40(3): 563-580.
|
|
XIA JINGWEN, FU YUNFEI, 2016. The vertical characteristics of temperature and humidity inside convective and stratiform precipitating clouds in the East Asian summer monsoon region and Indian summer monsoon region[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 40(3): 563-580. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [12] |
许春林, 王文波, 杨森槐, 等, 2009. 台风“鹦鹉”登陆过程中肇庆降水显著偏弱的原因[J]. 广东气象, 31(6): 32-35.
|
|
XU CHUNLIN, WANG WENBO, YANG SENHUAI, et al, 2009. Significantly weaker precipitation in Zhaoqing during the landfall of typhoon Nuri compared to historical cases[J]. Guangdong Meteorology, 31(6): 32-35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [13] |
徐建平, 林佩云, 1995. 台湾地形对过岛台风的影响[J]. 广东气象, (4): 42-44.
|
|
XU JIANPING, LIN PEIYUN, 1995. The influence of Taiwan topography on Typhoon crossing the island[J]. Guangdong Meteorology, (4): 42-44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [14] |
杨慧, 2019. 1960-2017年中国热带气旋降水气候特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院: 1-62.
|
|
YANG HUI, 2019. Research on the climate characteristics of Tropical cyclone precipitation in China from 1960 to 2017[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences: 1-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [15] |
杨云月, 许涛, 罗翠榆, 等, 2020. 典型厄尔尼诺期间台风降水δ18O变化分析: 以2018年22号台风“山竹”为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(4): 34-41.
|
|
YANG YUNYUE, XU TAO, LUO CUIYU, et al, 2020. Analysis on the variation of typhoon precipitation δ18O during typical El Niño event: A case study of Typhoon Mangkhut (2018)[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(4): 34-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [16] |
宇如聪, 李建, 陈昊明, 等, 2014. 中国大陆降水日变化研究进展[J]. 气象学报, 72(5): 948-968.
|
|
YU RUCONG, LI JIAN, CHEN HAOMING, et al, 2014. Progress in studies of the precipitation diurnal variation over contiguous China[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 72(5): 948-968. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [17] |
宇如聪, 李建, 2016. 中国大陆日降水峰值时间位相的区域特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 74(1): 18-30.
|
|
YU RUCONG, LI JIAN, 2016. Regional characteristics of diurnal peak phases of precipitation over contiguous China[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 74(1): 18-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [18] |
张长江, 薛利成, 马雷鸣, 等, 2018. 热带气旋客观定位的红外亮温方差方法[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 23(3): 450-457.
|
|
ZHANG CHANGJIANG, XUE LICHENG, MA LEIMING, et al, 2018. Infrared brightness-temperature variance method for the objective location of tropical cyclones[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 23(3): 450-457. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [19] |
张思齐, 2019. 全球再分析与中国观测资料对比研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究: 1-72.
|
|
ZHANG SIQI, 2019. Comparison research of observation and reanalysis data over China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences: 1-72.(in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [20] |
张学敏, 1991. 台风环流降水的诊断分析[J]. 海洋预报, 8(1): 76-83.
|
|
ZHANG XUEMIN,, 1991. Diagnostic analysis of typhoon circulation precipitation[J]. Marine Forecasts, 8(1): 76-83 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [21] |
周琴芳, 2019. 副热带高压对“灿鸿”和“苏迪罗”台风路径的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, (19): 196-197, 200.
|
|
ZHOU QINFANG, 2019. Influence of subtropical high on Typhoon track of “Canhong” and “Sudiro”[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, (19): 196-197, 200. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [22] |
邹丽丽, 谭桂容, 李任承, 等, 2017. 对流有效位能的本质和一种新的计算方法[J]. 气象科技进展, 7(3): 6-15.
|
|
ZOU LILI, TAN GUIRONG, LI RENCHENG, et al, 2017. On the essence and new computing method of convective available potential energy[J]. Advances in Meteorological Science and Technology, 7(3): 6-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [23] |
BESSHO K, DATE K, HAYASHI M, et al, 2016. An introduction to Himawari-8/9 - Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satellites[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan. Ser. Ⅱ, 94(2): 151-183.
|
| [24] |
CHANG A T C, CHIU L S, KUMMEROW C, et al, 1999. First results of the TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI) monthly oceanic rain rate: comparison with SSM/I[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 26(15): 2379-2382.
doi: 10.1029/1998GL900452
|
| [25] |
HU HAO, DUAN YIHONG, WANG YUQING, et al, 2017. Diurnal cycle of rainfall associated with Landfalling tropical cyclones in China from rain gauge observations[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 56(9): 2595-2605.
doi: 10.1175/JAMC-D-16-0335.1
|
| [26] |
NESBITT S W, ZIPSER E J, 2003. The diurnal cycle of rainfall and convective intensity according to three years of TRMM measurements[J]. Journal of Climate, 16(10): 1456-1475.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<1456:TDCORA>2.0.CO;2
|
| [27] |
SHEN YAN, XIONG ANYUAN, WANG YING, et al, 2010. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 115(D2): D02114.
|
| [28] |
YAO SUXIANG, HUANG QIAN, 2016. An analysis of extreme intraseasonal rainfall events during January-March 2010 over eastern China[J]. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 75: 22-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.dynatmoce.2016.04.001
|
| [29] |
YU RUCONG, ZHOU TIANJUN, XIONG ANYUAN, et al, 2007. Diurnal variations of summer precipitation over contiguous China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(1): L01704.
|
| [30] |
YUAN WEIHUA, YU RUCONG, ZHANG MINGHUA, et al, 2012. Regimes of diurnal variation of summer rainfall over subtropical East Asia[J]. Journal of Climate, 25(9): 3307-3320.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00288.1
|
| [31] |
ZHANG AOQI, CHEN YILUN, ZHOU S N, et al, 2020. Diurnal variation of Meiyu rainfall in the Yangtze plain during atypical Meiyu Years[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 125(1): e2019JD031742.
|
| [32] |
ZHANG AOQI, FU YUNFEI, 2018. Life cycle effects on the vertical structure of precipitation in East China measured by Himawari-8 and GPM DPR[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 146(7): 2183-2199.
doi: 10.1175/MWR-D-18-0085.1
|
 ), LI Weibiao1,2, ZHANG Aoqi1,2(
), LI Weibiao1,2, ZHANG Aoqi1,2( )
)