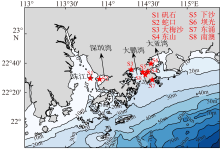
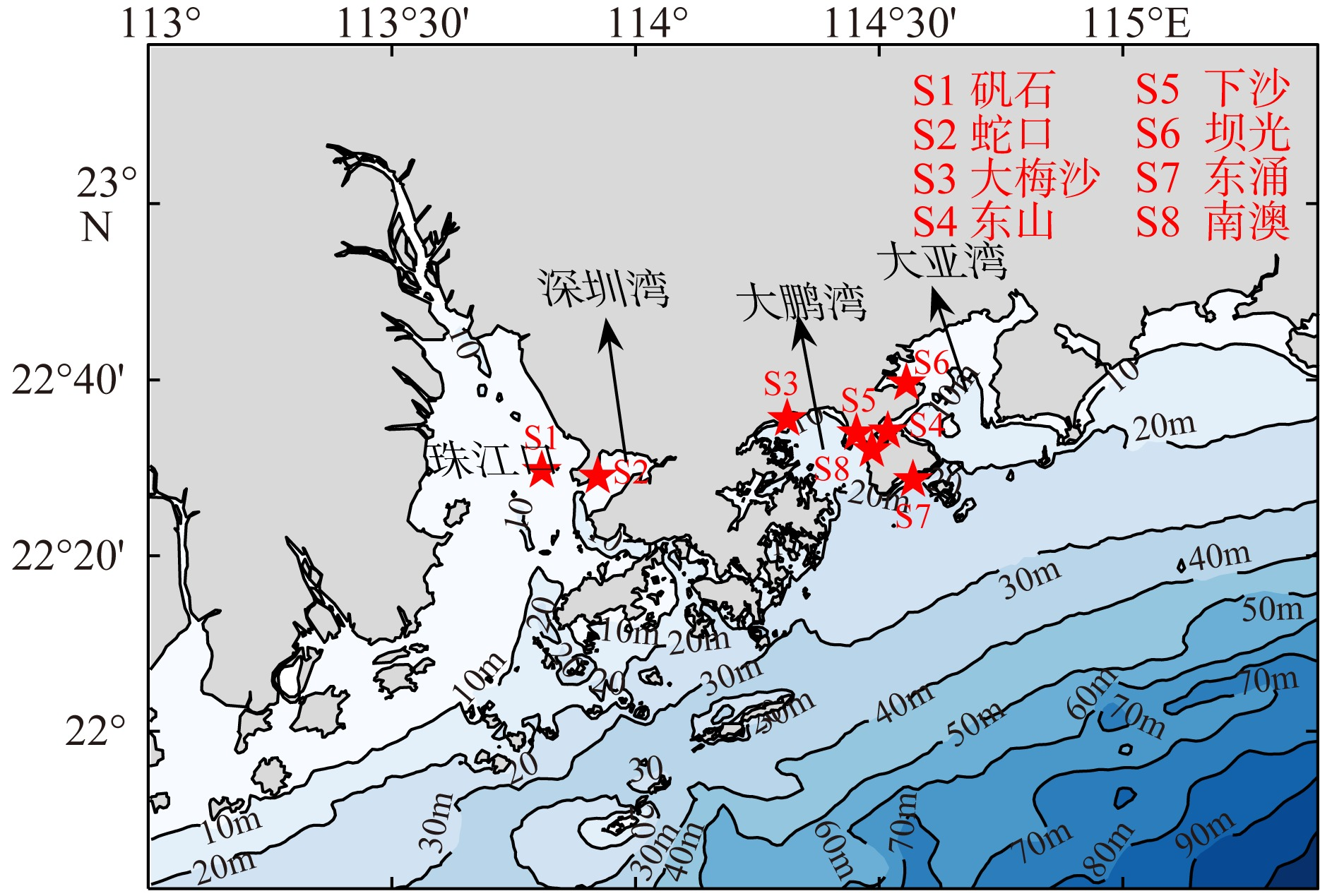
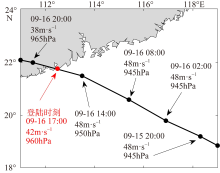
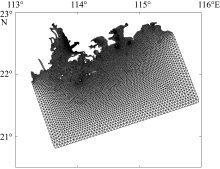
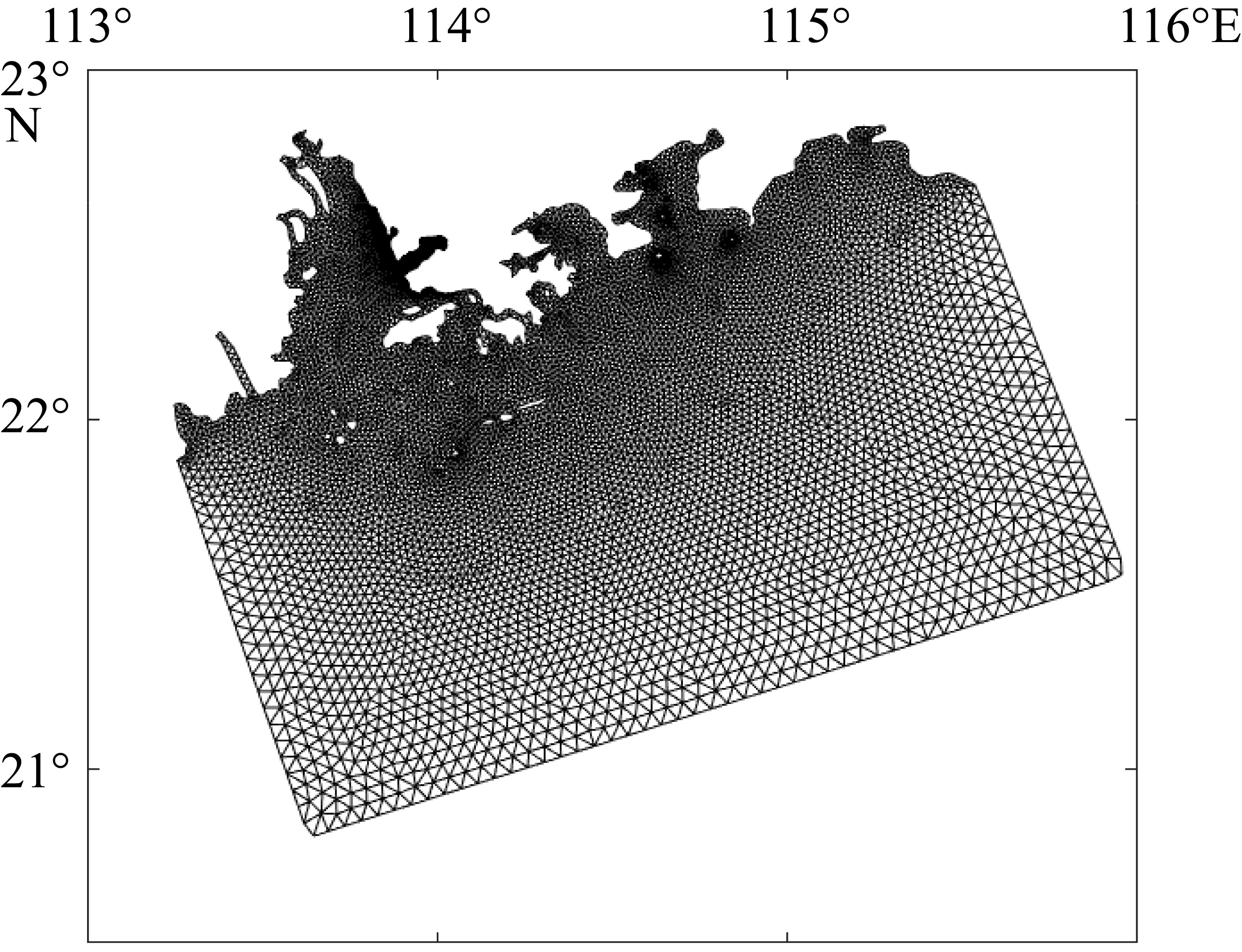
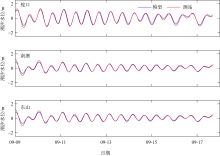
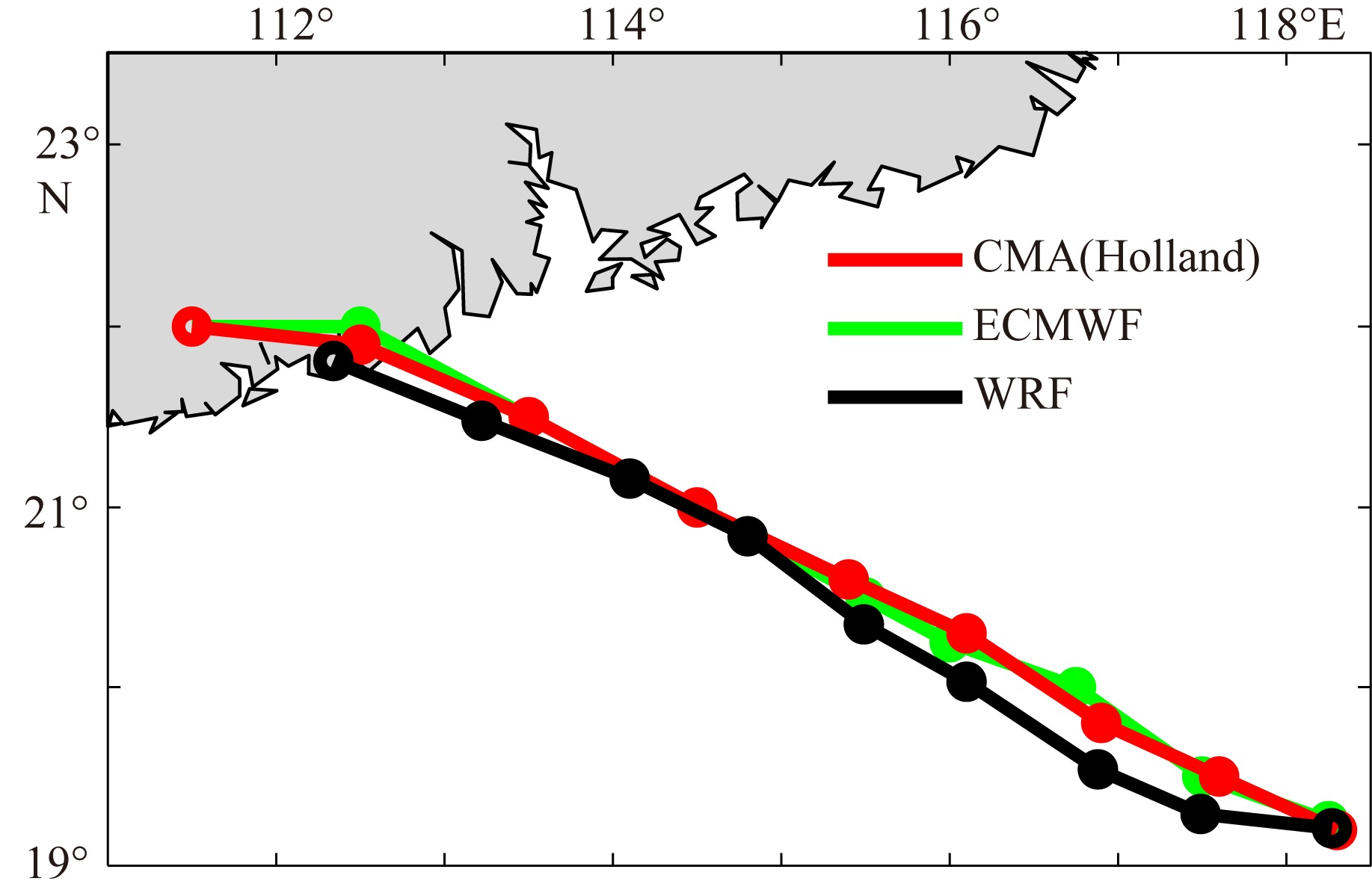
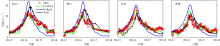
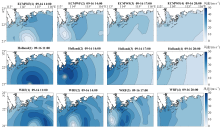
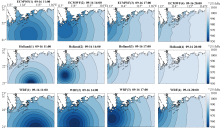
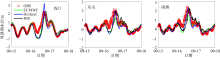
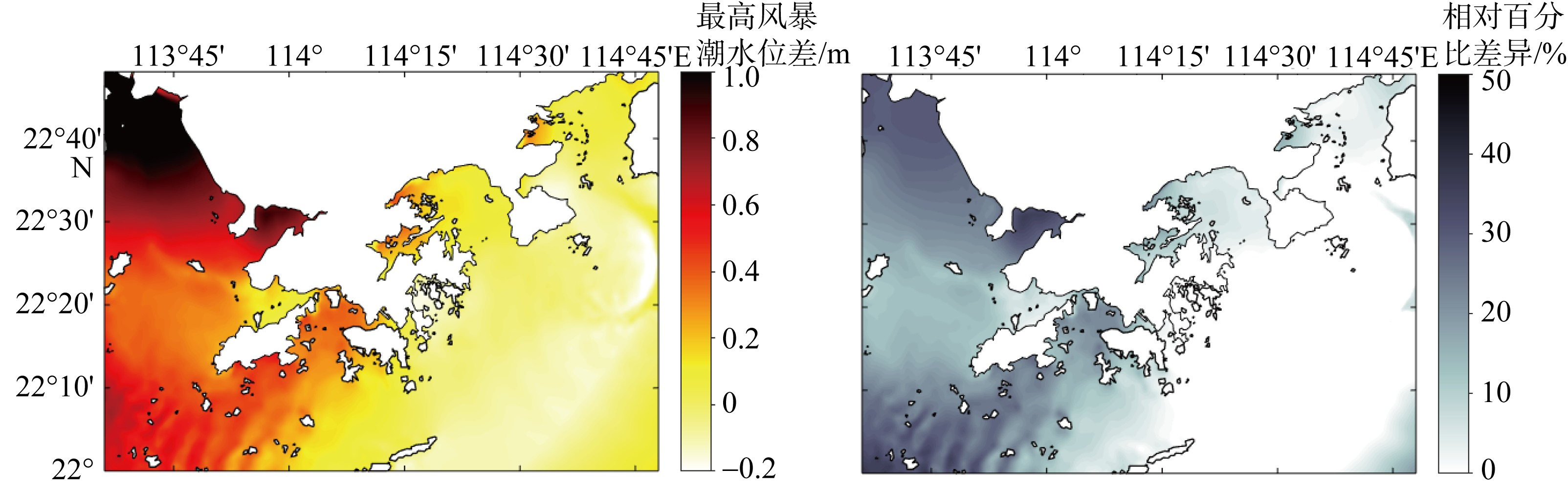
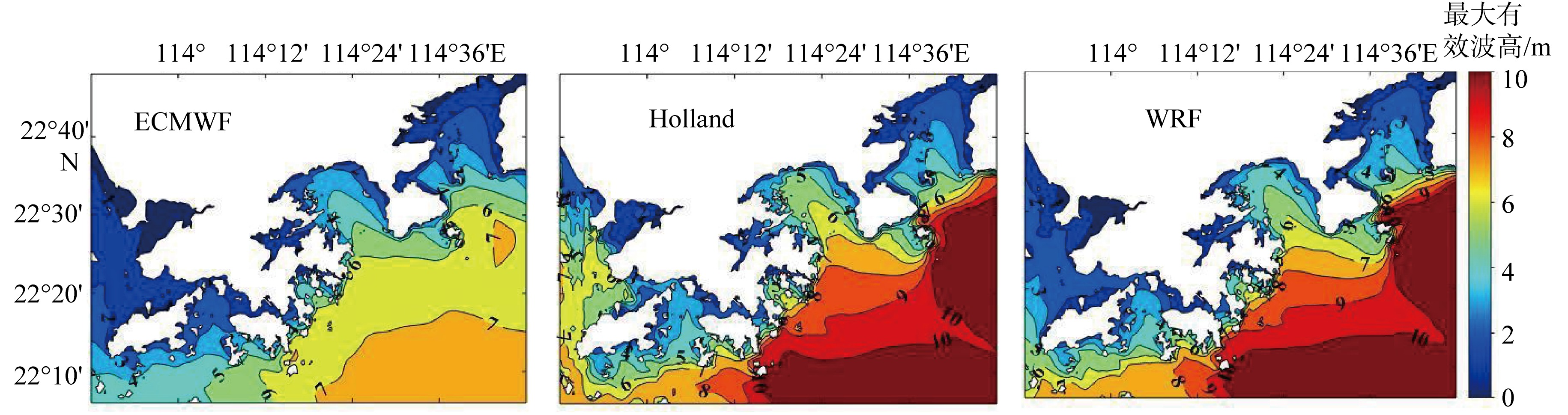
| [1] |
曹越男, 张增海, 原野, 等, 2014. 南海台风风暴潮数值模拟及其对气象强迫场的敏感性试验[J]. 热带气象学报, 30(6): 1119-1126.
|
|
CAO YUENAN, ZHANG ZENGHAI, YUAN YE, et al, 2014. Sensitivity tests of surface wind fields in typhoon storm surge modelling: Cases study in the south china sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 30(6): 1119-1126 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
邓国通, 刘敏聪, 邢久星, 等, 2022. 深圳近海风暴潮影响因素分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(3): 91-100.
doi: 10.11978/2021124
|
|
DENG GUOTONG, LIU MINCONG, XING JIUXING, et al, 2022. Analysis on the influencing factors of storm surges near Shenzhen[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 41(3): 91-100 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2021124
|
| [3] |
冯士筰, 李凤岐, 李少菁, 1999. 海洋学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [4] |
高钦钦, 朱建荣, 端义宏, 等, 2012. 对称和非对称台风对东海南海风暴潮影响比较[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 6: 57-72.
|
|
GAO QINQIN, ZHU JIANRONG, DUAN YIHONG, et al, 2012. Impacts of the symmetrical and unsymmetrical typhoons on the storm surge simulation in the East China and the South China Seas[J]. Journal of East China Normal University(Natural Science), 6: 57-72 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
蒋小平, 钟中, 张金善, 等, 2007. 台风浪模拟预报中的风场比较研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2: 11-19.
|
|
JIANG XIAOPING, ZHONG ZHONG, ZHANG JINSHAN, et al, 2007. Comparison study on the surface wind over ocean in typhoon waves simulation[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2: 11-19 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
梁必骐, 梁经萍, 温之平, 1995. 中国台风灾害及其影响的研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 1: 84-91.
|
|
LIANG BIQI, LIANG JINGPING, WEN ZHIPING, 1995. Study of typhoon disasters and its affects in China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 1: 84-91 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
林伟, 方伟华, 2013. 西北太平洋台风风场模型中Holland B系数区域特征研究[J]. 热带地理, 33(2): 124-132.
|
|
LIN WEI, FANG WEIHUA, 2013. Regional characteristics of Holland B Parameter in typhoon wind field model for Northwest Pacific[J]. Tropical Geography, 33(2): 124-132 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
毛献忠, 姜茜, 2012. 深圳香港海域可能最高潮位和浪高计算分析[J]. 海洋工程, 30(2): 129-135.
|
|
MAO XIANZHONG, JIANG QIAN, 2012. Possible maximum storm water level and wave height in Shenzhen and Hong Kong waters[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 30(2): 129-135 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
唐燕玲, 2018. 基于波流耦合模型的洋山海域风暴潮水动力特性研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
TANG YANLING, 2018. Numerical simulation of characteristics of storm tide in Yangshan Harbor based on tide-surge-wave model[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [10] |
文萍, 许映龙, 柳龙生, 2019. 台风“山竹”(1822)引发华南暴雨过程机制分析[J]. 海洋气象学报, 39(3): 29-35.
|
|
WEN PING, XU YINGLONG, LIU LONGSHENG, 2019. Analysis on mechanism of torrential rain in South China induced by Typhoon Mangkhut (1822)[J]. Journal of Marine Meteorology, 39(3): 29-35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
于福江, 傅赐福, 郭洪琳, 等, 2020. 现代风暴潮预报技术及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [12] |
曾祥锋, 2018. 基于WRF中尺度数值模式台风风场模拟及验证[D]. 广州: 广州大学.
|
|
ZENG XIANGFENG, 2018. Numerical simulation and verification of typhoon wind field by WRF mesoscale model[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
CHEN CHANGSHENG, BEARDSLEY R C, COWLES G, et al, 2012. An unstructured-grid, finite-volume community ocean model: FVCOM user manual[M]. Cambridge, MA, USA: Sea Grant College Program, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
|
| [14] |
CHEN CHANGSHENG, LIU HEDONG, BEARDSLEY R C, 2003. An unstructured grid, finite-volume, three-dimensional, primitive equations ocean model: Application to coastal ocean and estuaries[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 20(1): 159-186.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2003)020<0159:AUGFVT>2.0.CO;2
|
| [15] |
EGBERT G D, EROFEEVA S Y, 2002. Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 19(2): 183-204.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2002)019<0183:EIMOBO>2.0.CO;2
|
| [16] |
EMANUEL K, ROTUNNO R, 2011. Self-stratification of tropical cyclone outflow. Part I: Implications for storm structure[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 68(10): 2236-2249.
doi: 10.1175/JAS-D-10-05024.1
|
| [17] |
FUJITA T, 1952. Pressure distribution within typhoon[J]. Geophysical Magazine, 23(4): 437-451.
|
| [18] |
GENG SHANSHAN, SHI XIAOXIAO, YUE XINYANG, et al, 2022. Applicability analysis of the sea surface pressure and wind speed of ERA5 reanalysis data in the Bohai Sea and the Northern Huanghai Seas[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 24(2): 1-16.
|
| [19] |
HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al, 2018. ERA5 hourly data on single levels from 1979 to present[J]. Copernicus Climate Change Service (c3s) Climate Data Store (cds), 10(10. 24381).
|
| [20] |
HOLLAND G J, 1980. An analytic model of the wind and pressure profiles in hurricanes[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 108(8): 1212-1218.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108<1212:AAMOTW>2.0.CO;2
|
| [21] |
JELESNIANSKI C P, 1966. Numerical computations of storm surges without bottom stress[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 94(6): 379-394.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1966)094<0379:NCOSSW>2.3.CO;2
|
| [22] |
JELESNIANSKI C P, CHEN J, SHAFFER W, et al, 1984. SLOSH-A hurricane storm surge forecast model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, vol. 1984: 314-317.
|
| [23] |
KALNAY E, KANAMITSU M, KISTLER R, et al, 1996. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project[J]. Bulletin of the American meteorological Society, 77(3): 437-472.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2
|
| [24] |
LU XIAOQIN, YU HUI, YING MING, et al, 2021. Western North Pacific tropical cyclone database created by the China Meteorological Administration[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 38(4): 690-699.
doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-0211-7
|
| [25] |
MOON JIHONG, PARK JINYOUNG, CHA DONG-HYUN, et al, 2021. Five-day track forecast skills of WRF model for the western North Pacific tropical cyclones[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 36(4): 1491-1503.
|
| [26] |
QI JIANHUA, CHEN CHANGSHENG, BEARDSLEY R C, et al, 2009. An unstructured-grid finite-volume surface wave model (FVCOM-SWAVE): Implementation, validations and applications[J]. Ocean Modelling, 28(1-3): 153-166.
doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2009.01.007
|
| [27] |
SKAMAROCK W C, KLEMP J B, DUDHIA J, et al, 2019. A description of the advanced research WRF model version 4[R]. National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 145(145): 550.
|
| [28] |
WILLOUGHBY H E, RAHN M E, 2004. Parametric representation of the primary hurricane vortex. Part I: Observations and evaluation of the Holland (1980) model[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 132(12): 3033-3048.
doi: 10.1175/MWR2831.1
|
| [29] |
YANG JIE, LI LINLIN, ZHAO KUIFENG, et al, 2019. A comparative study of Typhoon Hato (2017) and Typhoon Mangkhut (2018)—Their impacts on coastal inundation in Macau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(12): 9590-9619.
doi: 10.1029/2019JC015249
|
| [30] |
YANG ZHEHAO, SHAO WEIZENG, DING YANG, et al, 2020. Wave simulation by the SWAN model and FVCOM considering the sea-water level around the Zhoushan Islands[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(10): 783.
doi: 10.3390/jmse8100783
|
| [31] |
YING MING, ZHANG WEI, YU HUI, et al, 2014. An overview of the China Meteorological Administration tropical cyclone database[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 31(2): 287-301.
doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-12-00119.1
|
 ), 胡俊洋2, 周凯2, 张鹏晖1, 邢久星1, 陈胜利1(
), 胡俊洋2, 周凯2, 张鹏晖1, 邢久星1, 陈胜利1( )
)
 ), HU Junyang2, ZHOU Kai2, ZHANG Penghui1, XING Jiuxing1, CHEN Shengli1(
), HU Junyang2, ZHOU Kai2, ZHANG Penghui1, XING Jiuxing1, CHEN Shengli1( )
)