热带海洋学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 164-171.doi: 10.11978/2021148CSTR: 32234.14.2021148
深圳大鹏湾一次球形棕囊藻藻华的发生过程及成因分析
- 深圳市海洋发展研究促进中心, 广东 深圳 518029
-
收稿日期:2021-11-01修回日期:2021-12-18发布日期:2021-12-23 -
通讯作者:刘悦 -
作者简介:刘悦(1965—), 女, 辽宁省大连市人, 高级工程师, 主要研究方向为海洋生态及资源监测。email:liuyue@pnr.sz.gov.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41606176)
Analysis of the bloom caused by colonial Phaeocystis globosa in Mirs Bay
LIU Yue( ), LI Li, ZHAI Xiaohui, ZHOU Juan, YE Penghao, HUANG Shengdong
), LI Li, ZHAI Xiaohui, ZHOU Juan, YE Penghao, HUANG Shengdong
- Marine Development Research and Promotion Center of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518029, China
-
Received:2021-11-01Revised:2021-12-18Published:2021-12-23 -
Contact:LIU Yue -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of China(41606176)
摘要:
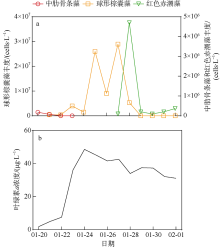
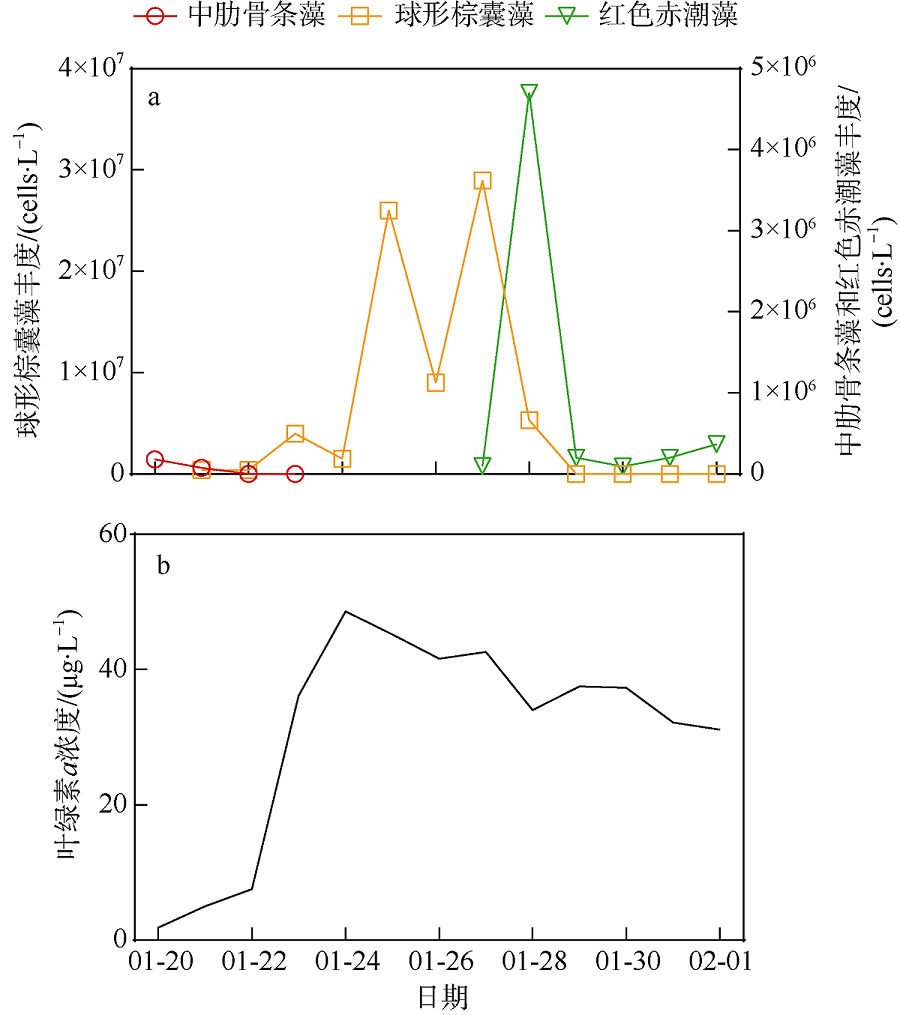
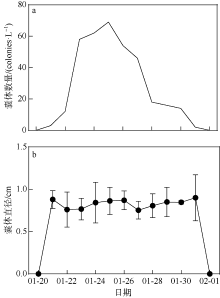
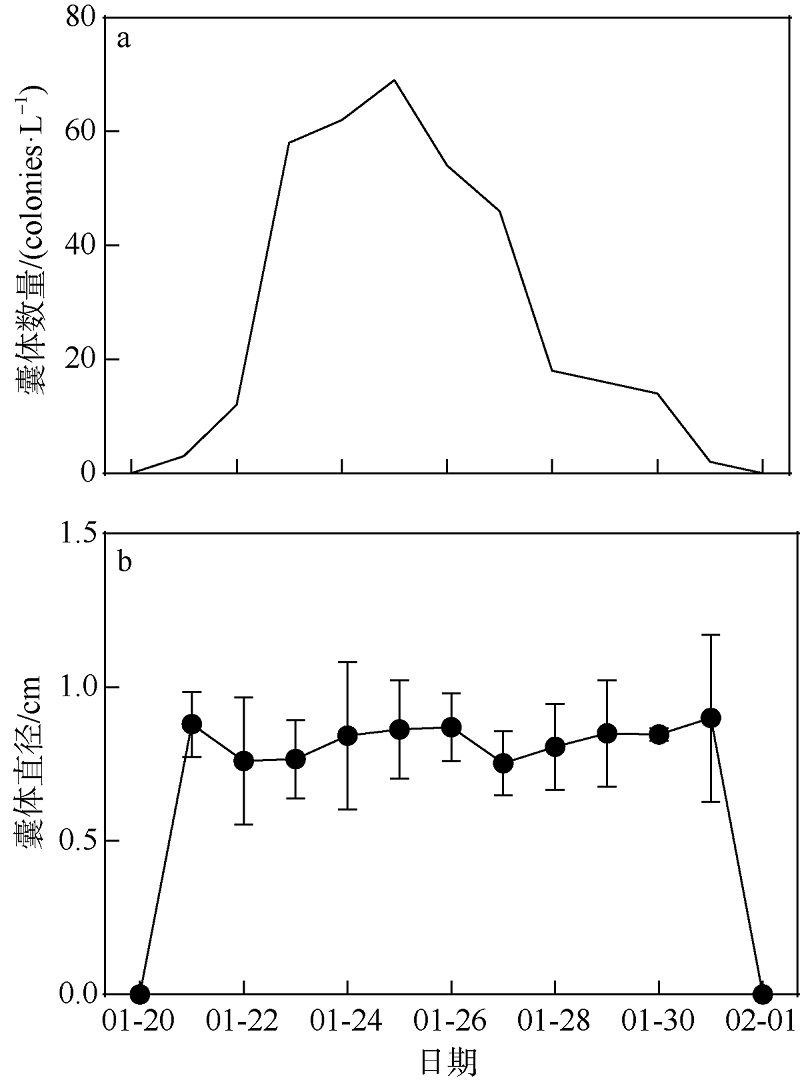
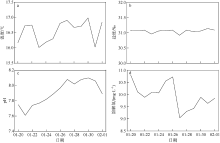
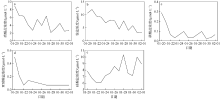
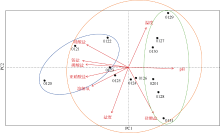
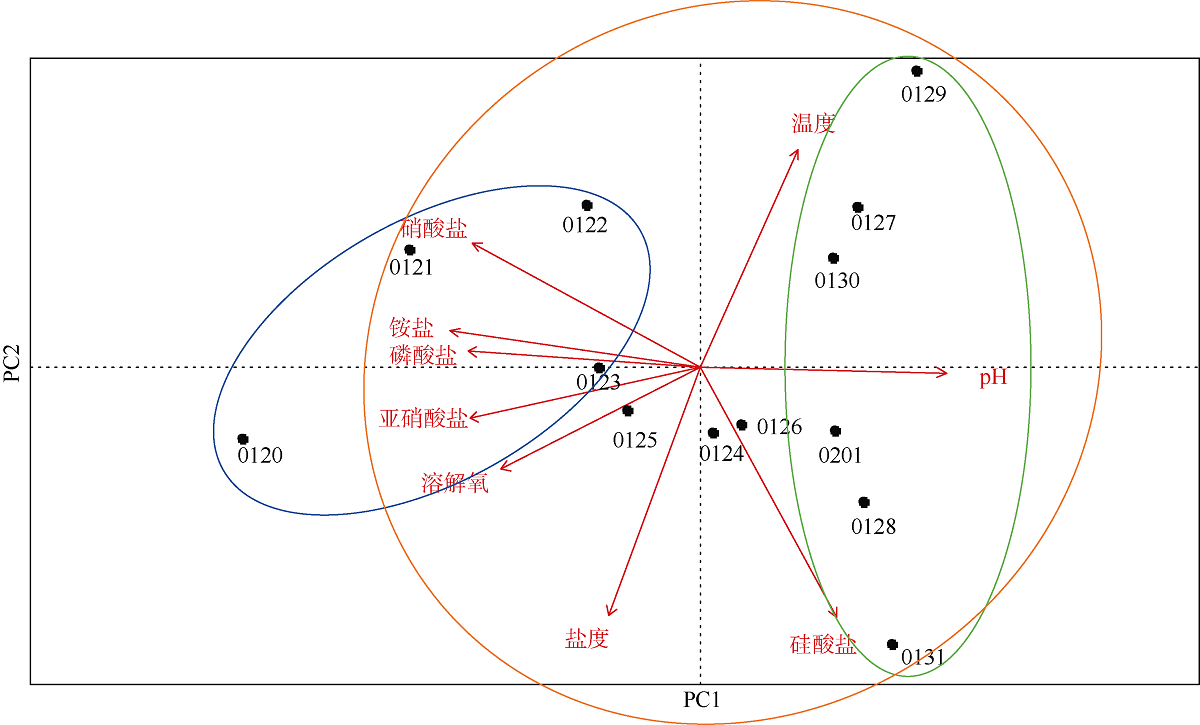
2021年1月下旬深圳大鹏湾沿岸海域发生球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)藻华。为了探究球形棕囊藻藻华发生动态特征及其影响因素, 于1月20日至2月1日系统调查分析了藻华发生过程中浮游植物优势种演替、球形棕囊藻囊体数量、营养盐水平以及其他环境因素的变化。结果表明: 1月20日, 中肋骨条藻(Skeletonema costatum)为绝对优势种, 1月21日球形棕囊藻囊体开始出现, 1月25日囊体数量达到最高, 达69colonies·L-1; 1月27日红色赤潮藻(Akashiwo sanguinea)藻华出现, 随后球形棕囊藻藻华逐渐消退。灰关联分析显示, 铵盐和硝酸盐是影响球形棕囊藻囊体丰度的最主要因素。水体扰动和球形棕囊藻在磷限制条件下的竞争优势也可能有利于球形棕囊藻藻华的发生。红色赤潮藻藻华可能是球形棕囊藻藻华消退的主要原因。球形棕囊藻藻华的发生和消亡是各种理化因素和生物因素共同作用的结果。
中图分类号:
- X55
引用本文
刘悦, 李丽, 翟晓辉, 周娟, 叶鹏浩, 黄盛东. 深圳大鹏湾一次球形棕囊藻藻华的发生过程及成因分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 164-171.
LIU Yue, LI Li, ZHAI Xiaohui, ZHOU Juan, YE Penghao, HUANG Shengdong. Analysis of the bloom caused by colonial Phaeocystis globosa in Mirs Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 164-171.
| [1] | 蔡卓平, 段璐洋, 肖群, 等, 2011. 风浪扰动促进中肋骨条藻和球形棕囊藻增殖的模拟研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 30(4): 473-476. |
| CAI ZHUOPING, DUAN LUYANG, XIAO QUN, et al, 2011. Simulation study on promoted proliferation of Skeletonema costatum and Phaeocystis globosa disturbed by wave[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 30(4): 473-476. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 陈菊芳, 徐宁, 江天久, 等, 1999. 中国赤潮新记录种──球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)[J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版), 20(3): 124-129. |
| CHEN JUFANG, XU NING, JIANG TIANJIU, et al, 1999. A report of Phaeocystis globosa bloom in coastal water of Southeast China[J]. Journal of Jinan University (Natural Science), 20(3): 124-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 贺成, 宋书群, 李才文, 2019. 广西北部湾海域球形棕囊藻囊体时空分布及其影响因素[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 50(3): 630-643. |
| HE CHENG, SONG SHUQUN, LI CAIWEN, 2019. The spatial-temperal distribution of Phaeocystis globosa colonies and related affecting factors in Guangxi Beibu Gulf[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 50(3): 630-643. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 黄博珠, 2016. 混合营养型甲藻红色赤潮藻对共存浮游植物的毒性效应[D]. 广州: 暨南大学: 1-59. |
| HUANG BOZHU, 2016. Toxic effects of mixotrophic dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea on co-occurring phytoplankton[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University: 1-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 黄肖阳, 龙寒, 莫钰, 等, 2021. 不同形态磷源对球形棕囊藻生长及囊体形成的影响[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (1): 116-122. |
| HUANG XIAOYANG, LONG HAN, MO YU, et al, 2021. Effects of different phosphorus sources on the growth and colony formation of Phaeocystis globosa[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (1): 116-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 李冬梅, 高永利, 田甜, 等, 2010. 水体扰动对多种赤潮藻生长的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(6): 65-70. |
| LI DONGMEI, GAO YONGLI, et al, 2010. Effects of turbulence on phytoplankton: species differences[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 29(6): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 吕旭宁, 2020. 硝酸盐在北部湾球形棕囊藻藻华过程中的关键影响作用[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所): 1-137. |
| LV XUNING, 2020. The key effect of nitrate on Phaeocystis globosa booms in the Beibu Gulf[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of oceanology, Chinese academy of Sciences): 1-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 沈萍萍, 齐雨藻, 欧林坚, 2018. 中国沿海球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)的分类、分布及其藻华[J]. 海洋科学, 42(10): 146-162. |
| SHEN PINGPING, QI YUZAO, OU LINJIAN, 2018. Phaeocystis globosa in coastal China: taxonomy, distribution, and its blooms[J]. Marine Sciences, 42(10): 146-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 田晶晶, 2010. 环境因子对球形棕囊藻细胞群体形成的影响[D]. 广州: 暨南大学: 1-69. |
| TIAN JINGJING, 2010. Effects of environmental factors on the colony formation of Phaeocystis globosa[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University: 1-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 王超, 李新辉, 赖子尼, 等, 2010. 珠江口球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)赤潮后期的浮游植物群落结构特征研究[J]. 生态科学, 29(2): 140-146. |
| WANG CHAO, LI XINHUI, LAI ZINI, et al, 2010. Study on phytoplankton community structure at the late stage of a Phaeocystis globosa bloom in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Ecological Science, 29(2): 140-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 王艳, 唐海溶, 2006. 不同形态的磷源对球形棕囊藻生长及碱性磷酸酶的影响[J]. 生态科学, 25(1): 38-40. |
| WANG YAN, TANG HAIRONG, 2006. Effects of different phosphorus on the growth and alkaline phospohatase activity in Phaeocystis globosa[J]. Ecologic Science, 25(1): 38-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 王艳, 邓坤, 王小冬, 2013. 球形棕囊藻囊体形成中光照、营养盐和共存硅藻的影响[J]. 生态科学, 32(2): 165-170. |
| WANG YAN, DENG KUN, WANG XIAODONG, 2013. The effects of light, nutrient and co-existing diatom on colony formation of Phaeocystis globosa[J]. Ecological Science, 32(2): 165-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | 徐宁, 齐雨藻, 陈菊芳, 等, 2003. 球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel)赤潮成因分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 23(1): 113-118. |
| XU NING, QI YUZAO, CHEN JUFANG, et al, 2003. Analysis on the cause of Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel red tide[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 23(1): 113-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [14] | 赵越, 于仁成, 张清春, 等, 2019. 北部湾海域微型、微微型浮游植物类群季节变化及其与棕囊藻赤潮的关系初探[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 50(3): 590-600. |
| ZHAO YUE, YU RENCHENG, ZHANG QINGCHUN, et al, 2019. Relationship between seasonal variation of pico-and nano-phytoplankton assemblages and phaeocystis red tides in Beibu Gulf[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 50(3): 590-600. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会 2008. GB 17378.4-2007 海洋监测规范第4部分: 海水分析[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration, 2008. GB 17378.4-2007 The specification for marine monitoring-Part 4: seawater analysis[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] |
BLAUW A N, LOS F J, HUISMAN J, et al, 2010. Nuisance foam events and Phaeocystis globosa blooms in Dutch coastal waters analyzed with fuzzy logic[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 83(3-4): 115-126.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.05.003 |
| [17] |
BORKMAN D G, LIBBY P S, MICKELSON M J, et al, 2016. Variability of winter-spring bloom Phaeocystis pouchetii abundance in Massachusetts Bay[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 39(4): 1084-1099.
doi: 10.1007/s12237-016-0065-5 |
| [18] |
BRUSSAARD C P D, BRATBAK G, BAUDOUX A C, et al, 2007. Phaeocystis and its interaction with viruses[J]. Biogeochemistry, 83(1-3): 201-215.
doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9096-0 |
| [19] |
HAI D N, LAM N N, DIPPNER J W, 2010. Development of Phaeocystis globosa blooms in the upwelling waters of the South Central coast of Viet Nam[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 83(3-4): 253-261.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.04.015 |
| [20] |
HAMM C E, 2000. Architecture, ecology and biogeochemistry of Phaeocystis colonies[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 43(3-4): 307-315.
doi: 10.1016/S1385-1101(00)00014-9 |
| [21] |
JEONG H J, YOO Y D, SEONG K A, et al, 2005. Feeding by the mixotrophic red-tide dinoflagellate Gonyaulax polygramma: mechanisms, prey species, effects of prey concentration, and grazing impact[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 38(3): 249-257.
doi: 10.3354/ame038249 |
| [22] | LANCELOT C, KELLER M D, ROUSSEAU V, et al, 1998. Autoecology of the marine haptophyte Phaeocystis sp[M]// ANDERSON D M, CEMBELLA A D, HALLEGRAEFF G M. Physiological ecology of harmful algal blooms. Berlin: Springer: 209-224. |
| [23] |
LANCELOT C, GYPENS N, BILLEN G, et al, 2007. Testing an integrated river-ocean mathematical tool for linking marine eutrophication to land use: the Phaeocystis-dominated Belgian coastal zone (Southern North Sea) over the past 50 years[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 64(1-4): 216-228.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2006.03.010 |
| [24] |
NEJSTGAARD J C, TANG K W, STEINKE M, et al, 2007. Zooplankton grazing on Phaeocystis: a quantitative review and future challenges[J]. Biogeochemistry, 83(1-3): 147-172.
doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9098-y |
| [25] |
NELSON D M, BRZEZINSKI M A, 1990. Kinetics of silicic acid uptake by natural diatom assemblages in two Gulf Stream warm-core rings[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 62(3): 283-292.
doi: 10.3354/meps062283 |
| [26] |
PEPERZAK L, COLIJN F, GIESKES W W C, et al, 1998. Development of the diatom- Phaeocystis spring bloom in the Dutch coastal zone of the North Sea: the silicon depletion versus the daily irradiance threshold hypothesis[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 20(3): 517-537.
doi: 10.1093/plankt/20.3.517 |
| [27] | POULTON A J, MOORE C M, SEEYAVE S, et al, 2007. Phytoplankton community composition around the Crozet Plateau, with emphasis on diatoms and Phaeocystis[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 54(18-20): 2085-2105. |
| [28] |
RIEGMAN R, NOORDELOOS A A M, CADÉE G C, 1992. Phaeocystis blooms and eutrophication of the continental coastal zones of the North Sea[J]. Marine Biology, 112(3): 479-484.
doi: 10.1007/BF00356293 |
| [29] |
ROUSSEAU V, VAULOT D, CASOTTI R, et al, 1994. The life cycle of Phaeocystis (Prymnesiophycaea): evidence and hypotheses[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 5(1): 23-39.
doi: 10.1016/0924-7963(94)90014-0 |
| [30] |
ROUSSEAU V, LEYNAERT A, DAOUD N, et al, 2002. Diatom succession, silicification and silicic acid availability in Belgian coastal waters (Southern North Sea)[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 236: 61-73.
doi: 10.3354/meps236061 |
| [31] |
ROUSSEAU V, CHRÉTIENNOT-DINET M J, JACOBSEN A, et al, 2007. The life cycle of Phaeocystis: state of knowledge and presumptive role in ecology[J]. Biogeochemistry, 83(1-3): 29-47.
doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9085-3 |
| [32] |
SANDERS R W, 1991. Mixotrophic protists in marine and freshwater ecosystems[J]. The Journal of Protozoology, 38(1): 76-81.
doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1991.tb04805.x |
| [33] |
SANDERSON M P, BRONK D A, NEJSTGAARD J C, et al, 2008. Phytoplankton and bacterial uptake of inorganic and organic nitrogen during an induced bloom of Phaeocystis pouchetii[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 51(2): 153-168.
doi: 10.3354/ame01178 |
| [34] |
SAZHIN A F, ARTIGAS L F, NEJSTGAARD J C, et al, 2007. The colonization of two Phaeocystis species (Prymnesiophyceae) by pennate diatoms and other protists: a significant contribution to colony biomass[J]. Biogeochemistry, 83(1-3): 137-145.
doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9086-2 |
| [35] |
SCHOEMANN V, BECQUEVORT S, STEFELS J, et al, 2005. Phaeocystis blooms in the global ocean and their controlling mechanisms: a review[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 53(1-2): 43-46.
doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2004.01.008 |
| [36] | SMITH JR W O, LIU XIAO, TANG K W, et al, 2014. Giantism and its role in the harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 101: 95-106. |
| [37] |
TUNGARAZA C, ROUSSEAU V, BRION N, et al, 2003. Contrasting nitrogen uptake by diatom and Phaeocystis-dominated phytoplankton assemblages in the North Sea[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 292(1): 19-41.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(03)00145-X |
| [38] |
VERITY P G, BRUSSAARD C P, NEJSTGAARD J C, et al, 2007. Current understanding of Phaeocystis ecology and biogeochemistry, and perspectives for future research[J]. Biogeochemistry, 83(1-3): 311-330.
doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9090-6 |
| [39] |
WANG KANG, CHEN BAOHONG, GAO YAHUI, et al, 2021a. Harmful algal blooms caused by Phaeocystis globosa from 1997 to 2018 in Chinese coastal waters[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 173: 112949.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112949 |
| [40] |
WANG XIAODONG, TANG K W, 2010. Buoyancy regulation in Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel colonies[J]. The Open Marine Biology Journal, 4(1): 115-121.
doi: 10.2174/1874450801004010115 |
| [41] |
WANG XIAODONG, WANG YAN, SMITH JR W O, 2011. The role of nitrogen on the growth and colony development of Phaeocystis globosa (Prymnesiophyceae)[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 46(3): 305-314.
doi: 10.1080/09670262.2011.602430 |
| [42] |
WANG XIAODONG, SONG HUIYIN, WANG YAN, et al, 2021b. Research on the biology and ecology of the harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa in China: progresses in the last 20 years[J]. Harmful Algae, 107: 102057.
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102057 |
| [43] |
YIN KEDONG, 2002. Monsoonal influence on seasonal variations in nutrients and phytoplankton biomass in coastal waters of Hong Kong in the vicinity of the Pearl River estuary[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 245: 111-122.
doi: 10.3354/meps245111 |
| [44] |
YIN KEDONG, 2003. Influence of monsoons and oceanographic processes on red tides in Hong Kong waters[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 262: 27-41.
doi: 10.3354/meps262027 |
| [1] | 王西艳, 薛玥, 孟不凡, 付峰, 沈萍萍. 球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel)细胞形态转变及转录组比较研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 49-57. |
| [2] | 郑承志, 左丽明, 马旺, 朱琴, 王火火, 吕颂辉, 陈亨, 黄凯旋. 不同温度下抑食金球藻、中肋骨条藻和海洋卡盾藻间的相互作用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 124-131. |
| [3] | 徐轶肖, 何喜林, 张腾, 蓝文陆. 北部湾棕囊藻藻华原因种分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(6): 122-130. |
| [4] | 郭晓慧, 涂志刚, 陈丹丹, 郭雅琼, 李扬. 微小辐环藻, 我国硅藻藻华的新记录种[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(4): 24-28. |
| [5] | 周凯 ,李绪录 ,夏华永 . 大鹏湾海水中各形态无机氮的分布变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(3): 105-111. |
| [6] | 姜发军,胡章立,胡超群. 大鹏湾浮游细菌时空分布与环境因子的关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(1): 96-100. |
| [7] | 邓利,陈大玮,黎韵,罗学峰,丘红梅. 深圳大鹏湾和大亚湾近岸海水及潮间带动物的有机锡污染[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(4): 112-117. |
| [8] | 尹平河,黄凤,赵玲. 载Fe3+纳米TiO2薄膜去除球形棕囊藻赤潮生物的研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(4): 102-106. |
| [9] | 王桂芬,曹文熙,杨跃忠,周雯,梁少君,. 珠江口藻华水体总吸收系数的变化特性及高光谱反演模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(2): 52-58. |
|
||