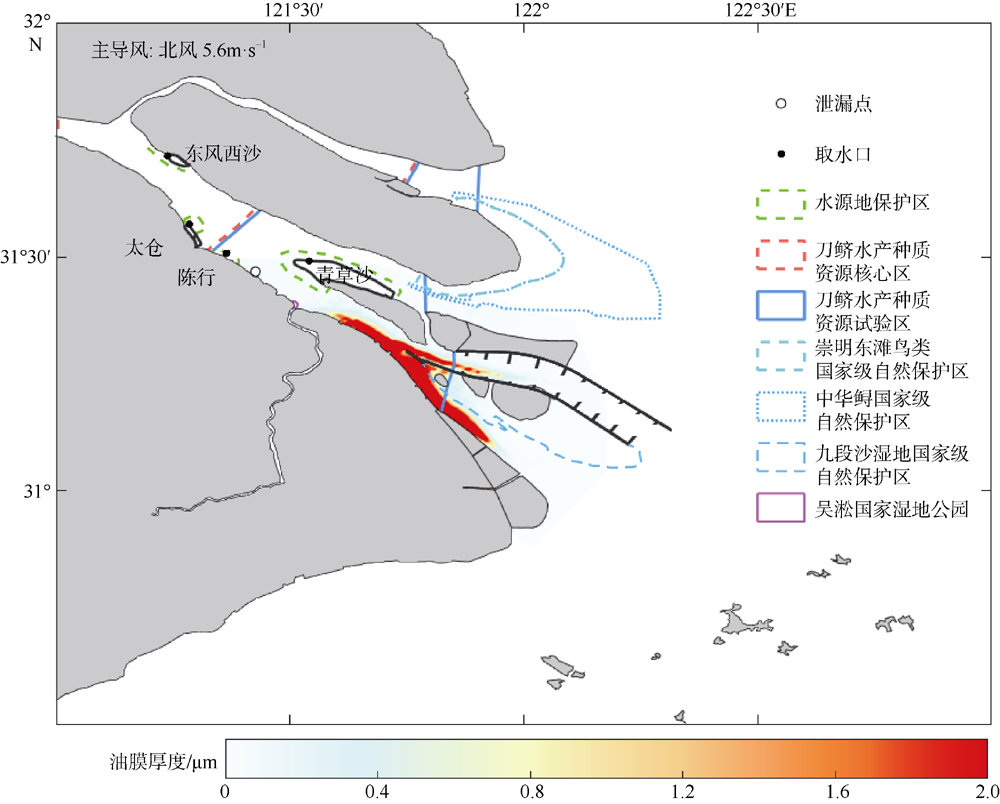
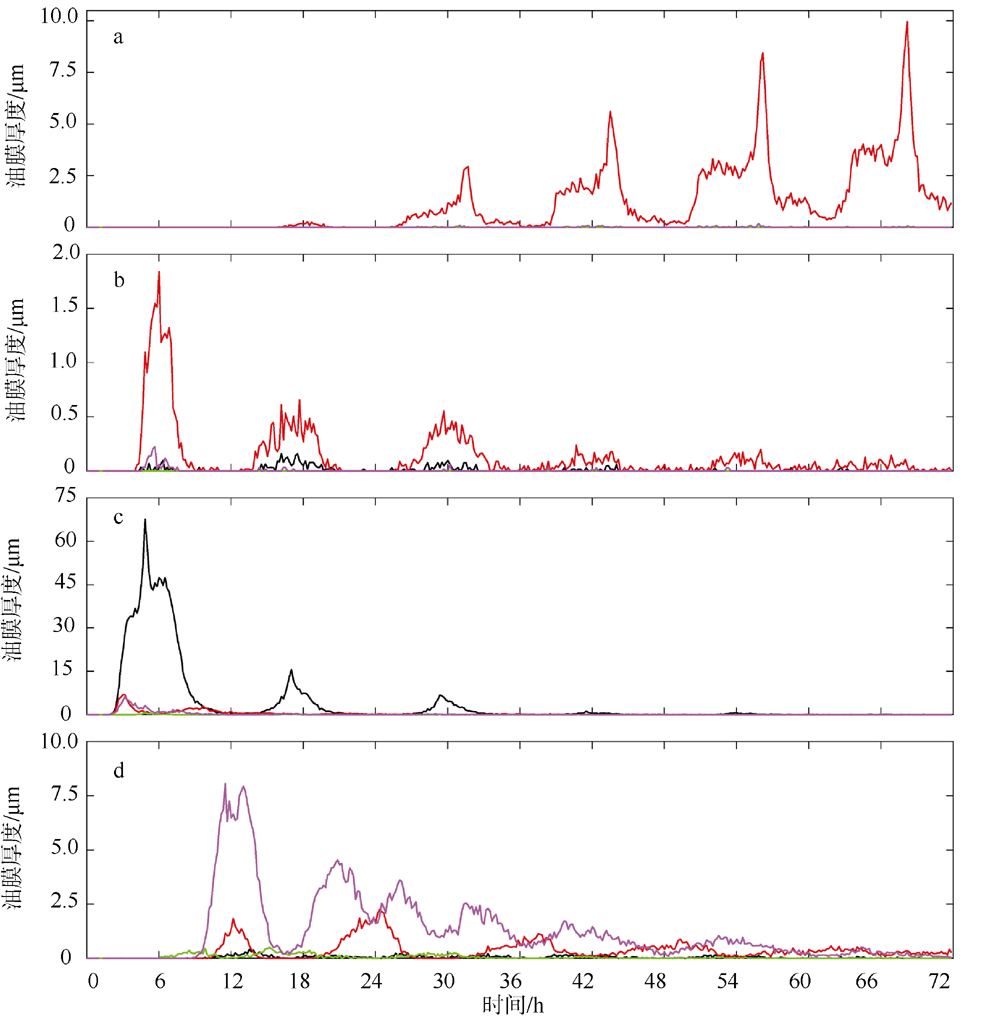
| [1] |
陈士谦, 朱建荣, 2012. 鸭绿江公路大桥溢油漂移扩散三维数值模拟[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (6): 46-56.
|
|
CHEN SHIQIAN, ZHU JIANRONG, 2012. Three- dimensional numerical simulation of the drift and diffusion of oil film at the highway bridge in the Yalu River[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (6): 46-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
陈义中, 朱建荣, 陈昞睿, 等, 2006. 渤海原油码头溢油漂移扩散的数值模拟[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (6): 25-33.
|
|
CHEN YIZHONG, ZHU JIANRONG, CHEN BINGRUI, et al, 2006. Numerical simulation of the drift and diffusion of oil film at the crude oil wharf in the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (6): 25-33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [3] |
傅利辉, 朱建荣, 陈昞睿, 等, 2008. 崇启大桥建成后流场变化及溢油的数值模拟. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (4): 114-123.
|
|
FU LIHUI, ZHU JIANRONG, CHEN BINGRUI, et al, 2008. Numerical simulation of current change and diffusion of oil film after the Chongqi bridge construction[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (4): 114-123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
郭运武, 刘栋, 钟宝昌, 等, 2008. 风对河道溢油扩展、漂移影响的实验研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 23(4): 446-452.
|
|
GUO YUNWU, LIU DONG, ZHONG BAOCHANG, et al, 2008. Experimental investigations of wind effect on the oil spill spread and drift[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 23(4): 446-452. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [5] |
李大鸣, 陈海舟, 付庆军, 2008. 海上溢油数学模型的研究与应用[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 29(12): 1291-1297.
|
|
LI DAMING, CHEN HAIZHOU, FU QINJUN, 2008. Research and application of mathematical modeling to oil spills on the sea[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 29(12): 1291-1297. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
刘栋, 林卫青, 钟宝昌, 等, 2006. 感潮河道溢油扩展、漂移特性实验[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 21(6): 744-751.
|
|
LIU DONG, LIN WEIQING, ZHONG BAOCHANG, et al, 2006. Characteristic experiment of spread and transport of oil spill in tidal river[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 21(6): 744-751. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [7] |
娄安刚, 王学昌, 孙长青, 等, 2001. 胶州湾海面溢油轨迹的数值模拟[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 19(1): 1-8.
|
|
LOU ANGANG, WANG XUECHANG, SUN CHANGQING, et al, 2001. A simulation of oil spill trajectory on sea surface of Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 19(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [8] |
娄厦, 刘曙光, 2008. 溢油模型理论及研究综述[J]. 环境科学与管理, 33(10): 33-37, 61.
|
|
LOU SHA, LIU SHUGUANG, 2008. Review in theory and study of oil spill models[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 33(10): 33-37, 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [9] |
孙宝楠, 杨永增, 于顺, 等, 2010. 基于分析法经典溢油蒸发模型的改进[J]. 海洋科学进展, 28(3): 364-371.
|
|
SUN BAONAN, YANG YONGZENG, YU SHUN, et al, 2010. Improvement for oil spill evaporation model based on classic analysis method[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 28(3): 364-371. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [10] |
孙长青, 赵可胜, 郭耀同, 2003. 渤海湾海面溢油数值计算[J]. 海洋科学, 27(11): 63-67.
|
|
SUN CHANGQING, ZHAO KESHENG, GUO YAOTONG, 2003. Digital modeling for oil-spill in Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 27(11): 63-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [11] |
张和庆, 李福娇, 2001. 近海海面油类漂流扩散的研究和预测实践[J]. 热带气象学报, 17(1): 83-89.
|
|
ZHANG HEQING, LI FUJIAO, 2001. Study and practice of the oil drift and diffusion on the sea surface in the offshore[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 17(1): 83-89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [12] |
CHEN QING, ZHU JIANRONG, LYU HANGHANG, et al, 2019. Impacts of topography change on saltwater intrusion over the past decade in the Changjiang estuary[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 231: 106469.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2019.106469
|
| [13] |
FINGAS M F, 1995. A literature review of the physics and predictive modelling of oil spill evaporation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 42(2): 157-175.
doi: 10.1016/0304-3894(95)00013-K
|
| [14] |
LYU HANGHANG, ZHU JIANRONG, 2018. Impact of the bottom drag coefficient on saltwater intrusion in the extremely shallow estuary[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 557: 838-850.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.01.010
|
| [15] |
MA RUI, ZHU JIANRONG, 2022. Water and Salt Transports in the Hengsha Channel of Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(1): 72.
doi: 10.3390/jmse10010072
|
| [16] |
PERIÁÑEZ R, PASCUAL-GRANGED A, 2008. Modelling surface radioactive, chemical and oil spills in the Strait of Gibraltar[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 34(2): 163-180.
doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2007.02.002
|
| [17] |
STIVER W, MACKAY D, 1984. Evaporation rate of spills of hydrocarbons and petroleum mixtures[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 18(11): 834-840.
doi: 10.1021/es00129a006
|
| [18] |
WANG SHOUDONG, SHEN YONGMING, GUO YAKUN, et al, 2008. Three-dimensional numerical simulation for transport of oil spills in seas[J]. Ocean Engineering, 35(5-6): 503-510.
doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2007.12.001
|
| [19] |
VIOLEAU D, BUVAT C, ABED-MERAIM K, et al, 2007. Numerical modelling of boom and oil spill with SPH[J]. Coastal Engineering, 54(12): 895-913.
doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2007.06.001
|
| [20] |
ZHU JIANRONG, CHENG XINYUE, LI LINJIANG, et al, 2020. Dynamic mechanism of an extremely severe saltwater intrusion in the Changjiang estuary in February 2014[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 24(10): 5043-5056.
doi: 10.5194/hess-24-5043-2020
|
 ), ZHU Jianrong(
), ZHU Jianrong( ), JIN Zhi
), JIN Zhi