热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 86-97.doi: 10.11978/2023088CSTR: 32234.14.2023088
红树林生态重建效果预测研究新模式
吴鸿博1( ), 罗锋1,2,3(
), 罗锋1,2,3( ), 陈治澎1, 朱飞1, 曾靖伟1, 张弛1, 李瑞杰3
), 陈治澎1, 朱飞1, 曾靖伟1, 张弛1, 李瑞杰3
- 1.河海大学港口海岸与近海工程学院, 江苏 南京 210098
2.南通河海大学海洋与近海工程研究院, 江苏 南通 226004
3.河海大学海岸灾害及防护教育部重点实验室, 江苏 南京 210098
-
收稿日期:2023-06-26修回日期:2023-09-11出版日期:2024-07-10发布日期:2024-07-22 -
作者简介:吴鸿博(2000—), 男, 江西南昌人, 硕士研究生, 主要从事河口海岸数值模拟研究。email: alexbala15879@gmail.com
-
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2022YFC3106100); 江苏省海洋科技创新项目(JSZRHYKJ202105); 南通社会民生科技计划项目(MS12022009); 南通社会民生科技计划项目(MS22022082); 南通社会民生科技计划项目(MS22022083)
A novel pattern for predicting the effects of mangrove ecological reconstruction
WU Hongbo1( ), LUO Feng1,2,3(
), LUO Feng1,2,3( ), CHEN Zhipeng1, ZHU Fei1, ZENG Jingwei1, ZHANG Chi1, LI Ruijie3
), CHEN Zhipeng1, ZHU Fei1, ZENG Jingwei1, ZHANG Chi1, LI Ruijie3
- 1. College of Harbour, Coastal and Offshore Engineering, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China
2. Nantong Ocean and Coastal Engineering Research Institute, Hohai University, Nantong 226004, China
3. Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Coastal Disaster and Protection, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China
-
Received:2023-06-26Revised:2023-09-11Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-07-22 -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFC3106100); Marine Science and Technology Innovation Project of Jiangsu Province(JSZRHYKJ202105); Nantong Science and Technology Bureau(MS12022009); Nantong Science and Technology Bureau(MS22022082); Nantong Science and Technology Bureau(MS22022083)
摘要:
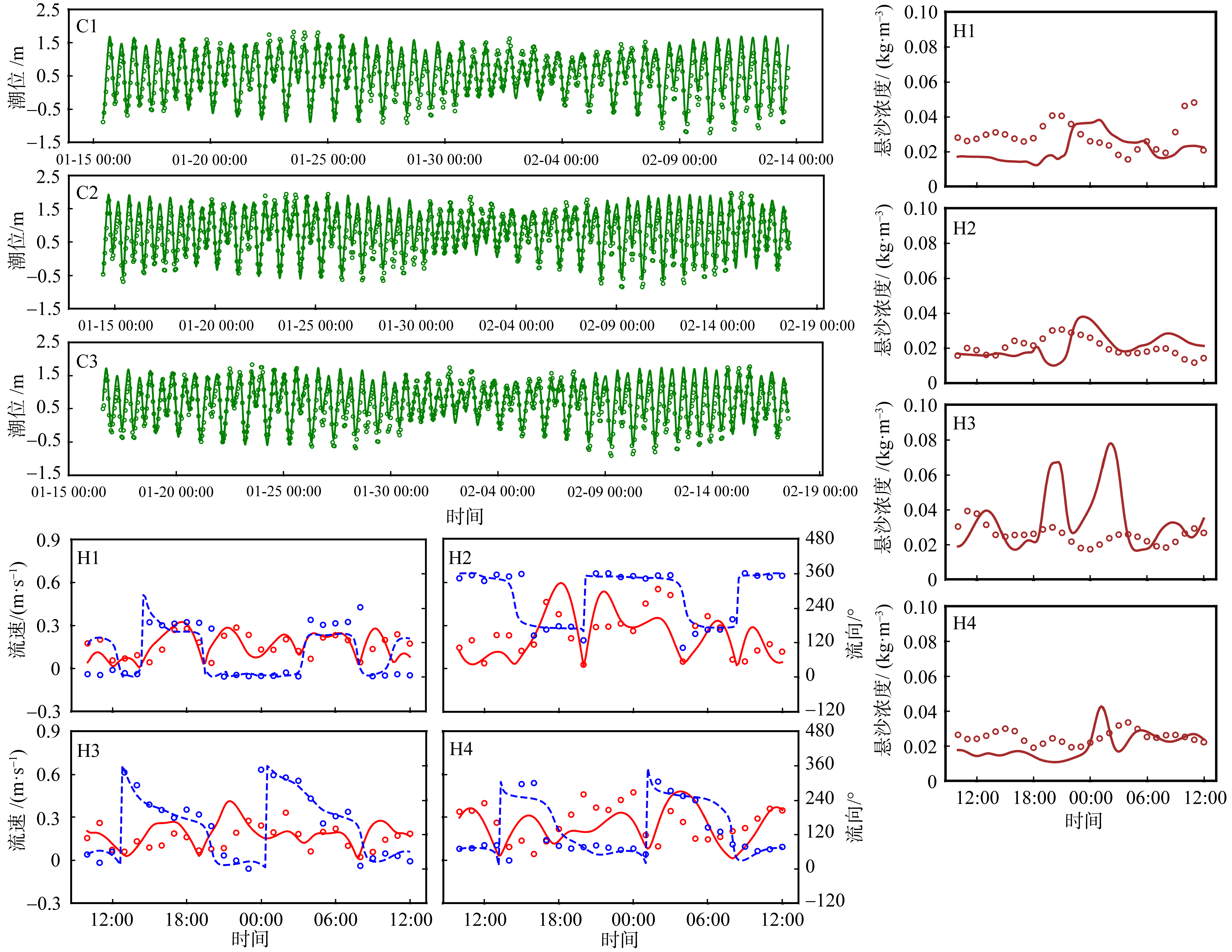
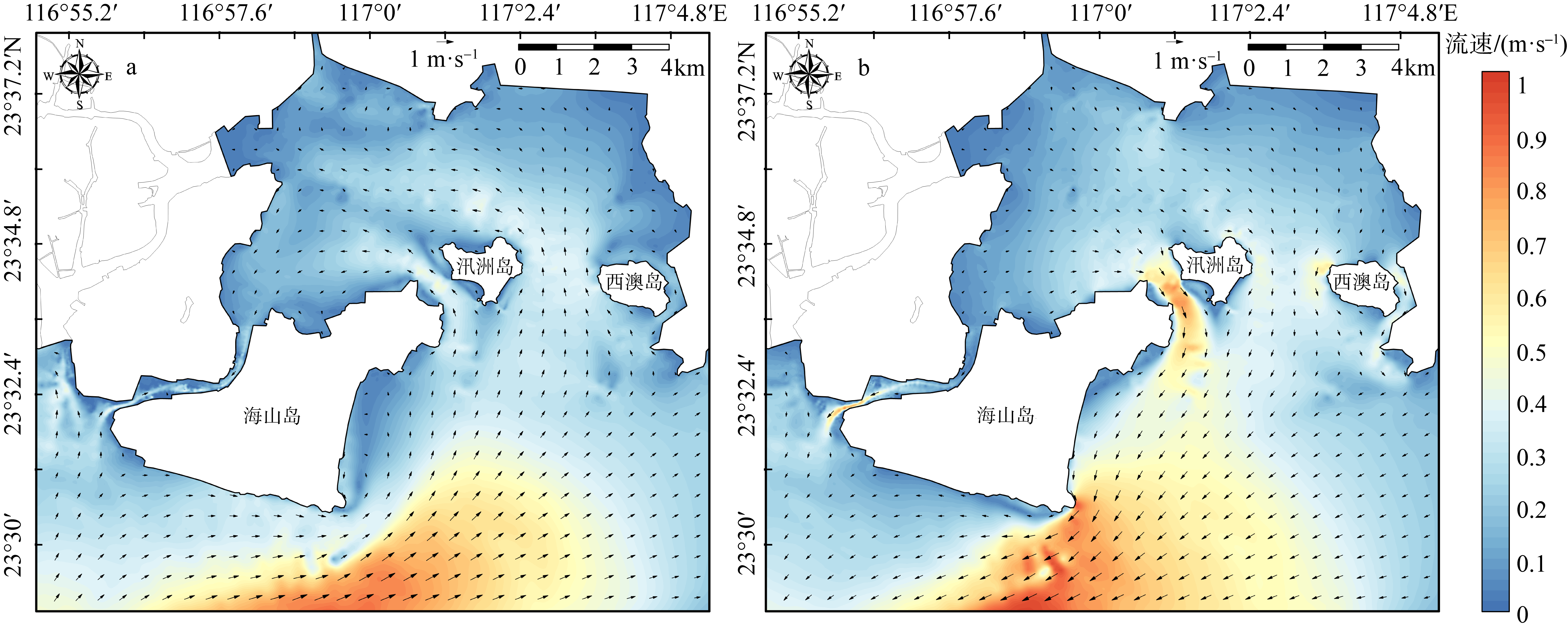
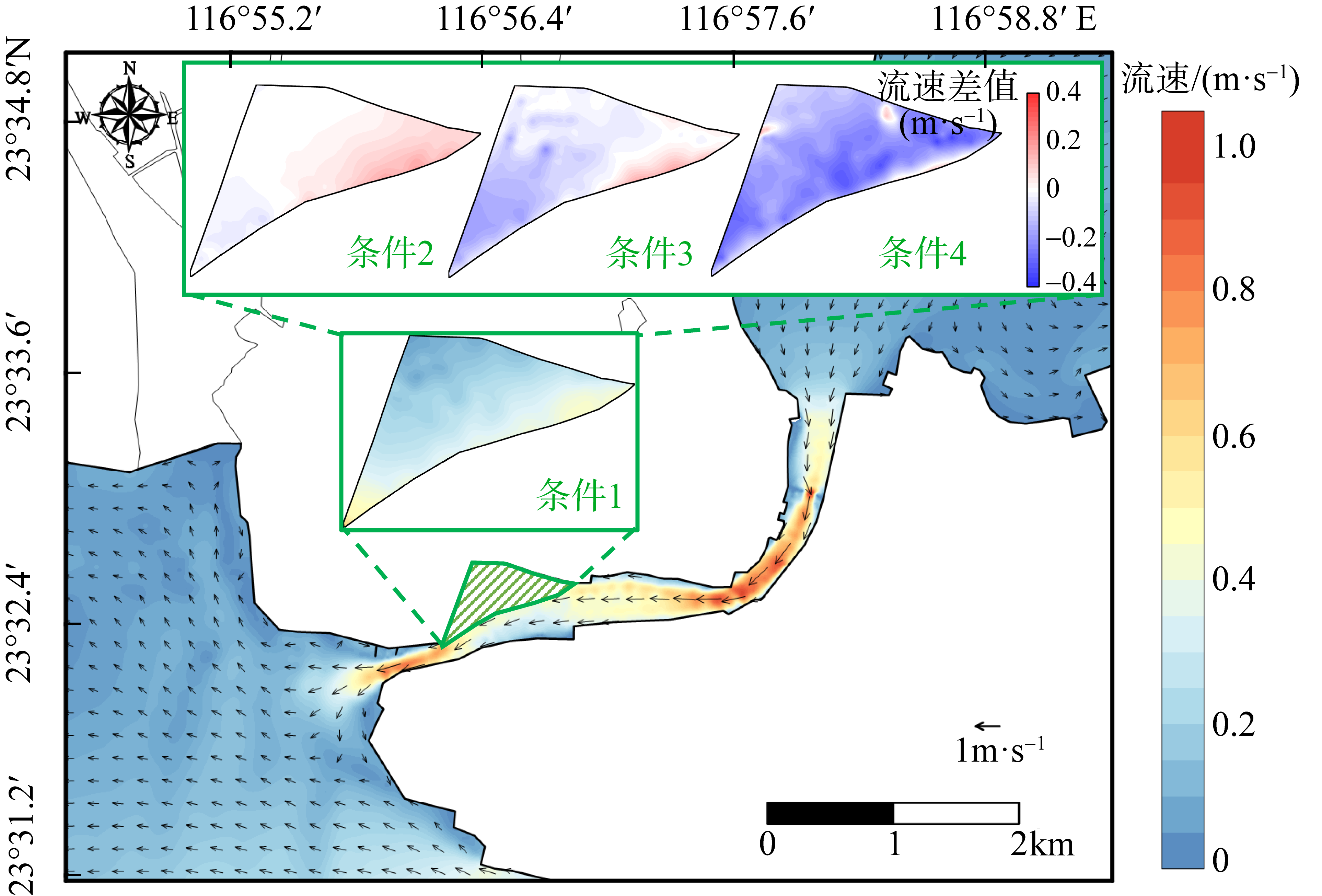
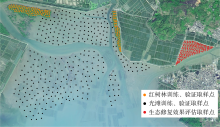
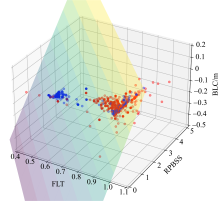
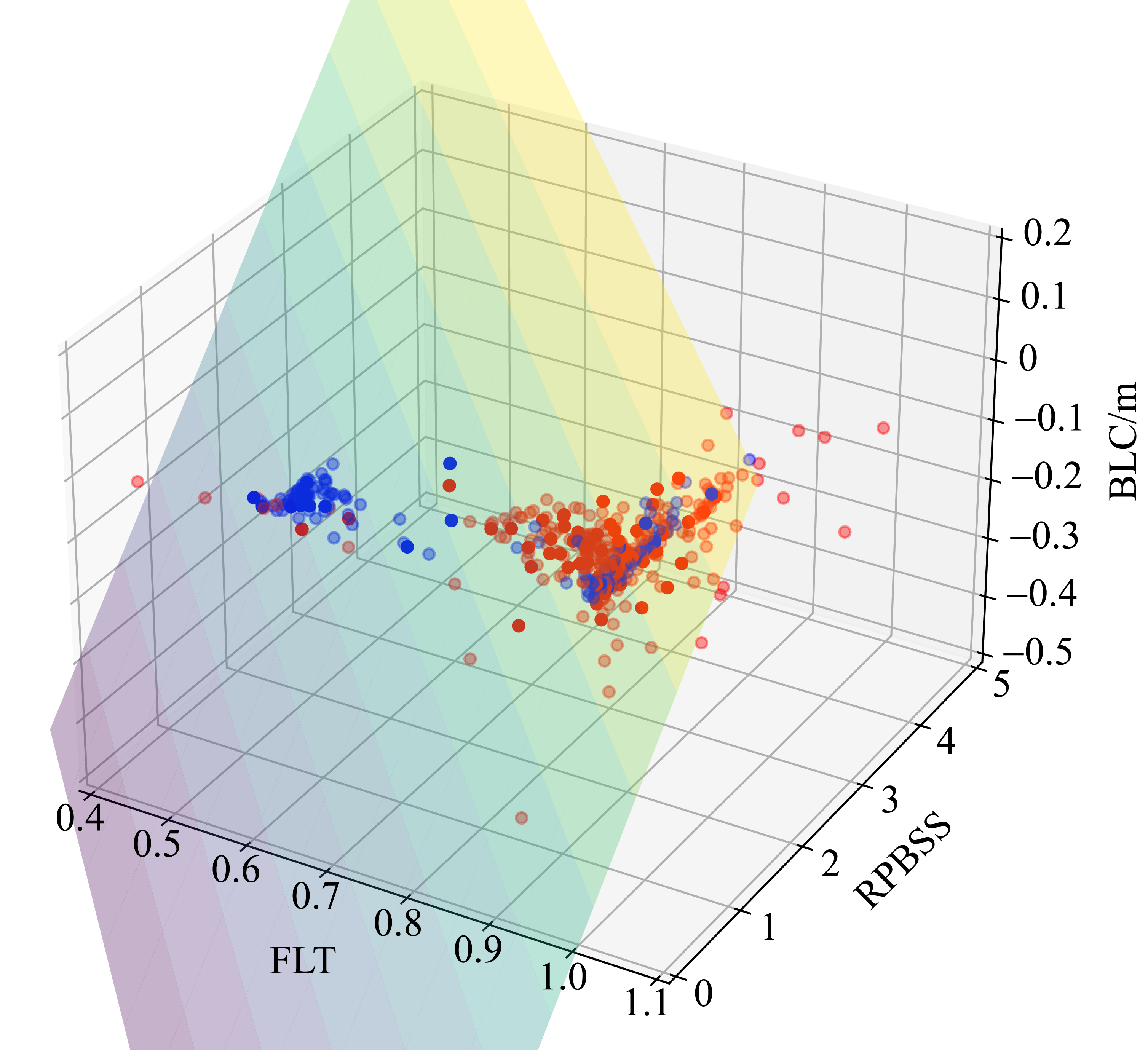
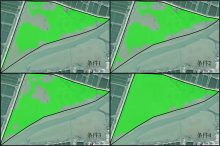
红树林是生态文明建设的组成部分, 对实现碳中和目标意义重大, 近年来实施了大量的保护和修复工程。然而, 目前缺少一种预测方法来比选有效的保护措施, 以指导红树林的生态重建工作。因此, 提出了一种“数值模拟模型+分类模型”的研究新模式。在模式应用中, 模拟了广东省柘林湾一年的水沙动力环境。通过考虑淹没时间、相对峰值底床切应力和底床高程变化, 描述了红树定植过程中所受到的胁迫, 对4种条件下笠港潮汐汊道内侧滩涂红树林的生态重建效果做出了预测。结果表明, 恢复汊道水深会轻微改变区域的水动力和泥沙冲淤环境, 导致生态重建成功率降低了3.12%; 提高区域底床高程会显著减小流速并加剧外侧冲刷, 提高0.5m和1.0m的高程分别使生态重建成功率提升了16.43%和32.75%。
引用本文
吴鸿博, 罗锋, 陈治澎, 朱飞, 曾靖伟, 张弛, 李瑞杰. 红树林生态重建效果预测研究新模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 86-97.
WU Hongbo, LUO Feng, CHEN Zhipeng, ZHU Fei, ZENG Jingwei, ZHANG Chi, LI Ruijie. A novel pattern for predicting the effects of mangrove ecological reconstruction[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 86-97.
| [1] |
蔡爱智, 1994. 粤东柘林湾的泥沙来源与沉积环境[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 33(4): 515-520.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈鹭真, 王文卿, 林鹏, 2005. 潮汐淹水时间对秋茄幼苗生长的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 27(2): 141-147.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈鹭真, 林鹏, 王文卿, 2006. 红树植物淹水胁迫响应研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 26(2): 586-593.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
郭旭东, 2017. 全球变化下外来红树植物无瓣海桑和本土红树植物秋茄的响应情况[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
黄凡非, 唐丽丽, 李瑞利, 2023. 近四十年来中国大陆红树林保护与恢复措施的生态效益分析[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 59(5): 813-822.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
蒋睢耀, 1993. 三百门港泥沙淤积研究[J]. 水道港口, (3): 28-35.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
欧素英, 罗凯文, 田枫, 2016. 柘林湾多口门潮汐汊道动力地貌的演变[J]. 热带海洋学报, 35(2): 83-92.
doi: 10.11978/2014129 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2014129 |
|
| [8] |
潘炜杰, 祝振昌, 蔡宴朋, 等, 2021. 潮滩冲淤扰动下外来与乡土红树植物幼苗稳定性差异[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(6): 120-127.
doi: 10.11978/2020133 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2020133 |
|
| [9] |
杨克用, 1990. 汕头柘林湾港区航道浚深后的回淤分析与计算[J]. 海岸工程, 9(3-4): 72-80.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
张乔民, 赵焕庭, 宋朝景, 1991. 华南海岸的汇潮水道[M]// 中国地理学会地貌与第四纪专业委员会. 地貌及第四纪研究进展. 北京: 测绘出版社: 211-217 (in Chinese).
|
| [11] |
张乔民, 于红兵, 陈欣树, 等, 1997. 红树林生长带与潮汐水位关系的研究[J]. 生态学报, 17(3): 258-265.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
张乔民, 隋淑珍, 张叶春, 等, 2001. 红树林宜林海洋环境指标研究[J]. 生态学报, 21(9): 1427-1437.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
自然资源部,国家林业和草原局, 2020. 自然资源部国家林业和草原局关于印发《红树林保护修复专项行动计划(2020-2025年)》的通知[R]. 北京: 自然资源部, 国家林业和草原局.
|
|
Ministry of Natural Resources, National Forestry and Grassland Administration, 2020. Notice of the national forestry and grassland administration of the ministry of natural resources on the issuance of the special action plan for mangrove protection and restoration (2020-2025)[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Natural Resources, National Forestry and Grassland Administration (in Chinese).
|
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1126/science.317.5834.41b pmid: 17615322 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.03.006 pmid: 26971817 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [1] | 王旭, 屈科, 王梓峻, 杨元平, 王超, 张良斌. 风对波状涌潮海塘越浪水动力特性影响的数值研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 116-130. |
| [2] | 郑法, 黄福林, 陈泽恒, 丁伟品. 基于LUCC和景观格局变化的广西山口红树林湿地动态研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 165-173. |
| [3] | 周治刚, 岳文, 李辉权, 林阳阳. 树种类型和潮滩高程对广东湛江高桥红树林碳储量的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 108-120. |
| [4] | 申键, 简焯锴, 欧阳雪敏, 艾彬. 结合潮位校正的雷州半岛红树林湿地动态变迁遥感监测[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 137-153. |
| [5] | 耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [6] | 张哲然, 胡俊洋, 周凯, 张鹏晖, 邢久星, 陈胜利. 不同类型台风气象场对深圳近海海域风暴潮模拟的比较研究—以台风“山竹”为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. |
| [7] | 董俊德, 黄小芳, 龙爱民, 王友绍, 凌娟, 杨清松. 红树林固氮微生物及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 1-11. |
| [8] | 梁寒峭, 陈文凤, 范益铠, 朱子冬, 马国需, 陈德力, 田婧. 红树林来源曲霉属和木霉属内生真菌次生代谢产物及活性研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 12-24. |
| [9] | 严静, 韦惺. 珠江黄茅海河口地貌形态变化及其动力响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 9-20. |
| [10] | 张程飞, 任广波, 吴培强, 胡亚斌, 马毅, 阎宇, 张菁锐. 基于高分光学与全极化SAR的海南八门湾红树林种间分类方法[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 153-168. |
| [11] | 张敏, 吴航星, 陆逸彬, 陆迪文, 米婕, 朱冬琳, 陈波. 海岸线围垦对广西钦州湾地形演变的影响分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 124-131. |
| [12] | 周月月, 王友绍. 广东沿海红树林区水质变化特征与富营养状态评估[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 1-11. |
| [13] | 吴伟志, 赵志霞, 杨升, 梁立成, 陈秋夏, 卢翔, 刘星, 张小伟. 浙江省红树林分布和造林成效分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 67-74. |
| [14] | 顾靖华, 朱建荣, 金智. 长江口宝钢码头溢油事故油膜漂移扩散数值模拟[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 159-170. |
| [15] | 郝露露, 柯明思, 朱奕秀, 许燕敏, 张颖, 郑春芳. 低温胁迫下红榄李(Lumnitzera littorea)DEAD-box RNA解旋酶基因的表达分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 44-55. |
|
||