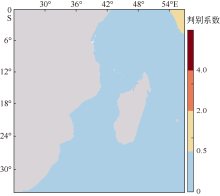
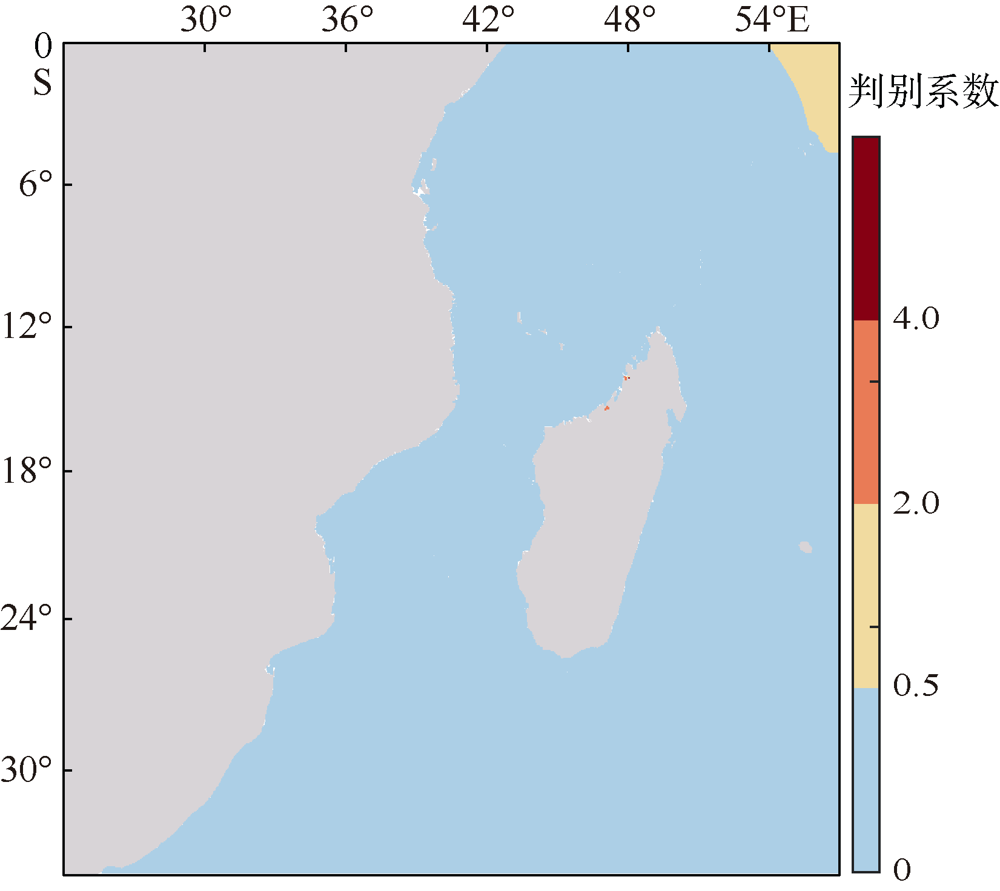
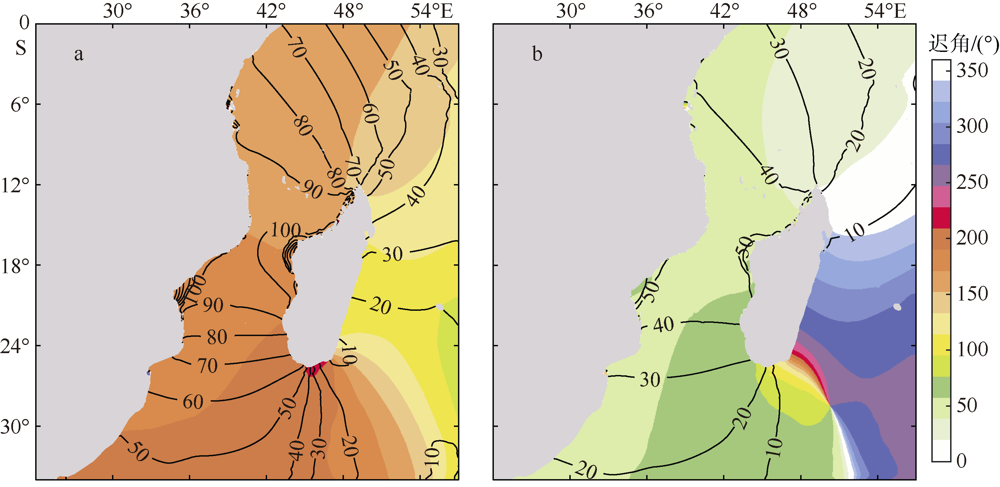
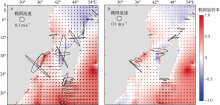
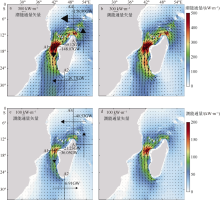
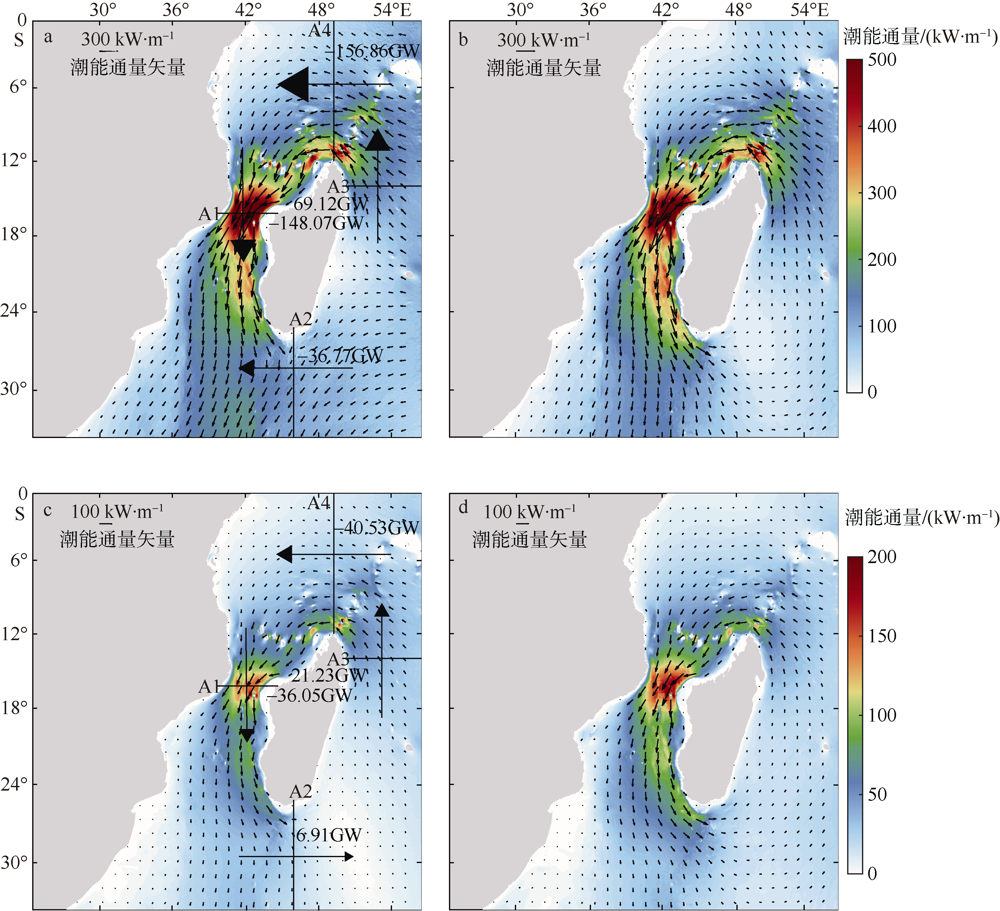
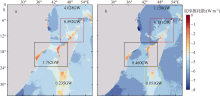
| [1] |
陈元杰, 程鹏, 2020. 东中国海潮能通量与耗散的数值模拟分析[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 59(1):61-70.
|
|
CHEN YUANJIE, CHENG PENG, 2020. Numerical modeling study of tidal energy and dissipation in the East China Seas[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 59(1):61-70 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
方国洪, 曹德明, 黄企洲, 1994. 南海潮汐潮流的数值模拟[J]. 海洋学报, 16(4):1-12 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
李蔷, 高郭平, 安佰超, 等, 2018. 白令海峡及其邻近海域潮汐潮能数值模拟[J]. 极地研究, 30(1):1-13.
|
|
LI QIANG, GAO GUOPING, AN BAICHAO, et al, 2018. Numerical study of the Barotropic tide and tidal energy distribution in the Bering strait and adjacent sea areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 30(1):1-13 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
刘谊, 王晓玮, 彭世球, 2018. 印度尼西亚海内潮生成及传播过程研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(2):1-9.
|
|
LIU YI, WANG XIAOWEI, PENG SHIQIU, 2018. On the generation and propagation of internal tides in the Indonesian Seas[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(2):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
罗丹, 2015. 渤、黄、东海潮汐潮流数值模拟研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
LUO DAN, 2015. Numerical simulations of tide and tidal current in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
孟云, 谢蓉, 2019. 渤海潮流、潮能通量和耗散的数值模拟[J]. 上海船舶运输科学研究所学报, 42(1):70-77.
|
|
MENG YUN, XIE RONG, 2019. Numerical simulation of tidal currents, energy fluxes and dissipation in the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ship and Shipping Research Institute, 42(1):70-77 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
佟景全, 雷方辉, 毛庆文, 等, 2010. 不考虑局地引潮势的南海正压潮能通量与潮能耗散[J]. 热带海洋学报, 29(3):1-9.
|
|
TONG JINGQUAN, LEI FANGHUI, MAO QINGWEN et al, 2010. Tidal energy fluxes and dissipation in the South China Sea without considering tide-generated potential energy[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 29(3):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
王斌, 2010. 乐清湾潮能和潮能通量的数值研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
WANG BIN, 2010. Numerical study of Tidal energy and Tidal energy flux in Yueqing Bay[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
夏综万, 1993. 介绍一种潮流椭圆要素的计算方法[J]. 海洋信息, (11):14 (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
张学庆, 王兴, 刘睿, 等, 2016. 辽河口潮能通量与潮能耗散的数值研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 35(1):20-26, 67.
|
|
ZHANG XUEQING, WANG XING, LIU RUI, et al, 2016. Numerical simulation of the tidal energy flux and tidal energy dissipation in Liaohe River Estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 35(1):20-26, 67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [11] |
周相乾, 胡松, 张瑜, 2019. 南极布兰斯菲尔德海峡正压潮数值模拟[J]. 极地研究, 31(1):56-68.
|
|
ZHOU XIANGQIAN, HU SONG, ZHANG YU, 2019. Numerical simulation of barotropic tide in the Bransfield Strait, Antarctica[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 31(1):56-68 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [12] |
朱怀鑫, 俎婷婷, 李健, 等, 2018. 基于高频地波雷达观测的粤西近海潮流潮能分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(5):25-32.
|
|
ZHU HUAIXIN, ZU TINGTING, LI JIAN, et al, 2018. Analysis of tidal current and tidal energy on the west coast of Guangdong Province based on High Frequency Ground Wave Radar observation[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(5):25-32 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [13] |
朱学明, 刘桂梅, 2012. 渤海、黄海、东海潮流、潮能通量与耗散的数值模拟研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 43(3):669-677.
|
|
ZHU XUEMING, LIU GUIMEI, 2012. Numerical study on the tidal currents, tidal energy fluxes and dissipation in the China Seas[J]. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica, 43(3):669-677 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [14] |
朱学明, 宋德海, 鲍献文, 等, 2014. 西北太平洋的潮能通量与耗散[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(1):1-9.
|
|
ZHU XUEMING, SONG DEHAI, BAO XIANWEN et al, 2014. Tidal energy flux and dissipation in the Northwest Pacific[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 33(1):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [15] |
AMANTE C, EAKINS B W, 2009. ETOPO1 1 Arc-minute global relief model: procedures, data sources and analysis[Z]. NOAA Technical Memorandum NESDIS NGDC-24. National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA.
|
| [16] |
BEAL L M, DE RUIJTER W P M, BIASTOCH A, et al, 2011. On the role of the Agulhas system in ocean circulation and climate[J]. Nature, 472(7344):429-436.
doi: 10.1038/nature09983
pmid: 21525925
|
| [17] |
BREITZKE M, WILES E, KROCKER R, et al, 2017. Seafloor morphology in the Mozambique Channel: evidence for long-term persistent bottom-current flow and deep-reaching eddy activity[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 38(3):241-269.
|
| [18] |
BUIJSMAN M C, LEGG S, KLYMAK J M, 2012. Double-ridge internal tide interference and its effect on dissipation in Luzon strait[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 42(8):1337-1356.
|
| [19] |
BUIJSMAN M C, KLYMAK J M, LEGG S, et al, 2014. Three-dimensional double-ridge internal tide resonance in Luzon strait[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 44(3):850-869.
|
| [20] |
CALDWELL P C, MERRIFIELD M A, THOMPSON P R, 2015. Sea level measured by tide gauges from global oceans - the Joint Archive for Sea Level holdings (NCEI Accession 0019568), Version 5.5[Z]. NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, Dataset.
|
| [21] |
DONOHUE K A, TOOLE J M, 2003. A near-synoptic survey of the Southwest Indian Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅱ: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 50(12-13):1893-1931.
|
| [22] |
EGBERT G D, RAY R D, 2000. Significant dissipation of tidal energy in the deep ocean inferred from satellite altimeter data[J]. Nature, 405(6788):775-778.
pmid: 10866194
|
| [23] |
EGBERT G D, RAY R D, 2001. Estimates of M2 tidal energy dissipation from TOPEX/Poseidon altimeter data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 106(C10):22475-22502.
|
| [24] |
EGBERT G D, EROFEEVA S Y, 2002. Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides[J]. Journal of Atmospheric & Oceanic Technology, 19(2):183-204.
|
| [25] |
GILL A E, 1982. Atmosphere-ocean dynamics[M]. London: Academic Press.
|
| [26] |
JEFFREYS H, SHAW W N, 1920. Tidal friction in shallow seas[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical or Physical Character 221: 239-264.
|
| [27] |
KANG DUJUAN, FRINGER O, 2012. Energetics of Barotropic and Baroclinic tides in the Monterey bay area[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 42(2):272-290.
|
| [28] |
MARSHALL J, ADCROFT A, HILL C, et al, 1997. A finite-volume, incompressible Navier Stokes model for studies of the ocean on parallel computers[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102(C3):5753-5766.
|
| [29] |
MUNK W, WUNSCH C, 1998. Abyssal recipes Ⅱ: Energetics of tidal and wind mixing[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ: Oceanographic Research Papers, 45(12):1977-2010.
|
| [30] |
PENG SHIQIU, QIAN YUKUN, LUMPKIN R, et al, 2015. Characteristics of the near-surface currents in the Indian Ocean as deduced from satellite-tracked surface drifters. Part Ⅰ: Pseudo-Eulerian statistics[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 45(2):441-458.
|
| [31] |
RIDDERINKHOF H, VAN DER WERF P M, ULLGREN J E, et al, 2010. Seasonal and interannual variability in the Mozambique Channel from moored current observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(C6):C06010.
|
| [32] |
SWART N C, LUTJEHARMS J R E, RIDDERINKHOF H, et al, 2010. Observed characteristics of Mozambique Channel eddies[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 115(C9):C09006.
|
| [33] |
TAYLOR G I, 1919. Tidal Friction in the Irish Sea[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character, 96(678):330.
|
| [34] |
TAYLOR G I, 1922. Tidal oscillations in gulfs and rectangular basins[J]. Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, 20(1):148-181.
|
| [35] |
WANG XIAOWEI, PENG SHIQIU, LIU ZHIYU, et al, 2016. Tidal mixing in the South China Sea: An estimate based on the internal tide energetics[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 46(1):107-124.
|
| [36] |
ZHONG LIEJUN, LI MING, 2006. Tidal energy fluxes and dissipation in the Chesapeake Bay[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 26(6):752-770.
|
 ), WEN Xixi1, PENG Shiqiu1,2,3,4(
), WEN Xixi1, PENG Shiqiu1,2,3,4( )
)