热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 9-20.doi: 10.11978/2022106CSTR: 32234.14.2022106
珠江黄茅海河口地貌形态变化及其动力响应
- 1.中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
-
收稿日期:2022-05-10修回日期:2022-06-10出版日期:2023-03-10发布日期:2022-06-13 -
通讯作者:韦惺。email:wes@scsio.ac.cn -
作者简介:严静(1980—), 女, 广西壮族自治区北海市人, 助理研究员, 从事海洋环境数值模拟研究。email: yanjing@scsio.ac.cn
-
基金资助:国家基金重大项目(41890851); 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(GML2019ZD0303); 热带海洋环境国家重点实验室自主研究项目(LTOZZ2202)
Geomorphological changes and dynamic responses of the Huangmaohai Estuary in the Pearl River Delta
- 1. South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
-
Received:2022-05-10Revised:2022-06-10Online:2023-03-10Published:2022-06-13 -
Contact:WEI Xing. email:wes@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41890851); Key Special Projects for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0303); Project of State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography(LTOZZ2202)
摘要:
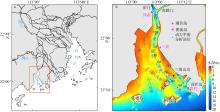
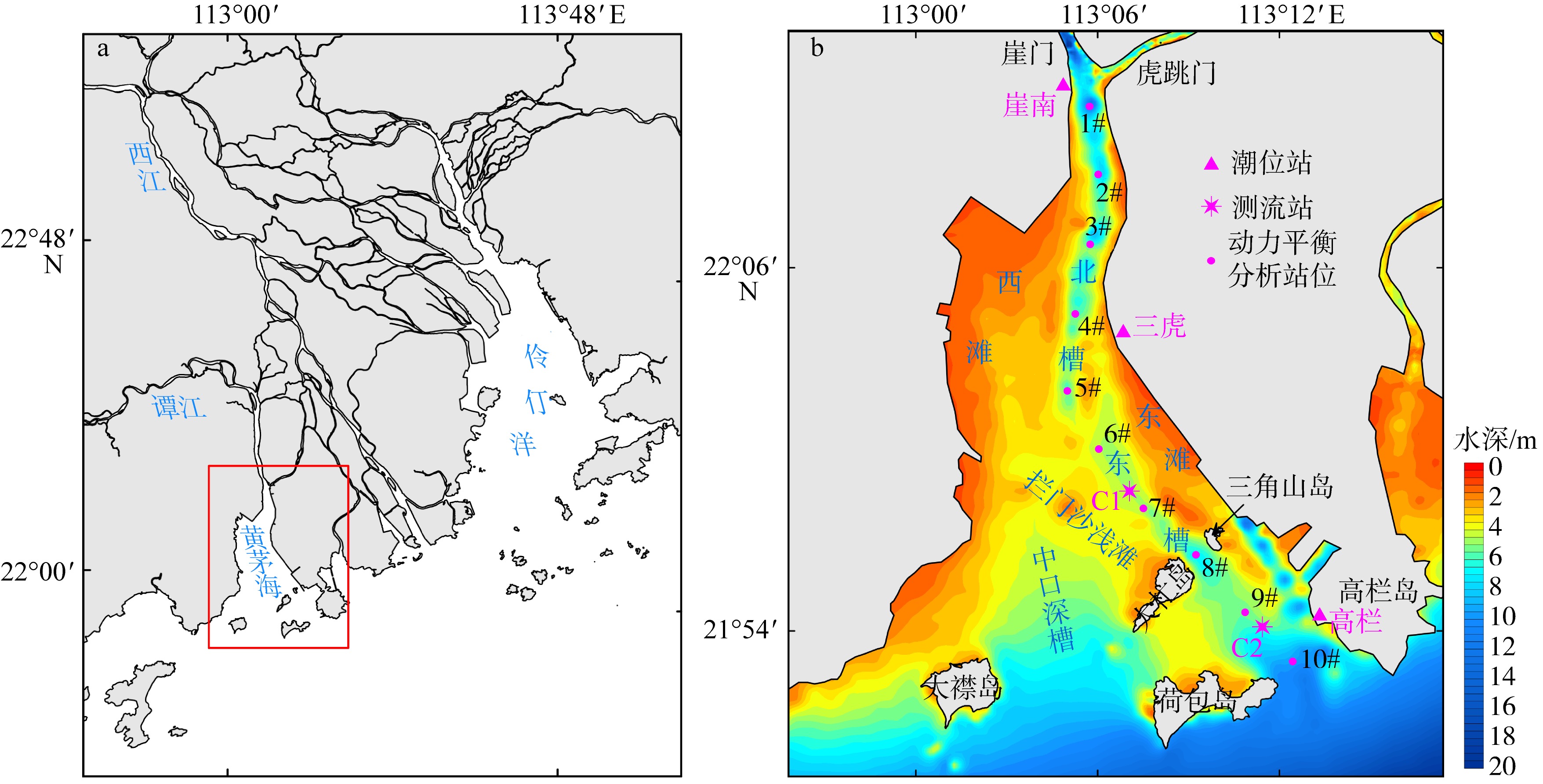
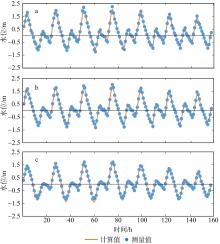
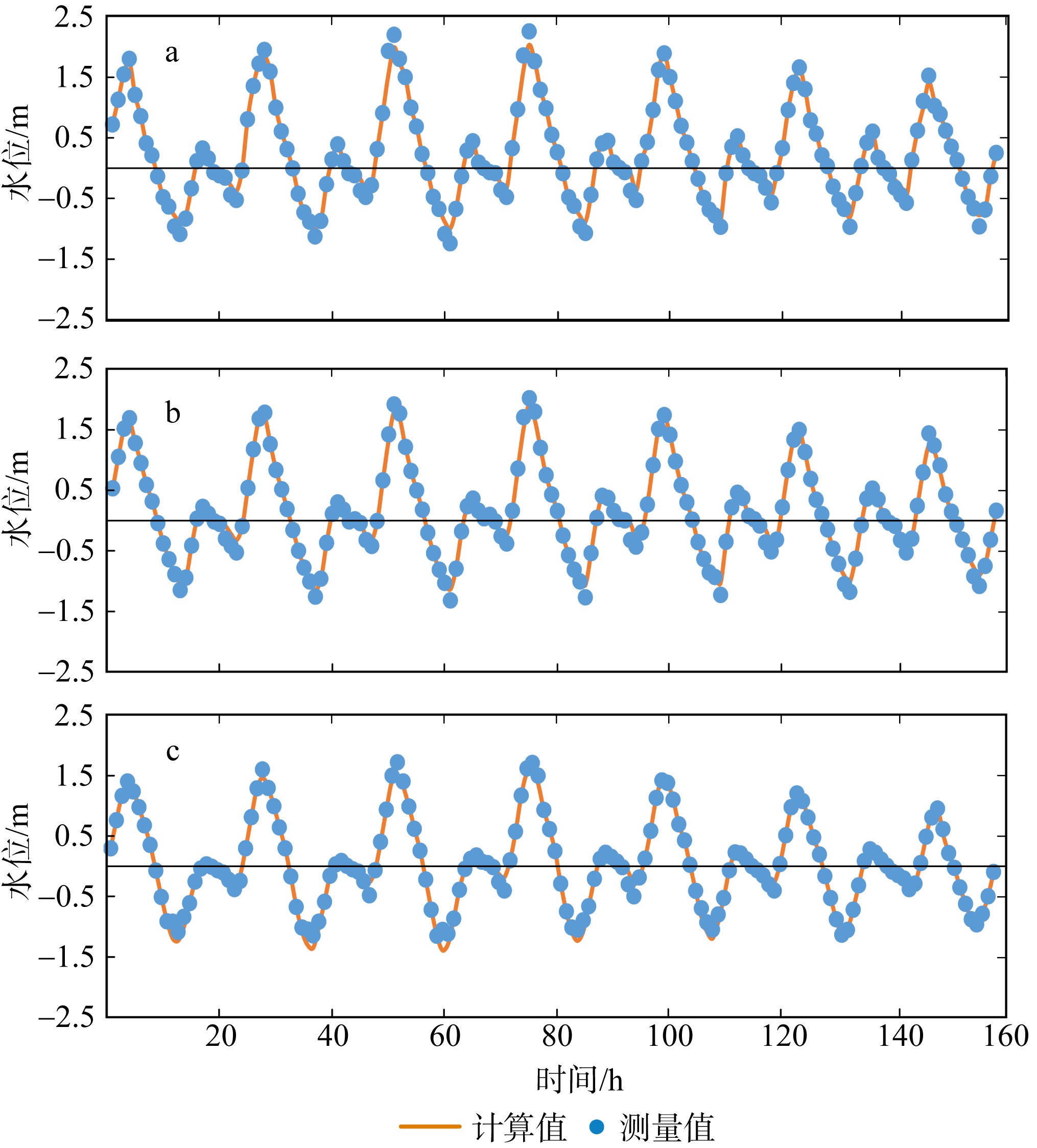
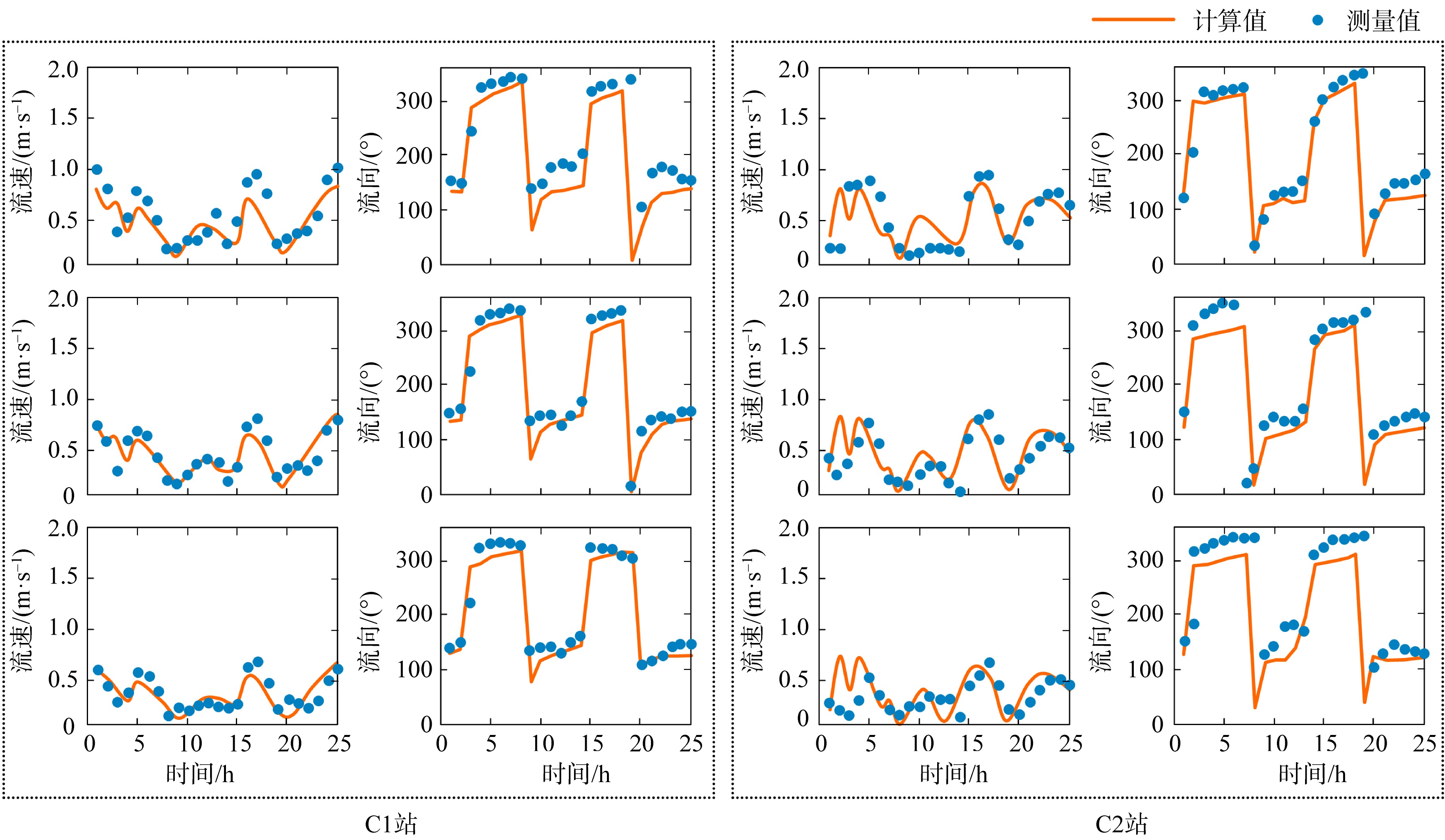
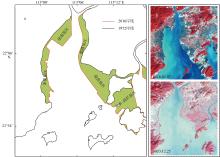
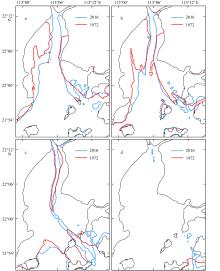
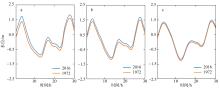
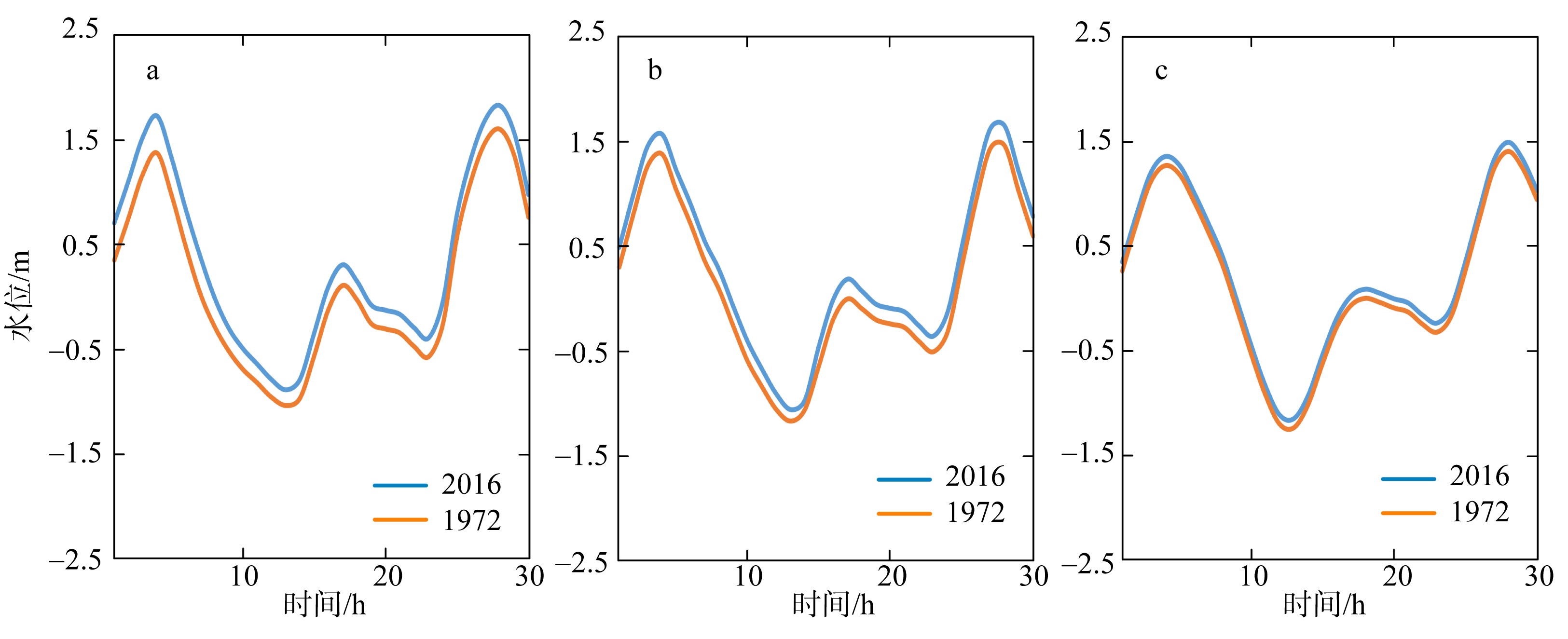
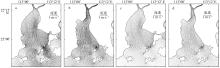
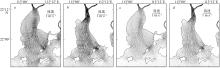
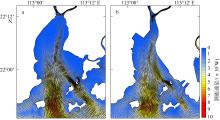
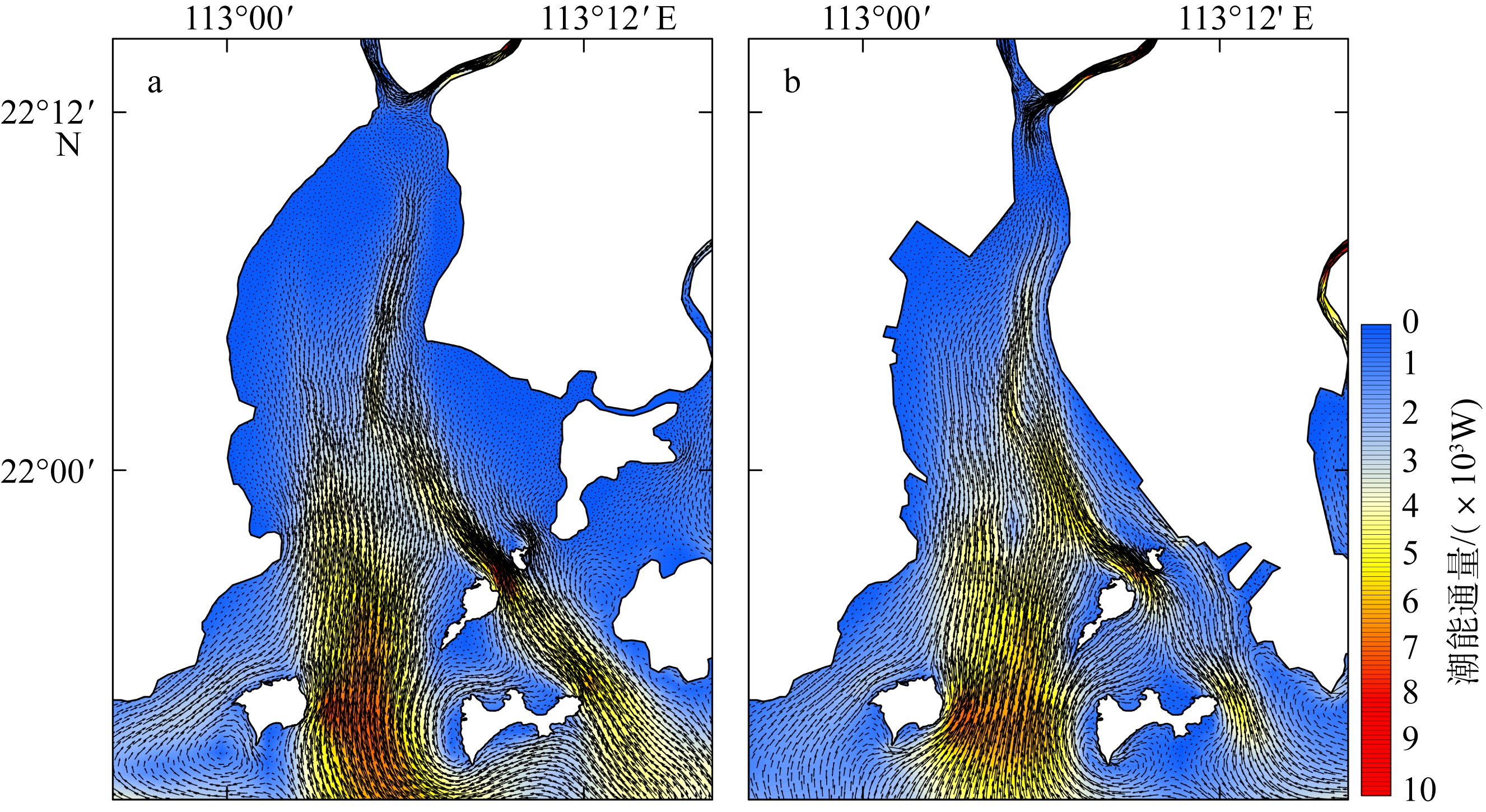
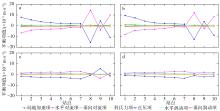
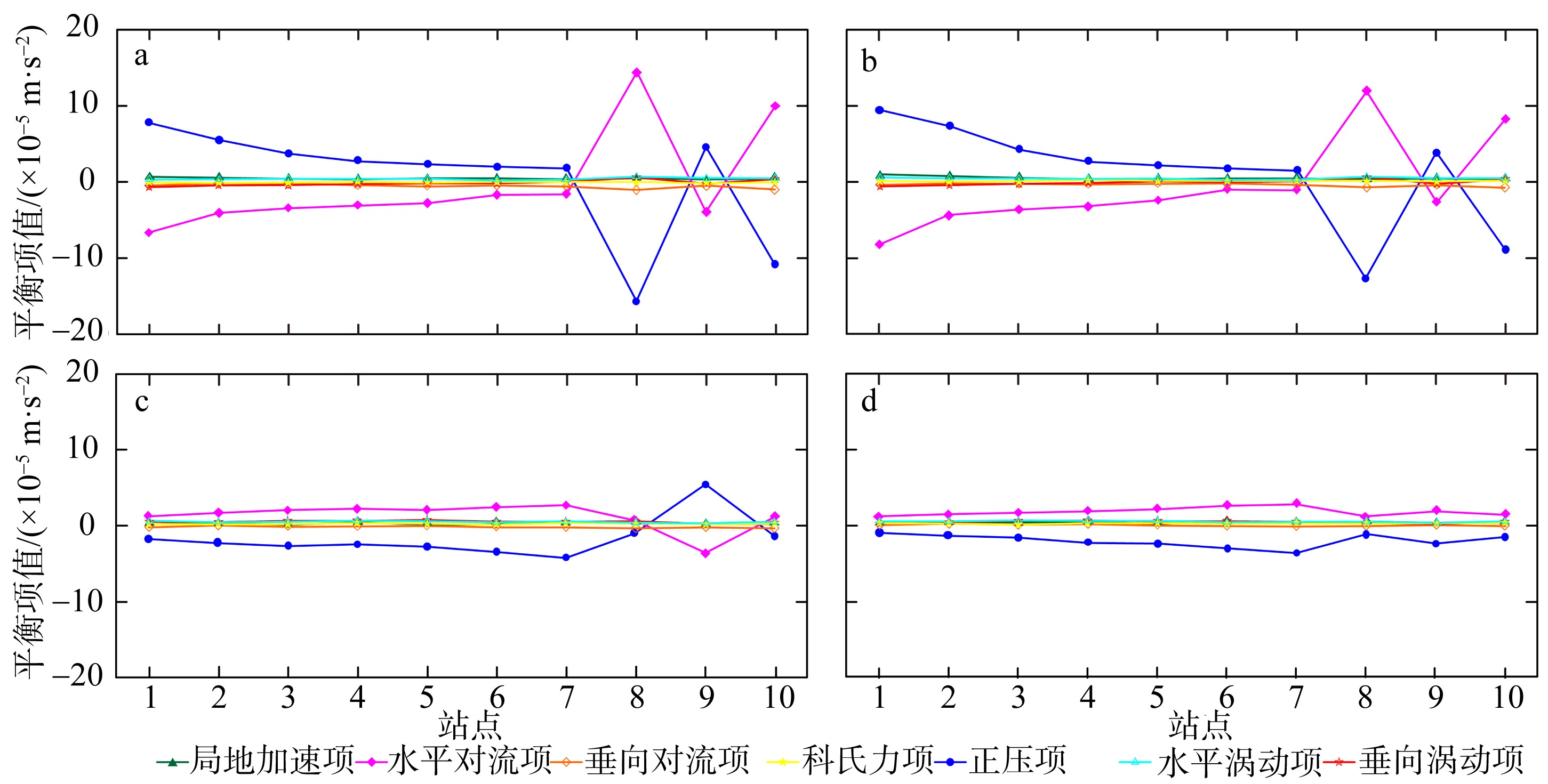
黄茅海是位于珠江三角洲西南部的一个喇叭形溺谷河口湾。近几十年来在自然过程和人类活动共同作用下河口的地貌形态发生了巨大变化。文章基于1972—2016年地形图和卫星遥感影像, 对河口岸线和水下地形的变化进行了量化分析, 并构建了三维水动力模型对河口动力对地貌形态变化的响应进行了讨论。结果显示, 土地围垦使得黄茅河口的口门和岸线急剧向海延伸, 水域面积大面积减少。受此影响, 河口的纳潮量减少了近19.61%, 由1972年的11.13亿m3减少为2016年的8.95亿m3。河口的束窄和形态的变化也使得河口出现水位抬升、径流动力增强, 潮差增加, 涨潮历时缩短, 落潮历时延长等变化。未来, 随着河口的淤积充填, 河口的潮汐动力将受到进一步削弱。
引用本文
严静, 韦惺. 珠江黄茅海河口地貌形态变化及其动力响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 9-20.
YAN Jing, WEI Xing. Geomorphological changes and dynamic responses of the Huangmaohai Estuary in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 9-20.
| [1] |
龚文平, 刘欢, 任杰, 等, 2012. 黄茅海河口潮波的传播特征与机理研究[J]. 海洋学报, 34(3): 41-54.
|
|
doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0648-1 |
|
| [2] |
黄方, 叶春池, 温学良, 等, 1994. 黄茅海盐度特征及其盐水楔活动范围[J]. 海洋通报, 13(2): 33-39.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
贾良文, 罗军, 任杰, 2012. 珠江口黄茅海拦门沙演变及成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 34(5): 120-127.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
贾良文, 文艺, 2013. 珠江口黄茅海枯季表层沉积物特性及输移研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 1: 60-66.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
蒋陈娟, 周佳楠, 杨清书, 2020. 珠江磨刀门河口潮汐动力变化对人类活动的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(6): 66-76.
doi: 10.11978/2019137 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2019137 |
|
| [6] |
李娜, 娄安刚, 张学庆, 等, 2019. 基于MIKE3的渤海三维温盐数值模拟[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2: 1-9.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
林中源, 龚文平, 贾良文, 2014. 珠江口黄茅海枯季的悬沙变化与泥沙输运[J]. 泥沙研究, 2: 27-37.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
罗丹, 1998. 黄茅海沿岸滩涂发育及岸线变化遥感浅析[J]. 人民珠江, 3: 45-47.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
罗军, 2010. 十年至百年尺度黄茅海地形演变及成因研究[D]. 广州: 中山大学.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
吴超羽, 1995. 黄茅海河口小尺度动力结构及其沉积作用[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 34(2): 86-94.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
吴创收, 刘欢, 武亚菊, 等, 2010. 黄茅湾河口沿程异常潮差: Ⅰ-理论模型研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 28(4): 436-444.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
武亚菊, 刘欢, 吴创收, 等, 2011. 黄茅海河口沿程异常潮差数值模拟研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 29(1): 16-28.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
杨美卿, 1993. 河流与海岸动力学[M]. 北京: 水利电力出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
杨名名, 吴加学, 张乾江, 等, 2016. 珠江黄茅海河口洪季侧向余环流与泥沙输移[J]. 海洋学报, 38(1): 31-45.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
杨雪舞, 王文介, 1994. 珠江口黄茅海河口湾水动力沉积和泥沙运动的统计研究[J]. 海洋工程, 12(4): 42-51.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
赵荻能, 2017. 珠江河口三角洲近165年演变及对人类活动响应研究[D]. 浙江: 浙江大学.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
赵峰, 吴梅桂, 周鹏, 等, 2015. 黄茅海——广海湾及其邻近海域表层沉积物中γ放射性核素含量水平[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(4): 77-82.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.04.011 |
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.04.011 |
|
| [18] |
自然资源部, 2021. 中国海平面公报[EB/OL][2020-04-28]. 北京: 自然资源部 (https://www.mnr.gov.cn/sj/sjfw/hy/gbgg/zghpmgb/). (in Chinese)
|
| [19] |
DHI, 2012. MIKE 3 Flow Model FM Hydrodynamic Module User Guide. DHI Water and Environment, Hørsholm.
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2002)019<0183:EIMOBO>2.0.CO;2 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.108057 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1007/s13344-013-0065-1 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(03)00143-2 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96183-0 pmid: 34404884 |
| [26] |
doi: S0025-326X(13)00449-9 pmid: 23972680 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4125-6 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1006/ecss.1999.0495 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2019.04.011 |
| [1] | 王旭, 屈科, 王梓峻, 杨元平, 王超, 张良斌. 风对波状涌潮海塘越浪水动力特性影响的数值研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 116-130. |
| [2] | 吴鸿博, 罗锋, 陈治澎, 朱飞, 曾靖伟, 张弛, 李瑞杰. 红树林生态重建效果预测研究新模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 86-97. |
| [3] | 张哲然, 胡俊洋, 周凯, 张鹏晖, 邢久星, 陈胜利. 不同类型台风气象场对深圳近海海域风暴潮模拟的比较研究—以台风“山竹”为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. |
| [4] | 张敏, 吴航星, 陆逸彬, 陆迪文, 米婕, 朱冬琳, 陈波. 海岸线围垦对广西钦州湾地形演变的影响分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 124-131. |
| [5] | 顾靖华, 朱建荣, 金智. 长江口宝钢码头溢油事故油膜漂移扩散数值模拟[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 159-170. |
| [6] | 邓国通, 刘敏聪, 邢久星, 申锦瑜, 周凯, 陈胜利. 深圳近海风暴潮影响因素分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 91-100. |
| [7] | 王仁政, 单正垛, 孟思雨, 宫响. 南海北部次表层叶绿素最大值年际变化特征分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 63-75. |
| [8] | 张华, 温茜茜, 彭世球. 莫桑比克海峡及其邻近海区正压潮流数值模拟与能量收支分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(2): 7-16. |
| [9] | 李娟, 刘军亮, 蔡树群. 台风“康森”产生的海洋近惯性能量的数值模拟研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 35-43. |
| [10] | 林夏艳, 董昌明, 陈大可. 台湾岛西南部一个暖涡的跨海盆粒子输运[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(3): 9-18. |
| [11] | 武文, 严聿晗, 宋德海. 大亚湾的潮汐动力学研究——I.潮波系统的观测分析与数值模拟*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(3): 34-45. |
| [12] | 严聿晗, 武文, 宋德海, 鲍献文. 大亚湾的潮汐动力学研究——Ⅱ.潮位和潮流双峰现象的产生机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(3): 46-54. |
| [13] | 马刚, 王云峰, 张晓辉, 顾成明, 钟波, 郭兴亮. 基于梯度信息的微波辐射亮温资料质量控制方法[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(2): 86-95. |
| [14] | 罗士浩, 经志友, 齐义泉, 谢强. 南海北部次中尺度过程数值研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(5): 10-19. |
| [15] | 叶丰, 包芸. 层结环境中热液羽流物质输运范围的模拟计算*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(5): 97-102. |
|
||