热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 69-80.doi: 10.11978/2023087CSTR: 32234.14.2023087
广西北部湾海域施氏獭蛤精巢发育、精子发生及超微结构观察
吴韬1,2( ), 潘英1,2(
), 潘英1,2( ), 刘一鸣1,2, 连昌朋1,2, 徐炳杰1,2, 王超奇1,2, 杨凌1,2
), 刘一鸣1,2, 连昌朋1,2, 徐炳杰1,2, 王超奇1,2, 杨凌1,2
- 1.广西大学动物科学技术学院, 广西 南宁 530004
2.广西高校水生生物健康养殖与营养调控重点实验室, 广西 南宁 530004
-
收稿日期:2023-06-26修回日期:2023-07-05出版日期:2024-03-10发布日期:2024-03-26 -
作者简介:吴韬(1997—), 男, 广西壮族自治区南宁市人, 硕士研究生, 从事海洋贝类遗传育种研究。 email: 214850470@qq.com
-
基金资助:广西创新驱动发展专项(Guike AA19254032)
Testis development, spermatogenesis and sperm ultrastructure of Lutraria sieboldii in the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi
WU Tao1,2( ), PAN Ying1,2(
), PAN Ying1,2( ), LIU Yiming1,2, LIAN Changpeng1,2, XU Bingjie1,2, WANG Chaoqi1,2, YANG Ling1,2
), LIU Yiming1,2, LIAN Changpeng1,2, XU Bingjie1,2, WANG Chaoqi1,2, YANG Ling1,2
- 1. College of Animal Science and Technology, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China
2. Key Laboratory of Aquatic Healthy Breeding and Nutrition Regulation of Guangxi Universities, Nanning 530004, China
-
Received:2023-06-26Revised:2023-07-05Online:2024-03-10Published:2024-03-26 -
Supported by:Guangxi Innovation Driven Development Project(Guike AA19254032)
摘要:
为探究广西北部湾海域施氏獭蛤精巢周年发育、精子发生的组织学和超微结构变化, 文章采用组织切片、扫描及透射电镜技术对广西北部湾海域施氏獭蛤精巢周年发育、精子发生和超微结构进行了研究。结果表明, 广西北部湾海域施氏獭蛤精巢发育周期为1年, 可划分为增殖期、生长期、成熟期、排放期和休止期, 繁殖盛期为12月至翌年4月, 每期5%~10%个体精巢发育略滞后。精子发生可划分为增殖期、生长期、成熟期和变态期。雄性生殖细胞的发育可划分为精原细胞期、初级精母细胞期、次级精母细胞期、精细胞期、成熟精子期。施氏獭蛤精子属于鞭毛型, 全长(39.76±0.50)μm。精子头部由近椭圆形的顶体和精核组成, 顶体底部与精核相连处凹陷形成亚顶体腔, 精核顶部形成核前窝, 精核底部形成核后窝, 细胞核内电子密度均匀, 核中部存在间隙。中心粒复合体周围有4个线粒体围绕组成精子中部, 线粒体近圆形, 内嵴明显。质膜包裹轴丝形成精子尾部, 尾部横切面可明显观察到“9+2”双联体微管结构。此外, 施氏獭蛤存在A、B两种不同类型的精原细胞, A型精原细胞核内核仁不明显, B型精原细胞核内核仁明显, B型精原细胞存在于增殖期和生长期。
引用本文
吴韬, 潘英, 刘一鸣, 连昌朋, 徐炳杰, 王超奇, 杨凌. 广西北部湾海域施氏獭蛤精巢发育、精子发生及超微结构观察[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 69-80.
WU Tao, PAN Ying, LIU Yiming, LIAN Changpeng, XU Bingjie, WANG Chaoqi, YANG Ling. Testis development, spermatogenesis and sperm ultrastructure of Lutraria sieboldii in the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 69-80.
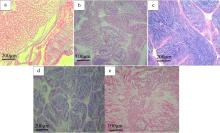
表2
施氏獭蛤精巢发育特点"
| 发育周期 | 各期特点 |
|---|---|
| 增殖期(Ⅰ) | 精巢透明, 结缔组织发达, 滤泡呈狭长状, 滤泡内空虚。滤泡壁上排列着单层精原细胞( |
| 生长期(Ⅱ) | 精巢开始增殖, 滤泡增大, 滤泡间隙减小, 滤泡壁增厚, 精原细胞增殖, 滤泡壁上出现多层精原细胞。部分精原细胞分化形成不同发育时期的精细胞( |
| 成熟期(Ⅲ) | 精巢扩展至软体部上缘, 精巢呈黄色, 肉眼可辨, 取部分精巢组织于载玻片上, 精巢内的精子遇水即散。滤泡间无结缔组织, 滤泡内充满成熟精子( |
| 排放期(Ⅳ) | 精巢仍较饱满, 滤泡间隙增大。滤泡收缩, 滤泡壁变厚, 滤泡内成熟精子排出, 滤泡大小不一, 呈流水状( |
| 休止期(Ⅴ) | 精巢消瘦, 肉眼无法分辨雌雄, 结缔组织增生, 滤泡萎缩。滤泡内大部分排空, 滤泡壁上可见部分未排出的精细胞紧贴滤泡壁固着、退化并被重吸收( |
表3
广西北部湾海域施氏獭蛤精巢发育各期的周年分布"
| 取样日期 | 盐度/‰ | 水温/℃ | 精巢发育分期 | 雄性总数/个 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | ||||
| 2020/11/26 | 27.4 | 22.0 | 10 | 1 | 11 | |||
| 2020/12/21 | 27.5 | 17.0 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 10 | ||
| 2021/1/8 | 29.4 | 15.0 | 2 | 9 | 11 | |||
| 2021/2/23 | 30.9 | 26.3 | 6 | 6 | ||||
| 2021/3/20 | 30.0 | 21.0 | 2 | 7 | 9 | |||
| 2021/4/22 | 30.0 | 27.5 | 8 | 8 | ||||
| 2021/5/26 | 28.0 | 29.5 | 1 | 7 | 8 | |||
| 2021/6/21 | 28.4 | 30.5 | 5 | 7 | 12 | |||
| 2021/7/14 | 29.0 | 29.7 | 5 | 3 | 8 | |||
| 2021/8/17 | 30.0 | 29.8 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 7 | |
| 2021/9/15 | 31.0 | 29.8 | 10 | 1 | 11 | |||
| 2021/10/20 | 29.0 | 25.5 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 11 | ||
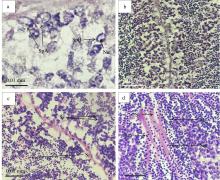
表4
施氏獭蛤精子发生各期特点"
| 发生分期 | 各期发生特点 |
|---|---|
| 增殖期 | 精原细胞紧贴滤泡壁大量增殖的时期, 出现在施氏獭蛤Ⅰ~Ⅲ期精巢, 尤以Ⅰ~Ⅱ期精巢最常见, 精原细胞在滤泡壁上多层排列( |
| 生长期 | 同一滤泡内雄性生殖细胞发育不同步, 部分精原细胞分化形成初级精母细胞, 细胞体积减小, 逐渐脱离滤泡壁。此期出现在施氏獭蛤Ⅰ~Ⅲ精巢( |
| 成熟期 | 滤泡壁上排列大量次级精母细胞, 部分次级精母细胞黏连, 呈分裂趋势。从组织切片看, 染色较上一期更深。此期出现在施氏獭蛤精巢Ⅲ~Ⅳ期( |
| 变态期 | 次级精母细胞分化形成精细胞。组织切片中此期染色最深, 体积最小, 可观察到呈圆形的头部横切面和不规则的精子纵切面。此期出现在施氏獭蛤精巢Ⅲ~Ⅴ期( |
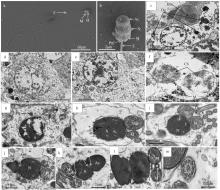
图4
施氏獭蛤雄性生殖细胞发育各期的超微结构 a. 精子全长, 示头部(H)、线粒体(M)、鞭毛(F), ×3000; b. 精子头部, 示顶体(Ac)、细胞核(N)、线粒体(M)、核后窝(Pnf)、鞭毛(F), ×20000; c. 精原细胞, 示基膜(Bm)、致密颗粒(Dg)、线粒体(M)、细胞核(N)、染色质丝(Ch)、核膜(Nm), ×3000; d. 初级精母细胞, 示致密颗粒(Dg)、线粒体(M)、细胞核(N)、染色质丝(Ch), ×3000; e. 初级精母细胞, 示致密颗粒(Dg)、线粒体(M)、核仁(Nu), ×3000; f. 次级精母细胞, 示致密颗粒(Dg)、线粒体(M)、细胞核(N)、染色质丝(Ch), ×4000; g. 次级精母细胞, 示致密颗粒(Dg)、线粒体(M)、远端中心粒(Dc)、核仁(Nu), ×4000; h. 精细胞前期, 示细胞核(N)、线粒体(M), ×7000; i. 精细胞中期, 示顶体泡(Av)、细胞核(N)、线粒体(M)、远端中心粒(Dc)、鞭毛(F), ×7000; j. 精细胞中期, 示顶体(Ac)、核前窝(Anf)、细胞核(N)、核后窝(Pnf)、线粒体(M)、鞭毛(F), ×7000; k. 精细胞后期, 示顶体(Ac)、亚顶体腔(Ss)、核前窝(Anf)、细胞核(N)、核后窝(Pnf)、线粒体(M)、远端中心粒(Dc)、鞭毛(F), ×7000; l. 精细胞后期, 示线粒体(M)、远端中心粒(Dc)、近端中心粒(Pc), ×4000; m. 精细胞尾部横切, ×7000"

表5
不同双壳贝类的精子超微结构比较"
| 种类 | 精子头部 | 精子中部 | 精子尾部 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 施氏獭蛤 Lutraria sieboldii | 顶体近圆球形, 细胞核近椭圆形,有核前窝和核后窝 | 4个线粒体环绕中心粒复合体排列 | “9+2”双联体微管结构 | 本文 |
| 栉江珧 Atrina pectinata | 顶体呈倒“V”形, 近顶体外膜有一弧状膜, 细胞核近圆形, 有核前窝, 无核后窝 | 5个线粒体辐射状排列在中心粒周围 | “9+2”双联体微管结构 | 顾向飞等( |
| 斧文蛤 Meretrix lamarkii | 顶体呈圆锥形, 细胞核为长圆柱形, 有核前窝和核后窝 | 5个线粒体单层梅花状围绕在中心粒周围 | “9+2”双联体微管结构 | 董迎辉等( |
| 钝缀锦蛤 Tapes conspersus | 顶体呈倒“V”形, 细胞核呈长圆柱形, 有核前窝和核后窝 | 5个圆环状线粒体包裹中心粒复合体 | “9+2”双联体微管结构 | 连昌朋等( |
| 文蛤 Meretrix meretrix | 顶体呈倒“V”形, 细胞核长圆柱形, 内含形状不规则的透明腔, 有核前窝和核后窝 | 5个线粒体围绕一对中心粒 | “9+2”双联体微管结构 | Gwo等( |
| 长牡蛎 Crassostrea gigas | 顶体突出, 成熟精子头部近似圆形, 头部包含亚顶体腔、细胞核, 有核前窝和核后窝 | 4个圆球形的线粒体围绕中心粒 | “9+2”双联体微管结构 | 韩龙江等( |
| [1] |
蔡英亚, 劳赞, 陈东, 2005. 施氏獭蛤的生态观察[J]. 湛江海洋大学学报, 25(1): 39-42.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
曹伏君, 刘永, 张春芳, 等, 2012. 施氏獭蛤(Lutraria sieboldii)性腺发育和生殖周期的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 43(5): 976-982.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈寅山, 饶小珍, 柯佳颖, 等, 2006. 沟纹巴非蛤精子发生过程的超微结构观察[J]. 海洋科学, 30(8): 28-33.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
崔龙波, 周雪莹, 陆瑶华, 2000. 皱纹盘鲍精巢及精子结构的研究[J]. 烟台大学学报, 13(2): 103-107.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
代培芳, 饶小珍, 陈寅山, 2004. 菲律宾蛤仔的精子发生和精子超微结构[J]. 动物学杂志, 39(2): 26-32.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
邓传敏, 孔令锋, 于瑞海, 等, 2017. 长牡蛎壳金选育群体性腺发育与营养成分的周年变化[J]. 中国水产科学, 24(1): 40-49.
|
|
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2017.16103 |
|
| [7] |
邓道贵, 谈奇坤, 2001. 褶纹冠蚌精子的超微结构研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 25(5): 481-485.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
董迎辉, 林志华, 柴雪良, 等, 2010. 文蛤(Meretrix meretrix)精子的超微结构及精子入卵过程的电镜观察[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 41(5): 726-732.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
董迎辉, 林志华, 姚韩韩, 2011. 斧文蛤精子超微结构与受精过程的细胞学变化[J]. 水产学报, 35(3): 356-364.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
杜晨, 龙玲利, 盛樟, 等, 2015. 褐蚶(Didimarca tenebrica)精子的超微结构[J]. 宁波大学学报, 28(3): 1-4.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
顾向飞, 边平江, 周小龙, 等, 2013. 栉江珧精子超微结构的电镜观察[J]. 海洋科学, 37(8): 67-71.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
郭恩棉, 王沈同, 崔亮, 等, 2017. 扇贝“渤海红”性腺结构及生殖细胞发生的组织学研究[J]. 海洋科学, 41(9): 9-12.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
韩厚伟, 高悦勉, 刘春凤, 等, 2008. 虾夷扇贝精子的超微结构[J]. 动物学杂志, 43(1): 75-81.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
韩龙江, 刘清华, 许飞, 等, 2017. 长牡蛎精子超低温冷冻后超微结构损伤研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 41(1): 220-227.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
黄瑞, 黄标武, 李林春, 等, 2011. 近江蛏精子超微形态结构观察及与缢蛏精子的比较[J]. 水产学报, 35(1): 58-65.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
焦宗垚, 刘永, 张春芳, 2010. 施氏獭蛤融合卯裂及其胚胎发育过程观察[J]. 动物学研究, 31(4): 408-414.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
柯巧珍, 李琪, 闫红伟, 等, 2012. 山东北部沿海四角蛤蜊性腺发育年周期研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 42(11): 28-34.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
李斌, 何俊锋, 区小玲, 等, 2011. 广西和广东地区施氏獭蛤3个自然群体的形态差异和遗传多样性分析[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 26(5): 414-421.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
李猛, 虞炯莹, 王卫民, 2022. 二倍体泥鳅与大鳞副泥鳅及杂交F1精子结构与活力[J]. 水产学报, 46(1): 41-50.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
李霞, 2019. 水产动物组织胚胎学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社:178- 179.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
连昌朋, 王超奇, 杨凌, 等, 2022. 广西北部湾钝缀锦蛤精巢发育、精子发生及超微结构研究[J]. 海洋科学, 46(6): 80-89.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
刘永, 梁飞龙, 毛勇, 等, 2006. 施氏獭蛤人工育苗技术的研究[J]. 湛江海洋大学学报, 26(3): 98-101.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
刘永, 余祥勇, 梁飞龙, 等, 2007. 施氏獭蛤幼虫和稚贝发育及行为的研究[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 27(1): 17-21.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
鹿瑶, 刘辉, 聂鸿涛, 等, 2015. 辽宁沿海薄片镜蛤的繁殖周期研究[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 30(6): 647-652.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
吕敏, 李琪, 2022. 山东田横岛海域长牡蛎性腺发育及生化成分周年变化[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 52(2): 33-40.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
宁军号, 常亚青, 宋坚, 等, 2015. 偏顶蛤的性腺发育和生殖周期[J]. 中国水产科学, 22(3): 469-477.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
潘英, 苏以鹏, 2007a. 大獭蛤的核型研究[J]. 海洋科学, 31(9): 87-90.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
潘英, 秦小明, 潘红平, 2007b. 大獭蛤软体部营养成分的分析与评价[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 27(3): 78-81.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
区小玲, 苏翔驹, 何俊锋, 等, 2015. 广西北部湾管角螺性腺发育与繁殖规律研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 45(11): 20-28.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
饶小珍, 2007. 长竹蛏精子发生和精子的超微结构观察[J]. 热带海洋学报, 26(2): 49-54.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
孙慧玲, 方建光, 王清印, 等, 2000. 泥蚶精子的超微结构[J]. 水产学报, 24(4): 297-302.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
王斌, 栗志民, 刘志刚, 等, 2015. 施氏獭蛤室内规模化人工育苗技术研究[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 35(1): 35-42.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
王超奇, 徐炳杰, 吴韬, 等, 2023. 广西北部湾滩涂施氏獭蛤中培及养成期养殖密度比较研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 19(4): 105-115.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
王朔, 于红, 李琪, 2022. 不同育性长牡蛎性腺发育过程中糖原和脂质的组织化学研究[J]. 水产学报, 46(12): 2297-2305.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
於锋, 罗帮, 陈雪芬, 等, 2016. 广西茅尾海的香港巨牡蛎(Crassostrea hongkongensis)在不同养殖区的性腺发育变化[J]. 渔业科学进展, 37(3): 134-142.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
吴洪流, 伍春雨, 陈雪芬, 等, 2000. 波纹巴非蛤雄性生殖腺的组织学观察[J]. 海南大学学报, 18(2): 169-174.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
吴丽云, 郑丹华, 高如承, 2010. 中国血蛤精子超微结构的研究[J]. 福建师范大学学报, 26(6): 92-96.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
巫旗生, 文宇, 曾志南, 2017. 钝缀锦蛤繁殖周期和胚胎发育[J]. 中国水产科学, 24(3): 488-496.
|
|
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2017.16280 |
|
| [39] |
吴韬, 徐炳杰, 刘一鸣, 等, 2023a. 广西北部湾海域不同月龄施氏獭蛤(Lutraria sieboldii)形态性状对体质量的相关性和通径分析[J]. 水产研究, 10(1): 37-46.
|
|
doi: 10.12677/OJFR.2023.101005 |
|
| [40] |
吴韬, 连昌朋, 刘一鸣, 等, 2023b. 广西北部湾施氏獭蛤卵巢发育、卵子和卵黄发生的研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(6): 137-149.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
武祥伟, 张跃环, 肖述, 等, 2020. 熊本牡蛎壳金品系与壳黑品系的生长、存活、性腺发育及生化成分的周期性变化[J]. 水生生物学报, 44(4): 728-735.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
徐凤山, 张素萍, 2008. 中国海产双壳类图志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社:162- 163.
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
杨学明, 吴明灿, 张立, 等, 2016. 糙海参精子的发生及超微形态结构[J]. 海洋科学, 40(5): 49-56.
|
|
|
|
| [44] |
叶婧, 姜建湖, 2012. 魁蚶精子发生的超微结构[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 21(2): 199-203.
|
|
|
|
| [45] |
余红卫, 2012. 彩虹明樱蛤精子发生的超微结构[J]. 电子显微学报, 31(1): 65-69.
|
|
|
|
| [46] |
张春芳, 刘永, 2010. 施氏獭蛤稚贝中间培育与海区养殖试验[J]. 水产养殖, 31(5): 5-8.
|
|
|
|
| [47] |
郑学斌, 张清科, 乐韵, 等, 2018. 香鱼(Plecoglossus altivelis)精子的超微结构及其与鲤形目及鲑形目其他鱼类精子结构的比较研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 49(4): 866-872.
|
|
|
|
| [48] |
周小龙, 董迎辉, 边平江, 等, 2012. 帘文蛤精子超微结构及与其他双壳贝类的比较[J]. 台湾海峡, 31(4): 495-500.
|
|
|
|
| [49] |
竺俊全, 杨万喜, 2004. 毛蚶与青蚶精子超微结构及其所反映的蚶科进化关系[J]. 动物学研究, 25(1): 57-62.
|
|
|
|
| [50] |
朱星海, 孙红振, 杨祖晶, 等, 2019. 风信标扇贝的性腺发育与繁殖周期规律研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 49(2): 52-58.
|
|
|
|
| [51] |
庄启谦, 2001. 中国动物志软体动物门双壳纲帘蛤科[M]. 北京:科学出版社:47- 48.
|
|
|
|
| [52] |
邹杰, 彭慧婧, 张守都, 等, 2020. 施氏獭蛤壳体表型性状对体质量的影响分析[J]. 水产科学, 39(4): 573-578.
|
|
|
|
| [53] |
邹杰, 张守都, 彭慧婧, 等, 2021. 施氏獭蛤早期生长性状遗传参数和育种值估计[J]. 海洋科学, 45(2): 99-105.
|
|
|
|
| [54] |
doi: 10.1016/S0305-0491(99)00187-X |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1111/ivb.2002.121.issue-4 |
| [56] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2020.101454 |
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
doi: 10.1007/s12562-010-0274-y |
| [59] |
doi: 10.2983/035.038.0109 |
| [60] |
doi: 10.1007/s12686-012-9774-7 |
| [1] | 徐炳杰, 刘一鸣, 邢清淦, 连昌朋, 吴韬, 潘英. 广西北部湾海域织锦巴非蛤精巢发育、精子发生及超微结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 59-68. |
| [2] | 徐炳杰, 刘一鸣, 连昌朋, 吴韬, 潘英. 广西北部湾海域织锦巴非蛤卵巢发育、卵子及卵黄发生的研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 48-58. |
| [3] | 吴韬, 潘英, 连昌朋, 刘一鸣, 徐炳杰, 王超奇, 杨凌. 广西北部湾施氏獭蛤卵巢发育、卵子和卵黄发生的研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 137-149. |
| [4] | 连昌朋, 吴韬, 王超奇, 杨凌, 潘英. 广西北海营盘海域钝缀锦蛤(Tapes conspersus)卵巢发育、卵子和卵黄发生的研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 170-179. |
| [5] | 周欢, 林岗, 饶小珍. 刺巨藤壶精子的发生及其超微结构[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(3): 98-105. |
| [6] | 宋悦凡, 曲翊, 曹旭鹏, 汪秋宽, 张卫. 南海小轴海绵的组织结构和细胞特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(4): 71-81. |
| [7] | 吴明灿, 张立, 潘英, 黄光华, 李咏梅, 杨学明. 糙海参卵子发生及卵黄发生的超微结构[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(3): 68-74. |
| [8] | 倪娜, 柳学周 徐永江, 赵明, 曲建忠. 雌性条斑星鲽脑垂体组织学观察[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(6): 97-102. |
| [9] | 肖云朴,徐善良,孙敏,吕慧明. 黑鱾精子发生过程中的超微结构变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2011, 30(1): 107-112. |
| [10] | 曹伏君,罗杰,李长玲,刘楚吾. 细角螺的生殖系统组织学研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(6): 57-64. |
| [11] | 许尤厚,刘学东,张吕平,胡超群. 凡纳滨对虾精子发生的超微结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(4): 89-93. |
| [12] | 张殿彩,饶小珍,林岗,许友勤,陈寅山. 大竹蛏精子发生和精子的超微结构[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2009, 28(6): 131-135. |
|
||