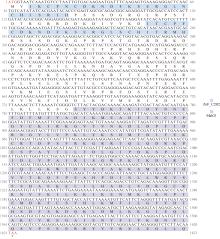
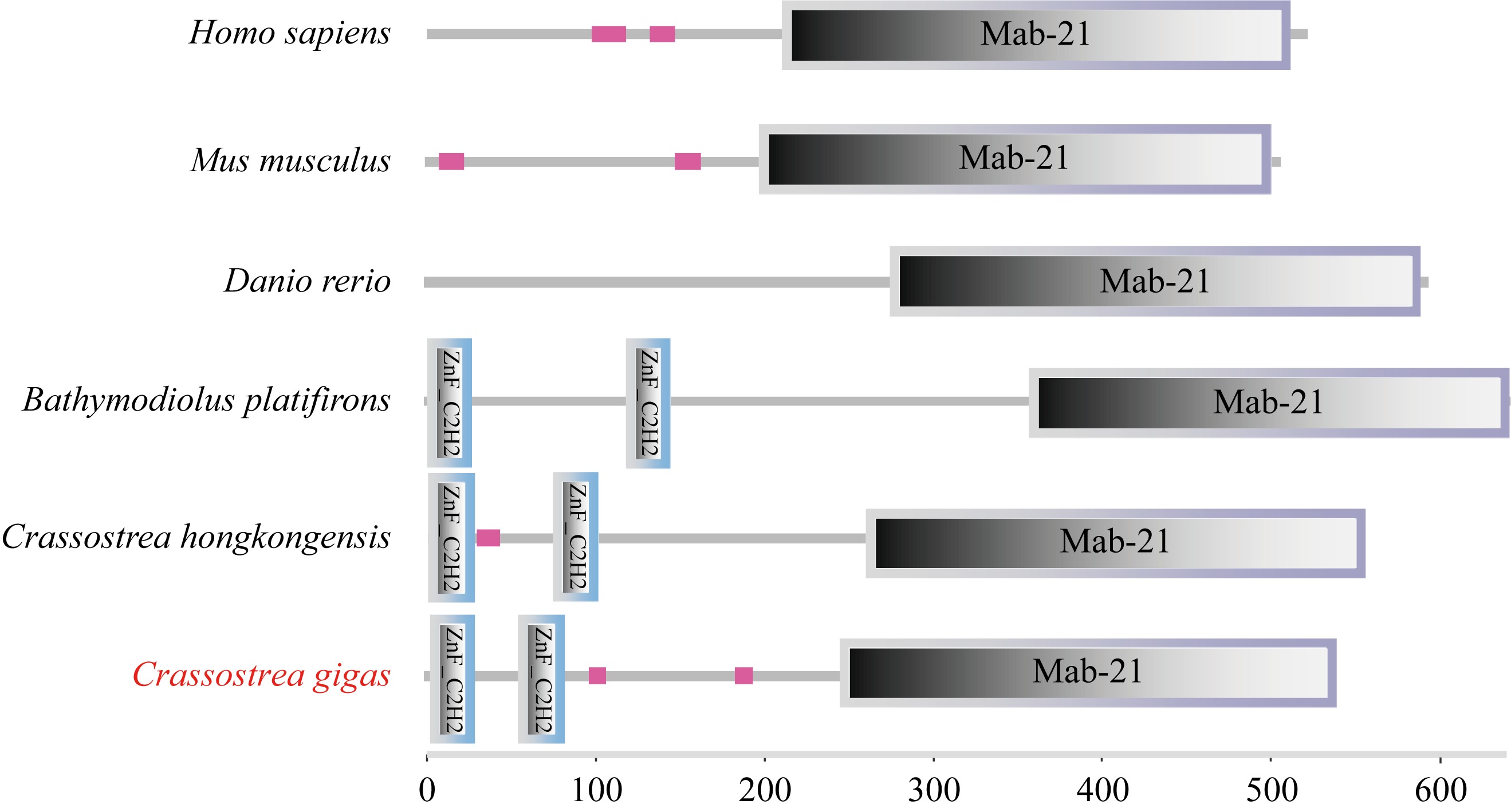
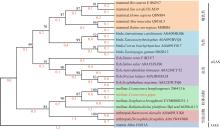
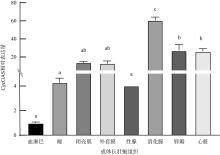
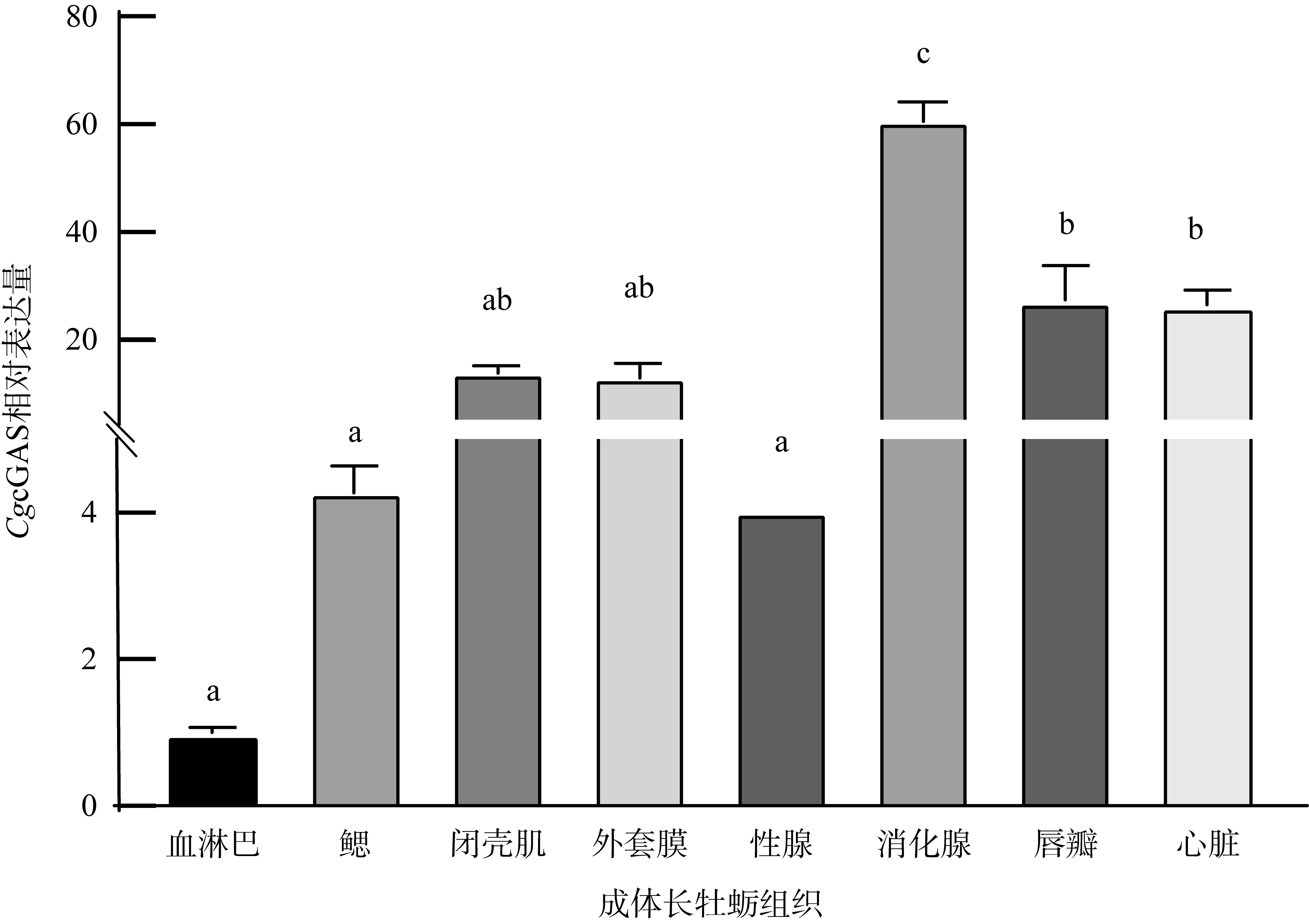
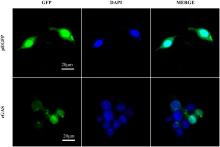
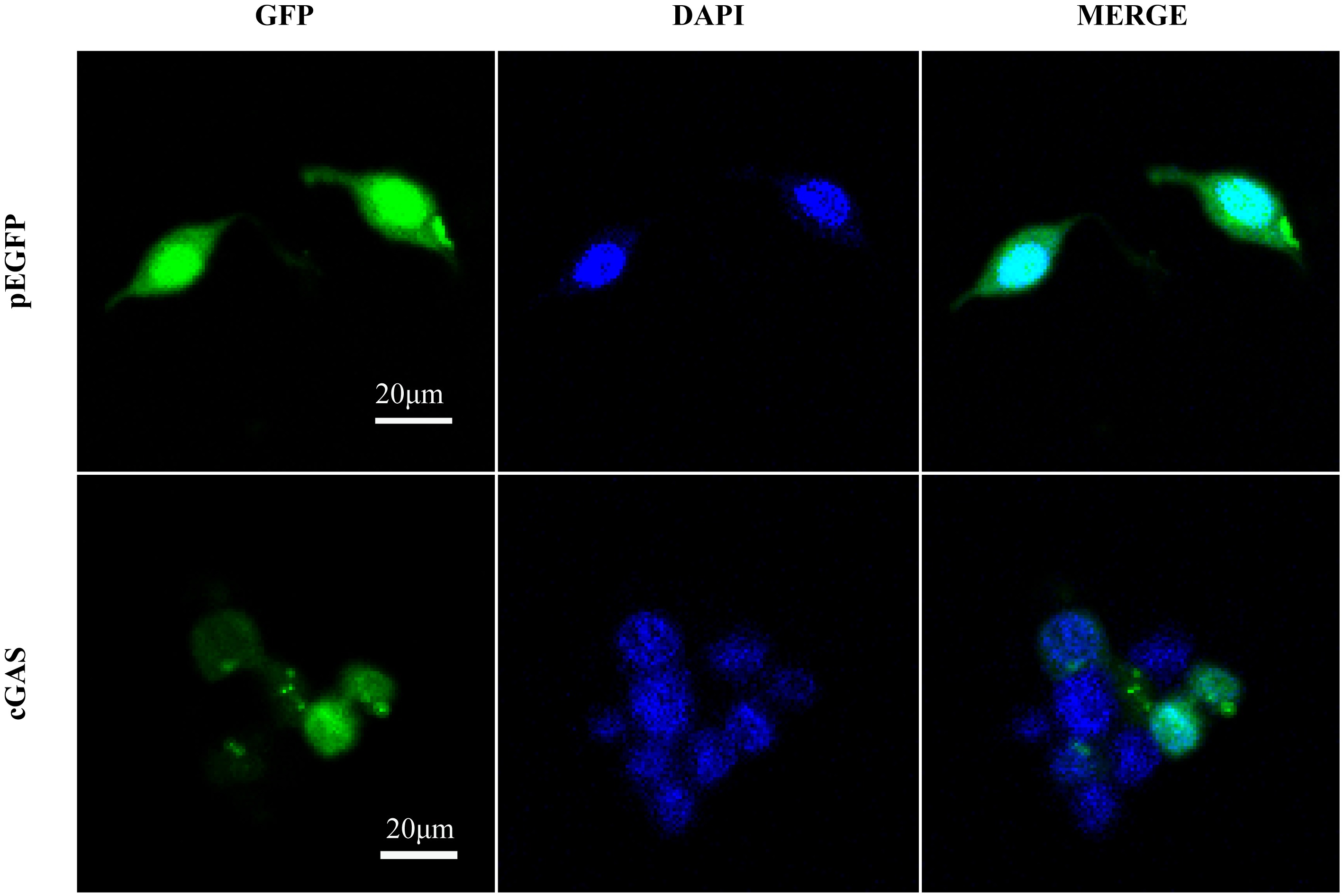
| [1] |
ALLEN E R, WHITEFOOT-KELIIN K M, PALMATIER E M, et al, 2022. Extracellular vesicles from A23187-treated neutrophils cause cGAS-STING-dependent IL-6 production by macrophages[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 13: 949451.
|
| [2] |
BENEDETTI F, SNYDER G A, GIOVANETTI M, et al, 2020. Emerging of a SARS-CoV-2 viral strain with a deletion in nsp1[J]. Journal of Translational Medicine, 18(1): 329.
|
| [3] |
BOYER J A, SPANGLER C J, STRAUSS J D, et al, 2020. Structural basis of nucleosome-dependent cGAS inhibition[J]. Science, 370(6515): 450-454.
|
| [4] |
CAI HUA, IMLER J L, 2021. cGAS-STING: insight on the evolution of a primordial antiviral signaling cassette[J]. Faculty Reviews, 10: 54.
|
| [5] |
CANESI L, GALLO G, GAVIOLI M, et al, 2002. Bacteria-hemocyte interactions and phagocytosis in marine bivalves[J]. Microscopy Research and Technique, 57(6): 469-476.
|
| [6] |
CHEN HAO, JIANG SHUAI, WANG LIN, et al, 2016a. Cgi-miR-92d indirectly regulates TNF expression by targeting CDS region of lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α factor 3 (CgLITAF3) in oyster Crassostrea gigas[J]. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 55: 577-584.
|
| [7] |
CHEN QI, SUN LIJUN, CHEN ZHIJIAN, 2016b. Regulation and function of the cGAS-STING pathway of cytosolic DNA sensing[J]. Nature Immunology, 17(10): 1142-1149.
|
| [8] |
CIVRIL F, DEIMLING T, DE OLIVEIRA MANN C C, et al, 2013. Structural mechanism of cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS[J]. Nature, 498(7454): 332-337.
|
| [9] |
CUI SHUFANG, YU QIUYA, CHU LEI, et al, 2020. Nuclear cGAS functions non-canonically to enhance antiviral immunity via recruiting methyltransferase Prmt5[J]. Cell Reports, 33(10): 108490.
|
| [10] |
DENG JIAN, YU XIAOQIANG, WANG PEIHUI, 2019. Inflammasome activation and Th17 responses[J]. Molecular Immunology, 107: 142-164.
|
| [11] |
DINER E J, BURDETTE D L, WILSON S C, et al, 2013. The innate immune DNA sensor cGAS produces a noncanonical cyclic dinucleotide that activates human STING[J]. Cell Reports, 3(5): 1355-1361.
|
| [12] |
GAO PU, ASCANO M, WU YANG, et al, 2013. Cyclic[G(2′ 5′)pA(3′ 5′)p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase[J]. Cell, 153(5): 1094-1107.
|
| [13] |
GREEN T J, SPECK P, GENG LU, et al, 2015. Oyster viperin retains direct antiviral activity and its transcription occurs via a signalling pathway involving a heat-stable haemolymph protein[J]. Journal of General Virology, 96(12): 3587-3597.
|
| [14] |
HOPFNER K P, HORNUNG V, 2020. Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 21(9): 501-521.
|
| [15] |
HUANG BAOYU, ZHANG LINLIN, DU YISHUAI, et al, 2017. Characterization of the mollusc RIG-I/MAVS pathway reveals an archaic antiviral signalling framework in invertebrates[J]. Scientific Reports, 7(1): 8217.
|
| [16] |
KATOH K, STANDLEY D M, 2013. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30(4): 772-780.
|
| [17] |
KRANZUSCH P J, WILSON S C, LEE A S Y, et al, 2015. Ancient origin of cGAS-STING reveals mechanism of universal 2′ 3′ cGAMP signaling[J]. Molecular Cell, 59(6): 891-903.
|
| [18] |
LAHAYE X, GENTILI M, SILVIN A, et al, 2018. NONO detects the nuclear HIV capsid to promote cGAS-mediated innate immune activation[J]. Cell, 175(2): 488-501.
|
| [19] |
LI DANYANG, WU MINGHUA, 2021. Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases[J] Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 6(1): 291.
|
| [20] |
LI HAOYANG, WANG SHENG, LI QINYAO, et al, 2024. Nucleic acid sensing by STING induces an interferon-like antiviral response in a marine invertebrate[J]. Journal of Immunology, 212(12):1945-1957.
|
| [21] |
LI JUN, ZHANG YANG, ZHANG YUEHUAN, et al, 2014. Genomic characterization and expression analysis of five novel IL-17 genes in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 40(2): 455-465.
|
| [22] |
LI JUN, ZHANG YUEHUAN, MAO FAN, et al, 2018a. The first morphologic and functional characterization of hemocytes in Hong Kong oyster, Crassostrea hongkongensis[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 81: 423-429.
|
| [23] |
LI TUO, CHEN Z J, 2018b. The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway connects DNA damage to inflammation, senescence, and cancer[J]. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 215(5): 1287-1299.
|
| [24] |
LI YAO, SLAVIK K M, TOYODA H C, et al, 2023. cGLRs are a diverse family of pattern recognition receptors in innate immunity[J]. Cell, 186(15): 3261-3276.
|
| [25] |
LIU HAIPENG, ZHANG HAIPING, WU XIANGYANG, et al, 2018. Nuclear cGAS suppresses DNA repair and promotes tumorigenesis[J]. Nature, 563(7729): 131-136.
|
| [26] |
LIU ZHIFEI, JI JIANFEI, JIANG XIAOFENG, et al, 2020. Characterization of cGAS homologs in innate and adaptive mucosal immunities in zebrafish gives evolutionary insights into cGAS-STING pathway[J]. The FASEB Journal, 34(6): 7786-7809.
|
| [27] |
MAO FAN, LIN YUE, ZHOU YINGLI, et al, 2018. Structural and functional analysis of interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) reveals a novel regulatory model in an invertebrate, Crassostrea gigas[J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology, 89: 14-22.
|
| [28] |
MOTWANI M, PESIRIDIS S, FITZGERALD K A, 2019. DNA sensing by the cGAS-STING pathway in health and disease[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 20(11): 657-674.
|
| [29] |
QIAO XUE, ZONG YANAN, LIU ZHAOQUN, et al, 2021. The cGAS/STING-TBK1-IRF regulatory axis orchestrates a primitive interferon-like antiviral mechanism in oyster[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 12: 689783.
|
| [30] |
SLAVIK K M, MOREHOUSE B R, RAGUCCI A E, et al, 2021. cGAS-like receptors sense RNA and control 3′2′-cGAMP signalling in Drosophila[J]. Nature, 597(7874): 109-113.
|
| [31] |
SUN HONG, HUANG YU, MEI SHAN, et al, 2021. A nuclear export signal is required for cGAS to sense cytosolic DNA[J]. Cell Reports, 34(1): 108586.
|
| [32] |
SUN LIJUN, WU JIAXI, DU FENGHE, et al, 2013. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway[J]. Science, 339(6121): 786-791.
|
| [33] |
TAMURA K, STECHER G, KUMAR S, 2021. MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38(7): 3022-3027.
|
| [34] |
VOLKMAN H E, CAMBIER S, GRAY E E, et al, 2019. Tight nuclear tethering of cGAS is essential for preventing autoreactivity[J]. eLife, 8: e47491.
|
| [35] |
WILLEMSEN J, NEUHOFF M T, HOYLER T, et al, 2021. TNF leads to mtDNA release and cGAS/STING-dependent interferon responses that support inflammatory arthritis[J]. Cell Reports, 37(6): 109977.
|
| [36] |
WU JIAXI, CHEN Z J, 2014a. Innate immune sensing and signaling of cytosolic nucleic acids[J]. Annual Review of Immunology, 32: 461-488.
|
| [37] |
WU JIAXI, SUN LIJUN, CHEN XIANG, et al, 2013. Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA[J]. Science, 339(6121): 826-830.
|
| [38] |
WU XIAOMEI, WU FEIHUA, WANG XIAOQIANG, et al, 2014b. Molecular evolutionary and structural analysis of the cytosolic DNA sensor cGAS and STING[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(13): 8243-8257.
|
| [39] |
YU YONGSHENG, LIU YU, AN WEISHUAI, et al, 2019. STING-mediated inflammation in Kupffer cells contributes to progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 129(2): 546-555.
|
| [40] |
ZHANG XU, SHI HEPING, WU JIAXI, et al, 2013. Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING[J]. Molecular Cell, 51(2): 226-235.
|
 ), 毛帆2, 刘客林2, 宋菁晨2, 喻子牛2, 张扬2(
), 毛帆2, 刘客林2, 宋菁晨2, 喻子牛2, 张扬2( )
)
 ), MAO Fan2, LIU Kelin2, SONG Jingchen2, YU Ziniu2, ZHANG Yang2(
), MAO Fan2, LIU Kelin2, SONG Jingchen2, YU Ziniu2, ZHANG Yang2( )
)