热带海洋学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 1-11.doi: 10.11978/2024223CSTR: 32234.14.2024223
• 综述 • 下一篇
中国边缘海沉积物有机碳分布及其储碳潜力研究进展
徐维海1,2( ), 钟秋燕1,3, 颜文1,3(
), 钟秋燕1,3, 颜文1,3( ), 黎刚1
), 黎刚1
- 1.热带海洋环境与岛礁生态全国重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.三亚海洋生态环境工程研究院, 海南 三亚572000
3.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2024-11-27修回日期:2025-02-17出版日期:2025-09-10发布日期:2025-10-14 -
通讯作者:徐维海, 颜文 -
作者简介:徐维海(1978—), 江苏省连云港市人, 研究员, 主要从事海洋沉积和珊瑚礁碳酸盐岩研究。email: whxu@scsio.ac.cn
-
基金资助:海南省自然科学基金创新研究团队项目(422CXTD533); 国家自然科学基金项目(42376079)
Research advances on organic carbon distribution and storage potential of sediments in the Chinese marginal seas
XU Weihai1,2( ), ZHONG Qiuyan1,3, YAN Wen1,3(
), ZHONG Qiuyan1,3, YAN Wen1,3( ), LI Gang1
), LI Gang1
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography, South China Sea Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Sanya Institute of Marine Ecological and Environmental Engineering, Sanya 572000, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2024-11-27Revised:2025-02-17Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-10-14 -
Contact:XU Weihai, YAN Wen -
Supported by:Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China(422CXTD533); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42376079)
摘要:
碳元素在海洋中以多种形式参与全球碳循环, 其中海洋沉积物埋藏的有机碳(total organic carbon, TOC)在全球碳循环中起到至关重要的作用。边缘海作为全球海洋物理能量和生产力较高的过渡区, 储存了全球海洋80%以上的有机碳。中国边缘海总面积约470×104km2, 具有显著的储碳能力和前景, 随着我国“双碳”目标的实施, 海洋储碳相关研究成为近年来的研究热点。文章综述了中国边缘海沉积物有机碳分布特征, 整体上呈现出从渤海向南海逐渐增加的趋势, 且沿岸海域和河流入海口周围含量显著高于远海。同时分析了有机碳主要来源和影响因素及其储碳潜力, 并对未来可能的重点研究方向进行了展望, 旨在为国内边缘海储碳和碳循环方面的相关工作提供一定的借鉴。
中图分类号:
- P744.9
引用本文
徐维海, 钟秋燕, 颜文, 黎刚. 中国边缘海沉积物有机碳分布及其储碳潜力研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(5): 1-11.
XU Weihai, ZHONG Qiuyan, YAN Wen, LI Gang. Research advances on organic carbon distribution and storage potential of sediments in the Chinese marginal seas[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(5): 1-11.
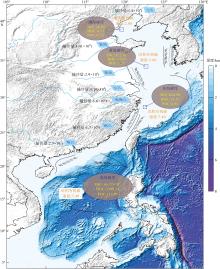
图1
中国主要入海河流输沙量和边缘海碳通量[(据焦念志等(2018)、王博士等(2005)、王尧(2023)修订] 该图基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站下载的审图号为GS(2023)2765的标准地图制作, 底图无修改。图中DIC (dissolved inorganic carbon)为溶解无机碳(单位: Tg·a−1)、PIC (particulate inorganic carbon)为颗粒无机碳(单位: Tg·a−1)、POC (particulate organic carbon)为颗粒有机碳(单位: Tg·a−1)、DOC (dissolved organic carbon)为溶解有机碳(单位: Tg·a−1), 图中沉积有机碳通量的单位为Tg·a−1"

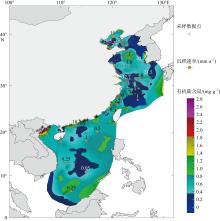
图2
中国边缘海表层沉积物有机碳含量分布和沉积速率图 该图基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站下载的审图号为GS(2023)2765的标准地图制作, 底图无修改。收集站位数据主要来源于参考文献(吴时国 等, 1995; 郭志刚 等, 1999; Duan, 2000; Kao et al, 2003; 王中波 等, 2004; 王博士 等, 2005; Hu et al, 2006; Szarek et al, 2009; 熊林芳, 2010; 陈彬 等, 2011; Xing et al, 2011; 孙书文, 2012; Hu et al, 2013; 文梅, 2013; Bao et al, 2016; 李文宝 等, 2017; Tue et al, 2018; Wan et al, 2019; Dan et al, 2020; Zhu et al, 2020; Chen et al, 2021; Miao et al, 2021; Pang et al, 2022; 陈芬 等, 2023; Dan et al, 2023; Lin et al, 2023; Duraimaran et al, 2024)。沉积速率来源于参考文献(石学法 等, 2024)"

表1
中国各边缘海有机碳、碳库与潜力比较"
| 海域 | 沉积物有机 碳含量/% | 海域DIC 碳库/Tg | 海域DOC 碳库/Tg | 海域POC 碳库/Tg | 整个海域固 碳潜力/(Tg·a−1) | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 渤海 | 0.12~1.13 | 36.95 | 4.51 | 0.52 | 8.66 | 陈彬等( |
| 黄海 | 0.4~1.8 | 422.01 | 31.07 | 7.22 | 78.09 | 高学鲁等( |
| 东海 | 0.5~3.5 | 844.50 | 33.57 | 6.91 | 222.99 | 李宁等( |
| 南海 | 0.3~3.3 | 162872.64 | 3390.34 | 117.95 | 545.06 | Dai等( |
| 中国边缘海 | 164176.10 | 3459.49 | 132.60 | 854.76 | 焦念志等( |
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [1] |
蔡进功, 包于进, 杨守业, 等, 2007. 泥质沉积物和泥岩中有机质的赋存形式与富集机制[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 37(2): 234-243.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈彬, 胡利民, 邓声贵, 等, 2011. 渤海湾表层沉积物中有机碳的分布与物源贡献估算[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 31(5): 37-42.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈芬, 黎刚, 朱小畏, 等, 2023. 南海南沙海区沉积有机质分布特征及其指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 43(2): 45-54.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
戴民汉, 翟惟东, 鲁中明, 等, 2004. 中国区域碳循环研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 19(1): 120-130.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
丁奕凡, 田军, 2022. 晚中新世以来印度尼西亚海道及印度尼西亚贯穿流的协同演化及其气候效应研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 37(11): 1165-1180.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2022.077 |
|
|
|
| [6] |
范德江, 杨作升, 毛登, 等, 2001. 长江与黄河沉积物中粘土矿物及地化成分的组成[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 21(4): 7-12.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
高学鲁, 2005. 中国近海典型海域溶解无机碳系统的生物地球化学特征[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所).
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
高学鲁, 宋金明, 李学刚, 等, 2009. 南黄海秋季溶解无机碳的分布特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 28(1): 17-21.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
郭志刚, 2003. 长江口泥质区的季节性沉积效应[J]. 中国地理科学文摘, 17(4): 9.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
郭志刚, 杨作升, 陈致林, 等, 2001. 东海陆架泥质区沉积有机质的物源分析[J]. 地球化学, 30(5): 416-424.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
郭志刚, 杨作升, 曲艳慧, 等, 1999. 东海中陆架泥质区及其周边表层沉积物碳的分布与固碳能力的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 30(4): 421-426.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
韩逸臻, 2022. 中国东部陆架海黑碳沉积记录及其对传统持久性有机污染物的迁移特性表征[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
侯贵廷, 钱祥麟, 蔡东升, 2000. 渤海中、新生代盆地构造活动与沉积作用的时空关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 21(3): 201-206.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
黄荣辉, 孙凤英, 1994. 热带西太平洋暖池的热状态及其上空的对流活动对东亚夏季气候异常的影响[J]. 大气科学, 18(2): 141-151.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
江春波, 2006. 南黄海春季CO2海-气交换通量及其与夏季的比较[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
焦念志, 梁彦韬, 张永雨, 等, 2018. 中国海及邻近区域碳库与通量综合分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(11): 1393-1421.
|
|
|
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [17] |
焦念志, 王荣, 李超伦, 1998. 东海春季初级生产力与新生产力的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 29(2): 135-140.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
李安春, 张凯棣, 2020. 东海内陆架泥质沉积体研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(4): 705-727.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
李宁, 王江涛, 2011. 春季东海北部近岸水体中的溶解无机碳和有机碳的分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋科学, 35(8): 5-10.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
李晟, 2021. 洞庭湖地区绿地生态网络构建及效能评价研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
李文宝, 王汝建, 万随, 2017. 沉积过程中有机碳及Globigerinoides ruber氧、碳同位素变化特征: 以南海南部为例[J]. 沉积学报, 35(4): 730-739.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
刘炳辰, 2013. 渤海中南部碎屑矿物特征与沉积环境[D]. 烟台: 鲁东大学.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
刘冬梅, 2010. 黄河干流有机碳及调水调沙时期碳输运规律[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
刘军, 于志刚, 臧家业, 等, 2015. 黄渤海有机碳的分布特征及收支评估研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 30(5): 564-578.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2015.05.564 |
|
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2015.05.564 |
|
| [25] |
刘茜, 郭香会, 尹志强, 等, 2018. 中国邻近边缘海碳通量研究现状与展望[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(11): 1422-1443.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
刘世东, 乔璐璐, 李广雪, 等, 2018. 东海内陆架悬浮体输运、通量及季节变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 49(1): 24-39.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
刘雪, 2014. 基于遥感的中国东部海域悬浮泥沙季节变化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
刘焱光, 2005. 近4万年来冲绳海槽物质来源的定量估计及其对气候变化的响应[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
陆孝平, 富曾慈, 2010. 中国主要江河水系要览[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
梅西, 李学杰, 密蓓蓓, 等, 2020. 中国海域表层沉积物分布规律及沉积分异模式[J]. 中国地质, 47(5): 1447-1462.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
商荣宁, 2011. 2010年黄、渤海有机碳的分布特征及影响因素[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
石学法, 2014. 中国近海海洋—海洋底质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
石学法, 吴斌, 乔淑卿, 等, 2024. 中国东部近海沉积有机碳的分布、埋藏及碳汇效应[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 54(10): 3113-3133.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
宋金明, 王启栋, 张润, 等, 2019. 70年来中国化学海洋学研究的主要进展[J]. 海洋学报, 41(10): 65-80.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
孙书文, 2012. 渤海及邻近海域表层沉积物中木质素的分布特征及其陆源有机质示踪意义[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
孙效功, 方明, 黄伟, 2000. 黄、东海陆架区悬浮体输运的时空变化规律[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 31(6): 581-587.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
孙晓燕, 李希彬, 2012. 近3 ka来东海陆架北部泥质沉积物地球化学特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 28(4): 10-16.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
谈谈, 2014. 熟读南海[J]. 石油知识, (5): 4-5, 11.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
王博士, 赵泉鸿, 翦知湣, 2005. 南海南部中上新世以来沉积有机碳与古生产力变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 25(2): 73-79.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
王尧, 2023. 中国主要河流的生源要素输出通量及其在大河河口的来源和迁移转化[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
王中波, 杨守业, 李从先, 2004. 南黄海中部沉积物岩芯常量元素组成与古环境[J]. 地球化学, 33(5): 483-490.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
文梅, 2013. 双台子河口颗粒有机碳的地球化学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
吴时国, 涂霞, 罗又郎, 等, 1995. 南沙群岛海区有机碳沉积作用与古生产力估算[J]. 热带海洋, 14(4): 58-66.
|
|
|
|
| [44] |
熊林芳, 2010. 南黄海—东海北部悬浮体与表层沉积物有机碳分布特征[D]. 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [45] |
杨作升, 范德江, 郭志刚, 等, 2002. 东海陆架北部泥质区表层沉积物碳酸盐粒级分布与物源分析[J]. 沉积学报, 20(1): 1-6.
|
|
|
|
| [46] |
张兰生, 2000. 全球变化[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [47] |
张明宇, 常鑫, 胡利民, 等, 2021. 东海内陆架有机碳的源-汇过程及其沉积记录[J]. 沉积学报, 39(3): 593-609.
|
|
|
|
| [48] |
张咏华, 吴自军, 2019. 陆架边缘海沉积物有机碳矿化及其对海洋碳循环的影响[J]. 地球科学进展, 34(2): 202-209.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.02.0202 |
|
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.02.0202 |
|
| [49] |
张玉荣, 丁跃平, 李铁军, 等, 2016. 东海区叶绿素a和初级生产力季节变化特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(1): 261-268.
|
|
|
|
| [50] |
赵海萍, 2019. 渤海湾有机碳时空特征及其循环过程生态水动力学模拟[D]. 天津: 天津大学.
|
|
|
|
| [51] |
赵美训, 丁杨, 于蒙, 2017. 中国边缘海沉积有机质来源及其碳汇意义[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 47(9): 70-76.
|
|
|
|
| [52] |
中华人民共和国水利部, 2020. 中国河流泥沙公报-2019[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [53] |
周晓静, 李安春, 万世明, 等, 2010. 东海陆架表层沉积物粘土矿物组成分布特征及来源[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 41(5): 667-675.
|
|
|
|
| [54] |
朱纯, 潘建明, 卢冰, 等, 2005a. 长江、老黄河口及东海陆架沉积有机质物源指标及有机碳的沉积环境[J]. 海洋学研究, 23(3): 36-46.
|
|
|
|
| [55] |
朱纯, 潘建明, 卢冰, 等, 2005b. 长江口及邻近海域现代沉积物中正构烷烃分子组合特征及其对有机碳运移分布的指示[J]. 海洋学报, 27(4): 59-67.
|
|
|
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
pmid: 22457981 |
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1161408 pmid: 18988852 |
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2386 pmid: 20601964 |
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [1] | 曾德斌, 彭光煜, 杨斌, 莫小荣, 周姣娣, 黄海方, 颜婷婷. 南海北部钦州湾茅尾海溶解碳水化合物的分布特征及影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(3): 197-205. |
| [2] | 吴雪, 赵鑫, 辜伟芳, 朱科桦, 葛振鸣. 浙南海岸带人工秋茄(Kandelia obovata)红树林与互花米草(Spartina alterniflora)盐沼土壤碳汇对比研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2025, 44(1): 172-181. |
| [3] | 高洁, 余克服, 许慎栋, 黄学勇, 陈飚, 王永刚. 西沙群岛永乐环礁礁外坡沉积物中有机碳的含量与来源分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [4] | 商博文, 吴云超, 江志坚, 刘松林, 黄小平. 珠江口沉积物有机质特征、来源及其对碳存储的意义[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 16-28. |
| [5] | 吴兰军, 黎刚. XRF岩心扫描估算海洋沉积物有机碳含量的适用性[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 112-120. |
| [6] | 陈焕焕, 王云涛, 齐义泉, 柴扉. 北太平洋大气沉降的时空特征及其对副极区海洋生态系统的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(1): 21-30. |
| [7] | 张立明, 谭烨辉, 李佳俊, 黄小平, 刘甲星. 大亚湾夏季浮游植物群落结构及对淡澳河输入的响应特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [8] | 郭亚娟, 周伟华, 袁翔城, 廖健祖, 江雷, 黄晖. 两种造礁石珊瑚对海水酸化和溶解有机碳加富的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(1): 57-63. |
| [9] | 张际标, 杨波, 陈涛, 陈春亮. 深圳西部海域河流入海口沉积物酸可挥发性硫、同步提取重金属分布特征与生物毒性评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(6): 89-101. |
| [10] | 郭威, 叶丰, 连忠廉, 贾国东. 珠江口水体有机碳的季节性变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(4): 40-50. |
| [11] | 宋晓晓, 李春峰. 西太平洋科学大洋钻探的地球动力学成果*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(1): 17-30. |
| [12] | 王桂芬 曹文熙 , 殷建平, 周雯 孙兆华, 杨倩. 海洋颗粒有机碳浓度水色遥感研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(6): 48-56. |
| [13] | 韩玉,张桂玲,赵玉川. 海南东部沿岸河流和潟湖中溶存甲烷的分布及通量 * [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(2): 87-95. |
| [14] | 雷菲,李志阳,张杰,陈蔚芳,贾国东. 百余年来珠江口及邻近西部海域有机碳来源及其埋藏记录 * [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(2): 62-66. |
| [15] | 田丽欣,吴莹,林晶,朱卓毅,张经. 冬季海南省东北部河流及近岸海区有机碳的分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(5): 136-141. |
|
||

