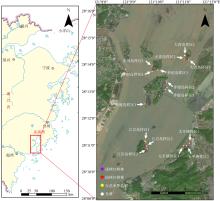
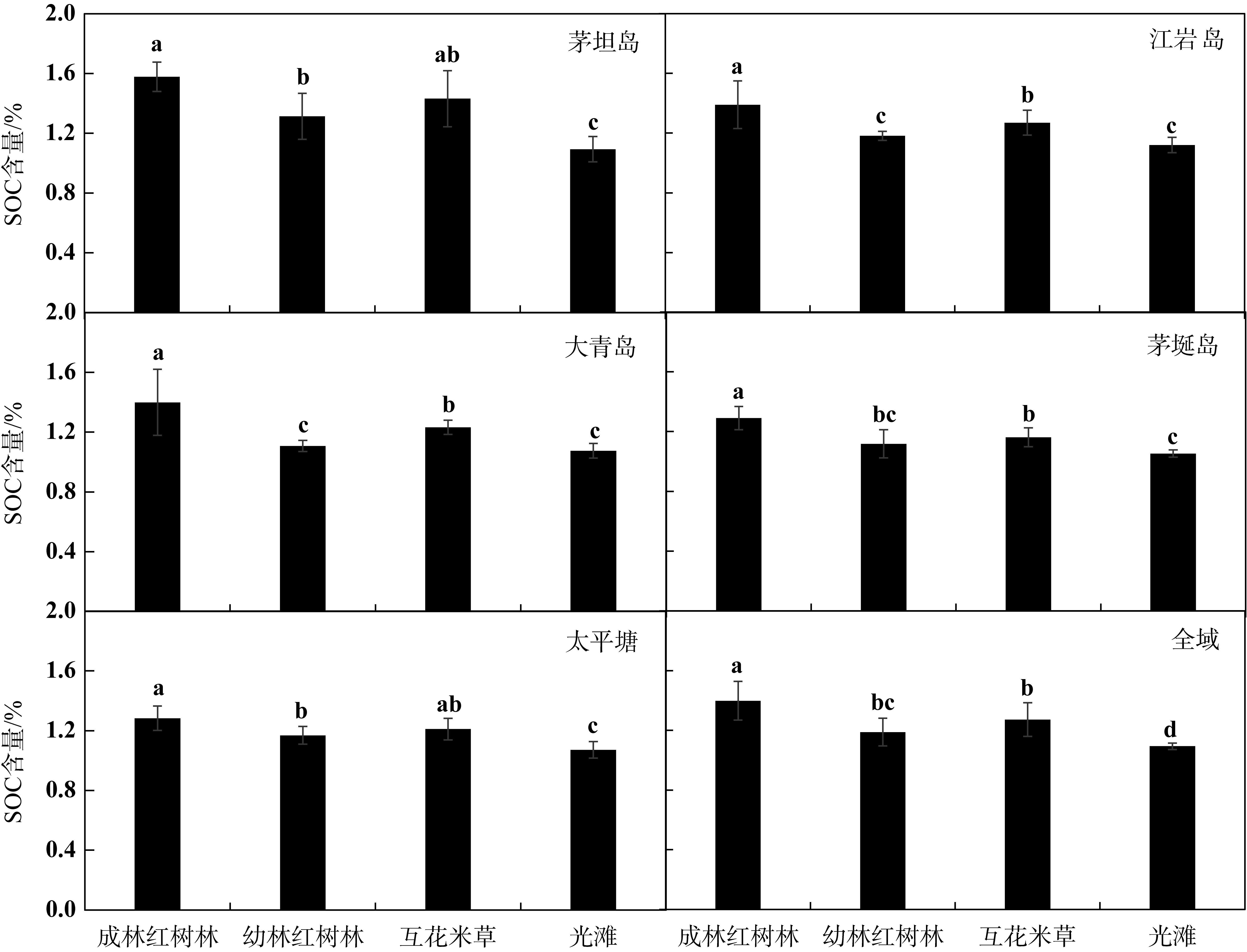
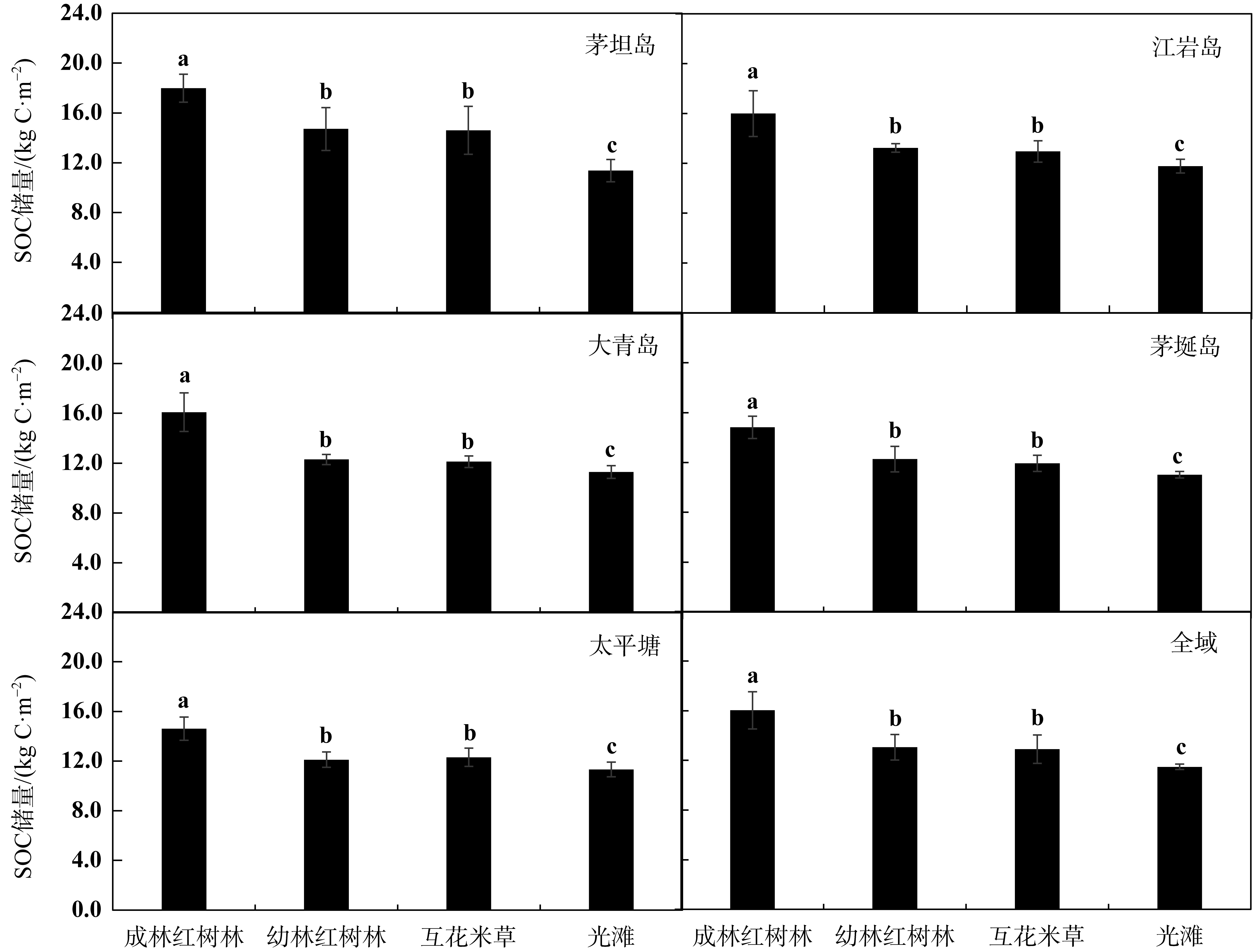
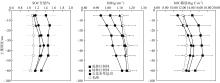
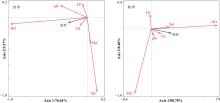
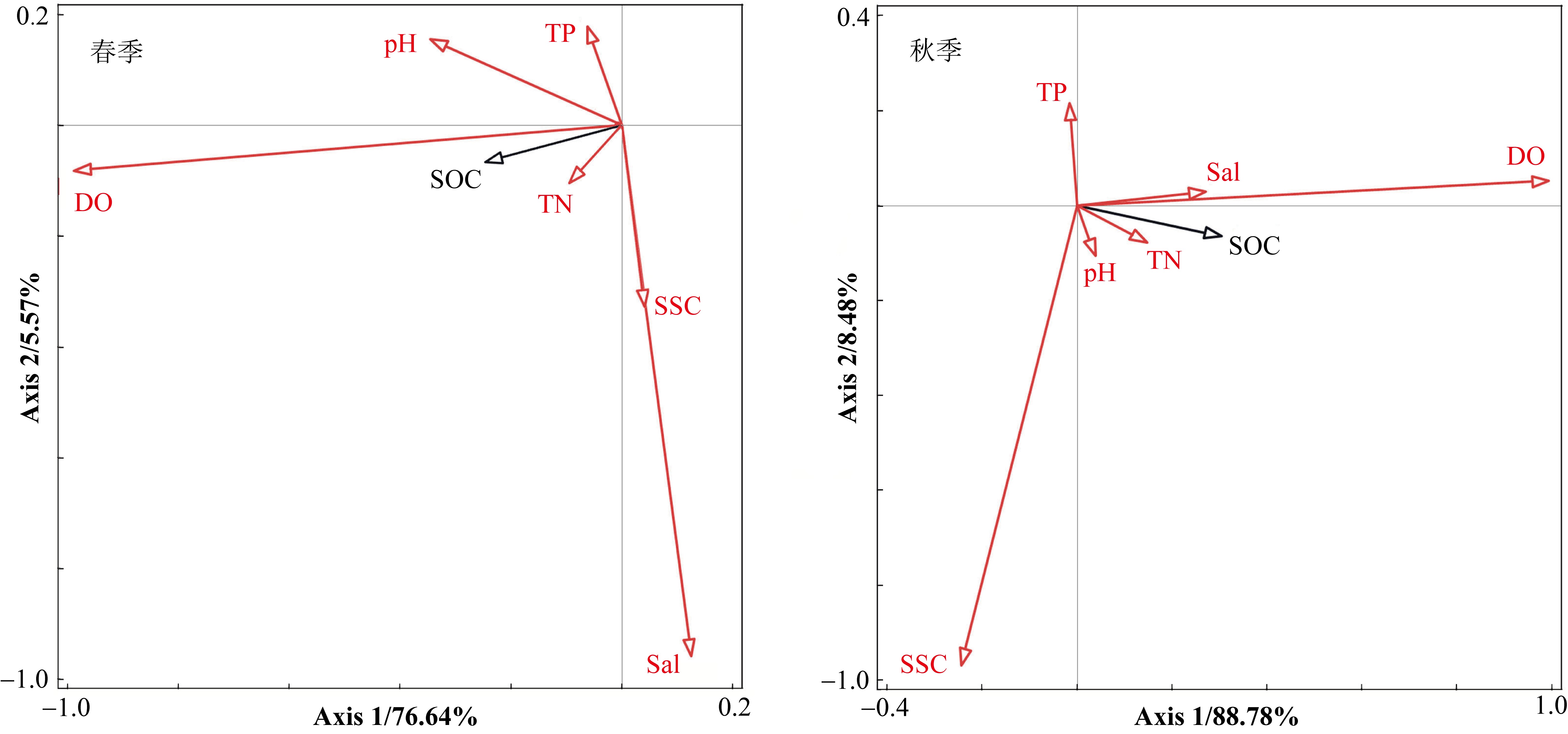
| [1] |
陈桂香, 高灯州, 陈刚, 等, 2017. 互花米草入侵对我国红树林湿地土壤碳组分的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 31(6): 249-256.
|
|
CHEN GUIXIANG, GAO DENGZHOU, CHEN GANG, et al, 2017. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on soil carbon fractions in mangrove wetlands of China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(6): 249-256 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
陈卉, 2013. 中国两种亚热带红树林生态系统的碳固定、掉落物分解及其同化过程[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
CHEN HUI, 2013. Carbon sequestration, litter, decomposition and consumption in two subtropical mangrove ecosystems of China[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
陈秋夏, 杨升, 王金旺, 等, 2019. 浙江红树林发展历程及探讨[J]. 浙江农业科学, 60(7): 1177-1181 (in Chinese).
|
| [4] |
胡雪红, 张立, 周炎武, 等, 2020. 我国滨海湿地生态修复领域规范的现状与分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(6): 131-139.
|
|
HU XUEHONG, ZHANG LI, ZHOU YANWU, et al, 2020. Present situation and analysis of standards for coastal wetland ecological restoration in China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 39(6): 131-139 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
刘景双, 杨继松, 于君宝, 等, 2003. 三江平原沼泽湿地土壤有机碳的垂直分布特征研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 17(3): 5-8.
|
|
LIU JINGSHUANG, YANG JISONG, YU JUNBAO, et al, 2003. Study on vertical distributon of soil organic carbon in wetlands Sanjiang plain[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 17(3): 5-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
逄柏鹏, 2012. 九龙江口不同恢复阶段秋茄红树林底质有机碳储量及其来源的研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
PANG BOPENG, 2012. Storages and origins of sediment organic carbon in Kandelia candel mangroves at different restoration stages in Jiulongjiang Estuary[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
唐剑武, 叶属峰, 陈雪初, 等, 2018. 海岸带蓝碳的科学概念、研究方法以及在生态恢复中的应用[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(6): 661-670.
|
|
TANG JIANWU, YE SHUFENG, CHEN XUECHU, et al, 2018. Coastal blue carbon: Concept, study method, and the application to ecological restoration[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(6): 637-646.
|
| [8] |
张天雨, 葛振鸣, 张利权, 等, 2015. 崇明东滩湿地植被类型和沉积特征对土壤碳、氮分布的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 35(3): 836-843.
|
|
ZHANG TIANYU, GE ZHENMING, ZHANG LIQUAN, et al, 2015. Influence of saltmarsh vegetation and sedimentation on the distribution of soil carbon and nitrogen in the Chongming Dongtan wetlands[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 35(3): 836-843 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
赵彩云, 李俊生, 赵相健, 等, 2015. 中国沿海互花米草入侵与防控管理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
ZHAO CAIYUN, LI JUNSHENG, ZHAO XIANGJIAN, et al, 2015. Invasion and management of Spartina alterniflora along China’s coast[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员, 2007. 海洋监测规范第4部分:海水分析GB17378. 4-2007 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 92-95.
|
|
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, 2007. The specification for marine monitoring—Part 4: Seawater analysis GB17378. 4-2007 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 92-95 (in Chinese).
|
| [11] |
中华人民共和国农业部, 2006. 土壤检测第16部分:土壤水溶性盐总量的测定 NT/Y1121. 16-2006 [S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 1-2.
|
|
Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China, 2006. Soil Testing—Part 16: Method for determination of total water-soluble salt NT/Y1121. 16-2006 [S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press: 1-2 (in Chinese).
|
| [12] |
ALONGI D M, 2020. Carbon balance in salt marsh and mangrove ecosystems: A global synthesis[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(10): 767.
|
| [13] |
AVNIMELECH Y, RITVO G, MEIJER L E, et al, 2001. Water content, organic carbon and dry bulk density in flooded sediments[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 25(1): 25-33.
|
| [14] |
BAI JIANKUN, MENG YUCHEN, GOU RUIKUN, et al, 2021. Mangrove diversity enhances plant biomass production and carbon storage in Hainan island, China[J]. Functional Ecology, 35(3): 774-786.
|
| [15] |
BIANCHI T S, ALLISON M A, ZHAO J, et al, 2013. Historical reconstruction of mangrove expansion in the Gulf of Mexico: Linking climate change with carbon sequestration in coastal wetlands[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 119: 7-16.
|
| [16] |
BOUILLON S, BORGES A V, CASTAÑEDA-MOYA E, et al, 2008. Mangrove production and carbon sinks: a revision of global budget estimates[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 22(2): GB2013.
|
| [17] |
BOUILLON S, DAHDOUH-GUEBAS F, RAO A V V S, et al, 2003. Sources of organic carbon in mangrove sediments: variability and possible ecological implications[J]. Hydrobiologia, 495: 33-39.
|
| [18] |
CADIZ P L, CALUMPONG H P, SINUTOK S, et al, 2020. Carbon storage potential of natural and planted mangals in Trang, Thailand[J]. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 18(3): 4383-4403.
|
| [19] |
CARNELL P E, PALACIOS M M, WARYSZAK P, et al, 2022. Blue carbon drawdown by restored mangrove forests improves with age[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 306: 114301.
|
| [20] |
CHEN GUANGCHENG, GAO MIN, PANG BOPENG, et al, 2018. Top-meter soil organic carbon stocks and sources in restored mangrove forests of different ages[J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 422: 87-94.
|
| [21] |
CHEN JINHAI, WANG LEI, LI YANLI, et al, 2012. Effect of Spartina alterniflora invasion and its controlling technologies on soil microbial respiration of a tidal wetland in Chongming Dongtan, China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 41: 52-59.
|
| [22] |
CHENG XIAOLI, LUO YIQI, CHEN JIQUAN, et al, 2006. Short-term C4 plant Spartina alterniflora invasions change the soil carbon in C3 plant-dominated tidal wetlands on a growing estuarine Island[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(12): 3380-3386.
|
| [23] |
CINCO-CASTRO S, HERRERA-SILVEIRA J A, COMÍN F, 2022. Sedimentation as a support ecosystem service in different ecological types of mangroves[J]. Frontiers in Forests and Global Change, 5: 733820.
|
| [24] |
CURTIN D, BEARE M H, HERNANDEZ-RAMIREZ G, 2012. Temperature and moisture effects on microbial biomass and soil organic matter mineralization[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 76(6): 2055-2067.
|
| [25] |
EID E M, SHALTOUT K H, 2016. Distribution of soil organic carbon in the mangrove Avicennia marina (Forssk.) Vierh. along the Egyptian Red Sea Coast[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 3: 76-82.
|
| [26] |
ESPERSCHÜTZ J, BUEGGER F, WINKLER J B, et al, 2009. Microbial response to exudates in the rhizosphere of young beech trees (Fagus sylvatica L.) after dormancy[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41(9): 1976-1985.
|
| [27] |
FENG JIANXIANG, WANG SHUGONG, WANG SHUJUAN, et al, 2019. Effects of invasive Spartina alterniflora Loisel. and subsequent ecological replacement by Sonneratia apetala Buch.-Ham. on soil organic carbon fractions and stock[J]. Forests, 10(2): 171.
|
| [28] |
JUMPROM N, RODCHAROEN E, WICHACHUCHERD B, 2021. The physicochemical properties of sediment and ground cover for a secondary mangrove system in Thailand[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 37(4): 784-792.
|
| [29] |
KIDA M, TOMOTSUNE M, IIMURA Y, et al, 2017. High salinity leads to accumulation of soil organic carbon in mangrove soil[J]. Chemosphere, 177: 51-55.
|
| [30] |
KRAMER C, GLEIXNER G, 2006. Variable use of plant- and soil-derived carbon by microorganisms in agricultural soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(11): 3267-3278.
|
| [31] |
KRISTENSEN E, BOUILLON S, DITTMAR T, et al, 2008. Organic carbon dynamics in mangrove ecosystems: A review[J]. Aquatic Botany, 89(2): 201-219.
|
| [32] |
KUSUMANINGTYAS M A, HUTAHAEAN A A, FISCHER H W, et al, 2019. Variability in the organic carbon stocks, sources, and accumulation rates of Indonesian mangrove ecosystems[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 218: 310-323.
|
| [33] |
LI YUHONG, SHAHBAZ M, ZHU ZHENKE, et al, 2021. Oxygen availability determines key regulators in soil organic carbon mineralisation in paddy soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 153: 108106.
|
| [34] |
OUYANG XIAOGUANG, LEE S Y, CONNOLLY R M, 2017. The role of root decomposition in global mangrove and saltmarsh carbon budgets[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 166: 53-63.
|
| [35] |
QU WENDI, LI JUANYONG, HAN GUANGXUAN, et al, 2019. Effect of salinity on the decomposition of soil organic carbon in a tidal wetland[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(2): 609-617.
|
| [36] |
SREELEKSHMI S, HARIKRISHNAN M, NANDAN S B, et al, 2022. Ecosystem carbon stock and stable isotopic signatures of soil organic carbon sources across the mangrove ecosystems of Kerala, Southern India[J]. Wetlands, 42(4): 29.
|
| [37] |
THURA K, SERRANO O, GU JIALI, et al, 2023. Mangrove restoration built soil organic carbon stocks over six decades: a chronosequence study[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 23(3): 1193-1203.
|
| [38] |
WALDROP M P, FIRESTONE M K, 2004. Microbial community utilization of recalcitrant and simple carbon compounds: impact of oak-woodland plant communities[J]. Oecologia, 138(2): 275-284.
|
| [39] |
World Meteorological Organization (WMO), (2022-10-26)[2024-03-07]. The state of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere based on global observations through 2021, World Meteorological Organization[R/OL]. WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin, 18. https://library.wmo.int/idurl/4/58743.
|
| [40] |
XIE LINA, GE ZHENMING, LI YALEI, et al, 2020. Effects of waterlogging and increased salinity on microbial communities and extracellular enzyme activity in native and exotic marsh vegetation soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 84(1): 82-98.
|
| [41] |
YAO HUAIYING, THORNTON B, PATERSON E, 2012. Incorporation of 13C-labelled rice rhizodeposition carbon into soil microbial communities under different water status[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 53: 72-77.
|
| [42] |
ZHALNINA K, LOUIE K B, HAO ZHAO, et al, 2018. Dynamic root exudate chemistry and microbial substrate preferences drive patterns in rhizosphere microbial community assembly[J]. Nature Microbiology, 3: 470-480.
|
 ), 赵鑫1,2(
), 赵鑫1,2( ), 辜伟芳1,2, 朱科桦3, 葛振鸣3
), 辜伟芳1,2, 朱科桦3, 葛振鸣3
 ), ZHAO Xin1,2(
), ZHAO Xin1,2( ), GU Weifang1,2, ZHU Kehua3, GE Zhenming3
), GU Weifang1,2, ZHU Kehua3, GE Zhenming3