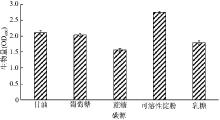
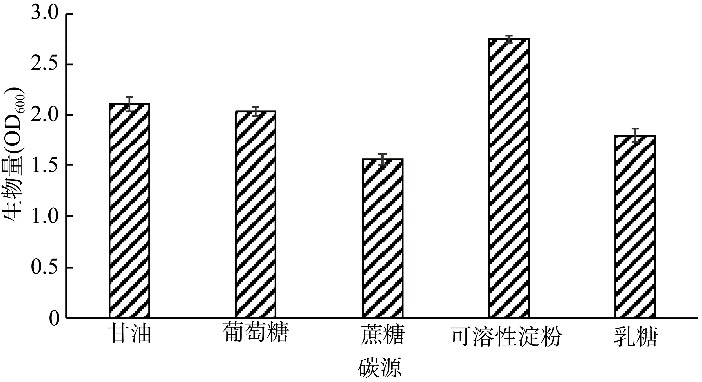
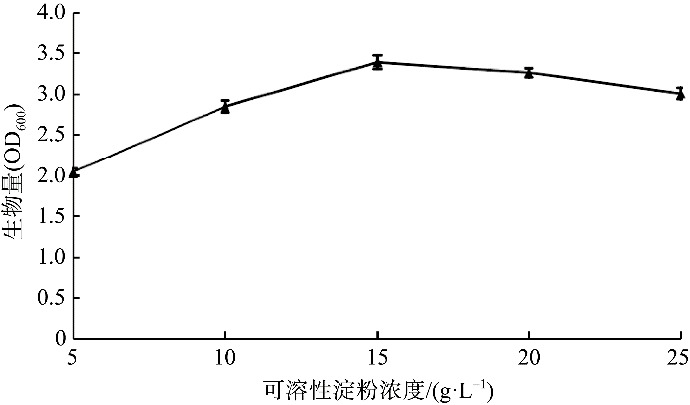
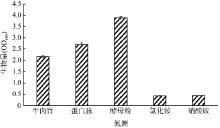
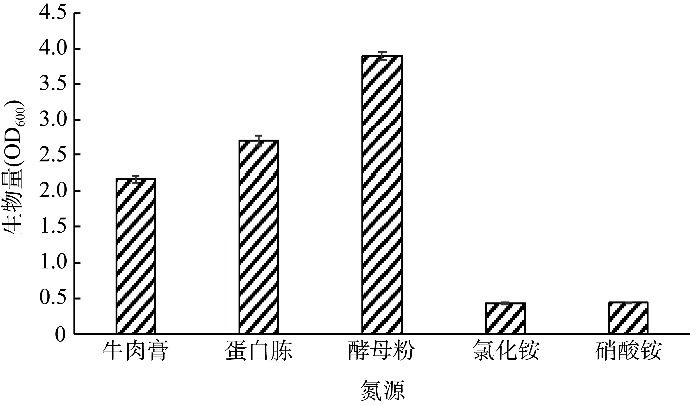
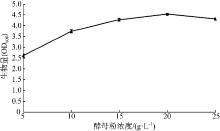
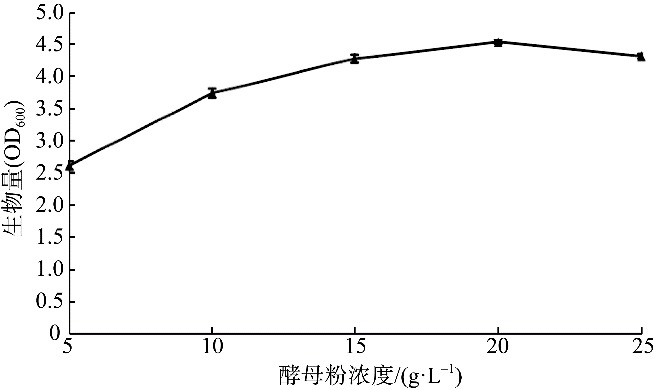
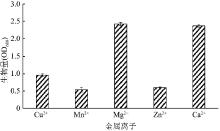
| [1] |
东秀珠, 蔡妙英, 2001. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
DONG XIUZHU, CAI MIAOYING, 2001. Common Bacterial System Identification Manual[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
何志伟, 董起钰, 刘锐, 等, 2021. 白斑蛾蚋幼虫肠道可培养细菌的分离鉴定与产消化酶活性分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 32(2): 224-229.
doi: 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2021.02.021
|
|
HE ZHIWEI, DONG QIYU, LIU RUI, et al, 2021. Isolation and identification of culturable intestinal bacteria from Clogmia albipunctata larvae and analysis of their digestive enzyme-producing activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control, 32(2): 224-229 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
梁飞龙, 毛勇, 余祥勇, 等, 2005. 方斑东风螺人工育苗试验[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 34(1): 79-85.
|
|
LIANG FEILONG, Mao YONG, et al, 2005. Experiment on artificial breeding of Babylonia areolata (lamrck)[J]. Haiyang Huzhao Tongbao, 34(1): 79-85 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
宋俊男, 2020. 水产养殖用益生菌的分离鉴定及其应用潜力评估[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学.
|
|
SONG JUNNAN, 2020. Genotyping of MLST and type 3 secretion system of a strain of Salmonella enteritidis[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
袁艳超, 2017. 蛋白酶高产菌株的筛选及其发酵芝麻粕制备芝麻多肽的研究[D]. 南昌: 江西师范大学.
|
|
YUAN YANCHAO, 2017. Screening of protease high yield strain and its application in preparation of Sesame Polypeptide from Sesame Meal[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
AMOAH K, DONG XIAOHUI, TAN BEIPING, et al, 2021. In vitro assessment of the safety and potential probiotic characteristics of three bacillus strains isolated from the intestine of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × Epinephelus lanceolatus♂)[J]. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 8: 675962.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.675962
|
| [7] |
DOBSON G T, DUY N D Q, PAUL N A, et al, 2020. Assessing potential for integrating sea grape (Caulerpa lentillifera) culture with sandfish (Holothuria scabra) and Babylon snail (Babylonia areolata) coculture[J]. Aquaculture, 522: 735135.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735135
|
| [8] |
GUPTA R S, PATEL S, SAINI N, et al, 2020. Robust demarcation of 17 distinct bacillus species clades, proposed as novel bacillaceae genera, by phylogenomics and comparative genomic analyses: description of Robertmurraya kyonggiensis sp. nov. and proposal for an emended genus bacillus limiting it only to the members of the Subtilis and Cereus clades of species[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 70(11): 5753-5798.
doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.004475
|
| [9] |
KIM M J, KU S, KIM S Y, et al, 2018. Safety evaluations of bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 and bifidobacterium longum BORI[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5): 1422.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19051422
|
| [10] |
KUEBUTORNYE F K A, ABARIKE E D, LU YIAHAN, 2019. A review on the application of bacillus as probiotics in aquaculture[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 87: 820-828.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.02.010
|
| [11] |
LEE R D, JOSPIN G, LANG J M, et al, 2015. Draft genome sequence of bacillus vietnamensis strain UCD-SED5 (Phylum Firmicutes)[J]. Genome Announcements, 3(6): e01376-15.
|
| [12] |
LIU YANBO, FU JUNYING, WANG LINLIN, et al, 2022. Isolation, identification, and whole-genome sequencing of high-yield protease bacteria from Daqu of Zhang Gong Laojiu[J]. PLoS One, 17(4): e0264677.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264677
|
| [13] |
NOGUCHI H, UCHINO M, SHIDA O, et al, 2004. Bacillus vietnamensis sp. nov., a moderately halotolerant, aerobic, endospore-forming bacterium isolated from Vietnamese fish sauce[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54(Pt6): 2117-2120.
doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02895-0
|
| [14] |
RUANGSRI J, THAWONSUWAN J, WANLEM S, et al, 2018. Effect of body size and sub-optimal water quality on some hemato-immunological parameters of spotted babylon snail babylonia areolata[J]. Fisheries Science, 84: 513-522.
doi: 10.1007/s12562-018-1191-8
|
| [15] |
TAMURA K, STECHER G, KUMAR S, 2021. MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38(7): 3022-3027.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120
pmid: 33892491
|
| [16] |
VERSCHUERE L, ROMBAUT G, SORGELOOS P, et al, 2000. Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 64(4): 655-671.
doi: 10.1128/MMBR.64.4.655-671.2000
pmid: 11104813
|
| [17] |
YI YANGLEI, ZHANG ZHENHUA, ZHAO FAN, et al, 2018. Probiotic potential of Bacillus velezensis JW: Antimicrobial activity against fish pathogenic bacteria and immune enhancement effects on Carassius auratus[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 78: 322-330.
doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.04.055
|
| [18] |
ZHAO WANG, HUANG XINGMEI, DENG ZHENGHUA, et al, 2022. Growth performance, digestive and immune enzyme activities, and the environmental effects of the ivory shell, Babylonia areolata (Link 1807) in integrated multi trophic aquaculture systems[J]. Aquaculture Research, 53(11): 4168-4177.
doi: 10.1111/are.v53.11
|
| [19] |
ZHOU JIANCONG, LIU CHUANG, YANG YUMEI, et al, 2023. Effects of long-term exposure to ammonia on growth performance, immune response, and body biochemical composition of juvenile ivory shell, Babylonia areolata[J]. Aquaculture, 562: 738857.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738857
|
| [20] |
ZOKAEIFAR H, BABAEI N, CHE R S, et al, 2014. Administration of Bacillus subtilis strains in the rearing water enhances the water quality, growth performance, immune response, and resistance against Vibrio harveyi infection in juvenile white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 36(1): 68-74.
|
 ), 高秀菊1,2, 葛东振2, 朱军2,3,4, 邹潇潇2,3,4, 黄惠琴2,3,4, 顾志峰1, 鲍时翔2,3,4(
), 高秀菊1,2, 葛东振2, 朱军2,3,4, 邹潇潇2,3,4, 黄惠琴2,3,4, 顾志峰1, 鲍时翔2,3,4( )
)
 ), GAO Xiuju1,2, GE Dongzhen2, ZHU Jun2,3,4, ZOU Xiaoxiao2,3,4, HUANG Huiqin2,3,4, GU Zhifeng1, BAO Shixiang2,3,4(
), GAO Xiuju1,2, GE Dongzhen2, ZHU Jun2,3,4, ZOU Xiaoxiao2,3,4, HUANG Huiqin2,3,4, GU Zhifeng1, BAO Shixiang2,3,4( )
)