热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 104-113.doi: 10.11978/2023178CSTR: 32234.14.2023178
2023年春季南沙珊瑚岛礁主要鱼类碳氮稳定同位素研究
邱星宇1,2( ), 刘庆霞2, 陈作志1,2, 蔡研聪2, 黄洪辉1,2,3(
), 刘庆霞2, 陈作志1,2, 蔡研聪2, 黄洪辉1,2,3( )
)
- 1.上海海洋大学水产与生命学院, 上海 201306
2.中国水产科学研究院南海水产研究所, 广东省渔业生态环境重点实验室, 广东 广州 510300
3.三亚热带水产研究院, 海南 三亚 572018
-
收稿日期:2023-11-27修回日期:2024-01-12出版日期:2024-11-10发布日期:2024-12-05 -
通讯作者:黄洪辉 -
作者简介:邱星宇(1995—), 男, 广东省茂名市人, 硕士研究生, 从事海洋生物与生态研究。email: 55874349@qq.com
-
基金资助:中国水产科学研究院中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费(2023TD15); 广东省渔业生态环境重点实验室开放基金项目(FEEL-2022-9); 中国水产科学研究院南海水产研究所中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费专项资金(2021SD03); 农业农村部财政专项(NFZX2021)
Characteristics of carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes of major fish species in coral reefs of the Nansha Islands in spring 2023
QIU Xingyu1,2( ), LIU Qingxia2, CHEN Zuozhi1,2, CAI Yancong2, HUANG Honghui1,2,3(
), LIU Qingxia2, CHEN Zuozhi1,2, CAI Yancong2, HUANG Honghui1,2,3( )
)
- 1. College of Fisheries and Life Science, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
2. South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fishery Ecology and Environment, Guangzhou 510300, China
3. Sanya Tropical Fisheries Research Institute, Sanya 572018, China
-
Received:2023-11-27Revised:2024-01-12Online:2024-11-10Published:2024-12-05 -
Contact:HUANG Honghui -
Supported by:Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS(2023TD15); Fund of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fishery Ecology and Environment(FEEL-2022-9); Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS(2021SD03); Financial Fund of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, P.R. China(NFZX2021)
摘要:
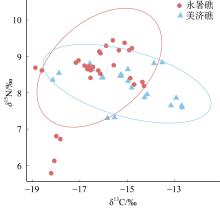
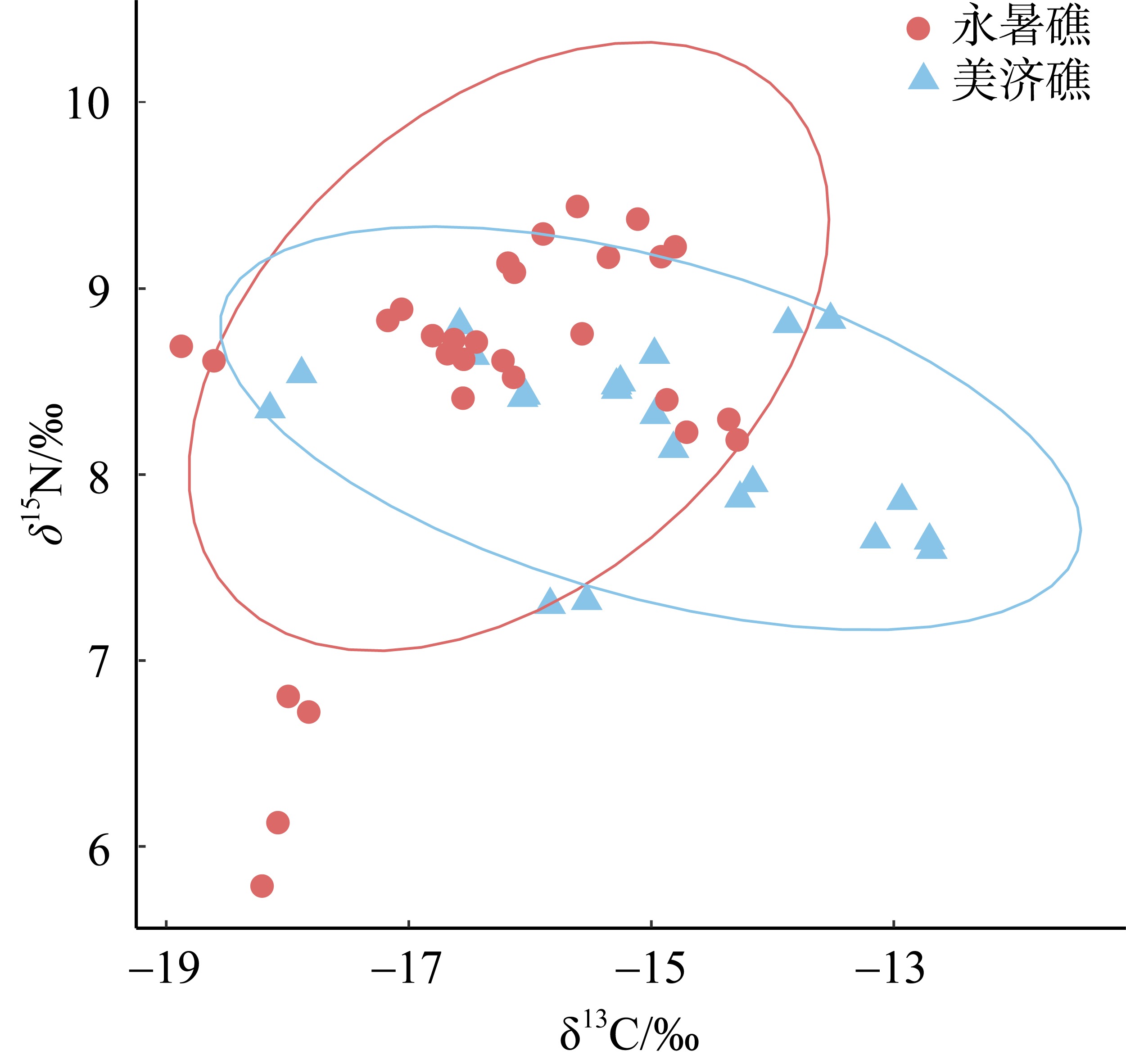
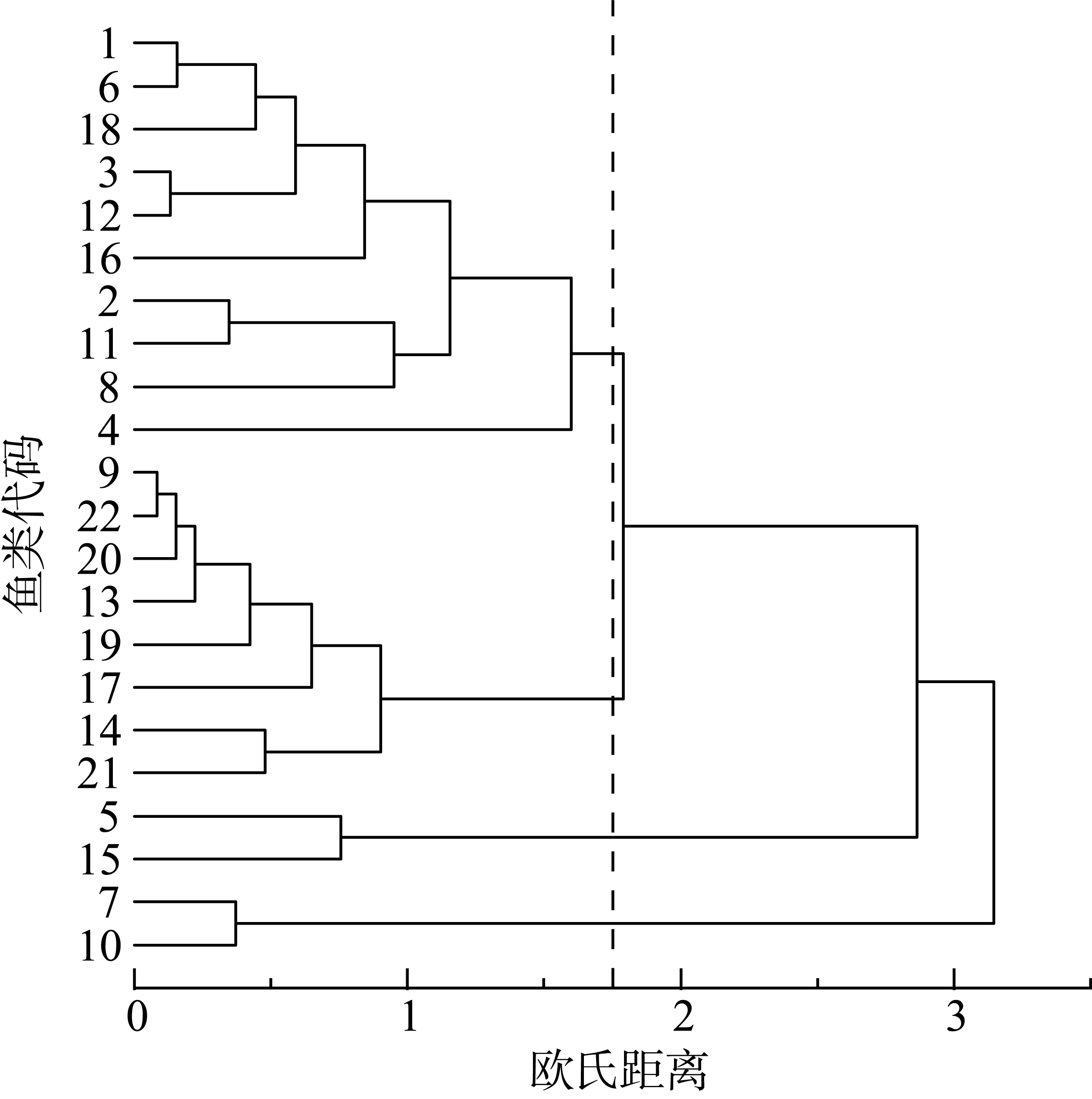
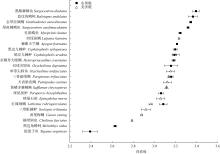
为了解南沙群岛珊瑚礁主要鱼类的营养结构特征, 本研究于2023年春季在南沙永暑礁和美济礁珊瑚礁海域采集了23种鱼类, 并应用碳、氮稳定同位素(δ13C和δ15N) 技术, 分析了珊瑚礁主要鱼类的营养结构特征和组成, 构建了连续营养级谱。永暑礁鱼类的δ13C介于-18.74‰~-14.33‰, 均值为(-16.33±1.28)‰; δ15N介于5.96‰~9.37‰, 均值为(8.46±0.48)‰。美济礁鱼类的δ13C介于-18.01‰~-12.70‰, 均值为(-15.02±1.53)‰; δ15N介于7.31‰~8.82‰, 均值为(8.21±0.93)‰。永暑礁和美济礁鱼类的δ13C值差异显著, 美济礁鱼类食物来源更广; δ15N值无显著性差异, 两者的营养层次结构组成相似。通过鱼类的碳氮稳定同位素聚类分析结果, 可将两个岛礁的鱼类均可划分为底栖性鱼类和底栖性、游泳性鱼类混合营养组群, 其中美济礁的营养组群划分模糊, 肉食性鱼类存在明显的摄食竞争情况。美济礁和永暑礁营养级范围分别为2.79~3.23和2.39~3.39, 两个珊瑚岛礁均以中、低营养级的肉食性鱼类为主, 大部分肉食性鱼类处于较窄的生态位范围内。与近岸热带亚热带海湾相比, 南沙珊瑚岛礁的鱼类群落营养结构组成更复杂, 食物来源更广泛, 群落冗余度较低。本研究结果可为南沙珊瑚岛礁渔业资源的保护和可持续管理提供基础资料和科学依据。
中图分类号:
- Q958
引用本文
邱星宇, 刘庆霞, 陈作志, 蔡研聪, 黄洪辉. 2023年春季南沙珊瑚岛礁主要鱼类碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 104-113.
QIU Xingyu, LIU Qingxia, CHEN Zuozhi, CAI Yancong, HUANG Honghui. Characteristics of carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes of major fish species in coral reefs of the Nansha Islands in spring 2023[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(6): 104-113.
表2
南沙群岛主要珊瑚礁鱼类的碳氮稳定同位素比值和基本信息"
| 珊瑚礁 | 代码 | 种类 | 科 | 属 | δ13 C/‰ | δ15 N/‰ | 体长范围/mm | 食性 | 主要食物来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 美济礁 | 1 | 单带尖唇鱼 Oxycheilinus unifasciatus | 隆头鱼科 | 尖唇鱼属 | -15.13±0.22 | 8.55±0.13 | 140~145 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、甲壳类 |
| 2 | 红裸颊鲷 Lethrinus rubrioperculatus | 裸颊鲷科 | 裸颊鲷属 | -14.22±0.07 | 7.91±0.06 | 154 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 3 | 蜂巢石斑 Epinephelus merra | 鮨科 | 石斑鱼属 | -14.89±0.11 | 8.23±0.13 | 124~127 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、小虾 | |
| 4 | 横带唇鱼 Cheilinus fasciatus | 隆头鱼科 | 尖唇鱼属 | -15.68±0.21 | 7.31±0.01 | 134 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物 | |
| 5 | 犬牙锥齿鲷 Pentapodus caninus | 金线鱼科 | 锥齿鲷属 | -18.01±0.18 | 8.45±0.13 | 133 | 肉食性 | 小鱼、浮游动物 | |
| 6 | 三带副绯鲤 Parupeneus trifasciatus | 羊鱼科 | 副绯鲤属 | -15.27±0.02 | 8.49±0.01 | 143~152 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 7 | 三带眶棘鲈 Scolopsis trilineata | 眶棘鲈科 | 眶棘鲈属 | -13.04±0.16 | 7.76±0.15 | 198 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 8 | 四线笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira | 笛鲷科 | 笛鲷属 | -13.7±0.25 | 8.82±0.02 | 145 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 9 | 尾纹九棘鲈 Cephalopholis urodeta | 鮨科 | 石斑鱼属 | -16.52±0.08 | 8.72±0.12 | 92~126 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、甲壳类 | |
| 10 | 黄尾梅鲷 Caesio cuning | 乌尾鮗科 | 梅鲷属 | -12.7±0.01 | 7.62±0.04 | 170 | 肉食性 | 浮游动物 | |
| 黄鳍多棘鳞鲀 Sufflamen chrysopterus | 鳞鲀科 | 鳞鲀属 | -16.05±0.04 | 9.219±0.17 | 152 | 杂食性 | 鱼类、藻类、底栖生物 | ||
| 永暑礁 | 11 | 斑尾拟鲈 Parapercis hexophthalma | 拟鲈科 | 拟鲈属 | -14.33±0.05 | 8.24±0.08 | 146~149 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物、浮游动物 |
| 12 | 红裸颊鲷 Lethrinus rubrioperculatus | 裸颊鲷科 | 裸颊鲷属 | -14.79±0.12 | 8.32±0.12 | 208 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 13 | 黑边九棘鲈 Cephalopholis spiloparaea | 鮨科 | 石斑鱼属 | -16.74±0.09 | 8.7±0.07 | 78~104 | 肉食性 | 鱼类 | |
| 14 | 黑鮨棘鳞鱼 Sargocentron diadema | 金鳞鱼科 | 棘鳞鱼属 | -15.75±0.2 | 9.37±0.1 | 127 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 15 | 灰鳍异大眼鲷 Heteropriacanthus cruentatus | 大眼鲷科 | 异大眼鲷属 | -18.74±0.19 | 8.65±0.06 | 95~141 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 16 | 金带齿颌鲷 Gnathodentex aureolineatus | 裸颊鲷科 | 裸颊鲷属 | -14.86±0.08 | 9.2±0.04 | 127~158 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 17 | 孔锯鳞鱼 Myripristis kuntee | 金鳞鱼科 | 棘鳞鱼属 | -17.12±0.08 | 8.86±0.04 | 83~114 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物 | |
| 18 | 棘眼天竺鲷 Apogon fraenatus | 天竺鲷科 | 天竺鲷属 | -15.57±0 | 8.76±0 | 108 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物 | |
| 19 | 三带副绯鲤 Parupeneus trifasciatus | 羊鱼科 | 副绯鲤属 | -16.18±0.06 | 8.57±0.06 | 111~145 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 20 | 双线尖唇鱼 Oxycheilinus digramma | 隆头鱼科 | 尖唇鱼属 | -16.5±0.08 | 8.56±0.21 | 180~192 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物 | |
| 21 | 尾斑棘鳞鱼 Sargocentron caudimaculatum | 金鳞鱼科 | 棘鳞鱼属 | -16.16±0.04 | 9.11±0.03 | 154 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 22 | 尾纹九棘鲈 Cephalopholis urodeta | 鮨科 | 石斑鱼属 | -16.59±0.06 | 8.67±0.07 | 91~112 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、甲壳类 | |
| 波纹钩鳞鲀 Balistapus undulatus | 鳞鲀科 | 鳞鲀属 | -15.23±0.17 | 9.27±0.14 | 175 | 杂食性 | 藻类、底栖生物、鱼类 | ||
| 黑边角鳞鲀 Melichthys vidua | 鳞鲀科 | 鳞鲀属 | -17.91±0.12 | 6.77±0.06 | 140~147 | 杂食性 | 藻类、底栖生物、鱼类 | ||
| 银篮子鱼 Siganus argenteus | 篮子鱼科 | 篮子鱼属 | -18.14±0.09 | 5.96±0.24 | 190~192 | 植食性 | 藻类 |
表3
永暑礁和美济礁主要鱼类群落营养结构指标参数"
| 参数指数 | 含义 | 美济礁 | 永暑礁 |
|---|---|---|---|
| δ15N范围(δ15N range, NR) | 指示生态系统中营养长度和多样性 | 1.51 | 3.41 |
| δ13C范围(δ13C range, CR) | 指示食物来源多样性 | 5.32 | 4.42 |
| 凸包总面积(total area, TA) | 表示食物网中营养多样性的总程度 | 5.15 | 8.40 |
| 到质心平均距离(average distance of centroid, CD) | 根据每个群落组成部分到质心的欧几里得距离计算, 表示生态位宽度和物种间距 | 1.31 | 1.27 |
| 平均最邻近距离(mean nearest neighbour distance, MNND) | 指示群落物种聚集的密度的均匀度, 表示营养生态位分布 | 0.64 | 0.52 |
| 最邻近距离标准差(standard deviation of nearest neighbour distance, SDNND) | 指群落物种空间密度均匀度参数, 表示营养冗余度 | 0.44 | 0.38 |
表4
南海及近岸主要渔业生物的营养结构指标对比"
| 区域 | CR | NR | MNND | SDNND |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南海中西部海域(黄佳兴 等, | 3.49 | 4.91 | 1.69 | 0.74 |
| 南沙群岛(宁加佳 等, | 3.4 | 4.3 | 0.37 | 0.43 |
| 大亚湾西南海域(张婉茹 等, | 2.83 | 4.18 | 0.31 | 0.23 |
| 南海中西部海域(孔业富 等, | 2.28 | 4.15 | - | - |
| 大亚湾珊瑚礁(朱文涛 等, | 5.92 | 3.72 | - | - |
| 华南典型海湾(张文博 等, | 4.45 | 4.66 | 0.6 | 0.54 |
| 大亚湾海域(汪慧娟 等, | 4.47 | 4.38 | 0.33 | 0.23 |
| 美济礁珊瑚岛礁(本研究) | 5.32 | 1.51 | 0.64 | 0.44 |
| 永暑礁珊瑚岛礁(本研究) | 4.42 | 3.41 | 0.52 | 0.38 |
表5
美济礁和永暑礁2016—2018年优势种鱼类"
| 永暑礁优势种鱼类 | 美济礁优势种鱼类 |
|---|---|
| 四带笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira* | 四带笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira* |
| 红牙鳞鲀Odonus niger | 长棘银鲈Gerres filamentosus |
| 金带齿颌鲷 Gnathodentex aureolineatus* | 无斑拟羊鱼Mulloidichthys vanicolensis* |
| 小鲔Euthynnus alletteratus | 蜂巢石斑鱼Epinephelus merra* |
| 榄色细齿笛鲷Aphareus furca* | 犬牙锥齿鲷 Pentapodus caninus* |
| 黑边角鳞鲀 Melichthys vidua* | 角棘鳞鱼Sargocentron cornutum* |
| 短吻弱棘鱼Malacanthus brevirostris | 黑斑条尾魟Taeniura melanospilos |
| 黄鳍多棘鳞鲀 Sufflamen chrysopterus | 太平洋裸颊鲷Lethrinus atkinsoni |
| 丝尾鼻鱼 Naso vlamingii | 红裸颊鲷 Lethrinus rubrioperculatus* |
| 黑边九棘鲈Cephalopholis spiloparaea* | 双带似天竺鲷Apogonichthyoides taeniatus* |
| 尾纹九棘鲈 Cephalopholis urodeta* | 尖吻棘鳞鱼argocentron spiniferum* |
| 桔带裸颊鲷 Lethrinus obsole | |
| 羽鳃鲐Rastrelliger kanagurta | |
| 隆背笛鲷 Lutjanus gibbus | |
| 三带眶棘鲈Scolopsis lineata* | |
| 三带副绯鲤 Parupeneus trifasciatus* | |
| 彼氏眶棘鲈Scolopsis affinis | |
| 横带唇鱼 Cheilinus fasciatus* |
| [1] |
陈玲, 王凯, 周曦杰, 等, 2016. 岛礁水域海藻场食物网基准生物的选择[J]. 海洋渔业, 38(4): 364-373.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈明强, 陈旭, 李有宁, 等, 2018. 美济礁合浦珠母贝吊笼养殖试验[J]. 水产科学, 37(3): 379-383.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈绍勇, 周伟华, 吴云华, 等, 2001. 南沙珊湖礁生态系生物体中δ13C的分布[J]. 海洋科学, 25(6): 4-7.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
何志成, 2001. 南沙美济礁鱼类养殖试验获得成功[J]. 中国水产, (3): 26 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
黄佳兴, 龚玉艳, 徐姗楠, 等, 2019. 南海中西部渔场主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(1): 76-84.
doi: 10.11978/2018041 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2018041 |
|
| [6] |
孔业富, 吴忠鑫, 颜云榕, 等, 2020. 基于碳氮稳定同位素的南海中西部海域春季中上层渔业生物群落营养结构[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(10): 3559-3567.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202010.038 |
|
|
|
| [7] |
刘华雪, 徐军, 李纯厚, 等, 2015. 南海南部浮游动物稳定同位素研究——氮稳定同位素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(2): 32-38.
|
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.02.005 |
|
| [8] |
刘胜, 林先智, 张黎, 等, 2021. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁鱼类生态图册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [9] |
宁加佳, 杜飞雁, 王雪辉, 等, 2016. 南沙群岛西南部陆架区底层鱼类营养结构研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(2): 468-475.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
石娟, 李纯厚, 王腾, 等, 2023. 万山群岛黄斑篮子鱼与云斑海猪鱼的营养生态位特征[J/OL]. 水产学报: 1-13. (2023-10-27)
|
|
[ 2023-11-26. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/31.1283.S.20231027.1614.002.
|
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
汪慧娟, 张文博, 黄洪辉, 等, 2021. 基于碳、氮稳定同位素的大亚湾渔业生物群落营养结构[J]. 南方水产科学, 17(5): 101-109.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
王静, 蒋日进, 胡翠林, 等, 2021. 基于胃含物分析和稳定同位素技术研究鳀的摄食生态[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(6): 2035-2044.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202106.029 |
|
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202106.029 |
|
| [13] |
王腾, 刘永, 李纯然, 等, 2022. 南沙美济礁海域隆背笛鲷繁殖和食性的初步研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 18(6): 78-84.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
徐雯, 杨蕊, 陈淦, 等, 2022. 基于胃含物和碳、氮稳定同位素研究浙江南部近海蓝圆鲹的摄食生态[J]. 应用生态学报, 33(11): 3097-3104.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202212.029 |
|
|
|
| [15] |
杨国欢, 孙省利, 侯秀琼, 等, 2012. 基于稳定同位素方法的珊瑚礁鱼类营养层次研究[J]. 中国水产科学, 19(1): 105-115.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
尹洪洋, 朱文涛, 马文刚, 等, 2022. 三亚蜈支洲岛海洋牧场区域夏季食物网研究[J]. 生态学报, 42(8): 3241-3253.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
张俊, 陈作志, 蔡研聪, 等, 2021. 南海美济礁瀉湖区鱼类优势种和生物多样性的长期变化[J]. 中国水产科学, 28(11): 1466-1476.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
张婉茹, 刘庆霞, 黄洪辉, 等, 2022. 2020年冬季大亚湾西南海域主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(3): 147-155.
doi: 10.11978/2021108 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2021108 |
|
| [19] |
张文博, 黄洪辉, 李纯厚, 等, 2019. 华南典型海湾主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 15(5): 9-14.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
赵焕庭, 宋朝景, 朱袁智, 1992. 南沙群岛“危险地带”腹地珊瑚礁的地貌与现代沉积特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 12(4): 368-377.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 等, 2022. 南海珊瑚礁鱼的食性探究[J]. 大自然, (4): 40-47 (in Chinese).
|
| [22] |
朱文涛, 秦传新, 马鸿梅, 等, 2020. 大亚湾珊瑚礁生态系统简化食物网的稳定同位素[J]. 水产学报, 44(7): 1112-1123.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00348-w pmid: 34697332 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2007)88[42:csirpf]2.0.co;2 pmid: 17489452 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [1] | 谢宏宇, 刘永, 李纯厚, 赵金发, 孙金辉, 沈建忠, 石娟, 王腾. 西沙群岛浪花礁珊瑚礁鱼类种类组成与演替[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(6): 114-128. |
| [2] | 雷明凤, 余克服, 廖芝衡, 陈飚, 黄学勇, 陈小燕. 西沙群岛银屿珊瑚礁的生态快速退化及其对鱼类的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 87-99. |
| [3] | 王子涵, 曾聪, 姜子禺, 曹玲. 东海及其邻近海域受胁鱼类保护空缺分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 66-86. |
| [4] | 张婉茹, 刘庆霞, 黄洪辉, 覃晓青, 李佳俊, 陈建华. 2020年冬季大亚湾西南海域主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [5] | 洪小帆, 陈作志, 江艳娥, 张俊, 王欢欢, 李媛洁, 李纲. 南海珊瑚礁海域黑缘尾九棘鲈生物学特征初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(4): 50-62. |
| [6] | 郑金海, 时健, 陈松贵. 珊瑚岛礁海岸多尺度波流运动特性研究新进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 44-56. |
| [7] | 陈启明, 刘松林, 张弛, 崔黎军, 江志坚, 吴云超, 黄小平. 海南典型热带海草床4种代表性鱼类的生长特征及其对海草资源量变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 62-70. |
| [8] | 李敏, 孔啸兰, 许友伟, 陈作志. 基于线粒体控制区序列的花斑蛇鲻遗传多态性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(4): 42-49. |
| [9] | 何思璇,何斌源. 防城河口湾鱼类群落结构及其与环境因子关系研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(5): 86-97. |
| [10] | 黄佳兴, 龚玉艳, 徐姗楠, 王欢欢, 张魁, 张俊, 陈作志. 南海中西部渔场主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(1): 76-84. |
| [11] | 司李真, 时伟, 杨敏, 龚理, 孔晓瑜. 硬骨鱼类核糖体基因间隔区的序列特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(6): 74-81. |
| [12] | 刘华雪, 许友伟, 陈作志, 张文博, 齐占会, 黄洪辉, 徐姗楠. 水母旺发对珠江口鱼类资源量的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(6): 68-73. |
| [13] | 管伟, 陈佳杰, 徐兆礼. 南日列岛西南部海区鱼类数量变化及其与水团关系*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(3): 65-71. |
| [14] | 张俊, 陈国宝, 江艳娥, 龚玉艳, 陈作志, 邱永松, 梁沛文. 南海中南部长钻光鱼渔业生物学初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(3): 62-67. |
| [15] | 肖瑜璋, 王蓉, 郑琰晶, 何薇. 珠江口鱼类浮游生物种类组成与数量分布[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(6): 80-87. |
|
||