热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 87-96.doi: 10.11978/2022057CSTR: 32234.14.2022057
基于ZooScan图像分析“海马”冷泉区浮游动物垂直分布特征
李若飞1,2( ), 柯志新1,2,3(
), 柯志新1,2,3( ), 李开枝1,2,3, 刘甲星1,2,3, 谭烨辉1,2,3
), 李开枝1,2,3, 刘甲星1,2,3, 谭烨辉1,2,3
- 1.中国科学院热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
-
收稿日期:2022-03-24修回日期:2022-05-01出版日期:2023-03-10发布日期:2022-05-05 -
通讯作者:柯志新。email:kzx@scsio.ac.cn -
作者简介:李若飞(1998—), 男, 研究方向为海洋浮游生态学。email: liruofei.ecology@foxmail.com
-
基金资助:南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(GML2019ZD0401); 国家自然科学基金项目(32171548); 国家自然科学基金项目(31971432); 国家自然科学基金项目(41976112); 国家科技基础资源调查专项(2017FY201404)
Vertical distribution of zooplankton in the “Haima” cold seep region based on ZooScan image analysis
LI Ruofei1,2( ), KE Zhixin1,2,3(
), KE Zhixin1,2,3( ), LI Kaizhi1,2,3, LIU Jiaxin1,2,3, TAN Yehui1,2,3
), LI Kaizhi1,2,3, LIU Jiaxin1,2,3, TAN Yehui1,2,3
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
-
Received:2022-03-24Revised:2022-05-01Online:2023-03-10Published:2022-05-05 -
Contact:KE Zhixin. email:kzx@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0401); National Natural Science Foundation of China(32171548); National Natural Science Foundation of China(31971432); National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976112); Science and Technology Basic Resources Investigation Program of China(2017FY201404)
摘要:
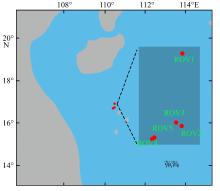
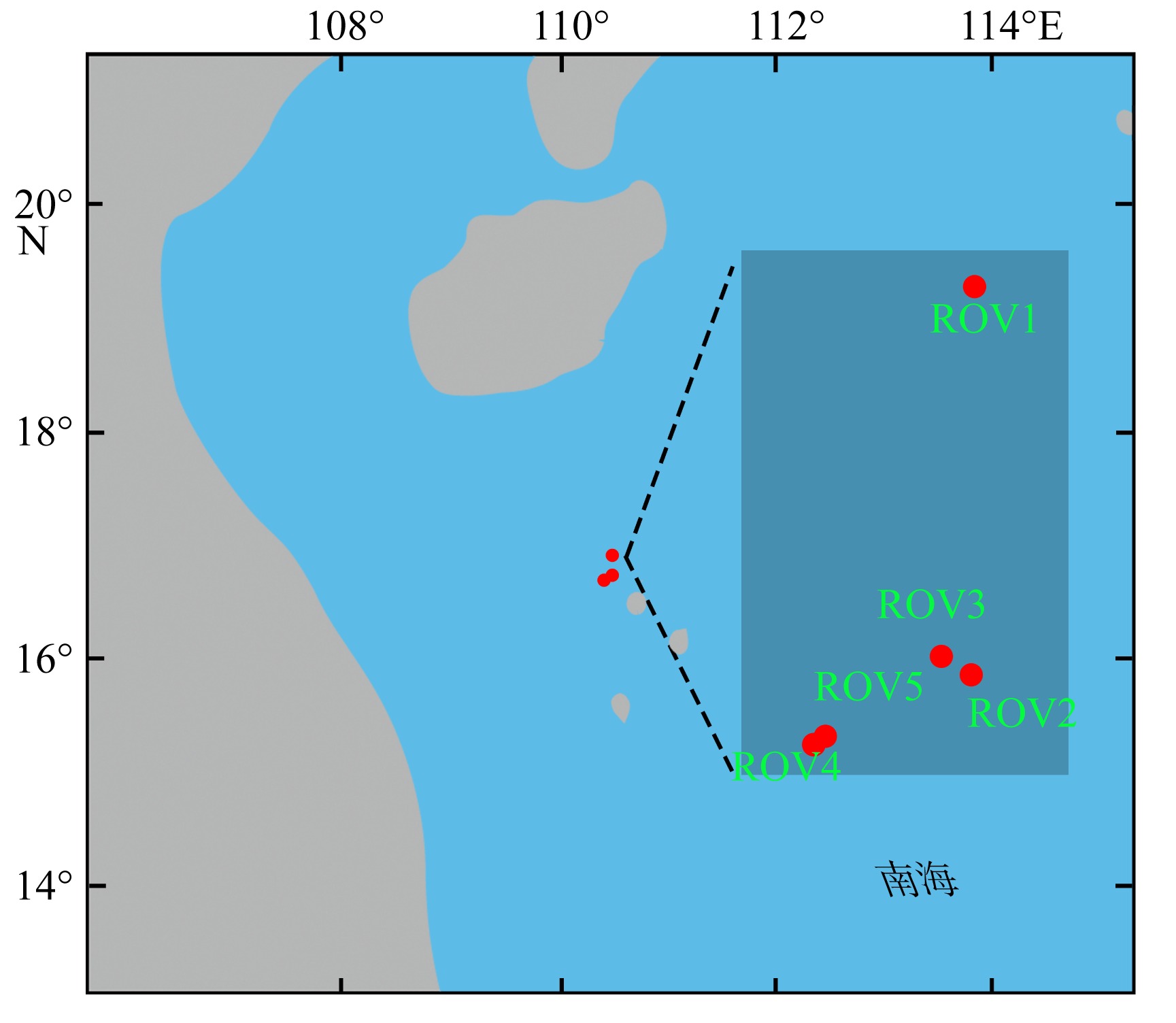
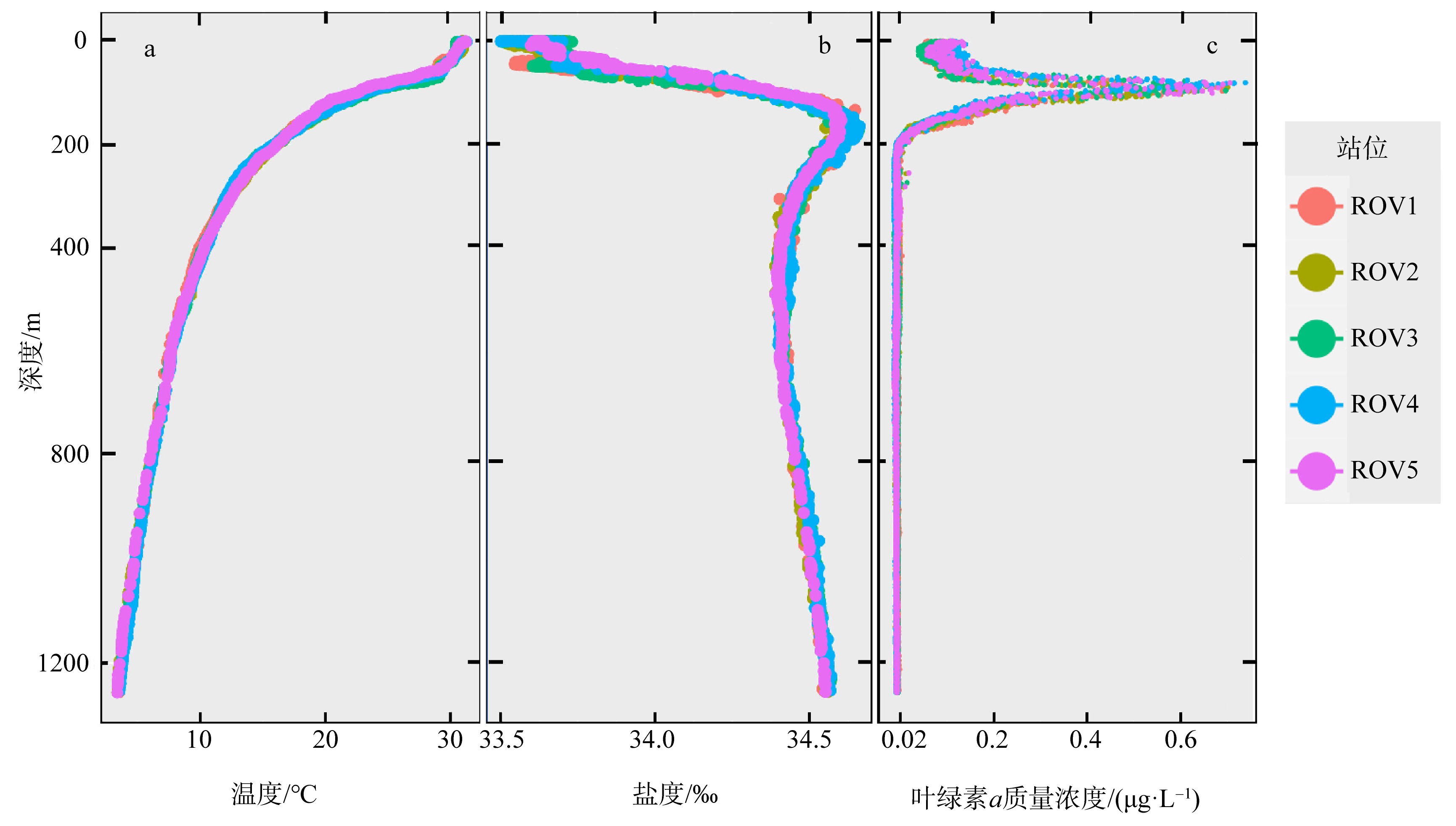
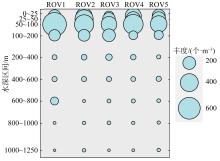
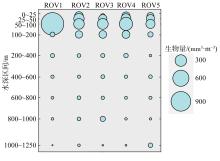
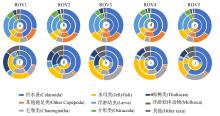
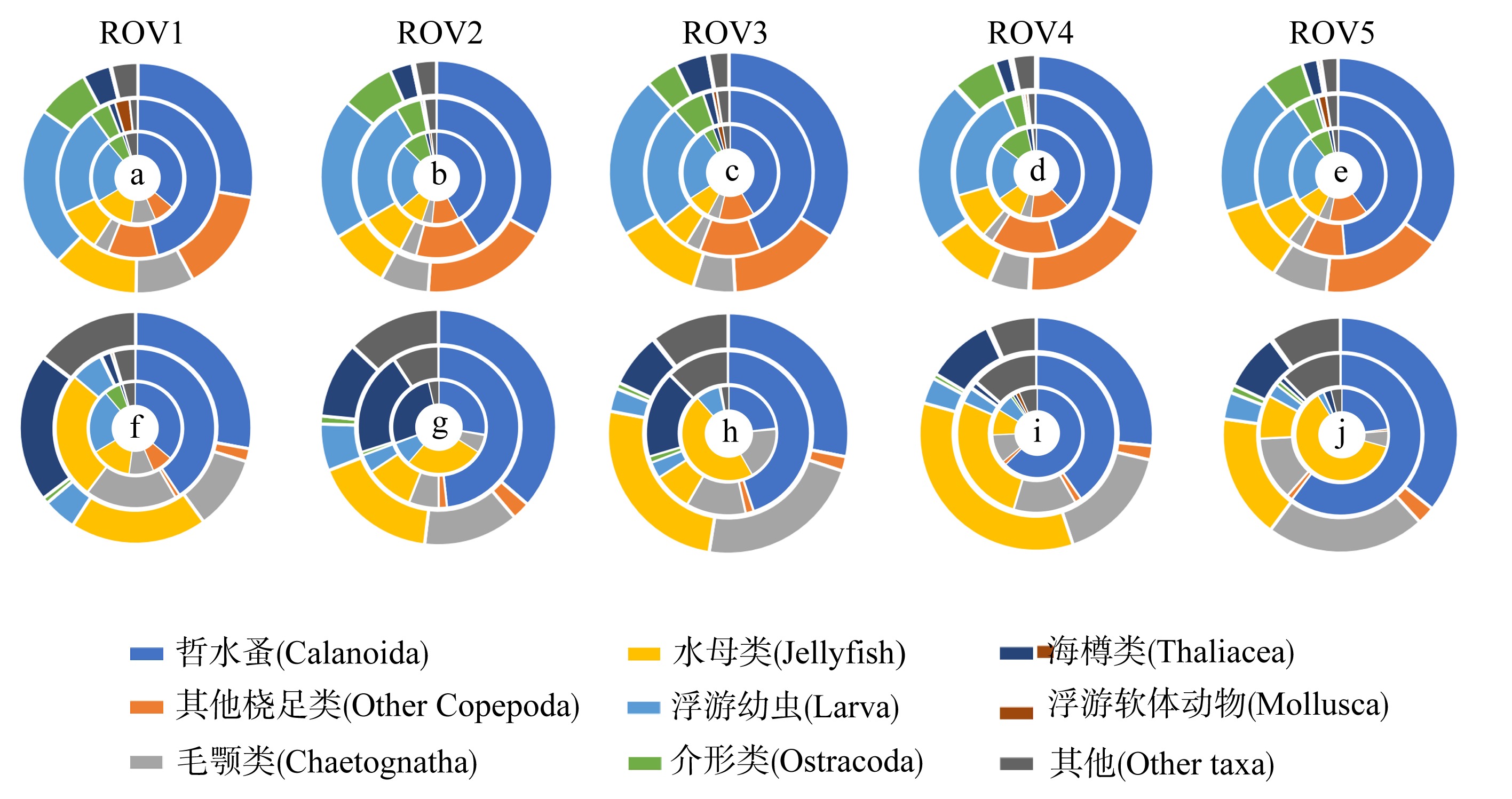
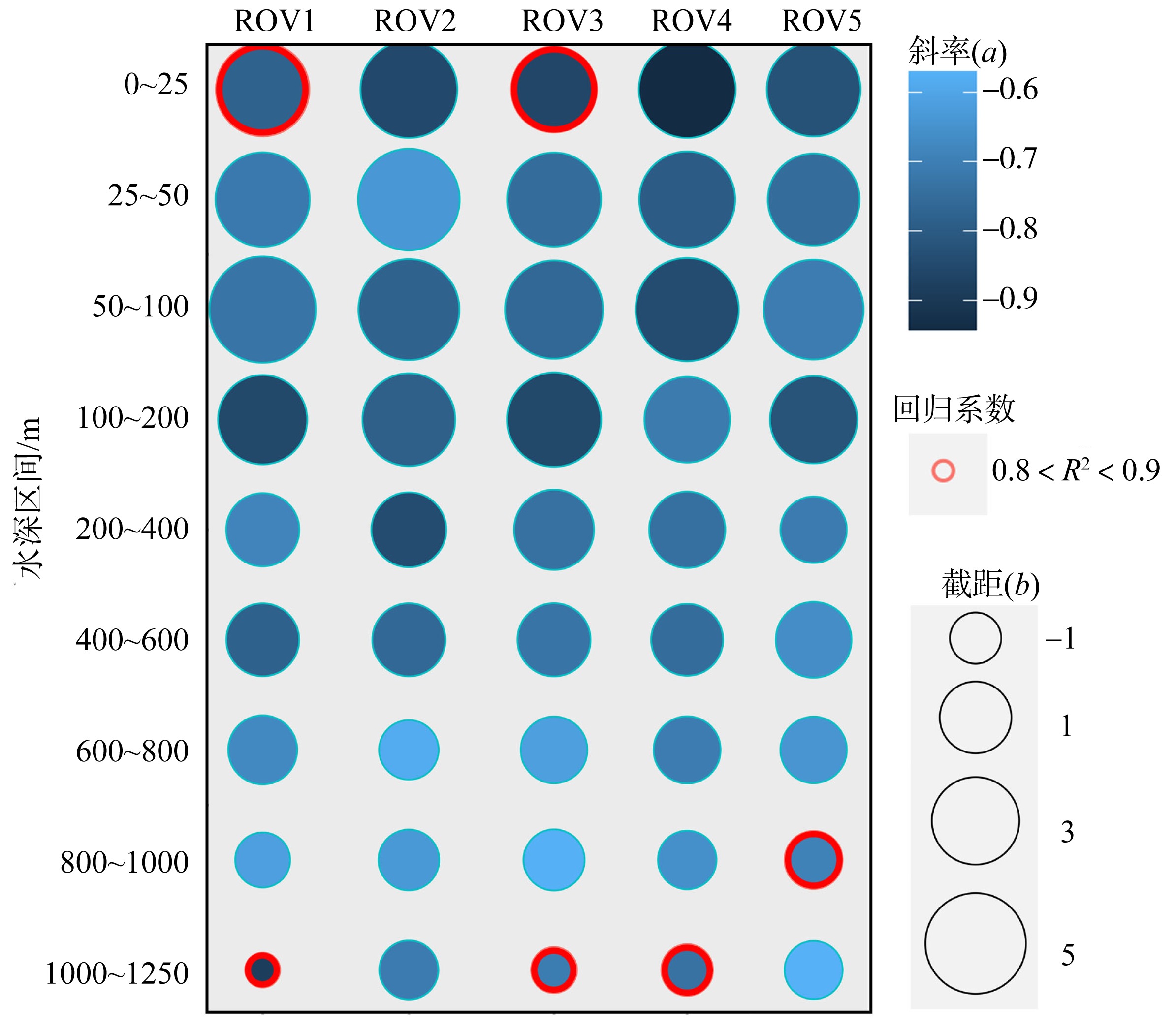
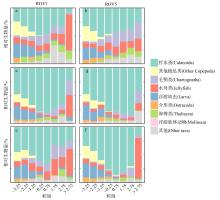
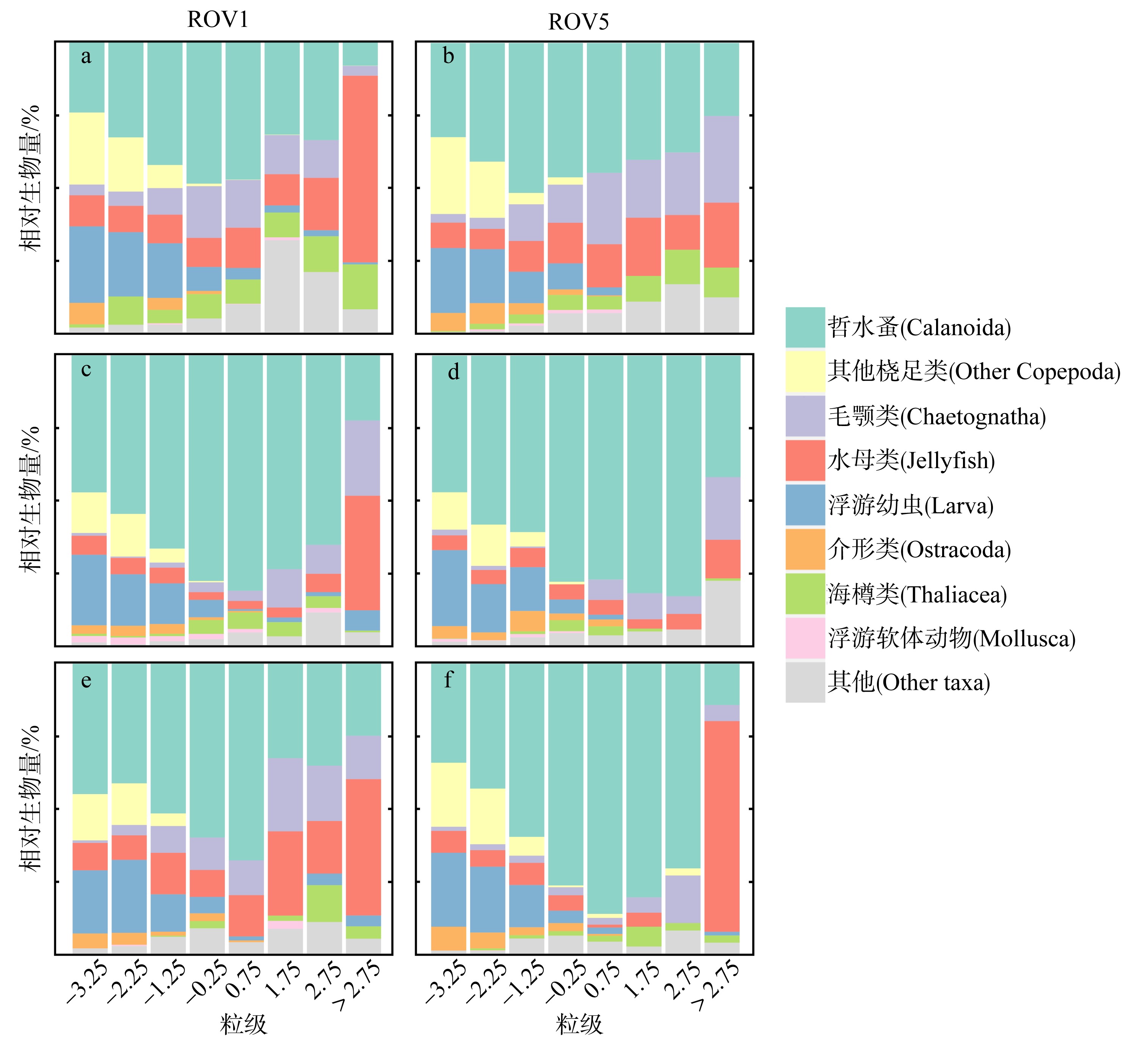
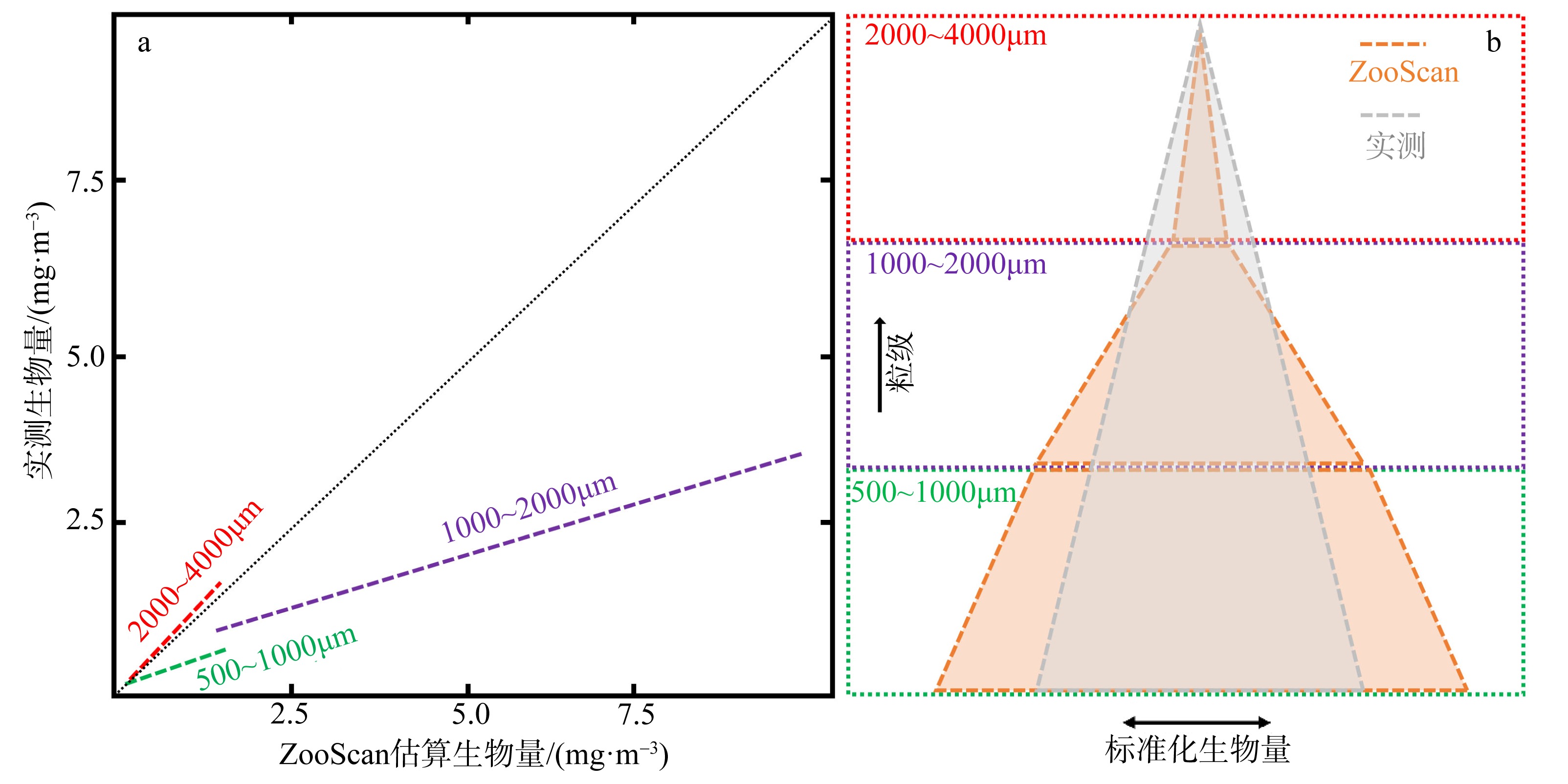
为了解“海马”冷泉区浮游动物的垂直分布以及冷泉活动可能对上方浮游动物群落产生的影响, 2020年9月在“海马”冷泉区的5个调查站位使用浮游生物分层拖网对1250m以浅的浮游动物垂直分布进行了调查。使用浮游动物图像扫描系统(ZooScan)对不同水层的浮游动物样品进行了分析, 获取了浮游动物的丰度、生物量和粒径谱的垂直分布特征。结果显示: 浮游动物丰度和生物量主要集中在0 ~ 100m水层, 低于100m后, 浮游动物的丰度和生物量随着水深增加均快速下降, 在1000 ~ 1250m水层平均分别仅为8.33个·m-3和12.10mm3·m-3。 总体看来, 桡足类是各水层浮游动物的优势类群, 胶质类浮游动物在深层中的占比上升。“海马”冷泉区不同站位和水层标准化生物量谱斜率的变动范围为-0.94 ~ -0.57, 截距的变化范围为-2.10 ~ 5.94。从表层到底层, 浮游动物标准化生物量谱基本呈现斜率逐渐增大而截距逐渐减小的趋势。这反映了浮游生态系统的生产力水平从表到底逐渐下降, 但浮游食物网的能量传递效率逐渐增加。甲烷气体渗漏强度最大的ROV1站位在1000 ~ 1250m水层表现出异常的粒径谱特征, 生物量谱的斜率a显著低于同水层其他站位, 同时在600 ~ 800m水层出现浮游动物丰度的相对高值, 推测该站位的浮游动物群落结构可能受到冷泉区甲烷渗漏的影响。
引用本文
李若飞, 柯志新, 李开枝, 刘甲星, 谭烨辉. 基于ZooScan图像分析“海马”冷泉区浮游动物垂直分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 87-96.
LI Ruofei, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, LIU Jiaxin, TAN Yehui. Vertical distribution of zooplankton in the “Haima” cold seep region based on ZooScan image analysis[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 87-96.
| [1] |
代鲁平, 李超伦, 王世伟, 等, 2016. 基于ZooScan图像技术的南黄海夏季浮游动物群落结构分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(4): 764-773.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
柯志新, 黄良民, 谭烨辉, 等, 2013. 2008年夏末南海北部叶绿素a的空间分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(4): 51-57.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.04.008 |
|
|
|
| [3] |
李开枝, 任玉正, 柯志新, 等, 2021. 南海东北部陆坡区中上层浮游动物的垂直分布[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(2): 61-73.
doi: 10.11978/2020061 |
|
|
|
| [4] |
连喜平, 谭烨辉, 刘永宏, 等, 2013. 两种浮游生物网对南海北部浮游动物捕获效率的比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(3): 33-39.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.03.005 |
|
|
|
| [5] |
孙松, 毕永坤, 孙晓霞, 2013. 基于图像技术的胶州湾浮游动物优势种体型参数与生物量转换关系研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 44(1): 15-22.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
赵静, 龚跃华, 何雪宝, 等, 2020. 南海北部陆坡西部海域“海马”冷泉甲烷渗漏及其海底表征[J]. 地球化学, 49(1): 108-118.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.3354/meps010257 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2016.12.003 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.06.018 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2012.12.012 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2015.11.004 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.3354/meps280163 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.2307/2937082 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.5697/oc.54-3.473 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2013.10.010 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbp124 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2011.10.003 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.2701 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1139/cjfas-2015-0222 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.5194/bg-12-5021-2015 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111699 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2020.103311 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.10.012 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.09.022 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.4319/lo.1993.38.2.0452 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1111/fwb.2013.59.issue-1 |
| [35] |
pmid: 17737352 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1002/lno.10640 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.4319/lo.1972.17.3.0327 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00951826 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(79)90066-9 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1080/00222933.2012.716866 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2018.07.004 |
| [43] |
pmid: 11847331 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.3354/meps130277 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.06.001 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1016/S0924-7963(01)00060-4 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.1080/17451000.2014.904882 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1007/s10872-013-0180-x |
| [49] |
doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbi119 |
| [1] | 柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | 李黛, 王旭东, 贾子策, 冯东. 深海极端环境黑碳的地球化学特征及其环境意义*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 20-32. |
| [3] | 胡思敏, 周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 李涛, 黄晖. 悬浮物对三亚珊瑚礁区浮游动物群落结构及其摄食的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [4] | 曾步燕, 梁志凤, 罗琴琴, 曾玲, 杨长庚, 王锂韫, 孙玉林. 深海真菌101#的分子鉴定、次生代谢产物及其生物活性研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 104-114. |
| [5] | 李牛, 邸鹏飞, 冯东, 陈多福. 冷泉渗漏对海洋沉积物氧化还原环境地球化学识别的影响——以南海东北部F站位活动冷泉为例*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 144-153. |
| [6] | 张兰兰, 程夏雯, 向荣, 邱卓雅, 常虎. 2019年春季孟加拉湾中部放射虫群落结构垂向变化*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [7] | 宋永相, 李晓悦, 鞠建华. 深海放线菌Streptomyces koyangensis SCSIO 5802中次级代谢产物neoabyssomicin H的分离鉴定*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 169-173. |
| [8] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [9] | 丛梦静, 胡怡伟, 赵凯, 张晓勇, 刘永宏, 王俊锋. 深海冷泉来源真菌Talaromyces helicus SCSIO41311中聚酮类化学成分研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 117-120. |
| [10] | 王俊锋, 周雯颖, 田新朋, 刘永宏. 深海热液真菌Fusarium sp. SCSIO 06196中抗病毒聚酮类化学成分研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 189-193. |
| [11] | 尹天齐, 王庆, 杨宇峰, 岑竞仪. 基于形态学和DNA分子鉴定的珠江口浮游动物群落结构比较研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 172-185. |
| [12] | 尹健强, 李开枝, 谭烨辉. 南海南部海域浮游介形类新种——南沙深海浮萤*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 193-197. |
| [13] | 李开枝, 柯志新, 王军星, 谭烨辉. 西沙群岛珊瑚礁海域浮游动物群落结构初步分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 121-131. |
| [14] | 王雪松, 陈忠, 许安涛, 田雨杭, 曹立, 张斌. 南海东北部深海盆末次冰盛期以来陆源碎屑粒度特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 158-170. |
| [15] | 洪义国, 吴佳鹏. 深海冷泉古菌厌氧甲烷氧化研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 76-82. |
|
||