热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 98-111.doi: 10.11978/2023107CSTR: 32234.14.2023107
人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征
柳原1,2( ), 柯志新1,3, 李开枝1(
), 柯志新1,3, 李开枝1( ), 谭烨辉1,2, 梁竣策1,2, 周伟华1
), 谭烨辉1,2, 梁竣策1,2, 周伟华1
- 1.中国科学院热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室, 广东省应用海洋生物学重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3.粤东上升流区海洋生态系统综合观测研究站, 广东 汕头 515041
-
收稿日期:2023-07-30修回日期:2023-09-02出版日期:2024-07-10发布日期:2024-07-22 -
作者简介:柳原(1997—), 男, 河南省郑州市人, 博士研究生, 主要从事海洋浮游动物生态学研究。email: liuyuan22@mails.ucas.ac.cn
-
基金资助:广东省科技计划项目(2021B1212050023); 广东省科技计划项目(2023B1212060047); 国家自然科学基金项目(32171548); 广东省基础与应用基础研究基金(2022A1515010656)
Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents
LIU Yuan1,2( ), KE Zhixin1,3, LI Kaizhi1(
), KE Zhixin1,3, LI Kaizhi1( ), TAN Yehui1,2, LIANG Junce1,2, ZHOU Weihua1
), TAN Yehui1,2, LIANG Junce1,2, ZHOU Weihua1
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Guangdong Provincial Observation and Research Station for Coastal Upwelling Ecosystem, Shantou 515041, China
-
Received:2023-07-30Revised:2023-09-02Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-07-22 -
Supported by:Special Fund for Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province of China(2021B1212050023); Special Fund for Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province of China(2023B1212060047); National Natural Science Foundation of China(32171548); Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2022A1515010656)
摘要:
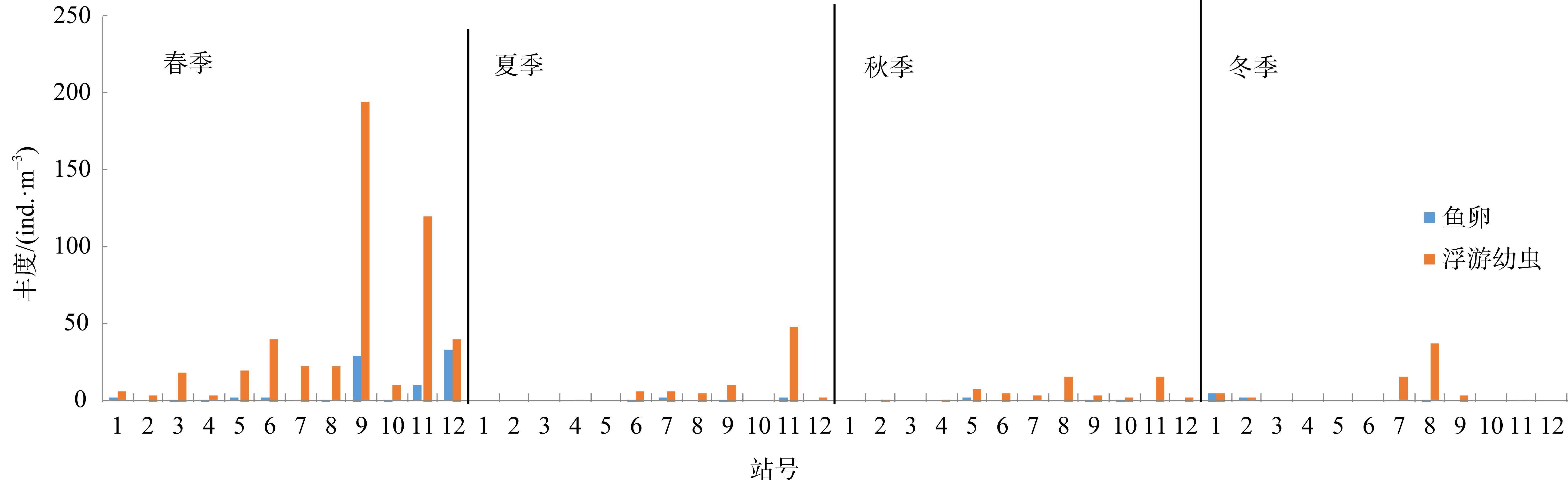
粤东附近海域具有丰富的渔业资源和复杂的水文环境。在气候变化背景下, 为系统提升该海域海洋观测水平和生态动力过程的认知, 于2022年5月(春季)、7月(夏季)、10月(秋季)和2023年1月(冬季)开展了四个季节的水文动力、生物、化学等生态环境要素的综合考察。基于镜检浮游动物的鉴定结果, 分析该海域浮游动物群落特征, 探讨其时空分布的影响因素。根据环境因子聚类, 调查海域可分为近岸(主要受人类活动影响)和远岸(主要为海流影响)区域, 不同季节和区域浮游动物群落结构存在显著差异。春、夏季浮游动物动物种类、生物量和丰度均高于秋、冬季; 远岸区浮游动物种数、生物量和丰度显著高于近岸, 并且浮游动物群落结构的季节差异在远岸区更加明显。桡足类和毛颚类为调查海域的主要浮游动物类群。浮游幼虫和鱼卵的丰度在春季显著高于其他季节, 并且峰值集中在南澳岛西南韩江口附近海域, 说明该区域为粤东重要的产卵场。受粤东沿岸上升流影响, 夏季桡足类的种类和丰度增加; 而冬季, 浮游动物主要由闽浙沿岸流所携带的暖温带种所组成, 中华哲水蚤(Calanus sinicus)在S8站位高达1000 ind.·m-3。另外, 近岸养殖区内的浮游动物出现种类少、生物量和丰度较低, 个别调查站网采样品基本无浮游动物检出。在人类活动和气候变化的双重影响下, 粤东近海浮游动物需要进行长期系统监测分析其对海洋环境变化的响应。
引用本文
柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 谭烨辉, 梁竣策, 周伟华. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 98-111.
LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111.
表1
2022年5月—2023年1月粤东近海浮游动物的种类组成"
| 类群 | 春季种类 | 夏季种类 | 秋季种类 | 冬季种类 | 合计 | 百分比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水螅水母类 Hydrozoa | 8 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 10 | 11.49 |
| 管水母类 Siphonophorae | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3.45 |
| 栉水母类 Ctenophores | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1.15 |
| 浮游多毛类 Polychaeta | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.15 |
| 浮游软体类 Mollusca | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2.30 |
| 枝角类 Cladocera | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.15 |
| 介形类 Ostracoda | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3.45 |
| 端足类 Amphipods | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2.30 |
| 桡足类Copepoda | 20 | 23 | 12 | 14 | 32 | 36.78 |
| 糠虾类 Mysids | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.15 |
| 磷虾类 Euphausiids | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2.30 |
| 十足类 Decapoda | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2.30 |
| 毛颚类 Chaetognatha | 7 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 9.20 |
| 浮游被囊类 Tunicates | 4 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 5.75 |
| 浮游幼虫 Planktonic larvae | 14 | 14 | 8 | 4 | 14 | 16.09 |
| 合计 Total | 67 | 72 | 36 | 32 | 87 | 100 |
表2
2022年5月—2023年1月粤东近海浮游动物各类群丰度(平均值±标准差, 单位为ind.·m-3)的变化"
| 类群 | 春季丰度 | 夏季丰度 | 秋季丰度 | 冬季丰度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水母类 Hydrozoa | 3.04±4.14 | 5.22±9.70 | 1.11±1.68 | 0.93±2.07 |
| 桡足类 Copepods | 9.12±12.44 | 36.78±12.44 | 12.72±14.26 | 34.20±40.23 |
| 毛颚类 Chaetognaths | 28.37±31.29 | 17.78±25.23 | 8.37±9.40 | 1.96±3.22 |
| 浮游被囊类 Pelagic tunicates | 8.94±18.39 | 3.51±6.19 | 0 | 2.00±5.29 |
| 浮游幼虫 Planktonic larvae | 41.61±55.11 | 6.54±12.97 | 4.86±5.35 | 5.24±10.41 |
| 其他类群Others | 6.70±11.59 | 7.73±10.63 | 3.53±4.81 | 0.71±0.84 |
表3
2022年5月—2023年1月粤东近海浮游动物优势种及其丰度(平均值±标准差, 单位为ind.·m-3)的变化"
| 类群 | 优势种 | 春季丰度 | 夏季丰度 | 秋季丰度 | 冬季丰度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 介形类 | 尖尾海萤Cypridina acuminata | - | - | 2.80±5.12 | - |
| 桡足类 | 太平洋纺锤水蚤Acartia pacifica | - | - | - | 2.68±7.51 |
| 刺尾纺锤水蚤Acartia spinicauda | - | 2.59±4.81 | - | - | |
| 厦门矮隆哲水蚤Bestiola amoyensis | - | - | - | 3.27 ±8.84 | |
| 中华哲水蚤Calanus sinicus | - | - | - | 18.20±24.38 | |
| 微刺哲水蚤Canthocalanus pauper | - | 3.68±6.20 | - | - | |
| 精致真刺水蚤Euchaeta concinna | - | - | 2.22±3.17 | 3.34±6.76 | |
| 亚强次真哲水蚤Subeucalanus subcrassus | - | 15.20±24.97 | 7.97±12.00 | 2.49±2.59 | |
| 锥形宽水蚤Temora turbinata | - | 5.60±8.58 | - | - | |
| 瘦歪水蚤Tortanus gracilis | - | 4.65±8.08 | - | - | |
| 十足类 | 亨生莹虾Lucifer hanseni | - | 4.67±7.85 | - | - |
| 毛颚类 | 肥胖箭虫Sagitta enflata | 25.07±33.60 | 15.57±21.55 | 1.99±3.14 | - |
| 拿卡箭虫Sagitta nagae | - | - | 5.09±9.22 | 1.32±1.75 | |
| 浮游被囊类 | 小齿海樽Doliolum denticulatum | 7.40±16.79 | - | - | - |
| 浮游幼虫 | 短尾类溞状幼虫Brachyura zoea larvae | 11.91±17.80 | - | 1.64±3.05 | - |
| 鱼卵Fish eggs | 6.94±11.12 | - | - | - | |
| 长尾类幼虫Macrura larvae | 14.19±22.29 | 3.32±7.28 | 2.15±2.70 | 4.32±10.08 |
表4
2022年5月—2023年1月粤东近海不同海区环境因子和浮游动物种数、生物量和丰度的季节变化及检验显著性"
| 季节和显著性检验 | 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | 叶绿素a浓度/(μg·L-1) | 浮游动物种数 | 浮游动物生物量 /(mg·m-3) | 浮游动物丰度 /(ind.·m-3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 近岸 | 春季 | 23.55±0.36 | 28.04±1.69 | 3.22±2.56 | 6±2 | 29.01±21.40 | 17.64±14.14 |
| 夏季 | 27.77±1.88 | 27.55±1.88 | 7.91±3.32 | 3±3 | 10.98±10.80 | 3.33±3.81 | |
| 秋季 | 25.79±0.34 | 29.55±1.40 | 1.81±0.94 | 5±2 | 56.45±63.79 | 18.58±29.80 | |
| 冬季 | 17.11±0.20 | 27.15±2.61 | 3.14±1.10 | 6±1 | 15.58±15.11 | 22.84±19.55 | |
| 远岸 | 春季 | 23.22±0.46 | 31.37±0.71 | 1.88±1.33 | 21±4 | 128.89±94.80 | 178.51±139.49 |
| 夏季 | 26.37±1.66 | 30.95±1.28 | 6.18±5.67 | 23±10 | 340.78±270.80 | 151.80±88.64 | |
| 秋季 | 25.91±0.16 | 31.33±1.47 | 1.07±0.35 | 16±2 | 117.97±115.30 | 42.61±21.70 | |
| 冬季 | 16.88±0.13 | 30.71±0.39 | 2.97±0.36 | 11±4 | 50.02±61.28 | 67.24±73.13 | |
| t-test | P=0.578 | P<0.001 | P=0.112 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | |
| [1] |
蔡德华, 陈振明, 唐书怿, 2020. 南澳岛周边海域海水质量近10年变化趋势浅析[J]. 环境影响评价, 42(2): 63-66.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
蔡尚湛, 靖春生, 许金电, 等, 2016. 粤东及闽南近岸上升流对局地风场变化的响应[J]. 海洋学报, 38(9): 1-12.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈丹婷, 柯志新, 谭烨辉, 等, 2020. 汕头南澳―东山海域营养盐季节分布特征及其对浮游植物生长的潜在性限制[J]. 生态科学, 39(4): 41-50.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
杜萍, 徐晓群, 徐旭丹, 等, 2017. 象山港三种不同养殖方式对浮游动物群落的影响[J]. 水产学报, 41(11): 1719-1733.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员, 2007. GB/T12763. 6-2007海洋调查规范第6部分:海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 6-37.
|
|
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, 2007. GB 17378. 6-2007 The specification for marine monitoring—Part 6: Marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 6-37 (in Chinese).
|
|
| [6] |
洪华生, 商少凌, 张彩云, 等, 2005. 台湾海峡生态系统对海洋环境年际变动的响应分析[J]. 海洋学报, 27(2): 63-69.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
黄长江, 陈善文, 何歆, 等, 2003. 2001—2002年粤东柘林湾浮游动物的生态学研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 34(2): 117-130.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
黄银爽, 欧林坚, 杨宇峰, 2017. 广东南澳岛大型海藻龙须菜与浮游植物对营养盐的竞争利用[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 48(4): 806-813.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
姜胜, 黄长江, 陈善文, 等, 2002. 2000—2001年柘林湾浮游动物的群落结构及时空分布[J]. 生态学报, 22(6): 828-840.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
柯志新, 陈丹婷, 谭烨辉, 等, 2019. 汕头南澳-东山海域初级生产力的时空特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 26(1): 44-52.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
黎素菊, 洪捷娴, 陈树鹏, 2022. 柘林湾养殖区氮、磷季节分布特征及富营养化评价[J]. 江西水产科技, (4): 45-47, 51. (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
连喜平, 谭烨辉, 黄良民, 等, 2011. 大亚湾大中型浮游动物的时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 海洋环境科学, 30(5): 640-645.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
刘陈, 魏南, 王庆, 等, 2019. 广东汕头南澳岛近岸海域浮游植物群落结构与环境特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(5): 1091-1098.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
刘萍, 宋洪军, 张学雷, 等, 2015. 桑沟湾浮游动物群落时空分布及养殖活动对其影响[J]. 海洋科学进展, 33(4): 501-511.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
潘翠红, 夏丽华, 吴志峰, 等, 2021. 柘林湾近岸水产养殖区水域叶绿素a浓度反演[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(1): 142-153.
doi: 10.11978/2019110 |
|
|
|
| [16] |
彭璇, 马胜伟, 陈海刚, 等, 2014. 夏季柘林湾-南澳岛海洋牧场营养盐的空间分布及其评价[J]. 南方水产科学, 10(6): 27-35.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
任玉正, 柯志新, 谭烨辉, 等, 2020. 广东省南澳岛东部海域浮游动物群落结构及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(2): 65-76.
doi: 10.11978/2019051 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2019051 |
|
| [18] |
舒业强, 王强, 俎婷婷, 2018. 南海北部陆架陆坡流系研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(3): 276-287.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
孙鲁峰, 李秀启, 徐兆礼, 2017. 东山湾浮游动物数量特征与养殖活动及水团关系分析[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 32(4): 465-472.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
孙松, 李超伦, 张光涛, 等, 2011. 胶州湾浮游动物群落长期变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 42(5): 625-631.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
孙松, 孙晓霞, 2014. 海洋生物功能群变动与生态系统演变[J]. 地球科学进展, 29(7): 854-858.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.07.0854 |
|
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.07.0854 |
|
| [22] |
王翠, 郭晓峰, 方婧, 等, 2018. 闽浙沿岸流扩展范围的季节特征及其对典型海湾的影响[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 37(1): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
王亮根, 杜飞雁, 陈丕茂, 等, 2016. 南澳岛北部海域浮游动物生态学特征及水团影响[J]. 南方水产科学, 12(5): 23-33.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
温浩, 宏波, 2020. 粤东沿岸上升流年际变化及其与渔业相关性分析[J]. 人民珠江, 41(7): 1-11, 17.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
许金电, 蔡尚湛, 宣莉莉, 等, 2014. 粤东至闽南沿岸海域夏季上升流的调查研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(2): 1-9.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2014.02.001 |
|
|
|
| [26] |
徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿, 1989. 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 8(4): 13-15, 19.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
义家吉, 颜历, 王洋, 等, 2023. 粤东近岸海域表层沉积物重金属污染评价及来源解析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 42(2): 200-208, 216.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
曾流明, 1986. 粤东沿岸上升流迹象的初步分析[J]. 热带海洋, 5(1): 68-73.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
张莹, 2022. 韩江口水体中营养盐的动力过程研究[D]. 汕头: 汕头大学.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
周枭, 颜秀利, 孙振宇, 等, 2023. 韩江口及邻近海域夏季营养盐和溶解有机质的河口化学特征[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 62(3): 385-396.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0913855107 pmid: 20479247 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25385-x pmid: 34471105 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1136256 pmid: 17510363 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36241-5 pmid: 36732509 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-015924 pmid: 27814033 |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [1] | 刘玓玓, 张喜洋, 孙富林, 王明壮, 谭飞, 施祺, 王冠, 杨红强. 南海海滩岩微生物群落结构和特定菌株对其成因机制的启示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [2] | 胡思敏, 周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 李涛, 黄晖. 悬浮物对三亚珊瑚礁区浮游动物群落结构及其摄食的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [3] | 江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [4] | 罗勇, 黄林韬, 杨剑辉, 练健生, 刘骋跃, 江雷, 梁宇娴, 陈伦举, 雷新明, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海南临高红牌—马袅沿岸海域造礁石珊瑚群落结构及其环境影响因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [5] | 许莉佳, 廖芝衡, 陈辉, 王永智, 黄柏强, 林巧云, 甘健锋, 杨静. 南海北部珊瑚群落结构特征及其对海洋热浪事件的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [6] | 赵明辉, 袁野, 张佳政, 张翠梅, 高金尉, 王强, 孙珍, 程锦辉. 南海北部被动陆缘洋陆转换带张裂-破裂研究新进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [7] | 耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [8] | 孙婷婷, 郝雯瑾, 徐鹏臻, 叶丽靖, 董志军. 海水酸化对海月水母螅状体共附生微生物的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 111-119. |
| [9] | 林少文, 任姮烨, 卢文芳. 越南沿岸上升流海表叶绿素的季节内尺度变异及机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 113-124. |
| [10] | 张兰兰, 程夏雯, 向荣, 邱卓雅, 常虎. 2019年春季孟加拉湾中部放射虫群落结构垂向变化*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [11] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [12] | 杨一凯, 曾丽丽. 挟带黑潮高盐水的中尺度涡在南海北部的时空特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 75-85. |
| [13] | 李若飞, 柯志新, 李开枝, 刘甲星, 谭烨辉. 基于ZooScan图像分析“海马”冷泉区浮游动物垂直分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 87-96. |
| [14] | 张金尚, 邹定辉, 马玉, 李锐祥, 刘愉强, 孟强, 刘同木, 史华明. 南海北部水团及中尺度现象对营养盐时空分布的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 168-181. |
| [15] | 陈靖夫, 钟瑜, 王磊, 郭雨沛, 邱大俊. 环境DNA分析大亚湾夜光藻藻华对真核浮游生物群落的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
|
||