热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 182-191.doi: 10.11978/2022120CSTR: 32234.14.2022120
大亚湾水质对人类活动响应的关键控制指标识别和量化解析
- 1.中国海洋大学, 海洋与大气学院, 山东 青岛 266100
2.中国海洋大学, 海洋发展研究院, 山东 青岛 266100
3.中国海洋大学, 物理海洋教育部重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266100
-
收稿日期:2022-05-25修回日期:2022-07-06出版日期:2023-01-10发布日期:2022-07-06 -
通讯作者:武文(1985—), 女, 山东枣庄人, 副教授, 博士, 主要研究方向为海洋管理。email:wenwu1985@ouc.edu.cn -
作者简介:姜迅(1996—), 女, 山东青岛人, 博士研究生, 主要研究方向为海洋管理。email: jiangxun@stu.ouc.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41806132)
Identification and quantitative analysis of key controlling factors of water quality response to human activities in the Daya Bay, China
JIANG Xun1( ), WU Wen1,2(
), WU Wen1,2( ), SONG Dehai3
), SONG Dehai3
- 1. College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
2. Institute of Marine Development of Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
3. Key Laboratory of Physical Oceanography, Ministry of Education, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, 266100, China
-
Received:2022-05-25Revised:2022-07-06Online:2023-01-10Published:2022-07-06 -
Contact:WU Wen. emails:wenwu1985@ouc.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41806132)
摘要:
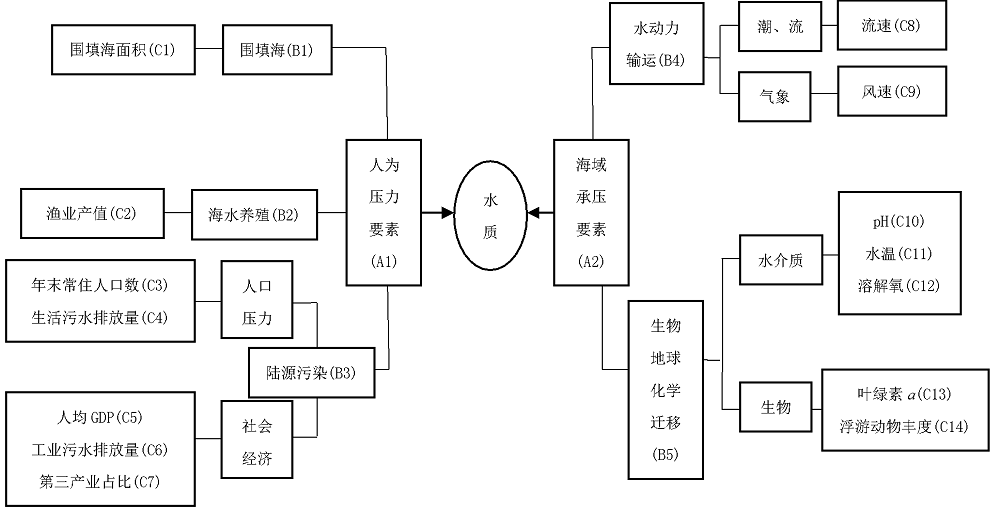
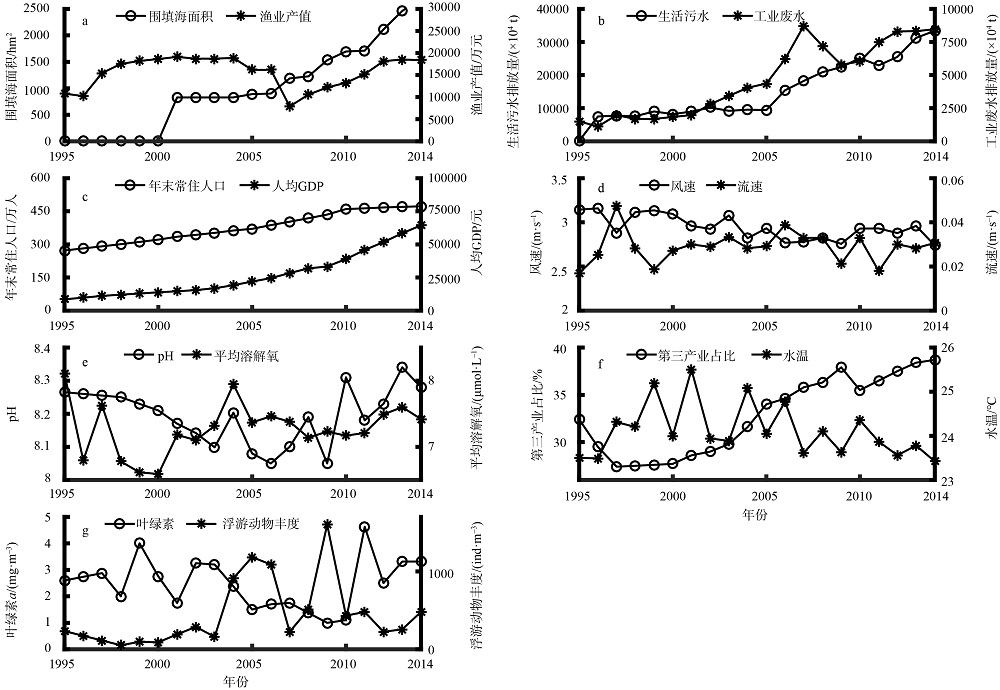
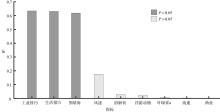
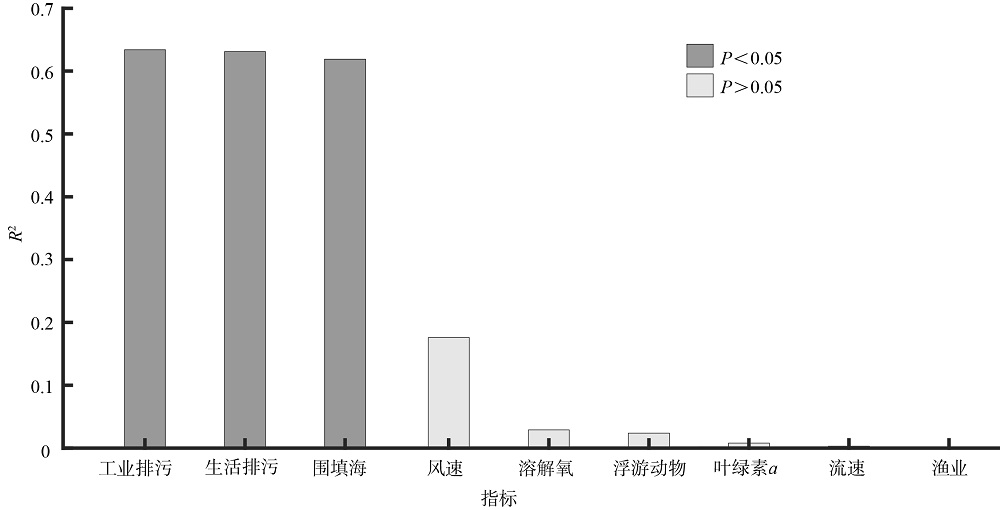
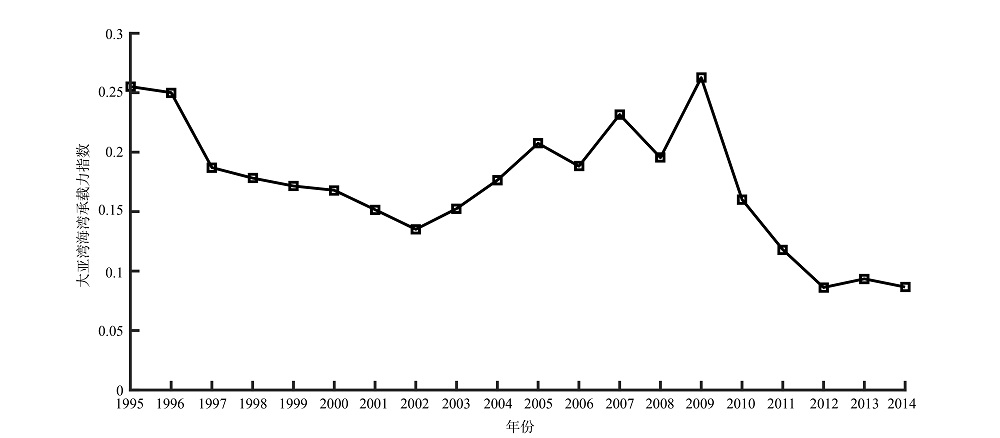
随着沿海地区经济和人口的不断发展, 人类活动对海湾水质状况的影响日渐加剧。本文以大亚湾为研究对象, 以近20年的调查统计数据为基础, 综合运用变异系数评价、双变量相关性分析、主成分分析、线性回归分析等方法, 对影响大亚湾水质的人为压力要素和海域承压要素所包含的指标进行筛选; 将自身变动幅度较大且对大亚湾水质产生主要影响的指标识别为关键控制指标, 并通过承载力占比的计算对关键控制指标进行量化解析, 继而对指标产生的水质效应进行定量评价。结果表明, 人为压力要素中的围填海面积、生活污水排放量和工业废水排放量这3个指标的变异性大、主成分综合载荷数较高且与大亚湾海域的主要污染物溶解无机氮含量的年际变化有显著相关性, 是影响大亚湾水质的关键控制指标。对这3个指标进行承载力占比计算的结果显示, 围填海面积、生活污水排放量和工业废水排放量的承载力占比分别为6.19%、5.07%和17.51%, 其中工业废水排放的占比最高, 对海湾承载力的影响最大。以上研究显示, 人类活动是造成大亚湾水质恶化的主要原因, 为有效改善大亚湾的海洋环境质量、提高管理水平, 应从岸线整治修复和陆源排污(尤其是工业废水的排放)控制入手, 科学制定管理方案, 推动大亚湾地区的可持续发展。
引用本文
姜迅, 武文, 宋德海. 大亚湾水质对人类活动响应的关键控制指标识别和量化解析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 182-191.
JIANG Xun, WU Wen, SONG Dehai. Identification and quantitative analysis of key controlling factors of water quality response to human activities in the Daya Bay, China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 182-191.
表1
Pearson相关性分析结果"
| 指标 | 围填海(C1) | 渔业(C2) | 人口(C3) | 生活污水(C4) | 人均GDP(C5) | 工业废水(C6) | 第三产业(C7) | 流速(C8) | 风速(C9) | DO(C12) | 叶绿素a (C13) | 浮游动物(C14) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 围填海(C1) | 1 | |||||||||||
| 渔业(C2) | 0.104 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 人口(C3) | 0.955** | 0.021 | 1 | |||||||||
| 生活污水(C4) | 0.941** | 0.008 | 0.948** | 1 | ||||||||
| 人均GDP(C5) | 0.962** | 0.09 | 0.937** | 0.966** | 1 | |||||||
| 工业废水(C6) | 0.891** | -0.158 | 0.930** | 0.892** | 0.889** | 1 | ||||||
| 第三产业(C7) | 0.874** | -0.28 | 0.890** | 0.846** | 0.868** | 0.916** | 1 | |||||
| 流速(C8) | -0.033 | -0.08 | -0.023 | -0.074 | 0.007 | -0.127 | 0.083 | 1 | ||||
| 风速(C9) | 0.635* | -0.101 | 0.659** | 0.611** | 0.551** | 0.726** | 0.650** | -0.416 | 1 | |||
| DO(C12) | -0.289 | 0.089 | -0.181 | -0.087 | -0.216 | -0.297 | -0.397 | 0.172 | -0.398 | 1 | ||
| 叶绿素a (C13) | 0.004 | 0.396 | -0.066 | 0.003 | 0.114 | -0.087 | -0.183 | 0.308 | -0.35 | 0.088 | 1 | |
| 浮游动物(C14) | -0.282 | 0.129 | -0.357 | -0.218 | -0.187 | -0.304 | -0.482* | -0.06 | -0.596** | 0.27 | 0.476* | 1 |
表2
主成分分析的解释总方差"
| 成分 | 初始特征值 | 旋转载荷平方和 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总计 | 方差百分比/% | 累积/% | 总计 | 方差百分比/% | 累积/% | |
| 1 | 3.776 | 41.952 | 41.952 | 3.366 | 37.402 | 37.402 |
| 2 | 1.754 | 19.488 | 61.44 | 1.797 | 19.971 | 57.373 |
| 3 | 1.162 | 12.912 | 74.353 | 1.528 | 16.98 | 74.353 |
| 4 | 0.926 | 10.288 | 84.641 | |||
| 5 | 0.832 | 9.245 | 93.886 | |||
| 6 | 0.341 | 3.786 | 97.672 | |||
| 7 | 0.115 | 1.275 | 98.947 | |||
| 8 | 0.071 | 0.793 | 99.741 | |||
| 9 | 0.023 | 0.259 | 100 | |||
表3
主成分矩阵及综合载荷数"
| 指标 | 主成分 | Fsum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | ||
| 围填海(C1) | 0.972 | 0.03 | -0.07 | 0.951 |
| 渔业(C2) | 0.044 | 0.742 | -0.2 | 0.593 |
| 生活污水(C4) | 0.953 | 0.025 | -0.018 | 0.909 |
| 工业废水(C6) | 0.935 | -0.151 | -0.116 | 0.910 |
| 流速(C8) | 0.024 | -0.084 | 0.925 | 0.863 |
| 风速(C9) | 0.678 | -0.358 | -0.526 | 0.865 |
| 溶解氧(C12) | -0.258 | 0.203 | 0.41 | 0.276 |
| 叶绿素a (C13) | 0.078 | 0.767 | 0.389 | 0.746 |
| 浮游动物(C14) | -0.323 | 0.677 | 0.134 | 0.581 |
| [1] |
黄小平, 黄良民, 宋金明, 等, 2019. 营养物质对海湾生态环境影响的过程与机理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
柯东胜, 李秀芹, 彭晓鹃, 等, 2010. 大亚湾生态环境问题及其调控策略[J]. 生态科学, 29(2): 186-191.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
李纯厚, 林琳, 徐姗楠, 等, 2013. 海湾生态系统健康评价方法构建及在大亚湾的应用[J]. 生态学报, 33(6): 1798-1810.
|
|
doi: 10.5846/stxb |
|
| [4] |
李纯厚, 徐姗楠, 杜飞雁, 等, 2015. 大亚湾生态系统对人类活动的响应及健康评价[J]. 中国渔业质量与标准, 5(1): 1-10.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
陆志强, 李吉鹏, 章耕耘, 等, 2015. 基于可变模糊评价模型的东山湾生态系统健康评价[J]. 生态学报, 35(14): 4907-4919.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
罗先香, 杨建强, 2009. 海洋生态系统健康评价的底栖生物指数法研究进展[J]. 海洋通报, 28(3): 106-112.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
彭云辉, 孙丽华, 陈浩如, 等, 2002. 大亚湾海区营养盐的变化及富营养化研究[J]. 海洋通报, 21(3): 44-49.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
曲修齐, 刘淼, 李春林, 等, 2019. 生态承载力评估方法研究进展[J]. 气象与环境学报, 35(4): 113-119.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
王聪, 林军, 陈丕茂, 等, 2009. 年平均风场作用下大亚湾水交换的数值模拟[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 18(3): 351-358.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
王淑萍, 2017. 青岛近海环境质量效控要素量化解析研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
王友绍, 王肇鼎, 黄良民, 2004. 近20年来大亚湾生态环境的变化及其发展趋势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 23(5): 85-95.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
王友绍, 2014. 大亚湾生态环境与生物资源[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
王肇鼎, 练健生, 胡建兴, 等, 2003. 大亚湾生态环境的退化现状与特征[J]. 生态科学, 22(4): 313-320.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
翁骏超, 袁琳, 张利权, 等, 2015. 象山港海湾生态系统综合承载力评估[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (4): 110-122.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
谢艳辉, 李涛, 简伟军, 等, 2015. 海水升温对大亚湾浮游植物群落结构和光合活性的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(2): 24-31.
|
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.02.004 |
|
| [16] |
杨进, 李纯厚, 贾晓平, 等, 2011. 大亚湾杨梅坑人工鱼礁区生态系统健康评价[J]. 生态科学, 30(4): 399-405, 410.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
杨文超, 黄道建, 陈继鑫, 等, 2020. 大亚湾海域2009—2015年氮、磷营养盐时空分布及富营养化评价[J]. 南方水产科学, 16(2): 54-61.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.1007/s12601-014-0029-2 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2005.07.021 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123988 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2011.03.010 |
| [22] |
pmid: 17418874 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101464 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.03.007 |
| [26] |
pmid: 17069873 |
| [27] |
pmid: 16206027 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2005.09.004 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: S0025-326X(19)30526-0 pmid: 31426174 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107310 |
| [32] |
pmid: 12946893 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.07.017 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2016.09.004 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124945 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111694 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.12.035 |
| [1] | 奚琛, 林宗轩, 萨如拉, 邓玺, 刘强, 倪亮, 罗来才, 马腾, 谢智杰, 陈思若, 陈松泽. 基于双浮标连续监测资料分析大亚湾西南部海域水体环境变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [2] | 孙翠慈, 岳维忠, 赵文杰, 王友绍. 大亚湾表层沉积物碳水化合物活性酶基因分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [3] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [4] | 陈靖夫, 钟瑜, 王磊, 郭雨沛, 邱大俊. 环境DNA分析大亚湾夜光藻藻华对真核浮游生物群落的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [5] | 郭俊丽, 时连强, 陈沈良, 张敏, 常洋, 张达恒. 台风季节朱家尖岛砂、砾质岬湾海滩的不同沉积地貌动态变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 82-96. |
| [6] | 张婉茹, 刘庆霞, 黄洪辉, 覃晓青, 李佳俊, 陈建华. 2020年冬季大亚湾西南海域主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [7] | 马玉婷, 蔡华阳, 杨昊, 刘锋, 陈欧, 谢荣耀, 欧素英, 杨清书. 珠江磨刀门河口水位分布演变特征及其对人类活动的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 52-64. |
| [8] | 李尧, 向晨晖, 江志坚, 宋星宇. 大亚湾夏季浮游群落生产代谢特征及其影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 83-92. |
| [9] | 向晨晖, 刘甲星, 柯志新, 周林滨, 谭烨辉. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构和种类组成对淡澳河河口水加富的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(2): 49-60. |
| [10] | 蔡建楠, 刘海龙, 姜波, 陈吟晖, 李杰鸿, 吴思晓, 梁建霞, 黄华, 邢前国. 珠江口河网水体非光学活性水质参数高光谱反演[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(1): 58-64. |
| [11] | 张立明, 谭烨辉, 李佳俊, 黄小平, 刘甲星. 大亚湾夏季浮游植物群落结构及对淡澳河输入的响应特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [12] | 赵聪蛟, 刘希真, 付声景, 姚炜民, 周燕, 马骏. 基于水质浮标在线监测的米氏凯伦藻赤潮过程及环境因子变化特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 88-97. |
| [13] | 杨留柱, 杨莉玲, 潘洪州, 刘超群, 喻丰华. 人类活动影响下的钦州湾近期滩槽冲淤演变特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(6): 41-50. |
| [14] | 王卉,李恒翔,李路,严岩. 大亚湾大型海藻丛的大角玻璃钩虾种群分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(4): 52-58. |
| [15] | 谢福武, 宋星宇, 谭烨辉, 谭美婷, 黄亚东, 刘华雪. 模拟升温和营养盐加富对大亚湾浮游生物群落代谢的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(2): 48-57. |
|
||