热带海洋学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 49-60.doi: 10.11978/2020040CSTR: 32234.14.2020040
大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构和种类组成对淡澳河河口水加富的响应*
向晨晖1,2,3,4( ), 刘甲星1, 柯志新1, 周林滨1, 谭烨辉1,2,3,4(
), 刘甲星1, 柯志新1, 周林滨1, 谭烨辉1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1.中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室, 广东省应用海洋生物学重点实验室, 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室, 广东 广州 510301
4.中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 广东 广州 510301
-
收稿日期:2020-04-14修回日期:2020-06-01出版日期:2021-03-10发布日期:2020-06-01 -
通讯作者:谭烨辉 -
作者简介:向晨晖(1992—), 女, 广东省珠海市人, 博士, 研究方向为海洋浮游生物生态学。email:xiangchenhui0615@163.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(31971432);国家自然科学基金(41506161);南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)项目(GML2019ZD0405);广东省海洋经济发展项目(GDOE[2019]A32);广东省省级科技计划项目(2017B0303014052);中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院自主部署项目(ISEE2018PY01)
Phytoplankton responses to Dan’ao River estuary water enrichment in terms of size structure and community composition*
XIANG Chenhui1,2,3,4( ), LIU Jiaxing1, KE Zhixin1, ZHOU Linbin1, TAN Yehui1,2,3,4(
), LIU Jiaxing1, KE Zhixin1, ZHOU Linbin1, TAN Yehui1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 510301, China
4. Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, 510301, China
-
Received:2020-04-14Revised:2020-06-01Online:2021-03-10Published:2020-06-01 -
Contact:TAN Yehui -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of China(31971432);Natural Science Foundation of China(41506161);Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0405);Guangdong Marine Economy Promotion Projects Fund(GDOE[2019]A32);Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China(2017B0303014052);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2018PY01)
摘要:
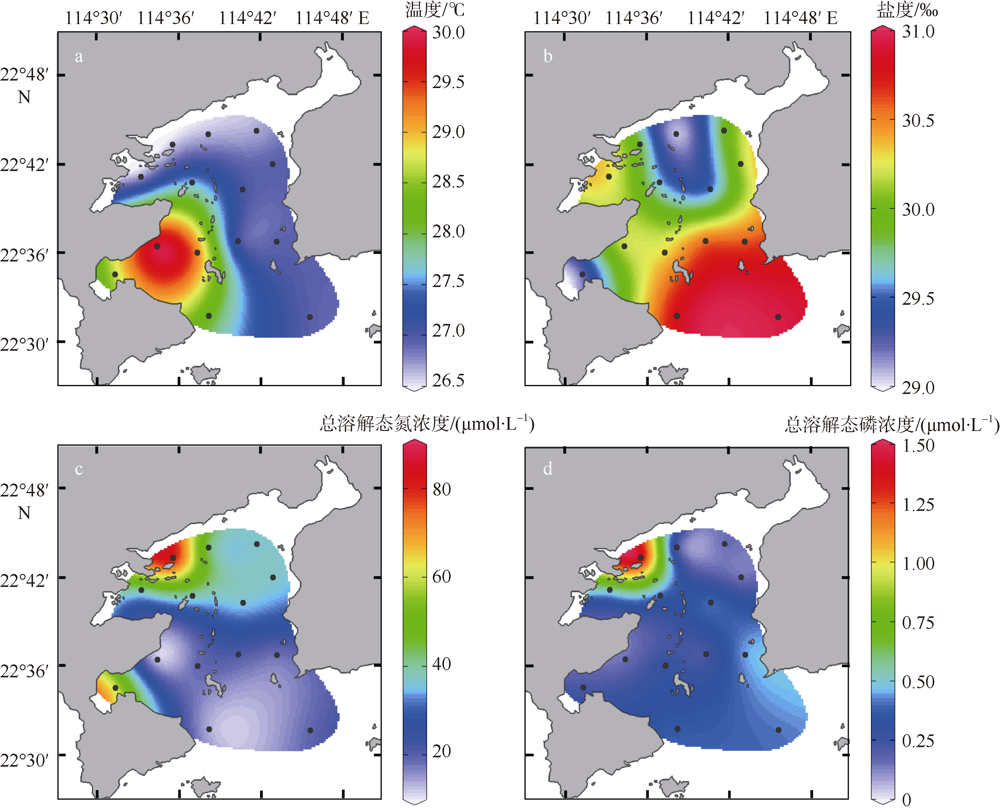
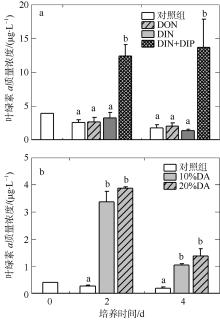
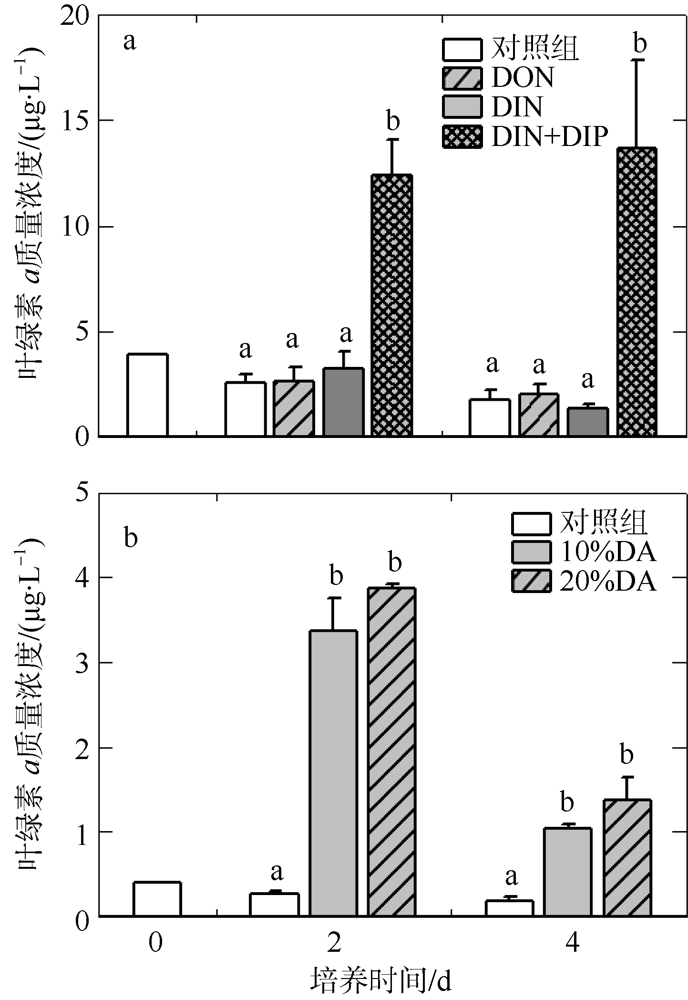
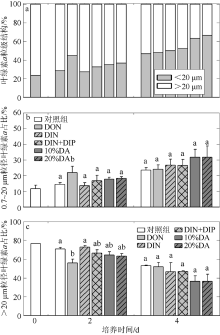
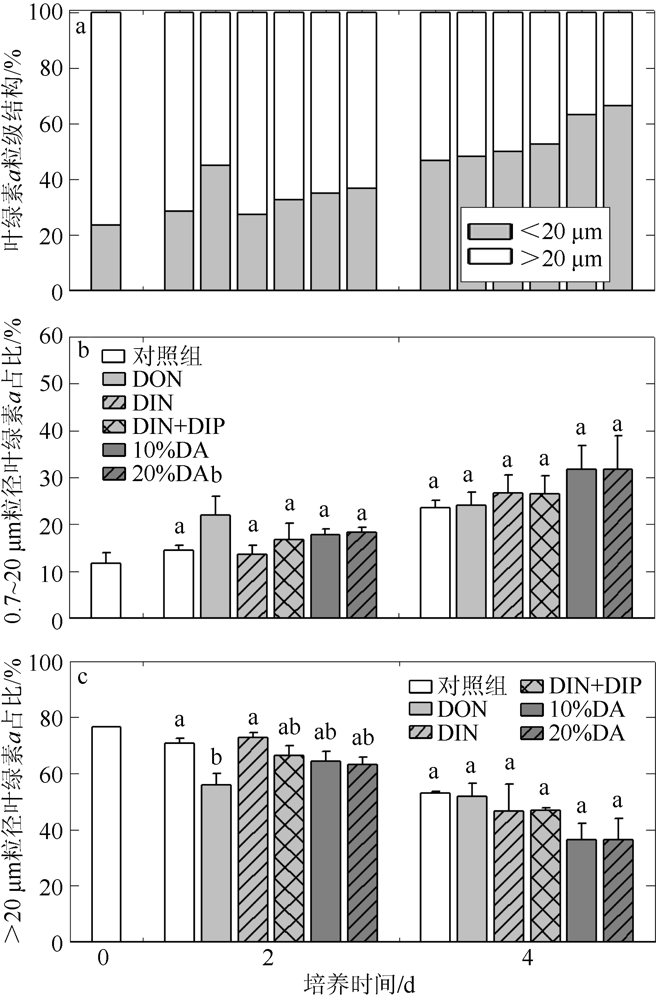
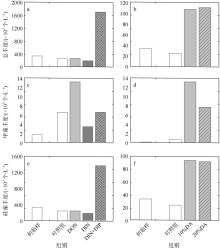
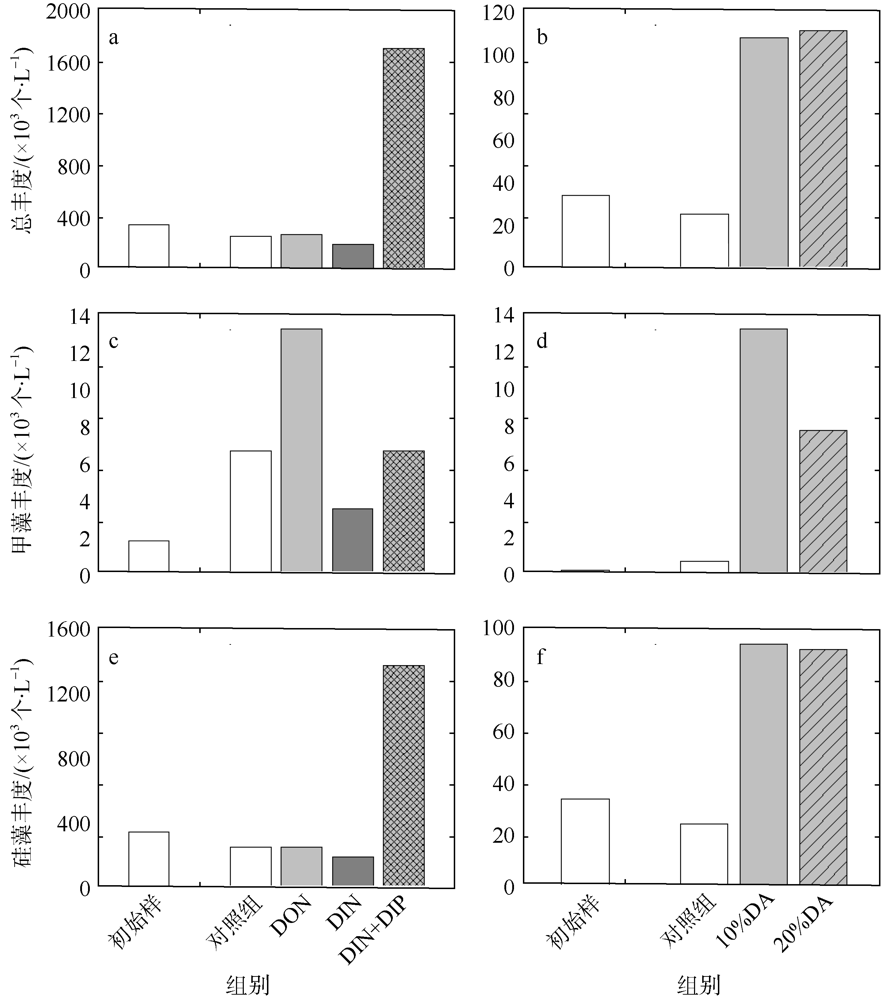
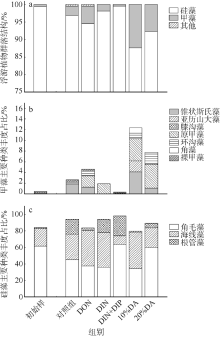
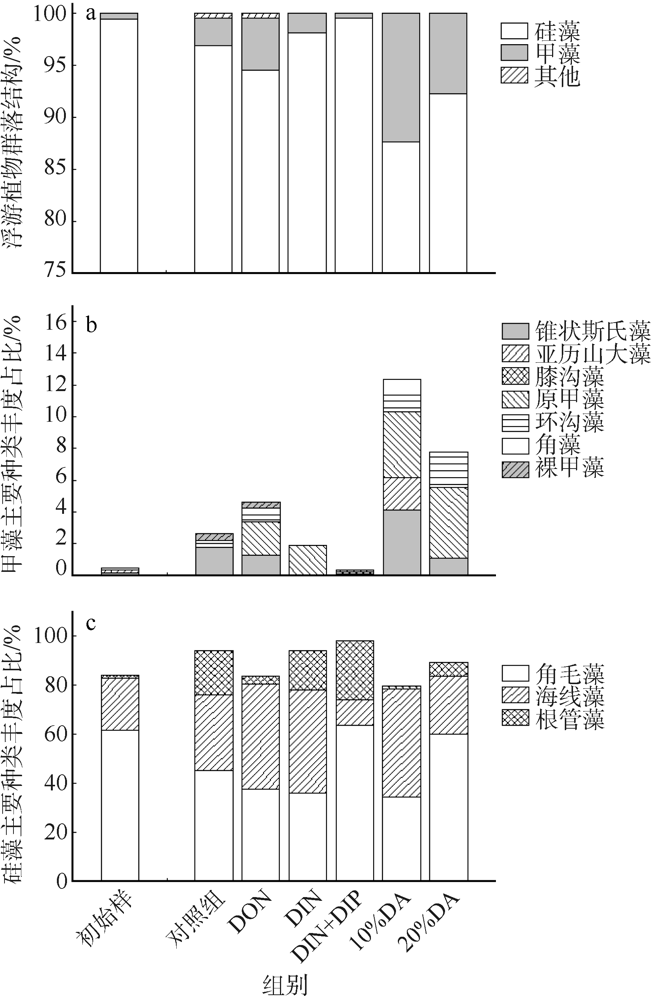
人类活动引起的营养物质输入导致大亚湾出现海水富营养化、赤潮频发和生物多样性下降等生态问题。为探究陆源输入影响下大亚湾湾顶淡澳河输入对湾内浮游植物粒级结构和种类组成的影响, 2016年10月在大亚湾进行了原位观测和培养试验。原位观测结果显示, 淡澳河口的总溶解态氮、磷浓度分别达到85.3μmol·L-1和1.5μmol·L-1。加富培养试验结果表明, 淡澳河河口水加富对总叶绿素a (Chl a)和总浮游植物丰度有显著促进作用, 并导致浮游植物粒级结构由小粒级Chl a (0.7~20μm)占主导; 浮游植物丰度中甲藻比例升高, 主要种类为锥状斯氏藻(Scrippsiella trochoidea)和原甲藻(Prorocentrum spp.)。同样, 尿素加富也促进了浮游植物群落中小粒级Chl a和甲藻的比例增加, 且主要甲藻种类与河口水加富结果一致。无机氮、磷同时加富促进了总Chl a和浮游植物总丰度增加, 而对浮游植物粒级结构和甲藻丰度则没有明显影响。对照河口水和氮、磷营养盐加富试验结果, 说明河口水携带的溶解性有机氮源可能是导致大亚湾浮游植物群落小型化, 促进甲藻生长的关键营养盐形态, 其携带的无机氮、磷同时促进总浮游植物丰度增加。本研究结果表明有机形态营养组分对大亚湾富营养化和有害藻华可能产生重要影响。
中图分类号:
- P735.121
引用本文
向晨晖, 刘甲星, 柯志新, 周林滨, 谭烨辉. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构和种类组成对淡澳河河口水加富的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(2): 49-60.
XIANG Chenhui, LIU Jiaxing, KE Zhixin, ZHOU Linbin, TAN Yehui. Phytoplankton responses to Dan’ao River estuary water enrichment in terms of size structure and community composition*[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(2): 49-60.
| [1] | 胡章喜, 徐宁, 段舜山, 等, 2010. 尿素对中国近海3种典型赤潮藻生长的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 30(6):1265-1270. |
| HU ZHANGXI, XU NING, DUAN SHUNSHAN, et al, 2010. Effects of urea on the growth of Phaeocystis globosa, Scrippsiella trochoidea, Skeletonema costatum[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 30(6):1265-1270 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 桓清柳, 庞仁松, 周秋伶, 等, 2016. 深圳近岸海域氮、磷营养盐变化趋势及其与赤潮发生的关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 35(6):908-914. |
| HUAN QINGLIU, PANG RENSONG, ZHOU QIULING, et al, 2016. Variation trends of nitrogen and phosphorus and the relationship with HABs in Shenzhen coastal waters[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 35(6):908-914 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 黄小平, 黄良民, 宋金明, 等, 2019. 营养物质对海湾生态环境影响的过程与机理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 16-17(in Chinese). |
| [4] | 赖海燕, 徐宁, 段舜山, 2011. 大亚湾裸甲藻种群动态及其关键调控因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(3):505-510. |
| LAI HAIYAN, XU NING, DUAN SHUNSHAN, 2011. Relationship between population dynamics of Gymnodinium spp. and key environmental factors in Daya Bay[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(3):505-510 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 李佳俊, 沈萍萍, 谭烨辉, 等, 2015. 南海东北部浮游植物对氮、磷加富的响应及与不同水团的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 37(10):88-99. |
| LI JIAJUN, SHEN PINGPING, TAN YEHUI, et al, 2015. Phytoplankton responses to nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment in relation to different water masses[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 37(10):88-99 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 李涛, 2007. 大亚湾水域浮游植物对环境变化的响应研究[D]. 广州: 中国科学院南海海洋研究所. |
| LI TAO, 2007. Responses of phytoplankton to the environment changes in the waters of Daya Bay[D]. Guangzhou: South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Science (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 刘冬燕, 赵建夫, 马利民, 等, 2004. 粒径分级叶绿素a对富营养水体生物修复的响应[J]. 生态学报, 24(11):2477-2483. |
| LIU DONGYAN, ZHAO JIANFU, MA LIMIN, et al, 2004. Responses of all size-fractionated chlorophyll-a contents to bioremediation in eutrophic water[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(11):2477-2483 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 任秀文, 姜国强, 刘爱萍, 等, 2013. 大亚湾主要入海河流污染物通量估算研究[C]// 2013中国环境科学学会学术年会. 昆明: 2912-2921 (in Chinese). |
| [9] | 宋淑华, 2009. 大亚湾浮游植物群落结构与赤潮藻分子鉴定研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学. |
| SONG SHUHUA, 2009. Studies on the phytoplankton community and molecular identification of typical HAB species in Daya Bay, South China Sea[D]. Guangzhou Jinan University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 王朝晖, 陈菊芳, 徐宁, 等, 2001. 大亚湾裸甲藻种群的季节变化与环境条件的关系[J]. 生态学报, 21(11):1825-1832. |
| WANG ZHAOHUI, CHEN JUFANG, XU NING, et al, 2001. Relationship between seasonal variations in Gymnodinium spp. population and environmental factors Daya Bay, the South China Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 21(11):1825-1832 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 王友绍, 王肇鼎, 黄良民, 2004. 近20年来大亚湾生态环境的变化及其发展趋势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 23(5):85-95. |
| WANG YOUSHAO, WANG ZHAODING, HUANG LIANGMIN, 2004. Environment changes and trends in Daya Bay in recent 20 years[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 23(5):85-95 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 肖咏之, 齐雨藻, 王朝晖, 等, 2001. 大亚湾海域锥状斯氏藻赤潮及其与孢囊的关系[J]. 海洋科学, 25(9):50-54. |
| XIAO YONGZHI, QI YUZAO, WANG ZHAOHUI, et al, 2001. The relationship between Scrippsiella trochoidea red tide and cysts in the Daya Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 25(9):50-54 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 谢福武, 刘华雪, 黄洪辉, 等, 2018. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构对温排水和营养盐输入的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(3):55-64. |
| XIE FUWU, LIU HUAXUE, HUANG HONGHUI, et al, 2008. Effects of thermal discharge and nutrients input on size structure of phytoplankton in Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(3):55-64 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [14] | 徐宁, 陈菊芳, 王朝晖, 等, 2001. 广东大亚湾藻类水华的动力学分析Ⅱ. 藻类水华与营养元素的关系研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 21(4):400-404. |
| XU NING, CHEN JUFANG, WANG ZHAOHUI, et al, 2001. Dynamic analyses on algal bloom events in Daya Bay of Guangdong province Ⅱ. A study of relationship between algal bloom and nutrients[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 21(4):400-404 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 易斌, 陈凯彪, 周俊杰, 等, 2018. 2009年至2016年华南近海赤潮分布特征[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (2):23-31. |
| YI BIN, CHEN KAIBIAO, ZHOU JUNJIE, et al, 2019. Characteristics of red tide in coastal region of South China from 2009 to 2016[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (2):23-31 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 张淑雯, 张云, 欧林坚, 等, 2012. 6种赤潮甲藻对荧光标记藻类的吞噬行为研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 43(3):602-608. |
| ZHANG SHUWEN, ZHANG YUN, OU LINJIAN, et al, 2012. Study on phagotrophic behavior of six harmful dinoflagellates on fluorescent labeled algae[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 43(3):602-608 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [17] | 张云, 黄凯旋, 欧林坚, 等, 2014. 大亚湾海域尿素与浮游生物脲酶活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(1):90-96. |
| ZHANG YUN, HUAGN KAIXUAN, OU LINJIAN, et al, 2014. Distributions of urea concentration and urease activity in the Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 33(1):90-96 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2008. GB/T 12763.4-2007 海洋调查规范第4部分: 海水化学要素调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| GENERAL ADMINISTRATION OF QUALITY SUPERVISION, INSPECTION AND QUARANTINE OF THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA, STANDARDIZATION ADMINISTRATION, 2008. GB/T 12763.4-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey-Part 4: Survey of chemical parameters in sea water[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese). | |
| [19] | 朱艾嘉, 黄良民, 许战洲, 2008. 氮、磷对大亚湾大鹏澳海区浮游植物群落的影响Ⅰ. 叶绿素a与初级生产力[J]. 热带海洋学报, 27(1):38-45. |
| ZHU AIJIA, HUANG LIANGMIN, XU ZHANZHOU, 2008. Impacts of nitrogen and phosphorus on phytoplankton community structure in Dapeng’ao area of Daya Bay Ⅰ. Chlorophyll a and primary productivity[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 27(1):38-45 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [20] | 朱艾嘉, 黄良民, 林秋艳, 等, 2009. 氮、磷对大亚湾大鹏澳海区浮游植物群落的影响: Ⅱ 种类组成[J]. 热带海洋学报, 28(6):103-111. |
| ZHU AIJIA, HUANG LIANGMIN, LIN QIUYAN, et al, 2001. Influence of nitrogen and phosphorus on phytoplankton community structure in the Dapeng’ao Bay, Daya Bay: Ⅱ Species composition[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 28(6):103-111 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [21] | ALTMAN J C, PAERL H W, 2012. Composition of inorganic and organic nutrient sources influences phytoplankton community structure in the New River Estuary, North Carolina[J]. Aquatic Ecology, 46(3):269-282. |
| [22] |
BERG G M, GLIBERT P M, JØRGENSEN N O G, et al, 2001. Variability in inorganic and organic nitrogen uptake associated with riverine nutrient input in the Gulf of Riga, Baltic Sea[J]. Estuaries, 24(2):204-214.
doi: 10.2307/1352945 |
| [23] |
COOPER J T, SINCLAIR G A, WAWRIK B, 2016. Transcriptome analysis of Scrippsiella trochoidea CCMP 3099 reveals physiological changes related to nitrate depletion[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 639.
pmid: 27242681 |
| [24] | FU TINGTING, CHEN BAOHONG, JI WEIDONG, et al, 2016. Size structure of phytoplankton community and its response to environmental factors in Xiamen Bay, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(9):734. |
| [25] |
GÁRATE-LIZÁRRAGA I, BAND-SCHMIDT C J, LÓPEZ- CORTÉS D J, et al, 2009. Bloom of Scrippsiella trochoidea (Gonyaulacaceae) in a shrimp pond in the southwestern Gulf of California, Mexico[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(1):145-149.
pmid: 18996544 |
| [26] |
GLIBERT P M, MAGNIEN R, LOMAS M W, et al, 2001. Harmful algal blooms in the Chesapeake and coastal bays of Maryland, USA: Comparison of 1997, 1998, and 1999 events[J]. Estuaries, 24(6):875-883.
doi: 10.2307/1353178 |
| [27] | GLIBERT P M, TRICE T M, MICHAEL B, et al, 2005. Urea in the tributaries of the Chesapeake and coastal bays of Maryland[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 160(1-4):229-243. |
| [28] | GLIBERT P M, HARRISON J, HEIL C, et al, 2006. Escalating worldwide use of urea - A global change contributing to coastal eutrophication[J]. Biogeochemistry, 77(3):441-463. |
| [29] |
GLIBERT P M, MAYORGA E, SEITZINGER S, 2008. Prorocentrum minimum tracks anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs on a global basis: application of spatially explicit nutrient export models[J]. Harmful Algae, 8(1):33-38.
doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2008.08.023 |
| [30] | GRASSSHOFF K, EHRARDT M, KREMLING K, 1983. Methods of sea water analysis[M]. 2nd ed. Weinheim, Germany: Verlag Chemie. |
| [31] | GUO C, YU J, HO T Y, et al, 2012. Dynamics of phytoplankton community structure in the South China Sea in response to the East Asian aerosol input[J]. Biogeosciences, 9(4):1519-1536. |
| [32] | HUANG BANGQIN, LAN WENLU, CAO ZHENRUI, et al, 2008. Spatial and temporal distribution of nanoflagellates in the northern South China Sea[J]. Hydrobiologia, 605(1):143-157. |
| [33] | JEONG H J, YOO Y D, PARK J Y, et al, 2005a. Feeding by phototrophic red-tide dinoflagellates: five species newly revealed and six species previously known to be mixotrophic[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 40: 133-150. |
| [34] | JEONG H J, YOO Y D, SEONG K A, et al, 2005b. Feeding by the mixotrophic red-tide dinoflagellate Gonyaulax polygramma: mechanisms, prey species, effects of prey concentration, and grazing impact[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 38: 249-257. |
| [35] |
JEONG H J, YOO D Y, KIM J S, et al, 2010. Growth, feeding and ecological roles of the mixotrophic and heterotrophic dinoflagellates in marine planktonic food webs[J]. Ocean Science Journal, 45(2):65-91.
doi: 10.1007/s12601-010-0007-2 |
| [36] | KIM Y O, HAN M S, 2000. Seasonal relationships between cyst germination and vegetative population of Scrippsiella trochoidea (Dinophyceae)[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 204: 111-118. |
| [37] |
LECHER A L, MACKEY K, KUDELA R, et al, 2015. Nutrient loading through submarine groundwater discharge and phytoplankton growth in Monterey Bay, CA[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(11):6665-6673.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b00909 pmid: 25988258 |
| [38] | LEE Y J, YANG E J, YOUN S, et al, 2018. Influence of the Changjiang diluted waters on the nanophytoplankton distribution in the northern East China Sea[J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 98(7):1535-1545. |
| [39] | LU DOUDING, GOEBEL J, QI YUZAO, et al, 2005. Morphological and genetic study of Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu from the East China Sea, and comparison with some related Prorocentrum species[J]. Harmful Algae, 4(3):493-505. |
| [40] |
MARTÍNEZ-SOTO M C, BASTERRETXEA G, GARCÉS E, et al, 2015. Species-specific variation in the phosphorus nutritional sources by microphytoplankton in a Mediterranean estuary[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2: 54.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00054 pmid: 21833310 |
| [41] |
MATANTSEVA O, SKARLATO S, VOGTS A, et al, 2016. Superposition of individual activities: urea-mediated suppression of nitrate uptake in the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum revealed at the population and single-cell levels[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 1310.
pmid: 27610101 |
| [42] | MAUGENDRE L, GATTUSO J P, LOUIS J, et al, 2015. Effect of ocean warming and acidification on a plankton community in the NW Mediterranean Sea[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 72(6):1744-1755. |
| [43] | MOSCHONAS G, GOWEN R J, PATERSON R F, et al, 2017. Nitrogen dynamics and phytoplankton community structure: the role of organic nutrients[J]. Biogeochemistry, 134(1-2):125-145. |
| [44] | OU LINJIAN, LUNDGREN V, LU SONGHUI, et al, 2014. The effect of riverine dissolved organic matter and other nitrogen forms on the growth and physiology of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum (Pavillard) Schiller[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 85: 499-507. |
| [45] | PARSONS T R, MAITA Y, LALLI C M, 1984. A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press. |
| [46] |
RUTTENBERG K C, DYHRMAN S T, 2005. Temporal and spatial variability of dissolved organic and inorganic phosphorus, and metrics of phosphorus bioavailability in an upwelling- dominated coastal system[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 110(C10): C10S13, doi: 10.1029/2004JC002837.
pmid: 31763112 |
| [47] | SANDERS R W, PORTER K G, BENNETT S J, 1990. Heterotrophic, autotrophic, and mixotrophic nanoflagellates: seasonal abundances and bacterivory in a eutrophic lake[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 35(8):1821-1832. |
| [48] | SHANGGUAN Y, GLIBERT P M, ALEXANDER J, et al, 2017. Phytoplankton assemblage response to changing nutrients in Florida Bay: Results of mesocosm studies[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 494: 38-53. |
| [49] |
SONG XINGYU, HUANG LIANGMIN, ZHANG JIANLIN, et al, 2009. Harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Daya Bay, China: an in situ study of primary production and environmental impacts[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(9):1310-1318.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.04.030 pmid: 19501846 |
| [50] | TANG DANLING, DI BAOPING, WEI GUIFENG, et al, 2006. Spatial, seasonal and species variations of harmful algal blooms in the South Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Hydrobiologia, 568: 245-253. |
| [51] | TEIRA E, MARTÍNEZ-GARCÍA S, CARREIRA C, et al, 2011. Changes in bacterioplankton and phytoplankton community composition in response to nutrient additions in coastal waters off the NW Iberian Peninsula[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 426: 87-104. |
| [52] | UTERMÖHL H, 1958. Methods of collecting plankton for various purposes are discussed[J]. SIL Communications, 1953—1996, 9(1):1-38. |
| [53] |
WANG YOUSHAO, LOU ZHIPING, SUN CUICI, et al, 2008. Ecological environment changes in Daya Bay, China, from 1982 to 2004[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56(11):1871-1879.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.07.017 pmid: 18783802 |
| [54] | WU MEILIN, WANG YOUSHAO, SUN CUICI, et al, 2012. Monsoon-driven dynamics of water quality by multivariate statistical methods in Daya Bay, South China Sea[J]. Oceanological and Hydrobiological Studies, 41(4):66-76. |
| [55] | WU MEILIN, WANG YOUSHAO, WANG YUTU, et al, 2017. Scenarios of nutrient alterations and responses of phytoplankton in a changing Daya Bay, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 165: 1-12. |
| [56] | YUAN XIANGCHENG, GLIBERT P M, XU JIE, et al, 2012. Inorganic and organic nitrogen uptake by phytoplankton and bacteria in Hong Kong waters[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 35(1):325-334. |
| [57] | ZHANG XIA, SHI ZHEN, HUANG XIAOPING, et al, 2017. Abiotic and biotic factors influencing nanoflagellate abundance and distribution in three different seasons in PRE, South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 143: 1-8. |
| [58] |
ZHANG XIA, ZHANG JINGPING, SHEN YUAN, et al, 2018. Dynamics of alkaline phosphatase activity in relation to phytoplankton and bacteria in a coastal embayment Daya Bay, South China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 131: 736-744.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.008 pmid: 29887001 |
| [1] | 奚琛, 林宗轩, 萨如拉, 邓玺, 刘强, 倪亮, 罗来才, 马腾, 谢智杰, 陈思若, 陈松泽. 基于双浮标连续监测资料分析大亚湾西南部海域水体环境变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [2] | 孙翠慈, 岳维忠, 赵文杰, 王友绍. 大亚湾表层沉积物碳水化合物活性酶基因分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [3] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [4] | 姜迅, 武文, 宋德海. 大亚湾水质对人类活动响应的关键控制指标识别和量化解析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 182-191. |
| [5] | 陈靖夫, 钟瑜, 王磊, 郭雨沛, 邱大俊. 环境DNA分析大亚湾夜光藻藻华对真核浮游生物群落的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [6] | 张婉茹, 刘庆霞, 黄洪辉, 覃晓青, 李佳俊, 陈建华. 2020年冬季大亚湾西南海域主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [7] | 李尧, 向晨晖, 江志坚, 宋星宇. 大亚湾夏季浮游群落生产代谢特征及其影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 83-92. |
| [8] | 张立明, 谭烨辉, 李佳俊, 黄小平, 刘甲星. 大亚湾夏季浮游植物群落结构及对淡澳河输入的响应特征*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [9] | 王卉,李恒翔,李路,严岩. 大亚湾大型海藻丛的大角玻璃钩虾种群分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(4): 52-58. |
| [10] | 谢福武, 宋星宇, 谭烨辉, 谭美婷, 黄亚东, 刘华雪. 模拟升温和营养盐加富对大亚湾浮游生物群落代谢的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(2): 48-57. |
| [11] | 谢福武, 刘华雪, 黄洪辉, 宋星宇. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构对温排水和营养盐输入的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(3): 55-64. |
| [12] | 徐翠莲, 李涛, 胡思敏, 王有军, 黄晖, 刘胜. 大亚湾核电站邻近水域桡足幼体现场摄食研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(2): 17-25. |
| [13] | 武文, 严聿晗, 宋德海. 大亚湾的潮汐动力学研究——I.潮波系统的观测分析与数值模拟*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(3): 34-45. |
| [14] | 严聿晗, 武文, 宋德海, 鲍献文. 大亚湾的潮汐动力学研究——Ⅱ.潮位和潮流双峰现象的产生机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(3): 46-54. |
| [15] | 袁涛萍, 李恒翔, 李路, 王卉, 杨长平. 夏季大亚湾大型底栖动物群落结构*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(1): 41-47. |
|
||