热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 76-91.doi: 10.11978/2022216CSTR: 32234.14.2022216
大亚湾表层沉积物碳水化合物活性酶基因分布特征
孙翠慈1,2( ), 岳维忠3,4, 赵文杰1,5, 王友绍1,2(
), 岳维忠3,4, 赵文杰1,5, 王友绍1,2( )
)
- 1. 热带海洋环境国家重点实验室(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
2. 大亚湾海洋生物综合实验站(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 深圳 518121
3. 海洋环境工程中心(中国科学院南海海洋研究所), 广东 广州 510301
4. 阳江海上风电实验室, 广东 阳江 529500
5. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2022-10-10修回日期:2022-11-22出版日期:2023-09-10发布日期:2023-01-09 -
作者简介:孙翠慈(1977—), 女, 河北省辛集市人, 副研究员, 博士, 从事海洋环境生态研究。email: scuici@scsio.ac.cn
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42073078); 国家自然科学基金项目(U1901211); 广东省基础与应用基础研究基金项目(2020A1515011137); 国家重点研发计划项目(2017FY100700)
Distribution of the microbial Carbohydrate-Active enzymes genes in the surface sediment of the Daya Bay, China
SUN Cuici1,2( ), YUE Weizhong3,4, ZHAO Wenjie1,5, WANG Youshao1,2(
), YUE Weizhong3,4, ZHAO Wenjie1,5, WANG Youshao1,2( )
)
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Daya Bay Marine Biology Research Station (Chinese Academy of Sciences), Shenzhen 518121, China
3. Marine Environmental Center (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
4. Yangjiang Offshore Wind Power Laboratory, Yangjiang 529500, China
5. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2022-10-10Revised:2022-11-22Online:2023-09-10Published:2023-01-09 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42073078); National Natural Science Foundation of China(U1901211); Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2020A1515011137); National Key Research and Development Program of China(2017FY100707)
摘要:
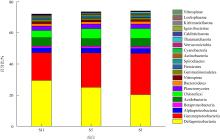
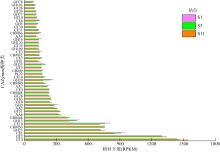
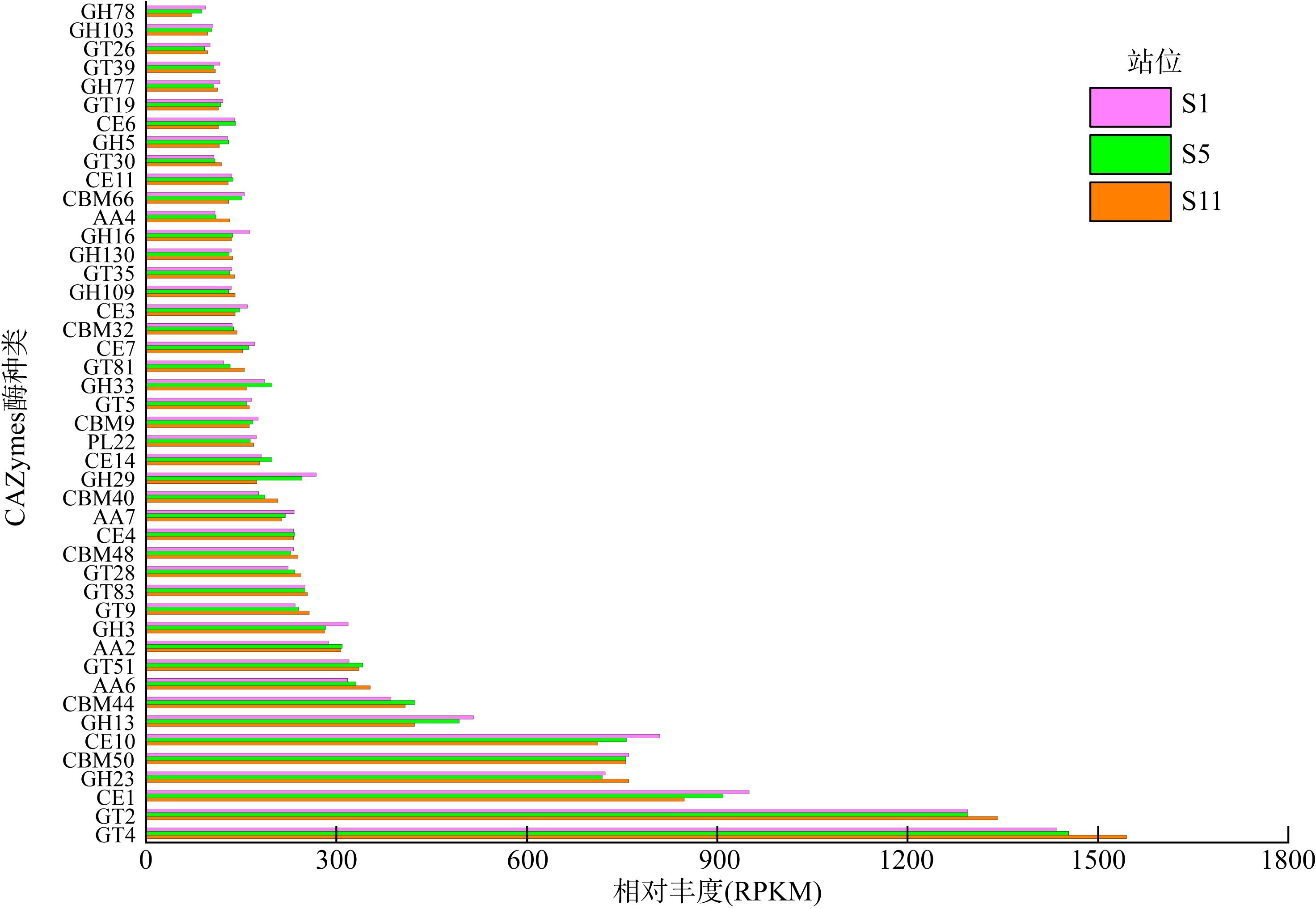
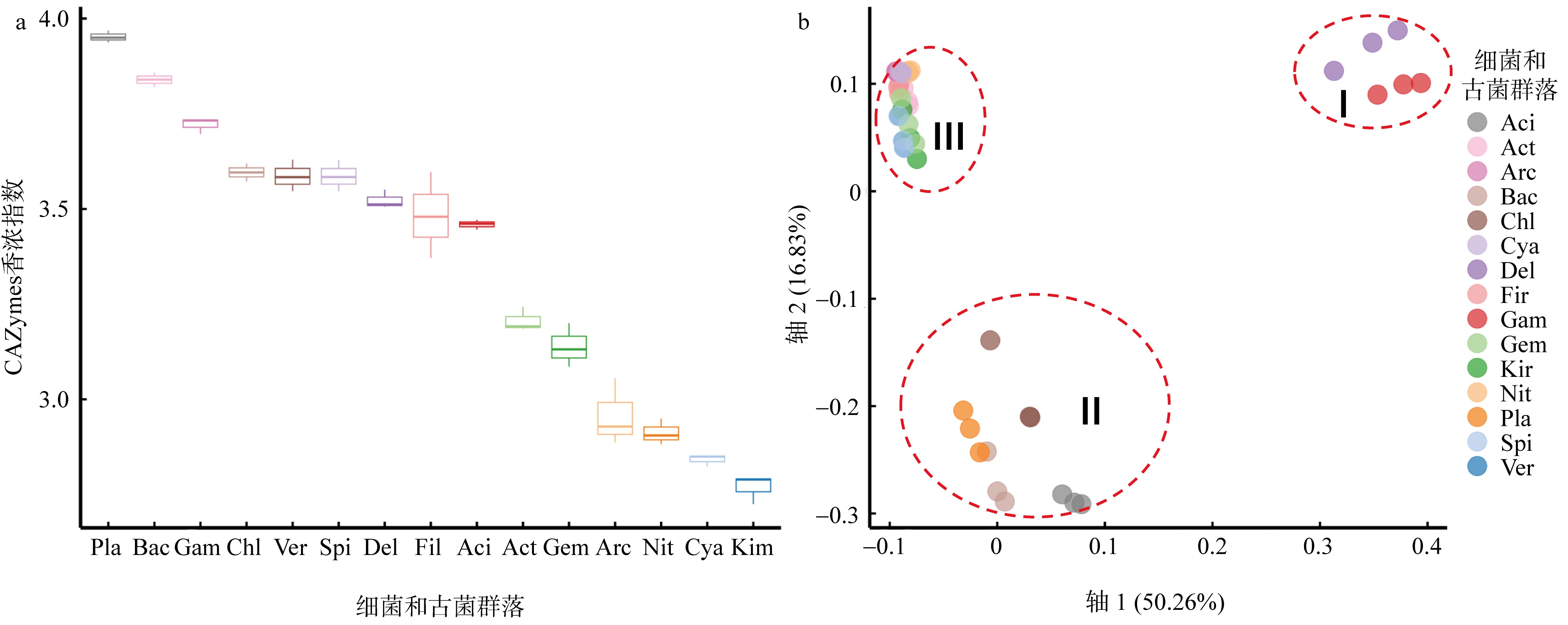
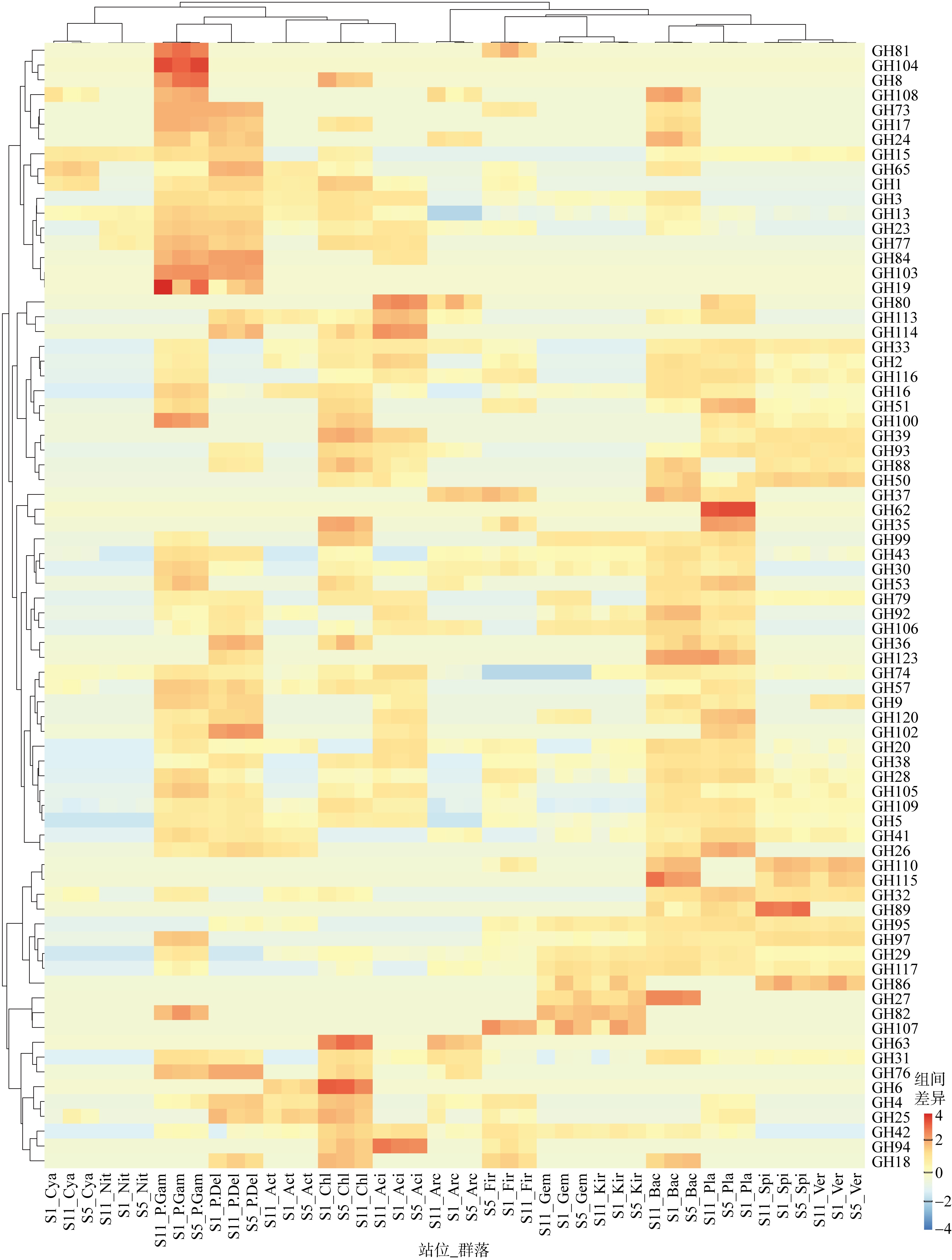
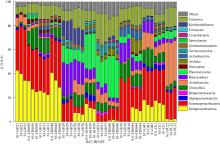
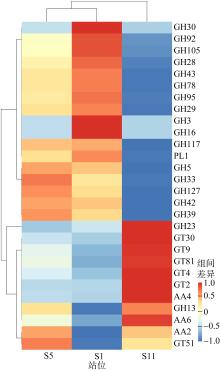
微生物的碳水化合物活性酶(carbohydrate active enzymes, CAZymes)是海洋沉积物有机碳降解过程中的关键。文章基于大亚湾2020年春季表层沉积物的宏基因组数据, 分析鉴定编码CAZymes序列种类及其在微生物中的分布, 并预测了微生物群落对不同结构聚糖的利用。结果表明, 表层沉积物微生物群落对不同结构聚糖的利用能力不同。δ-变形菌纲是编码降解肽聚糖和几丁质相关酶类序列的最大贡献者; γ-变形菌纲、拟杆菌门和浮霉菌门具有最高的CAZymes家族的α-生态多样性(香浓指数), 是编码降解结构复杂多糖(岩藻聚糖、昆布多糖、纤维素等)的CAZymes基因优势种群; 酸杆菌是编码裂解寡聚半乳糖醛酸多糖酶序列的优势菌群。古菌对大部分CAZymes贡献低于1%, 但对编码降解纤维素和半纤维素的碳水化合物酯酶(carbohydrate esterase, CE)序列、结合模块(carbohydrate binding module, CBM)基因序列贡献较突出(贡献介于2.18%~ 11.1%)。CAZymes的底物主要源自于湾内自生的有机碎屑, 降解藻源有机碎屑的CAZymes序列的相对丰度于湾口高于湾东北部。与木质素降解相关的辅助活性家族(auxiliary activity families, AAs)序列相对丰度在湾东北部最高, 主导的AAs可能有助于增加木质纤维素的溶解度, 进而提高糖苷酶对木质纤维素的生物利用度。大亚湾表层沉积物中微生物及其CAZymes序列组成主要与上层水体有机颗粒沉降以及水深相关。
引用本文
孙翠慈, 岳维忠, 赵文杰, 王友绍. 大亚湾表层沉积物碳水化合物活性酶基因分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 76-91.
SUN Cuici, YUE Weizhong, ZHAO Wenjie, WANG Youshao. Distribution of the microbial Carbohydrate-Active enzymes genes in the surface sediment of the Daya Bay, China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 76-91.
表1
调查期间大亚湾3个站位理化因子"
| 站位 | S1 | S5 | S11 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 经度 | 114°37′59.88″E | 114°33′42.12″E | 114°43′0.12″E |
| 纬度 | 22°31′59.88″N | 22°35′35.88″N | 22°46′0.12″N |
| 水深/m | 19.5 | 13.5 | 8.0 |
| 含水率/% | 38.2 | 35.1 | 62.4 |
| 砂土百分比/% | 13.4 | 5.9 | 0 |
| 粉砂土百分比/% | 64.9 | 71.9 | 62.7 |
| 黏土百分比/% | 21.7 | 22.2 | 37.54 |
| 平均粒径/μm | 6.4 | 6.4 | 7.59 |
| 中值粒径/μm | 6.6 | 6.3 | 7.49 |
| 总有机碳(TOC)/(%·g-1) | 0.50±0.02 | 0.47±0.01 | 1.63±0.05 |
| 硫化物含量/(μg· g-1) | 33.41±1.12 | 81.8±2.37 | 218.7±5.49 |
| 总磷(TP)/(mg·kg-1) | 160.5±8.27 | 130.7±5.18 | 142.4±6.76 |
| 总氮(TN)/(mg·kg-1) | 214.5±8.1 | 248.8±9.3 | 441.6±12.8 |
| TOC : TN | 27.3 | 22.0 | 43.1 |
| 水体叶绿素浓度/(μg·L-1) | 1.47 | 1.51 | 1.76 |
表S1
CAZymes 主要功能列表"
| 序号 | CAZymes | 名称或主要功能 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GH3 | β-葡萄糖苷酶/β-N-乙酰基己糖胺酶 | ||
| 2 | GH4 | α-半乳糖醛酸酶/麦芽糖-6-磷酸葡萄糖苷酶/6-磷酸-β-葡萄糖苷 | ||
| 3 | GH5 | 内葡聚糖酶 | ||
| 4 | GH13 | 异淀粉酶/1,4-α-葡聚糖分支酶/α-葡萄糖苷酶/α淀粉酶 | ||
| 5 | GH15 | 葡聚糖酶/α-海藻糖酶/糖化酶 | ||
| 6 | GH16 | 内切-1,3-β-葡聚糖酶 | ||
| 7 | GH17 | 内切-1,3-β-葡萄糖苷酶 | ||
| 8 | GH18 | 几丁质酶 | ||
| 9 | GH20 | 己糖胺酶 | ||
| 10 | GH23 | 溶菌酶/可溶性溶菌素转糖基酶/膜结合溶菌素转糖基酶 | ||
| 11 | GH29 | α-L-岩藻糖苷酶 | ||
| 12 | GH30 | β-葡萄糖苷酶/葡糖基神经酰胺酶/β-葡萄糖醛酸酶/内切-β-1,6-半乳糖苷酶 | ||
| 13 | GH31 | α-D-木糖苷木糖水解酶/α-葡萄糖苷酶/寡糖4-α-D-葡萄糖基转移酶 | ||
| 14 | GH32 | 果聚糖内切酶 | ||
| 15 | GH33 | 唾液酸酶或神经氨酸酶/反式唾液酸酶/脱水唾液酸酶/2-酮-3-脱氧壬酸水解酶 | ||
| 16 | GH43 | 木聚糖1,4-β-木糖苷酶 | ||
| 17 | GH57 | 1,4-α-葡聚糖分支酶 | ||
| 18 | GH65 | 麦芽糖磷酸化酶/海藻糖磷酸化 | ||
| 19 | GH73 | 溶菌酶 | ||
| 20 | GH77 | 4-α-葡聚糖转移酶 | ||
| 21 | GH78 | α-L-氨苷酶 | ||
| 22 | GH95 | α-L-岩藻糖苷酶2 | ||
| 23 | GH102 | 肽聚糖裂解转糖苷酶 | ||
| 24 | GH103 | 肽聚糖裂解转糖苷酶 | ||
| 25 | GH105 | 不饱和鼠李糖乳糖酰水解酶 | ||
| 26 | GH106 | α-L-鼠李糖苷酶 | ||
| 27 | GH108 | N-乙酰胞壁质酶 | ||
| 28 | GH109 | N-乙酰氨基己糖苷酶 | ||
| 29 | GH127 | β-L-阿拉伯糖苷酶 | ||
| 30 | GH130 | β-1,2-甘露糖磷酸化酶 | ||
| 31 | GH145 | L-鼠李糖-α-1,4-D-葡萄糖醛酸裂解酶 | ||
| 32 | GH149 | β-1,3-葡聚糖磷酸化酶 | ||
| 33 | CE1 | 乙酰木聚糖酯酶/S-甲酰谷胱甘肽水解酶/聚羟基丁酸解聚酶/ /羧酸酯酶 | ||
| 34 | CE2 | 乙酰木聚糖酯酶 | ||
| 35 | CE3 | 乙酰木聚糖酯酶 | ||
| 36 | CE4 | 乙酰木聚糖酯酶/甲壳素脱乙酰酶/壳寡糖脱乙酰酶肽聚糖脱乙酰酶/肽聚糖 N-乙酰胞壁酸脱乙酰酶 | ||
| 37 | CE6 | 乙酰木聚糖酯酶 | ||
| 38 | CE7 | 乙酰木聚糖酯酶 | ||
| 39 | CE8 | 果胶酯酶 | ||
| 40 | CE9 | N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖6-磷酸脱乙酰酶/N-乙酰氨基半乳糖6-磷酸脱乙酰酶 | ||
| 41 | CE10 | 芳香酯酶/羧基酯酶等 | ||
| 42 | CE11 | 尿苷二磷酸-3-O-[3-羟基肉豆蔻酰基]N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖脱乙酰酶/尿苷二磷酸-3-O-[3-羟基肉豆蔻酰]N-乙酰基葡萄糖胺脱乙酰酶/3-羟基酰基-[酰基载体蛋白]脱水酶 | ||
| 43 | CE12 | 果胶乙酰酯酶 | ||
| 44 | CE13 | 果胶乙酰酯酶 | ||
| 45 | CE14 | 二乙酰基壳二糖去乙酰化酶 | ||
| 46 | CE15 | 4-O-甲基葡萄糖醛酸甲酯酶 | ||
| 47 | CE16 | 乙酰酯酶 | ||
| 48 | AA2 | 过氧化氢酶过氧化物酶 | ||
| 49 | AA3 | 葡萄糖-甲醇-胆碱氧化还原酶家族/胆碱脱氢酶 | ||
| 50 | AA4 | 乙醇酸氧化酶/D-乳酸脱氢酶(细胞色素) | ||
| 51 | AA6 | 醌还原酶 | ||
| 52 | AA7 | 葡萄糖氧化酶/壳寡糖氧化酶/纤维低聚糖脱氢酶 | ||
| 53 | AA9 | 依赖铜的裂解多糖单加氧酶 | ||
| 54 | AA12 | 吡咯喹啉醌依赖性氧化还原酶 | ||
| 55 | AA13 | 依赖铜的裂解多糖单加氧酶 | ||
| 56 | PL1 | 果胶裂解酶 | ||
| 57 | PL2 | 果胶裂解酶 | ||
| 58 | PL4 | 鼠李糖半乳糖醛酸内切酶 | ||
| 59 | PL5 | 海藻酸裂解酶 | ||
| 60 | PL6 | 海藻酸裂解酶 | ||
| 61 | PL7 | 海藻酸裂解酶 | ||
| 62 | PL8 | 软骨素裂解酶 | ||
| 63 | PL9 | 果胶裂解酶 | ||
| 64 | PL10 | 果胶裂解酶 | ||
| 65 | PL12 | 硫酸肝素裂解酶 | ||
| 66 | PL14 | 聚(β-甘露糖醛酸)裂解酶/M-特异性海藻酸裂解酶 | ||
| 67 | PL15 | 海藻酸裂解酶/肝素裂解酶/肝素裂解酶 I/肝素-硫酸盐裂解酶/肝素裂解酶 Ⅲ | ||
| 68 | PL17 | 海藻酸裂解酶 | ||
| 69 | PL18 | 海藻酸裂解酶 | ||
| 70 | PL21 | 肝素裂解酶/肝素-硫酸盐裂解酶/阿查兰-硫酸盐裂解酶 | ||
| 71 | PL22 | 低聚半乳糖醛酸裂解酶 | ||
| 72 | PL24 | 石莼多糖裂解酶 | ||
| 73 | CBM6 | 结合纤维素、β-1,4-木聚糖、β-1,13-葡聚糖、β-1, 3-1,4-葡聚糖和β-1,3-葡聚糖 | ||
| 74 | CBM9 | 结合纤维素 | ||
| 75 | CBM11 | 与β-1,4-葡聚糖和β-1,3-1,4-混合连接葡聚糖结合 | ||
| 76 | CBM16 | 结合纤维素和葡甘聚糖 | ||
| 77 | CBM13 | 与纤维素结合 | ||
| 78 | CBM20 | 与淀粉结合 | ||
| 79 | CBM23 | 与甘露聚糖结合 | ||
| 80 | CBM32 | 结合半乳糖、乳糖和N-乙酰-D-乳糖胺 | ||
| 81 | CBM37 | 与木聚糖、几丁质、显微晶质和磷酸纤维素结合 | ||
| 82 | CBM40 | 与GH33结合 | ||
| 83 | CBM41 | 与α-葡聚糖-直链淀粉、支链淀粉、普鲁兰聚糖结合 | ||
| 84 | CBM44 | 结合纤维素和木聚糖 | ||
| 85 | CBM47 | 与岩藻糖结合 | ||
| 86 | CBM48 | 附加到GH13模块 | ||
| 87 | CBM50 | 附着于GH18、GH19、GH23、GH24、GH25和GH73家族的各种酶, 即裂解甲壳素或肽聚糖的酶 | ||
| 88 | CBM57 | 附着于各种糖苷酶 | ||
| 89 | CBM66 | 与果聚糖的果糖苷末端结合, 辅助β-果糖苷外切酶 | ||
| 90 | CBM67 | 与L-鼠李糖结合 | ||
| 91 | GT2 | 纤维素、几丁质、葡聚糖、甘露聚糖、透明质酸合成酶/N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖基转移酶等 | ||
| 92 | GT4 | 蔗糖合成酶/蔗糖-磷酸合成酶/α-葡萄糖基转移酶/脂多糖N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖基转移酶等 | ||
| 93 | GT9 | 脂多糖-乙酰氨基葡萄糖转移酶 | ||
| 94 | GT26 | β-N-乙酰甘露糖苷酰转移酶/β-1,4-葡萄糖基转移酶β-1,4-半乳糖基转移酶 | ||
| 95 | GT28 | 1,2-二酰甘油3-β-半乳糖基转移酶; 1,2-二酰甘油3-β-葡萄糖基转移酶/β-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖基转移酶/双半乳糖基二酰甘油合成酶 | ||
| 96 | GT30 | α-3-脱氧-D-甘露聚糖-辛酸转移酶 | ||
| 97 | GT35 | 糖原或淀粉磷酸化酶 | ||
| 98 | GT39 | 蛋白α-甘露糖基转移酶 | ||
| 99 | GT51 | 胞壁质聚合酶 | ||
| 100 | GT81 | 葡萄糖基-3-磷酸甘油酸合成酶/甘露糖基 -3-磷酸甘油酸合成酶/ 葡萄糖基-2-甘油酸合成酶/甘露糖基-3-磷酸甘油酸合成酶/3-磷酸甘油酸α-甘露糖基转移酶 | ||
| 101 | GT83 | 4-氨基-4-脱氧-β-L-阿拉伯糖基转移酶/半乳糖醛酸基转移酶 | ||
| [1] |
牟新悦, 陈敏, 张琨, 等, 2017. 夏季大亚湾悬浮颗粒有机物碳、氮同位素组成及其物源指示[J]. 海洋学报, 39(2): 39-52.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局和中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2007. 海洋监测规范(GB17378. 5—2007)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1007/s00248-016-0911-9 pmid: 28070679 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.02.008 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1146/marine.2021.13.issue-1 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1002/lno.v66.9 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01063-4 pmid: 33975640 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-00928-8 pmid: 33649555 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15550 pmid: 33973326 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170 pmid: 24695404 |
| [11] |
pmid: 21141030 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028742 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31433-x pmid: 35790765 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00836-7 pmid: 32482164 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.06.027 pmid: 23816787 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1111/emi4.2014.6.issue-6 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1186/s40793-021-00385-y pmid: 34404489 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.036 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2331-y pmid: 19908036 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-0588-4 pmid: 31988474 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0252-4 pmid: 30116038 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13142 pmid: 26626228 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1038/nature12033 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22765-1 pmid: 33927199 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.174 pmid: 24108328 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1007/s00284-016-1089-6 pmid: 27363425 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0047-9 pmid: 29062087 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0720-2 pmid: 32451471 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02475 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aan4834 pmid: 28839072 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.84 pmid: 27300277 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.24 pmid: 26943623 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1218344 pmid: 22556258 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.7554/eLife.11888 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00253 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21009-6 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00055-15 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117267 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2014.225 pmid: 25478683 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1093/nar/gky418 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz4354 |
| [45] |
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15650 pmid: 34196089 |
| [1] | 莫丹杨, 宁志铭, 杨斌, 夏荣林, 刘志金. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁区沉积物硝酸盐异化还原过程对温度变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [2] | 奚琛, 林宗轩, 萨如拉, 邓玺, 刘强, 倪亮, 罗来才, 马腾, 谢智杰, 陈思若, 陈松泽. 基于双浮标连续监测资料分析大亚湾西南部海域水体环境变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [3] | 高洁, 余克服, 许慎栋, 黄学勇, 陈飚, 王永刚. 西沙群岛永乐环礁礁外坡沉积物中有机碳的含量与来源分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [4] | 孙婷婷, 郝雯瑾, 徐鹏臻, 叶丽靖, 董志军. 海水酸化对海月水母螅状体共附生微生物的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(6): 111-119. |
| [5] | 邢楠楠, 任润馨, 唐振洲, 罗志宏, 夏辰曦, 刘永宏, 彭亮, 陈显强. 涠洲岛海洋沉积物来源真菌Aspergillus sp. GXIMD02003的代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 154-160. |
| [6] | 董俊德, 黄小芳, 龙爱民, 王友绍, 凌娟, 杨清松. 红树林固氮微生物及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 1-11. |
| [7] | 宋星宇, 林雅君, 张良奎, 向晨晖, 黄亚东, 郑传阳. 粤港澳大湾区近海中小型浮游动物分布特征及影响因素*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [8] | 姜迅, 武文, 宋德海. 大亚湾水质对人类活动响应的关键控制指标识别和量化解析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(1): 182-191. |
| [9] | 叶锦成, 陈毅青, 高琳, 周鲜娇, 钟才荣, 张颖, 王芸. 红树植物拟海桑及其亲本的根际细菌群落特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 75-89. |
| [10] | 陈靖夫, 钟瑜, 王磊, 郭雨沛, 邱大俊. 环境DNA分析大亚湾夜光藻藻华对真核浮游生物群落的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [11] | 李震, 李云凯, 刘永虎, 程前, 张硕. 渤海表层沉积物中化学浸取不同形态氮的释放潜力[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 163-171. |
| [12] | 王朝晖, 张宇宁, 王文婷, 谢昌良, 陈佳卓, 郑虎, 王军星. 福建东山湾表层沉积物中甲藻孢囊分布研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 154-162. |
| [13] | 张婉茹, 刘庆霞, 黄洪辉, 覃晓青, 李佳俊, 陈建华. 2020年冬季大亚湾西南海域主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [14] | 李存, 崔林青, 杨红强, 龙丽娟, 田新朋. 三份南海岛礁珊瑚砂样品中可培养细菌多样性[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 149-158. |
| [15] | 李华薇, 徐向荣. 中国典型红树林沉积物中多溴联苯醚和替代型溴系阻燃剂污染特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 117-130. |
|
||