热带海洋学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 57-67.doi: 10.11978/2023096CSTR: 32234.14.2023096
印度尼西亚—澳大利亚海盆上层海洋层结变化及其影响因素
- 1.热带海洋环境国家重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2023-07-12修回日期:2023-08-15出版日期:2024-07-10发布日期:2024-07-22 -
作者简介:林桂焕(1998—), 男, 广东省中山市人, 硕士研究生, 从事印度洋和印度贯穿流研究。email: linguihuan21@mails.ucas.ac.cn
-
基金资助:中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(XDB42010000); 国家自然科学基金(42276023); 中国科学院地球系统模式的耦合初始化研究(ZDBS-LY-DQC010)
Ocean stratification in the Indonesian-Australian basin and its influencing factors
LIN Guihuan1,2( ), YAN Youfang1(
), YAN Youfang1( ), LIU Ying1,2
), LIU Ying1,2
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Environment, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2023-07-12Revised:2023-08-15Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-07-22 -
Supported by:Special Project on Strategic Pioneering Science and Technology of Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDB42010000); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42276023); Coupled Initialization of Earth System Model of Chinese Academy of Sciences(ZDBS-LY-DQC010)
摘要:
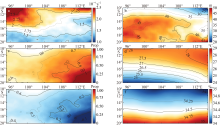
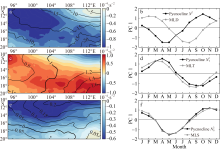
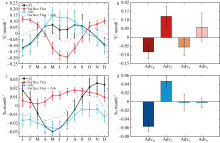
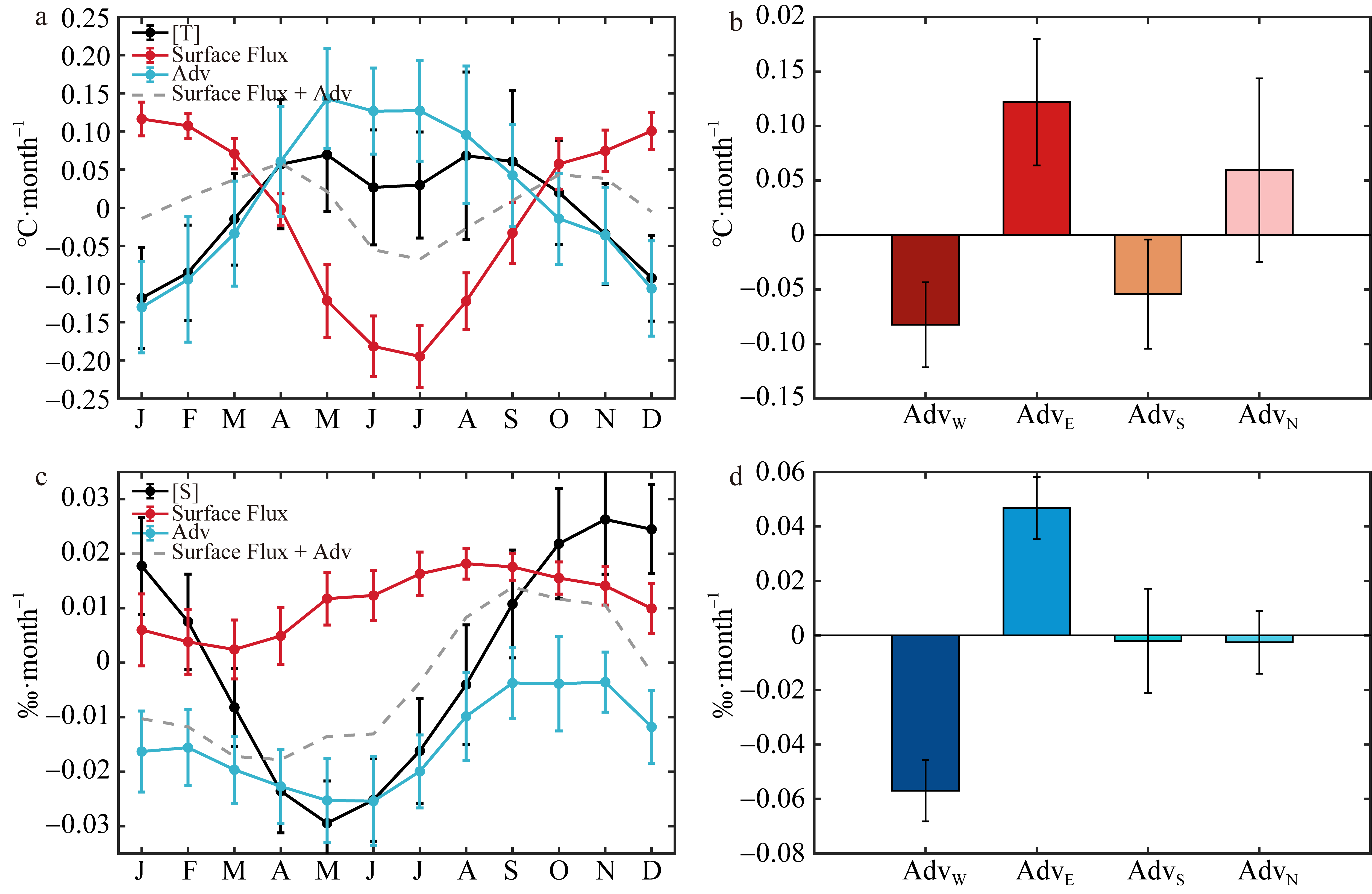
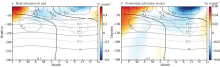
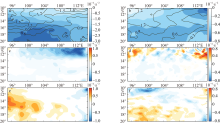
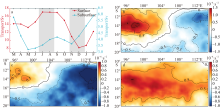
本文基于ORAS5(ocean reanalysis system)和ERA5(ECMWF reanalysis v5)再分析数据, 利用密度跃层底的浮力频率表征海洋层结的强度对印度尼西亚—澳大利亚海盆及其周边海域的海洋层结特性及其影响因素进行研究。结果显示: 该海盆海洋层结在空间上表现为北部较强、南部较弱, 在时间上表现为北半球春季较强、秋季较弱。对海盆内混合层温度和盐度变化的影响因素分析表明, 海表通量和海洋平流作用的贡献非常显著, 特别是与印尼贯穿流相关的纬向平流通过影响次表层密度结构进而对跃层底层结产生重要影响。进一步分析印尼贯穿流通量对海盆内海洋层结的影响, 发现了印尼贯穿流通量与该海盆的混合层界面上下的温盐异常密切相关, 该盐度异常通过影响其垂向密度梯度进而对海洋层结的季节变化产生影响。
引用本文
林桂焕, 严幼芳, 刘颖. 印度尼西亚—澳大利亚海盆上层海洋层结变化及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 57-67.
LIN Guihuan, YAN Youfang, LIU Ying. Ocean stratification in the Indonesian-Australian basin and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 57-67.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1038/srep16050 pmid: 26522168 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1002/2016GL072494 pmid: 28405053 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10109-z pmid: 31068581 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [1] | 孙泽铭, 韩树宗, 王明杰, 苏翰祥. 不同路径台风对中国近海海温的影响特征统计分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 17-31. |
| [2] | 齐焕东, 朱程, 李序春, 景昕蒂, 宋德瑞. 基于规则集和多层感知机的Argo温度数据质量控制方法*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(5): 190-202. |
| [3] | 吕泓柯, 巩远发, 王桂华. 印度洋海表盐度预报的线性马尔可夫模型及其改进办法[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 151-158. |
| [4] | 唐超礼, 陶鑫华, 魏圆圆, 戴聪明, 魏合理. 东亚及西太平洋地表温度时空模态分析及预测研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 183-192. |
| [5] | 董兰芳, 许明珠, 刘海娟, 曾梦清, 陈瑞芳, 李世才. 盐度对中国鲎幼鲎生长、蜕壳、Na+-K+-ATP酶活性、免疫指标和抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 156-163. |
| [6] | 廖莹, 夏晓敏. 盐度对广盐型聚球藻K1生长及转录组的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 159-169. |
| [7] | 陈克海, 解学通, 张金兰, 郑艳. 一种温度相关的HY-2A散射计地球物理模型函数[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2): 90-102. |
| [8] | 李杨, 黄鹏起, 鲁远征, 屈玲, 郭双喜, 岑显荣, 周生启, 张佳政, 丘学林. 基于精细温度观测的南海东北部陆坡-深海盆底层湍流混合*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 62-74. |
| [9] | 邱爽, 叶海军, 张玉红, 唐世林. 基于航次观测和再分析资料的南海海表二氧化碳分压反演及变化机制分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 106-116. |
| [10] | 汪浩, 王静, 郑佳喻. 南印度洋热带气旋快速增强事件气候特征及其年际变率[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 94-105. |
| [11] | 何子康, 王喜冬, 陈志强, 范开桂. 利用海洋温度剖面与海表盐度反演盐度剖面方法研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(6): 41-51. |
| [12] | 陆梦莹, 苏冒亮, 张俊彬. 盐度变化对金钱鱼感染嗜水气单胞菌后血清及肾脏免疫状态的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 114-123. |
| [13] | 郑承志, 左丽明, 马旺, 朱琴, 王火火, 吕颂辉, 陈亨, 黄凯旋. 不同温度下抑食金球藻、中肋骨条藻和海洋卡盾藻间的相互作用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 124-131. |
| [14] | 刘磊, 许兰芳, 管红香, 孙治雷, 王利波, 茅晟懿, 刘丽华, 吴能友. 冲绳海槽中部8.2ka以来GDGTs组成及温度重建*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(6): 77-92. |
| [15] | 严瑾, 林明晴, 曹文浩, 林岳光, 邹立. 温度对网纹纹藤壶幼虫发育和附着的生物学效应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 55-61. |
|
||