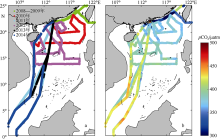
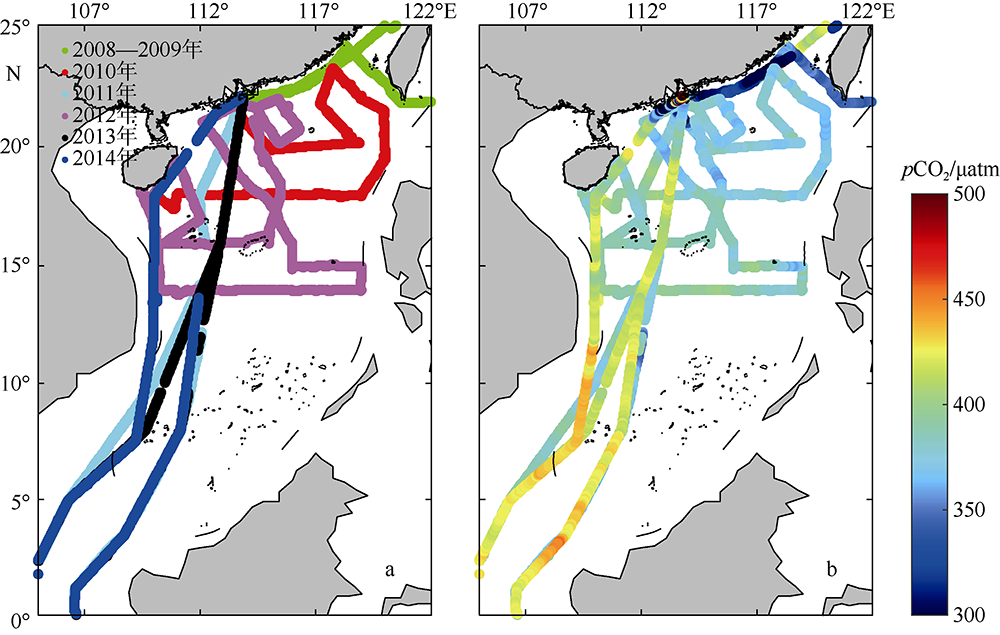
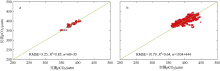
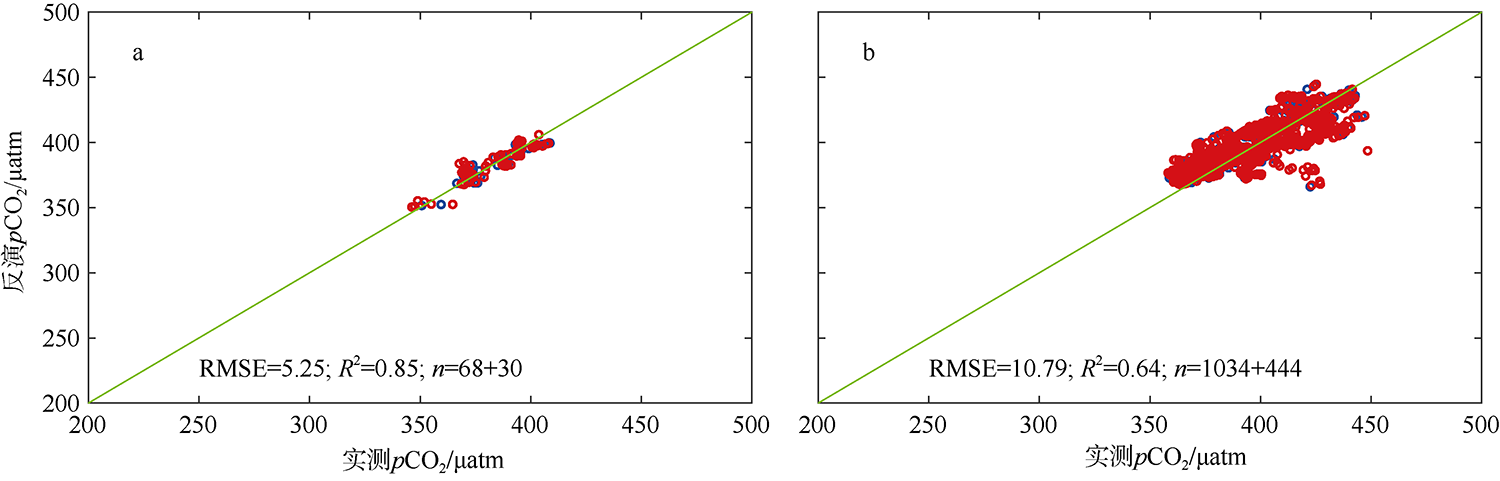
| [1] |
陈海花, 李洪平, 何林洁, 等, 2015. 基于SODA数据集的南海海表面盐度分布特征与长期变化趋势分析[J]. 海洋技术学报, 34(4): 48-52.
|
|
CHEN HAIHUA, LI HONGPING, HE LINJIE, et al, 2015. Analysis on the distribution characteristics of sea surface salinity and its long-term variation trend in the South China Sea based on soda data set[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 34(4): 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
傅圆圆, 程旭华, 张玉红, 等, 2017. 近二十年南海表层海水的盐度淡化及其机制[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(4): 18-24.
|
|
FU YUANYUAN, CHENG XUHUA, ZHANG YUHONG, et al, 2017. The freshening trend of surface salinity in the South China Sea in recent two decades and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(4): 18-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [3] |
韩玉康, 周林, 吴炎成, 2016. 基于HYCOM的南海中尺度涡数值模拟[J]. 海洋通报, 35(3): 299-316.
|
|
HAN YUKANG, ZHOU LIN, WU YANCHENG, 2016. Numerical simulation of the mesoscale eddy in the South China Sea based on HYCOM[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 35(3): 299-316. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
姜亦飞, 王辉, 乔然, 等, 2014. 南海东北部春季海表pCO2分布及海-气CO2通量[J]. 海洋学报, 36(6): 18-24.
doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1124-x
|
|
JIANG YIFEI, WANG HUI, QIAO RAN, et al, 2014. The distribution of pCO2 in surface water and CO2 flux at air-sea interface in northeast part of the South China Sea in spring[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36(6): 18-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1124-x
|
| [5] |
吕航宇, 白雁, 李骞, 等, 2018. 夏季珠江口海域海水CO2分压的卫星遥感反演[J]. 海洋学研究, 36(2): 1-11.
|
|
LÜ HANGYU, BAI YAN, LI QIAN, et al, 2018. Satellite remote sensing retrieval of aquatic pCO2 in summer in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 36(2): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [6] |
邱春华, 贾英来, 2009. 南海北部深水海域温度以及盐度的季节及年际变化特征[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 39(3): 375-380, 386.
|
|
QIU CHUNHUA, JIA YINGLAI, 2009. Seasonal and inter-annual variations of temperature and salinity in the northern South China Sea[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 39(3): 375-380, 386. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [7] |
王静, 赵飞达, 齐义泉, 2015. 夏末秋初南海18°N断面混合层结构特征分析[J]. 海洋通报, 34(1): 52-58.
|
|
WANG JING, ZHAO FEIDA, QI YIQUAN, 2015. Characteristics of mixed layer cross section 18° N in the South China Sea during late summer and early autumn[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 34(1): 52-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [8] |
许欣, 于培松, 蔡小霞,等, 2016. 南海西部秋季海表$p_{{CO}_{2}}$分布与海气CO2通量[J]. 热带海洋学报, 35(3): 55-64.
|
|
XU XIN, YU PEISONG, CAI XIAOXIA,et al, 2016. Distributions of partial pressure of carbon dioxide and sea-air CO2 flux in the western South China Sea in autumn[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 35(3): 55-64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
翟惟东, 2015. 南海北部春季非水华期的CO2分压及其调控[J]. 海洋学报, 37(6): 31-40.
|
|
ZHAI WEIDONG, 2015. Sea surface partial pressure of CO2 and its controls in the northern South China Sea in the non-bloom period in spring[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 37(6): 31-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [10] |
ATLAS R, HOFFMAN R N, ARDIZZONE J, et al, 2011. A cross-calibrated, multiplatform ocean surface wind velocity product for meteorological and oceanographic applications[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 92(2): 157-174.
doi: 10.1175/2010BAMS2946.1
|
| [11] |
CIAIS P, SABINE C, BALA G, et al, 2013. Carbon and other biogeochemical cycles[M]// STOCKERT F, QIND, PLATTNERG K, et al. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis:contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 465-570.
|
| [12] |
DAI MINHAN, CAO ZHIMIAN, GUO XIANGHUI, et al, 2013. Why are some marginal seas sources of atmospheric CO2?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 40(10): 2154-2158.
doi: 10.1002/grl.50390
|
| [13] |
DAI MINHAN, LU ZHONGMING, ZHAI WEIDONG, et al, 2009. Diurnal variations of surface seawater pCO2 in contrasting coastal environments[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 54(3): 735-745.
doi: 10.4319/lo.2009.54.3.0735
|
| [14] |
DENVIL-SOMMER A, GEHLEN M, VRAC M, et al,2018. FFNN-LSCE: a two-step neural network model for the reconstruction of surface ocean pCO2 over the Global Ocean[J]. Geoscientific Model Development Discussions, (2018):1-27.
|
| [15] |
DLUGOKENCKY E, TANS P,[2021-02-21]. Trends in atmospheric carbon dioxide. NOAA/ESRL[R/OL]. http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/ .
|
| [16] |
FASSBENDER A J, RODGERS K B, PALEVSKY H I, et al, 2018. Seasonal asymmetry in the evolution of surface ocean pCO2 and pH thermodynamic drivers and the influence on sea-air CO2 flux[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 32(10): 1476-1497.
doi: 10.1029/2017GB005855
|
| [17] |
JIAO NIANZHI, ZHANG YAO, ZHOU KUANBO, et al, 2014. Revisiting the CO2 "source" problem in upwelling areas - a comparative study on eddy upwellings in the South China Sea[J]. Biogeosciences, 11(9): 2465-2475.
doi: 10.5194/bg-11-2465-2014
|
| [18] |
JO Y H, DAI MINHAN, ZHAI WEIDONG, et al, 2012. On the variations of sea surface pCO2 in the northern South China Sea: a remote sensing based neural network approach[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117(C8): C08022.
|
| [19] |
LARUELLE G G, LAUERWALD R, PFEIL B, et al, 2014. Regionalized global budget of the CO2 exchange at the air-water interface in continental shelf seas[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 28(11): 1199-1214.
doi: 10.1002/2014GB004832
|
| [20] |
LARUELLE G G, CAI WEIJUN, HU XINPING, et al, 2018. Continental shelves as a variable but increasing global sink for atmospheric carbon dioxide[J]. Nature Communications, 9(1): 454.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02738-z
|
| [21] |
LI QIAN, GUO XIANGHUI, ZHAI WEIDONG, et al, 2020. Partial pressure of CO2 and air-sea CO2 fluxes in the South China Sea: synthesis of an 18-year dataset[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 182: 102272.
doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2020.102272
|
| [22] |
LIU FENFEN, TANG SHILIN, CHEN CHUQUN, 2009. Remotely sensed study of air-sea CO2 fluxes variability in the northern South China Sea[C]// Proceedings of 2009 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium. Cape Town: IEEE: III-361-III-364.
|
| [23] |
LU HANGYU, BAI YAN, CHEN XIAOYAN, et al, 2017. Satellite remote sensing of the aquatic pCO2 in the basin of the South China Sea[C]// Proceedings of SPIE 10422, remote sensing of the ocean, sea ice, coastal waters, and large water regions. Warsaw, Poland: SPIE.
|
| [24] |
MOSTOFA K M G, LIU CONGQIANG, ZHAI WEIDONG, et al, 2016. Reviews and Syntheses: ocean acidification and its potential impacts on marine ecosystems[J]. Biogeosciences, 13(6): 1767-1786.
doi: 10.5194/bg-13-1767-2016
|
| [25] |
NAN FENG, XUE HUIJIE, CHAI FEI et al, 2013. Weakening of the kuroshio intrusion into the South China Sea over the past two decades[J]. Journal of Climate, 26(20): 8097-8110.
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00315.1
|
| [26] |
QU TANGDONG, MITSUDERA H, YAMAGATA T, 2000. Intrusion of the North Pacific waters into the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 105(C3): 6415-6424.
|
| [27] |
RÖDENBECK C, KEELING R F, BAKKER D C E, et al, 2013. Global surface-ocean pCO2 and sea-air CO2 flux variability from an observation-driven ocean mixed-layer scheme[J]. Ocean Science, 9(2): 193-216.
|
| [28] |
SHEU D D, CHOU WENCHEN, WEI CHINGLING, et al, 2010. Influence of El Nino on the sea-to-air CO2 flux at the SEATS time-series site, northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 115(C10): C10021.
|
| [29] |
SUN QINGYANG, TANG DANLING, LEGENDRE L, et al, 2014. Enhanced sea-air CO2 exchange influenced by a tropical depression in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(10): 6792-6804.
doi: 10.1002/2014JC010131
|
| [30] |
WANG GUIZHI, DAI MINHAN, SHEN S S P, et al, 2014. Quantifying uncertainty sources in the gridded data of sea surface CO2partial pressure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(8): 5181-5189.
doi: 10.1002/2013JC009577
|
| [31] |
WANNINKHOF R, 2014. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean revisited[J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 12(6): 351-362.
doi: 10.4319/lom.2014.12.351
|
| [32] |
WOOSLEY R J, 2018. Complexity of marine CO2 system highlighted by seasonal asymmetries[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 32(10): 1434-1436.
doi: 10.1029/2018GB006081
|
| [33] |
YAN HONGQIANG, YU KEFU, SHI QI, et al, 2016. Seasonal variations of seawater pCO2 and sea-air CO2 fluxes in a fringing coral reef, northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121(1): 998-1008.
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v121.1
|
| [34] |
YANG YIKAI, WANG DONGXIAO, WANG QIANG, et al, 2019. Eddy‐induced transport of saline kuroshio water into the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(9): 6673-6687.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014847
|
| [35] |
YE HAIJUN, SHENG JINYU, TANG DANLING, et al, 2017. Storm-induced changes in pCO2 at the sea surface over the northern South China Sea during Typhoon Wutip[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(6): 4761-4778.
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v122.6
|
| [36] |
ZENG LILI, LIU W T, XUE HUIJIE, et al, 2014. Freshening in the South China Sea during 2012 revealed by Aquarius and in situ data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(12): 8296-8314.
doi: 10.1002/2014JC010108
|
| [37] |
ZHAI WEIDONG, DAI MINHAN, CAI WEIJUN, et al, 2005. High partial pressure of CO2 and its maintaining mechanism in a subtropical estuary: the pearl river estuary, china[J]. Marine Chemistry, 93(1), 21-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2004.07.003
|
| [38] |
ZHAI WEIDONG, DAI MINHAN, CHEN BAOSHAN, et al, 2013. Seasonal variations of sea-air CO2 fluxes in the largest tropical marginal sea (South China Sea) based on multiple-year underway measurements[J]. Biogeosciences, 10(11): 7775-7791.
doi: 10.5194/bg-10-7775-2013
|
| [39] |
ZHU YU, SHANG SHAOLING, ZHAI WEIDONG, et al, 2009. Satellite-derived surface water pCO2 and air-sea CO2 fluxes in the northern South China Sea in summer[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 19(6): 775-779.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.09.004
|
 ), 叶海军1,3, 张玉红1,2,3(
), 叶海军1,3, 张玉红1,2,3( ), 唐世林1,2,3
), 唐世林1,2,3
 ), YE Haijun1,3, ZHANG Yuhong1,2,3(
), YE Haijun1,3, ZHANG Yuhong1,2,3( ), TANG Shilin1,2,3
), TANG Shilin1,2,3